Abstract
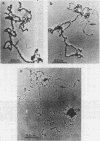
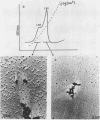
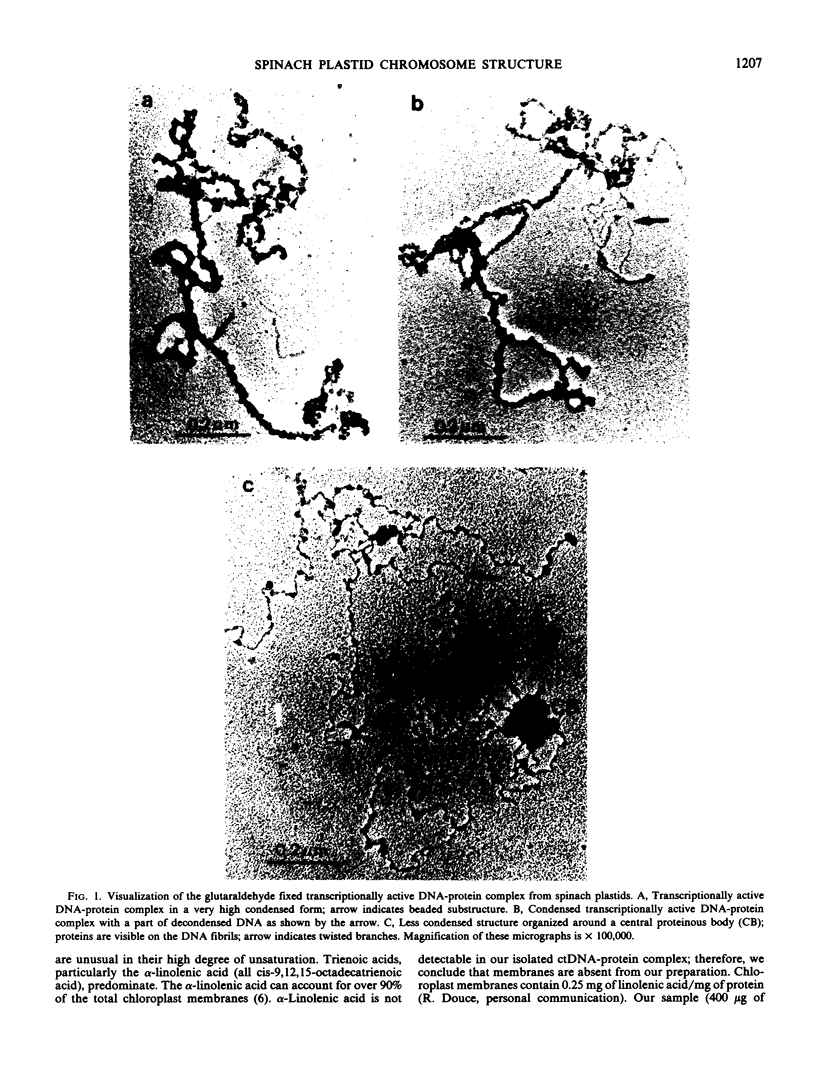
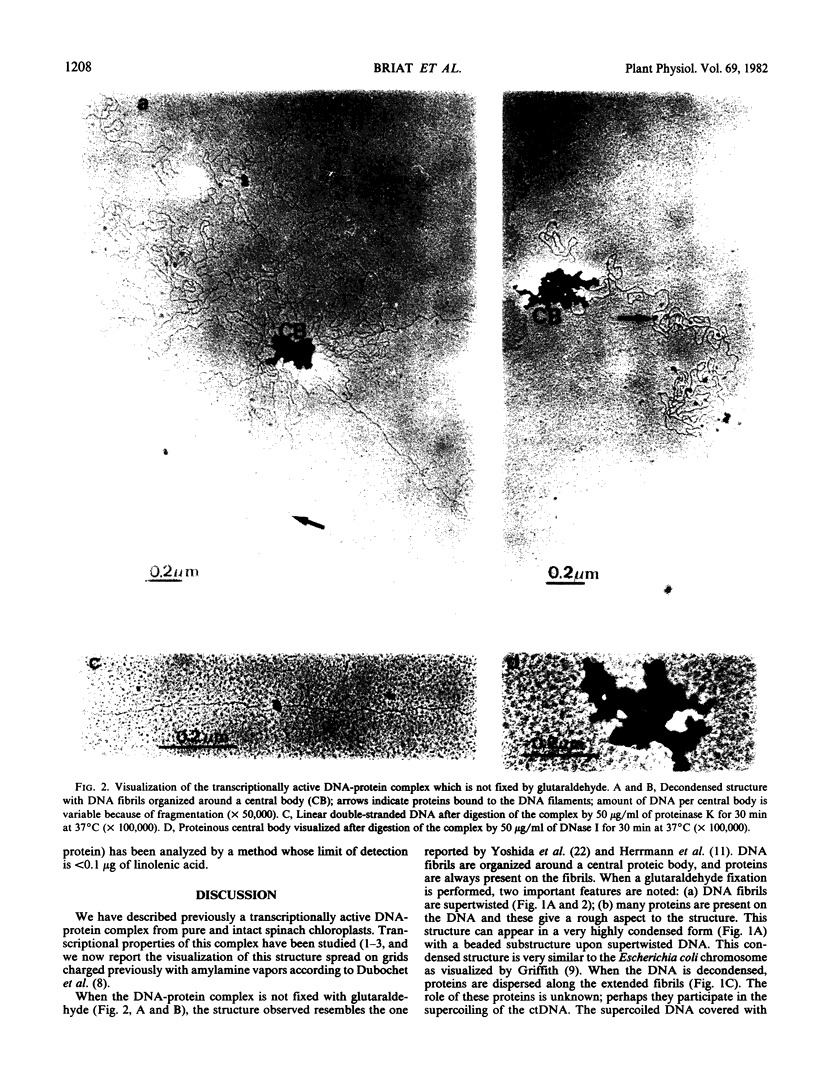
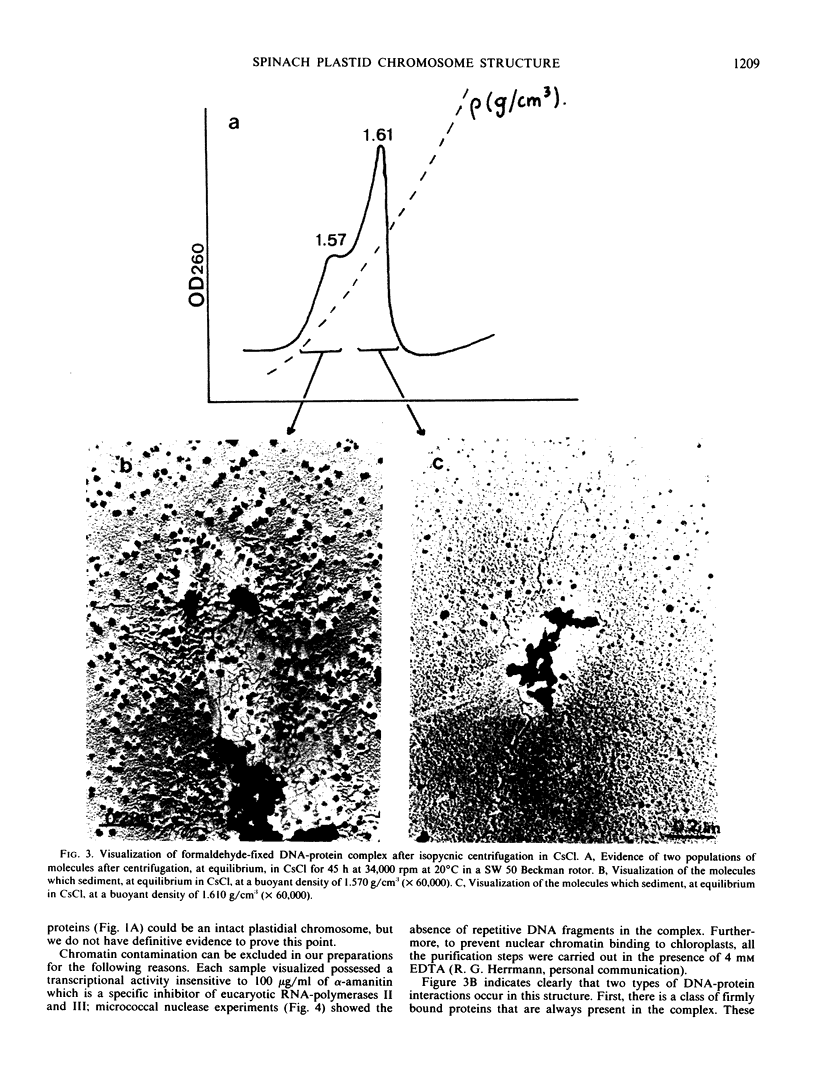
A transcriptionally active DNA-protein complex isolated from spinach Spinacia oleracea plastids is visualized by electron microscopy in different conditions. This structure, after glutaraldehyde fixation, is highly condensed. DNA is supertwisted with proteins bound to it producing