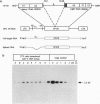
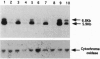
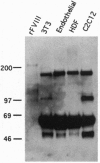
Abstract
Continuous delivery of factor VIII (FVIII) protein in hemophiliacs by gene therapy will represent a major clinical advance over the current practice of infrequent administration of purified FVIII. Conceptually, retroviral vectors that can permanently insert the FVIII gene into the DNA of the host cell appear the most suitable vehicles for this specific purpose. However, most retroviral vector systems have shown a poor performance in the production of FVIII from primary cells in vitro and in vivo. Here we report the retroviral-mediated gene delivery of a B-domain-deleted human FVIII by using the MFG vector system. This vector permitted efficient transduction of the majority of the primary cells in culture without the use of a selectable marker. High levels of FVIII were produced by various transduced primary cells in vitro. Upon transplantation of primary fibroblasts into mice, therapeutic levels of FVIII in the circulation were obtained for > 1 week. The capacity of primary cells to deliver the FVIII into the circulation was strongly dependent on the site of implantation. These results represent a major step forward in development of gene therapy for treating hemophilia A.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aledort L. M. Lessons from hemophilia. N Engl J Med. 1982 Mar 11;306(10):607–608. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198203113061011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antonarakis S. E., Youssoufian H., Kazazian H. H., Jr Molecular genetics of hemophilia A in man (factor VIII deficiency). Mol Biol Med. 1987 Apr;4(2):81–94. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brettler D. B., Levine P. H. Factor concentrates for treatment of hemophilia: which one to choose? Blood. 1989 Jun;73(8):2067–2073. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinkhous K. M., Sandberg H., Garris J. B., Mattsson C., Palm M., Griggs T., Read M. S. Purified human factor VIII procoagulant protein: comparative hemostatic response after infusions into hemophilic and von Willebrand disease dogs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8752–8756. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8752. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke R. L., Pachl C., Quiroga M., Rosenberg S., Haigwood N., Nordfang O., Ezban M. The functional domains of coagulation factor VIII:C. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 25;261(27):12574–12578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danos O., Mulligan R. C. Safe and efficient generation of recombinant retroviruses with amphotropic and ecotropic host ranges. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(17):6460–6464. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.17.6460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dranoff G., Jaffee E., Lazenby A., Golumbek P., Levitsky H., Brose K., Jackson V., Hamada H., Pardoll D., Mulligan R. C. Vaccination with irradiated tumor cells engineered to secrete murine granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor stimulates potent, specific, and long-lasting anti-tumor immunity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 15;90(8):3539–3543. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton D. L., Wood W. I., Eaton D., Hass P. E., Hollingshead P., Wion K., Mather J., Lawn R. M., Vehar G. A., Gorman C. Construction and characterization of an active factor VIII variant lacking the central one-third of the molecule. Biochemistry. 1986 Dec 30;25(26):8343–8347. doi: 10.1021/bi00374a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton D., Rodriguez H., Vehar G. A. Proteolytic processing of human factor VIII. Correlation of specific cleavages by thrombin, factor Xa, and activated protein C with activation and inactivation of factor VIII coagulant activity. Biochemistry. 1986 Jan 28;25(2):505–512. doi: 10.1021/bi00350a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulcher C. A., Roberts J. R., Holland L. Z., Zimmerman T. S. Human factor VIII procoagulant protein. Monoclonal antibodies define precursor-product relationships and functional epitopes. J Clin Invest. 1985 Jul;76(1):117–124. doi: 10.1172/JCI111933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldsmith M. F. Hemophilia, beaten on one front, is beset on others. JAMA. 1986 Dec 19;256(23):3200–3200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoeben R. C., Einerhand M. P., Briët E., van Ormondt H., Valerio D., van der Eb A. J. Toward gene therapy in haemophilia A: retrovirus-mediated transfer of a factor VIII gene into murine haematopoietic progenitor cells. Thromb Haemost. 1992 Mar 2;67(3):341–345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoeben R. C., Fallaux F. J., Van Tilburg N. H., Cramer S. J., Van Ormondt H., Briët E., Van Der Eb A. J. Toward gene therapy for hemophilia A: long-term persistence of factor VIII-secreting fibroblasts after transplantation into immunodeficient mice. Hum Gene Ther. 1993 Apr;4(2):179–186. doi: 10.1089/hum.1993.4.2-179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoeben R. C., van der Jagt R. C., Schoute F., van Tilburg N. H., Verbeet M. P., Briët E., van Ormondt H., van der Eb A. J. Expression of functional factor VIII in primary human skin fibroblasts after retrovirus-mediated gene transfer. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 5;265(13):7318–7323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israel D. I., Kaufman R. J. Retroviral-mediated transfer and amplification of a functional human factor VIII gene. Blood. 1990 Mar 1;75(5):1074–1080. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. The scanning model for translation: an update. J Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;108(2):229–241. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.2.229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine P. H. Efficacy of self-therapy in hemophilia. A study of 72 patients with hemophilia A and B. N Engl J Med. 1974 Dec 26;291(26):1381–1384. