Abstract
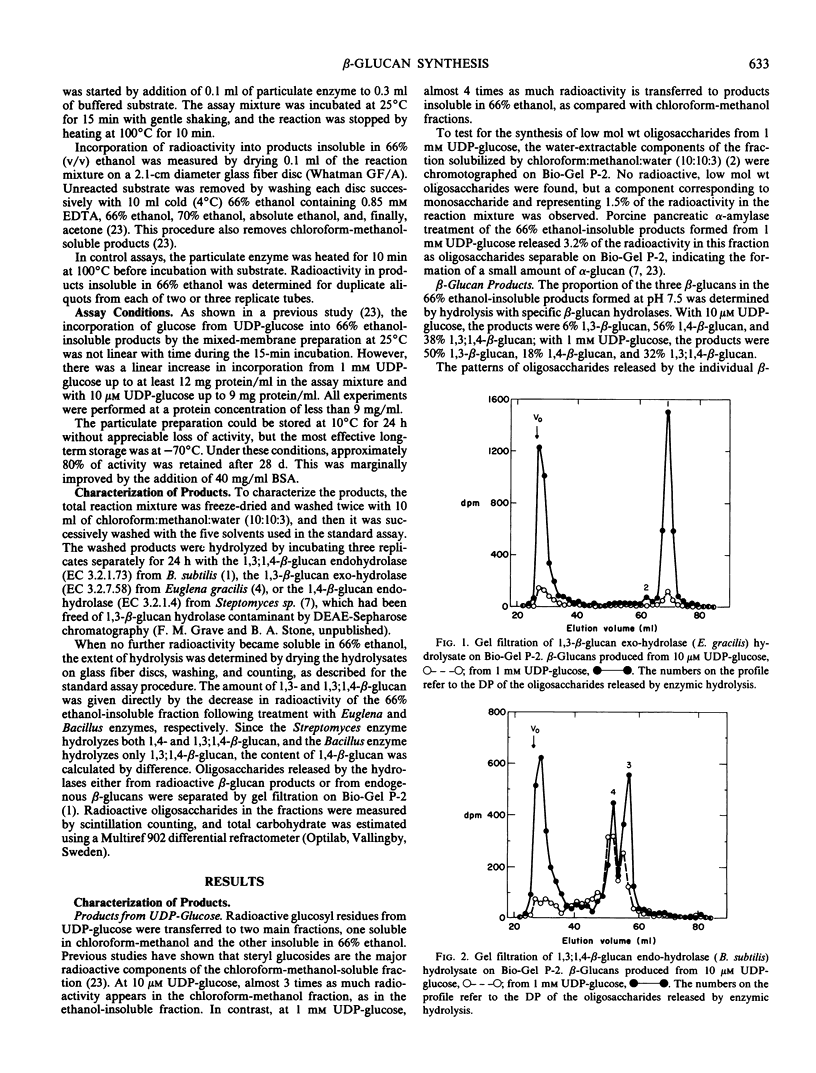
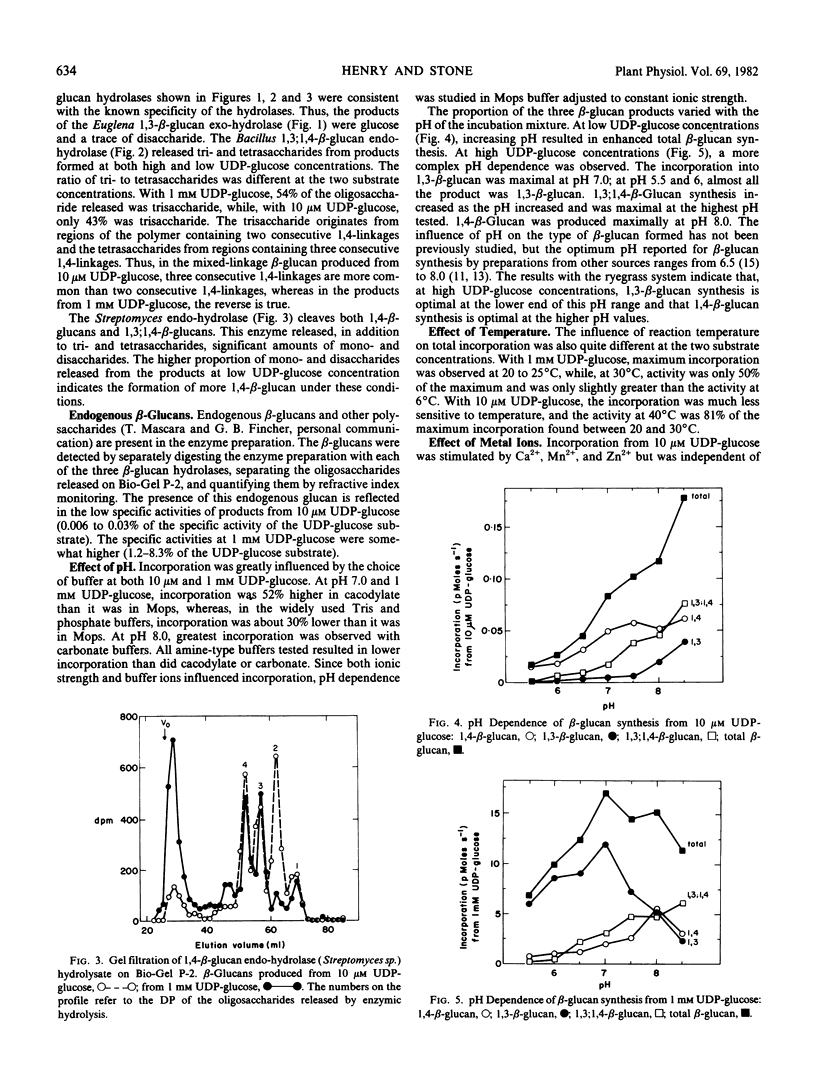
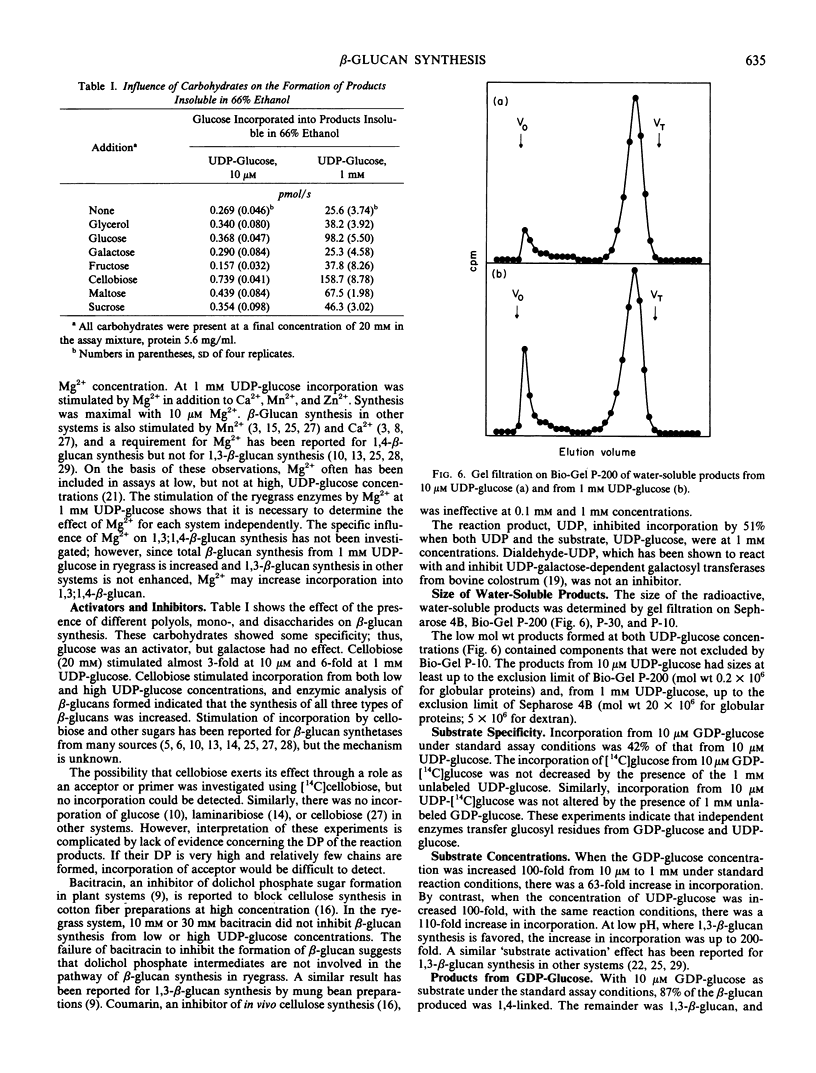
Particulate enzymes from suspension-cultured ryegrass (Lolium multiflorum Lam.) endosperm cells incorporated glucosyl residues from UDP-glucose and GDP-glucose into β-glucans. Three types of β-glucans were produced from UDP-glucose: 1,3-β-glucan; 1,4-β-glucan; and mixed-linkage 1,3;1,4-β-glucan. As in other systems, relatively more 1,4-β-glucan was produced from a low (10 micromolar) UDP-glucose concentration, and relatively more 1,3-β-glucan was produced from a high (1 millimolar) UDP-glucose concentration. However, in ryegrass, 1,3;1,4-β-glucan represented a major proportion of the products at both low and high UDP-glucose concentrations. The arrangement of linkages in the 1,3;1,4-β-glucan was different at the two concentrations; at the low UDP-glucose concentration, more sequences of three consecutive 1,4-linkages were produced.
The effects of pH, temperature, and metal ion concentrations on incorporation were dependent on the UDP-glucose concentration. At the low UDP-glucose concentration, incorporation into all three types of β-glucan increased with increasing pH. At the high UDP-glucose concentration, 1,3-β-glucan was the major product at pH 7 and below; 1,4-β-glucan synthesis was optimal at pH 8; and synthesis of 1,3;1,4-β-glucan was greatest above pH 8.
