Abstract
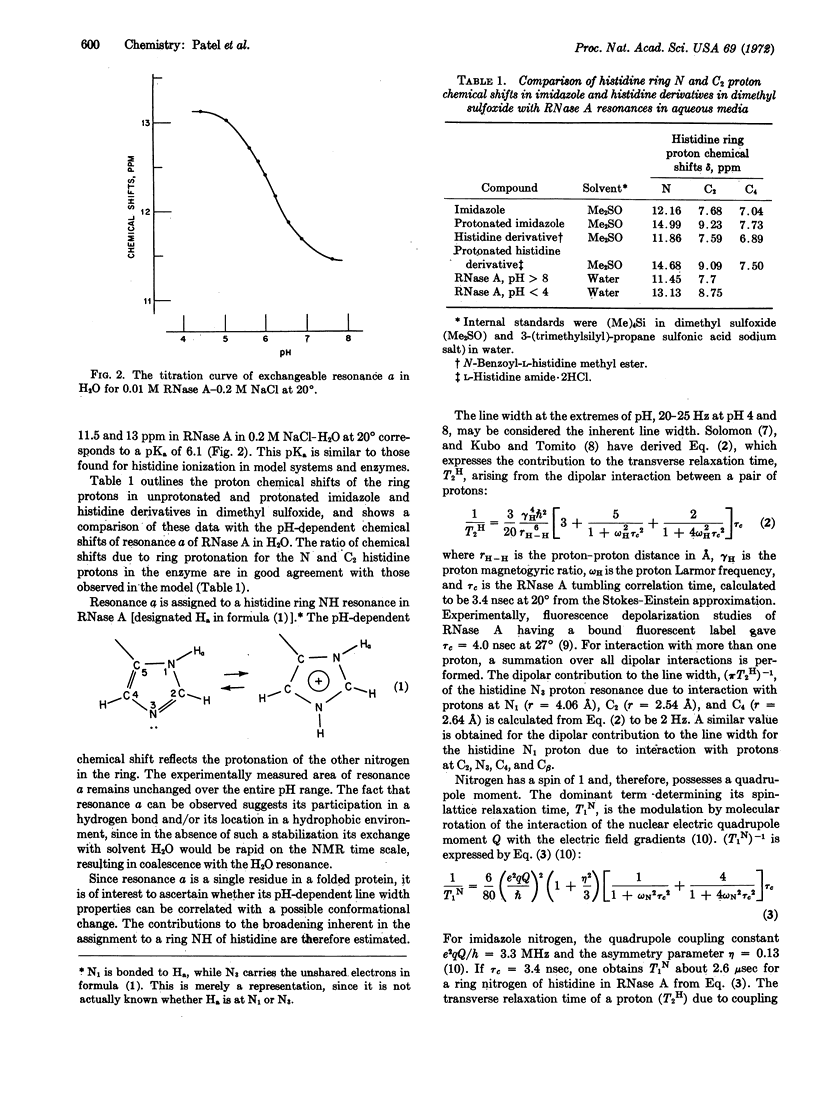
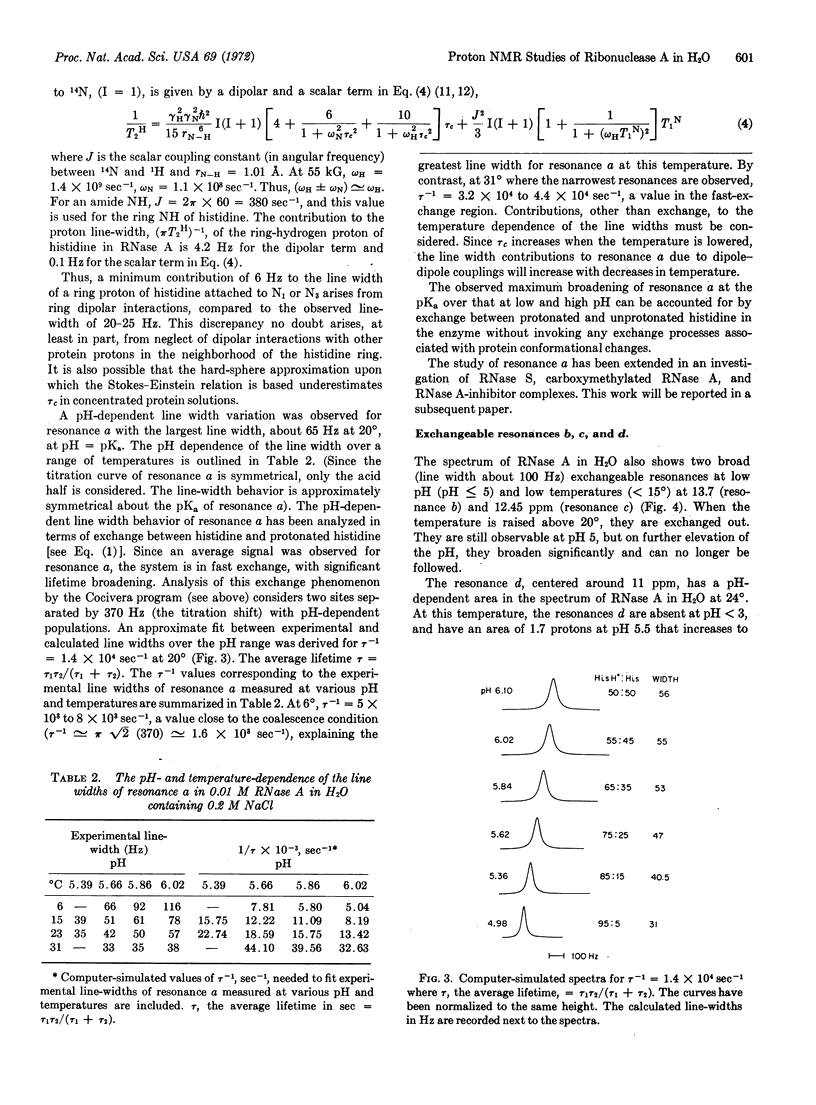
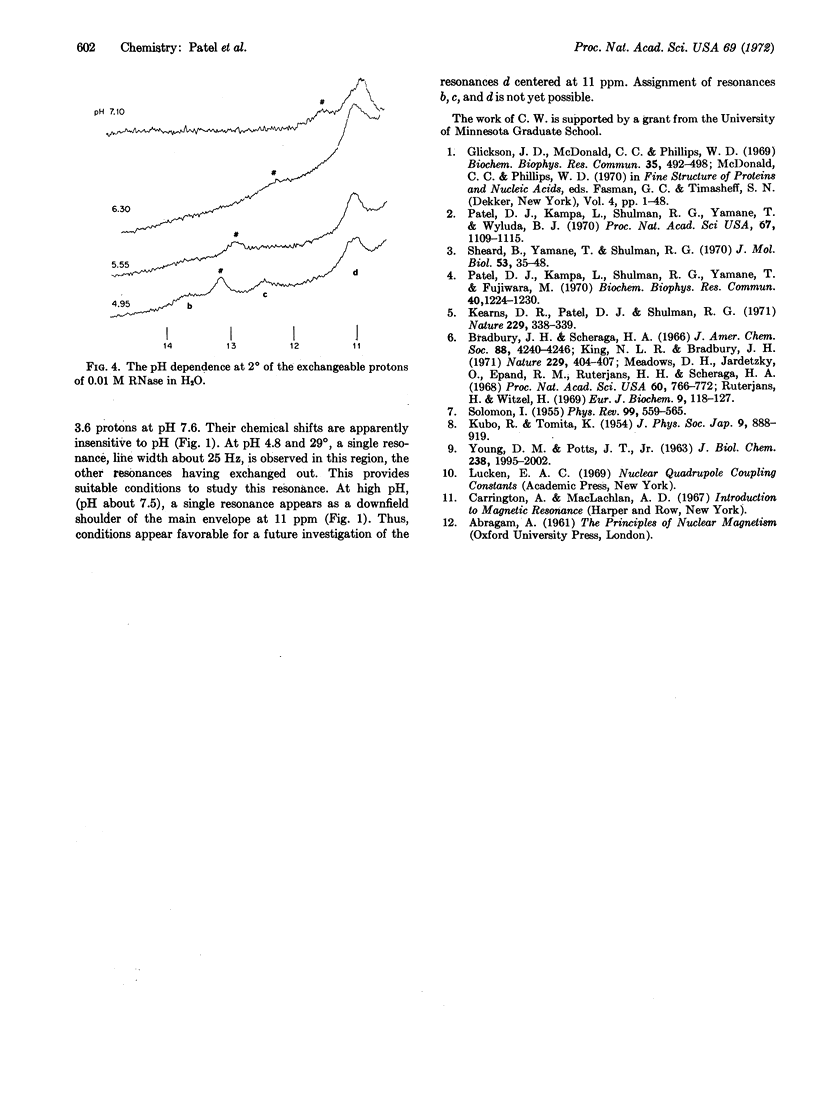
A resonance (designated a) due to an exchangeable proton titrates (pKa = 6.1) between 11.5 and 13 ppm in the nuclear magnetic resonance spectrum of RNase A-0.2 M NaCl in H2O at 20°. Comparison with models has permitted assignment to a ring-nitrogen proton of histidine in slow exchange with solvent H2O. The pH and temperature-dependent line-width changes of resonance a are analyzed in terms of an exchange between histidine and protonated histidine, without the necessity to invoke any exchange processes associated with protein conformational changes. Several other resonances due to exchangeable protons are observed between 10 and 15 ppm in the nuclear magnetic resonance spectrum of RNase A in H2O.
Keywords: histidine, NMR exchangeable protons
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Glickson J. D., McDonald C. C., Phillips W. D. Assignment of tryptophan indole NH proton resonances of lysozyme. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 May 22;35(4):492–498. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90373-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kearns D. R., Patel D. J., Shulman R. G. High resolution nuclear magnetic resonance studies of hydrogen bonded protons of tRNA in water. Nature. 1971 Jan 29;229(5283):338–339. doi: 10.1038/229338a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meadows D. H., Jardetzky O., Epand R. M., Ruterjans H. H., Scheraga H. A. Assignment of the histidine peaks in the nuclear magnetic resonance spectrum of ribonuclease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Jul;60(3):766–772. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.3.766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel D. J., Kampa L., Shulman R. G., Yamane T., Fujiwara M. Proton NMR studies of hemoglobin in H2O. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Sep 10;40(5):1224–1230. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90926-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel D. J., Kampa L., Shulman R. G., Yamane T., Wyluda B. J. Proton nuclear magnetic resonance studies of myoglobin in H2O. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Nov;67(3):1109–1115. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.3.1109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rüterjans H., Witzel H. NMR-studies on the structure of the active site of pancreatic ribonuclease A. Eur J Biochem. 1969 May 1;9(1):118–127. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00584.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheard B., Yamane T., Shulman R. G. Nuclear magnetic resonance study of cyanoferrimyoglobin; identification of pseudocontact shifts. J Mol Biol. 1970 Oct 14;53(1):35–48. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90044-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YOUNG D. M., POTTS J. T., Jr Structural transformations of bovine pancreatic ribonuclease in solution: a study of polarization of fluorescence. J Biol Chem. 1963 Jun;238:1995–2002. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