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197412262912604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lusher J. M., Arkin S., Abildgaard C. F., Schwartz R. S. Recombinant factor VIII for the treatment of previously untreated patients with hemophilia A. Safety, efficacy, and development of inhibitors. Kogenate Previously Untreated Patient Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1993 Feb 18;328(7):453–459. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199302183280701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch C. M., Israel D. I., Kaufman R. J., Miller A. D. Sequences in the coding region of clotting factor VIII act as dominant inhibitors of RNA accumulation and protein production. Hum Gene Ther. 1993 Jun;4(3):259–272. doi: 10.1089/hum.1993.4.3-259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. D. Progress toward human gene therapy. Blood. 1990 Jul 15;76(2):271–278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moullier P., Bohl D., Heard J. M., Danos O. Correction of lysosomal storage in the liver and spleen of MPS VII mice by implantation of genetically modified skin fibroblasts. Nat Genet. 1993 Jun;4(2):154–159. doi: 10.1038/ng0693-154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson I. M., Berntorp E., Löfqvist T., Pettersson H. Twenty-five years' experience of prophylactic treatment in severe haemophilia A and B. J Intern Med. 1992 Jul;232(1):25–32. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2796.1992.tb00546.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohashi T., Boggs S., Robbins P., Bahnson A., Patrene K., Wei F. S., Wei J. F., Li J., Lucht L., Fei Y. Efficient transfer and sustained high expression of the human glucocerebrosidase gene in mice and their functional macrophages following transplantation of bone marrow transduced by a retroviral vector. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 1;89(23):11332–11336. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.23.11332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer T. D., Rosman G. J., Osborne W. R., Miller A. D. Genetically modified skin fibroblasts persist long after transplantation but gradually inactivate introduced genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1330–1334. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavirani A., Meulien P., Harrer H., Dott K., Mischler F., Wiesel M. L., Mazurier C., Cazenave J. P., Lecocq J. P. Two independent domains of factor VIII co-expressed using recombinant vaccinia viruses have procoagulant activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 May 29;145(1):234–240. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)91311-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittman D. D., Alderman E. M., Tomkinson K. N., Wang J. H., Giles A. R., Kaufman R. J. Biochemical, immunological, and in vivo functional characterization of B-domain-deleted factor VIII. Blood. 1993 Jun 1;81(11):2925–2935. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittman D. D., Kaufman R. J. Proteolytic requirements for thrombin activation of anti-hemophilic factor (factor VIII). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2429–2433. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittman D. D., Millenson M., Marquette K., Bauer K., Kaufman R. J. A2 domain of human recombinant-derived factor VIII is required for procoagulant activity but not for thrombin cleavage. Blood. 1992 Jan 15;79(2):389–397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosén S. Assay of factor VIII:C with a chromogenic substrate. Scand J Haematol Suppl. 1984;40:139–145. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1984.tb02556.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scharfmann R., Axelrod J. H., Verma I. M. Long-term in vivo expression of retrovirus-mediated gene transfer in mouse fibroblast implants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 1;88(11):4626–4630. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.11.4626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz R. S., Abildgaard C. F., Aledort L. M., Arkin S., Bloom A. L., Brackmann H. H., Brettler D. B., Fukui H., Hilgartner M. W., Inwood M. J. Human recombinant DNA-derived antihemophilic factor (factor VIII) in the treatment of hemophilia A. recombinant Factor VIII Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1990 Dec 27;323(26):1800–1805. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199012273232604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekhsaria S., Gallin J. I., Linton G. F., Mallory R. M., Mulligan R. C., Malech H. L. Peripheral blood progenitors as a target for genetic correction of p47phox-deficient chronic granulomatous disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Aug 15;90(16):7446–7450. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.16.7446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toole J. J., Pittman D. D., Orr E. C., Murtha P., Wasley L. C., Kaufman R. J. A large region (approximately equal to 95 kDa) of human factor VIII is dispensable for in vitro procoagulant activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5939–5942. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truett M. A., Blacher R., Burke R. L., Caput D., Chu C., Dina D., Hartog K., Kuo C. H., Masiarz F. R., Merryweather J. P. Characterization of the polypeptide composition of human factor VIII:C and the nucleotide sequence and expression of the human kidney cDNA. DNA. 1985 Oct;4(5):333–349. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White G. C., 2nd, McMillan C. W., Kingdon H. S., Shoemaker C. B. Use of recombinant antihemophilic factor in the treatment of two patients with classic hemophilia. N Engl J Med. 1989 Jan 19;320(3):166–170. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198901193200307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zatloukal K., Cotten M., Berger M., Schmidt W., Wagner E., Birnstiel M. L. In vivo production of human factor VII in mice after intrasplenic implantation of primary fibroblasts transfected by receptor-mediated, adenovirus-augmented gene delivery. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 May 24;91(11):5148–5152. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.11.5148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]