With 10 micromolar GDP-glucose as substrate, 1,4-β-glucan, but no 1,3;1,4-β-glucan, was produced. Incorporation from either UDP-glucose or GDP-glucose was not influenced by the presence of the other.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson M. A., Stone B. A. A new substrate for investigating the specificity of beta-glucan hydrolases. FEBS Lett. 1975 Apr 1;52(2):202–207. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80806-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARBER H. A., ELBEIN A. D., HASSID W. Z. THE SYNTHESIS OF CELLULOSE BY ENZYME SYSTEMS FROM HIGHER PLANTS. J Biol Chem. 1964 Dec;239:4056–4061. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey D. S., Dürr M., Burke J., Maclachlan G. The assembly of lipid-linked oligosaccharides in plant and animal membranes. J Supramol Struct. 1979;11(2):123–138. doi: 10.1002/jss.400110203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barras D. R., Stone B. A. Beta-1,3-glucan hydrolases from Euglena gracilis. II. Purification and properties of the beta-1,3-glucan exo-hydrolase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Nov 4;191(2):342–353. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(69)90253-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brummond D. O., Gibbons A. P. Enzymatic cellulose synthesis from UDP-(14C)-glucose by Lupinus albus. Biochem Z. 1965 Aug 6;342(3):308–318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delmer D. P., Heiniger U., Kulow C. UDP-glucose: Glucan Synthetase in Developing Cotton Fibers: I. Kinetic and Physiological Properties. Plant Physiol. 1977 Apr;59(4):713–718. doi: 10.1104/pp.59.4.713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ericson M. C., Gafford J., Elbein A. D. Bacitracin Inhibits the Synthesis of Lipid-linked Saccharides and Glycoproteins in Plants. Plant Physiol. 1978 Sep;62(3):373–376. doi: 10.1104/pp.62.3.373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FEINGOLD D. S., NEUFELD E. F., HASSID W. Z. Synthesis of a beta-1, 3-linked glucan by extracts of Phaseolus aureus seedlings. J Biol Chem. 1958 Oct;233(4):783–788. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopp H. E., Romero P. A., Daleo G. R., Pont Lezica R. Synthesis of cellulose precursors. The involvement of lipid-linked sugars. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Mar 15;84(2):561–571. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12199.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARECHAL L. R., GOLDEMBERG S. H. URIDINE DIPHOSPHATE GLUCOSE-BETA-1,3-GLUCAN BETA-3-GLUCOSYLTRANSFERASE FROM EUGLENA GRACILIS. J Biol Chem. 1964 Oct;239:3163–3167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ordin L., Hall M. A. Cellulose synthesis in higher plants from UDP glucose. Plant Physiol. 1968 Mar;43(3):473–476. doi: 10.1104/pp.43.3.473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell J. T., Brew K. Affinity labeling of bovine colostrum galactosyltransferase with a uridine 5'-diphosphate derivative. Biochemistry. 1976 Aug 10;15(16):3499–3505. doi: 10.1021/bi00661a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Péaud-Lenoël C., Axelos M. Structural features of the beta-glucans enzymatically synthesized from uridine diphosphate glucose by wheat seedlings. FEBS Lett. 1970 Jun 8;8(4):224–228. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(70)80270-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RANDERATH K., RANDERATH E. ION-EXCHANGE CHROMATOGRAPHY OF NUCLEOTIDES ON POLY-(ETHYLENEIMINE)-CELLULOSE THIN LAYERS. J Chromatogr. 1964 Oct;16:111–125. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)82445-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raymond Y., Fincher G. B., Maclachlan G. A. Tissue Slice and Particulate beta-Glucan Synthetase Activities from Pisum Epicotyls. Plant Physiol. 1978 Jun;61(6):938–942. doi: 10.1104/pp.61.6.938. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. M., Stone B. A. Beta-glucan synthesis by cell-free extracts from Lolium multiflorum endosperm. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jun 20;313(1):72–94. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(73)90189-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southworth D., Dickinson D. B. beta-1, 3-Glucan Synthase from Lilium longiflorum Pollen. Plant Physiol. 1975 Jul;56(1):83–87. doi: 10.1104/pp.56.1.83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. M., Hassid W. Z. Solubilization and Separation of Uridine Diphospho-d-glucose: beta-(1 --> 4) Glucan and Uridine Diphospho-d-glucose:beta-(1 --> 3) Glucan Glucosyltransferases from Coleoptiles of Avena sativa. Plant Physiol. 1971 Jun;47(6):740–744. doi: 10.1104/pp.47.6.740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. M., Hassid W. Z. Substrate Activation of beta-(1 --> 3) Glucan Synthetase and Its Effect on the Structure of beta-Glucan Obtained from UDP-d-glucose and Particulate Enzyme of Oat Coleoptiles. Plant Physiol. 1973 Jun;51(6):998–1001. doi: 10.1104/pp.51.6.998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