a beaded substructure. When glutaraldehyde fixation is omitted this structure is less condensed and DNA fibrils come out from a proteinous central body. The DNA-protein complex can be separated into two populations by CsCl centrifugation: one with a buoyant density of 1.570 grams per cubic centimeter and the other of 1.610 grams per cubic centimeter. By visualization of these two populations, it is concluded that proteins are either firmly bound to DNA in the central body, or more loosely bound to the DNA fibrils. These latter proteins could play a role in enzymic functions and/or in the supercoiling of DNA.
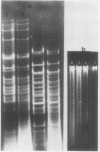
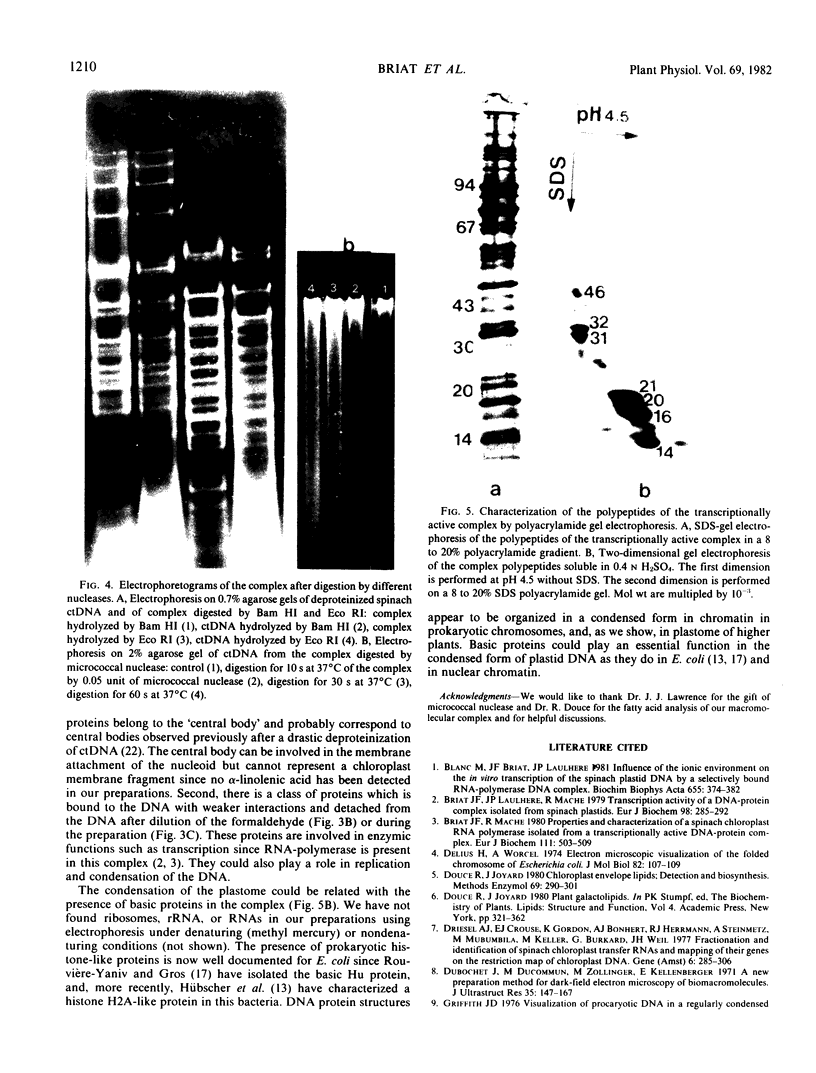
The DNA from the DNA-protein complex possesses all fragments that belong to pure circular chloroplast DNA hydrolyzed by two restriction enzymes: Bam HI and Eco RI. Some molecules observed in a supercondensed form with a beaded substructure probably contain entire chloroplast DNA molecules.
