Abstract
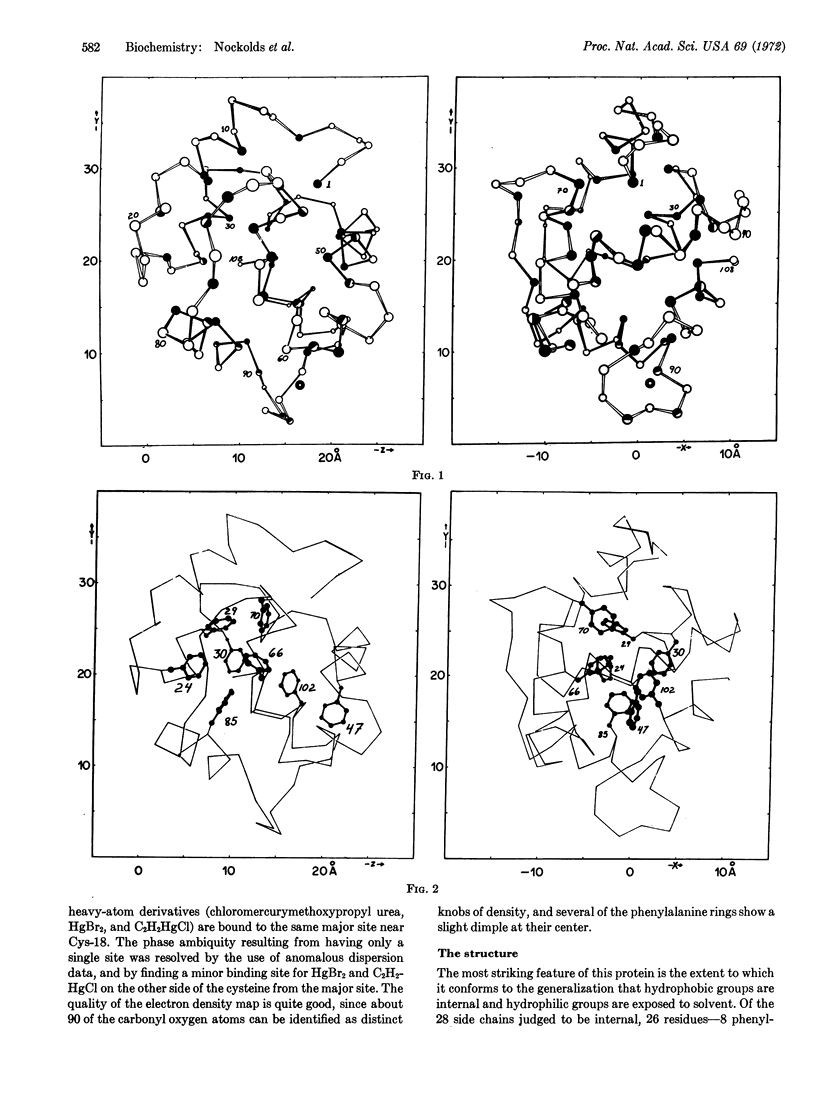
The amino-acid sequence and three-dimensional structure of a calcium-binding protein prepared from carp muscle has been determined. This protein, designated carp-muscle calcium-binding protein B, is one of three closely related parvalbumins found in this tissue. The electron density map, calculated by heavyatom substitution crystallographic methods to 2.0-Å resolution, reveals the orientation of most of the amino-acid side chains. The calcium coordination site consists of one glutamic- and three aspartic-acid carboxyl groups in a tetrahedral arrangement. The core of this spherical molecule is remarkably hydrophobic, with 8 of its 10 phenylalanine side chains packed in an approximate herringbone pattern. 52 of the 108 residues are in six α-helixes; there is no β-pleated sheet. The acetylated amino-terminal alanine appears not to be accessible to solvent. All of the heavy-atom derivatives are bound at the sole cysteine. The properties of this protein suggest a relationship to troponin A of mammalian tissue.
Keywords: muscle, x-ray analysis, amino-acid sequence, troponin
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnone A., Bier C. J., Cotton F. A., Day V. W., Hazen E. E., Jr, Richardson D. C., Yonath A., Richardson J. S. A high resolution structure of an inhibitor complex of the extracellular nuclease of Staphylococcus aureus. I. Experimental procedures and chain tracing. J Biol Chem. 1971 Apr 10;246(7):2302–2316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebashi S., Endo M., Otsuki I. Control of muscle contraction. Q Rev Biophys. 1969 Nov;2(4):351–384. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500001190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebashi S., Wakabayashi T., Ebashi F. Troponin and its components. J Biochem. 1971 Feb;69(2):441–445. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a129486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greaser M. L., Gergely J. Reconstitution of troponin activity from three protein components. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jul 10;246(13):4226–4233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAMOIR G., KONOSU S. CARP MYOGENS OF WHITE AND RED MUSCLES. GENERAL COMPOSITION AND ISOLATION OF LOW-MOLECULAR-WEIGHT COMPONENTS OF ABNORMAL AMINO ACID COMPOSITION. Biochem J. 1965 Jul;96:85–97. doi: 10.1042/bj0960085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartshorne D. J., Theiner M., Mueller H. Studies on troponin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Mar;175(2):320–330. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(69)90009-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KONOSU S., HAMOIR G., PECHERE J. F. CARP MYOGENS OF WHITE AND RED MUSCLES. PROPERTIES AND AMINO ACID COMPOSITION OF THE MAIN LOW-MOLECULAR-WEIGHT COMPONENTS OF WHITE MUSCLE. Biochem J. 1965 Jul;96:98–112. doi: 10.1042/bj0960098. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kretsinger R. H., Dangelat D., Bryan R. F. Crystal data for low molecular weight albumins of carp. J Mol Biol. 1971 Jul 14;59(1):213–214. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90423-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis P. N., Momany F. A., Scheraga H. A. Folding of polypeptide chains in proteins: a proposed mechanism for folding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Sep;68(9):2293–2297. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.9.2293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PECHERE J. F., FOCANT B. CARP MYOGENS OF WHITE AND RED MUSCLES. GROSS ISOLATION ON SEPHADEX COLUMNS OF THE LOW-MOLECULAR-WEIGHT COMPONENTS AND EXAMINATION OF THEIR PARTICIPATION IN ANAEROBIC GLYCOGENOLYSIS. Biochem J. 1965 Jul;96:113–118. doi: 10.1042/bj0960113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



