Abstract
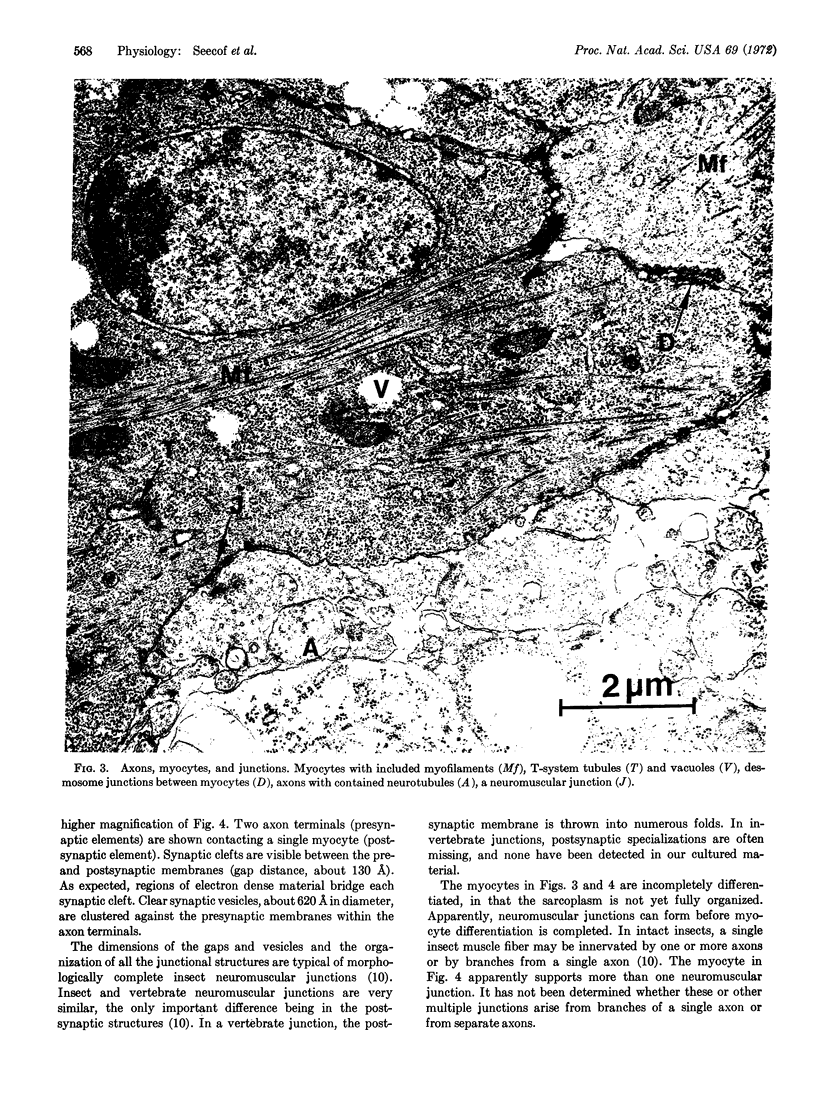
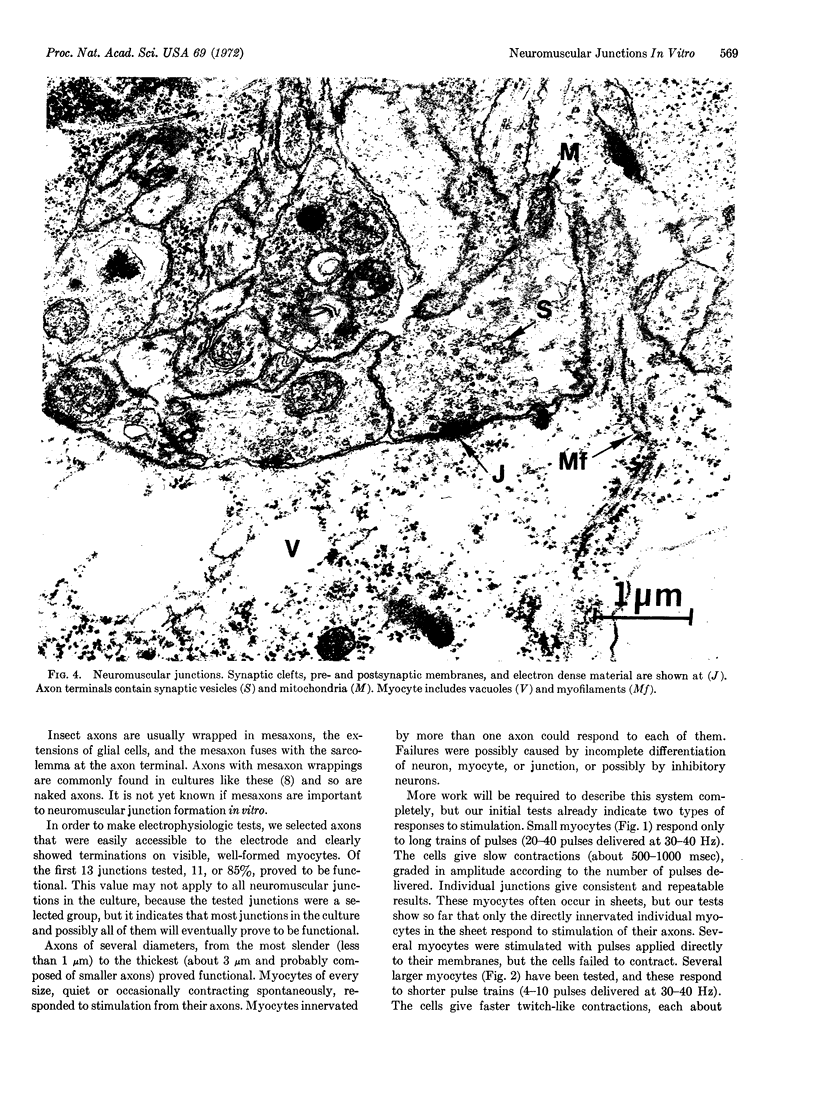
Cultures were prepared of embryonic cells from Drosophila melanogaster. Neurons and myocytes differentiated in vitro from their respective stem cells. Electron microscopy showed that neuromuscular junctions formed where axons contacted myocytes. Electrical stimuli were applied to axons and these caused contractions of innervated myocytes. This is the first report of insect or other invertebrate neuromuscular junctions differentiating in vitro. In addition, this is the first system reported in which the neurons, myocytes, and junctions are completely differentiated in vitro from neuroblasts and myoblasts.
Keywords: neurons, myocytes, electron microscopy, electrophysiology
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Crain S. M. Bioelectric interactions between cultured fetal rodent spinal cord and skeletal muscle after innervation in vitro. J Exp Zool. 1970 Apr;173(4):353–369. doi: 10.1002/jez.1401730403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischbach G. D. Synaptic potentials recorded in cell cultures of nerve and muscle. Science. 1970 Sep 25;169(3952):1331–1333. doi: 10.1126/science.169.3952.1331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James D. W., Tresman R. L. De novo formation of neuro-muscular junctions in tissue culture. Nature. 1968 Oct 26;220(5165):384–385. doi: 10.1038/220384a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins N., Yonezawa T. Developing neuromuscular junctions: first signs of chemical transmission during formation in tissue culture. Science. 1971 Apr 23;172(3981):395–398. doi: 10.1126/science.172.3981.395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seecof R. L., Alléaume N., Teplitz R. L., Gerson I. Differentiation of neurons and myocytes in cell cultures made from Drosophila gastrulae. Exp Cell Res. 1971 Nov;69(1):161–173. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(71)90321-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seecof R. L., Unanue R. L. Differentiation of embryonic Drosophila cells in vitro. Exp Cell Res. 1968 Jun;50(3):654–660. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(68)90430-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimada Y., Fischman D. A., Moscona A. A. Formation of neuromuscular junctions in embryonic cell cultures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Mar;62(3):715–721. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.3.715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veneroni G., Murray M. R. Formation de novo and development of neuromuscular junctions in vitro. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1969 Apr;21(2):369–382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]