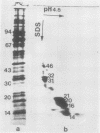
A hydrolysis test with microccocal nuclease gives no indication of the presence of `nucleosome-like' structures. Thirty-six polypeptides with molecular weights ranging from 12,000 to 180,000 are present in the complex, and seven of them are highly soluble in 0.4 n H2SO4; their molecular weights range from 14,000 to 46,000 as shown by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis.
No linolenic acid can be detected in the preparation, indicating the absence of chloroplast membranes.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blanc M., Briat J. F., Laulhere J. P. Influence of the ionic environment on the in vitro transcription of the spinach plastid DNA by a selectively bound RNA-polymerase DNA complex. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Oct 27;655(3):374–382. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(81)90048-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briat J. F., Laulhere J. P., Mache R. Transcription activity of a DNA-protein complex isolated from spinach plastids. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Jul;98(1):285–292. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13187.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briat J. F., Mache R. Properties and characterization of a spinach chloroplast RNA polymerase isolated from a tanscriptionally active DNA-protein complex. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Oct;111(2):503–509. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04966.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delius H., Worcel A. Letter: Electron microscopic visualization of the folded chromosome of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1974 Jan 5;82(1):107–109. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90577-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driesel A. J., Crouse E. J., Gordon K., Bohnert H. J., Herrmann R. G., Steinmetz A., Mubumbila M., Keller M., Burkard G., Weil J. H. Fractionation and identification of spinach chloroplast transfer RNAs and mapping of their genes on the restriction map of chloroplast DNA. Gene. 1979 Aug;6(4):285–306. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(79)90070-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubochet J., Ducommun M., Zollinger M., Kellenberger E. A new preparation method for dark-field electron microscopy of biomacromolecules. J Ultrastruct Res. 1971 Apr;35(1):147–167. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(71)80148-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith J. D. Visualization of prokaryotic DNA in a regularly condensed chromatin-like fiber. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Feb;73(2):563–567. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.2.563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallick R. B., Lipper C., Richards O. C., Rutter W. J. Isolation of a transcriptionally active chromosome from chloroplasts of Euglena gracilis. Biochemistry. 1976 Jul 13;15(14):3039–3045. doi: 10.1021/bi00659a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann R. G., Possingham J. V. Plastid DNA-the plastome. Results Probl Cell Differ. 1980;10:45–96. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-38255-3_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hübscher U., Lutz H., Kornberg A. Novel histone H2A-like protein of escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5097–5101. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouvière-Yaniv J., Gros F. Characterization of a novel, low-molecular-weight DNA-binding protein from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3428–3432. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rushlow K. E., Orozco E. M., Jr, Lipper C., Hallick R. B. Selective in vitro transcription of Euglena chloroplast ribosomal RNA genes by a transcriptionally active chromosome. J Biol Chem. 1980 Apr 25;255(8):3786–3792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitfeld P. R., Herrmann R. G., Bottomley W. Mapping of the ribosomal RNA genes on spinach chloroplast DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Jun;5(6):1741–1751. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.6.1741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]