Abstract
American children consume up to 27% of calories from high-fat and high-sugar snacks. Both sugar and fat consumption have been implicated as a cause of hepatic steatosis and obesity but the effect of meal pattern is largely understudied. We hypothesized that a high meal frequency, compared to consuming large meals, is detrimental in the accumulation of intrahepatic and abdominal fat. To test this hypothesis, we randomized 36 lean, healthy men to a 40% hypercaloric diet for 6 weeks or a eucaloric control diet and measured intrahepatic triglyceride content (IHTG) using proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy (1H-MRS), abdominal fat using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and insulin sensitivity using a hyperinsulinemic euglycemic clamp with a glucose isotope tracer before and after the diet intervention. The caloric surplus consisted of fat and sugar (high-fat-high-sugar; HFHS) or sugar only (high-sugar; HS) and was consumed together with, or between, the three main meals, thereby increasing meal size or meal frequency. All hypercaloric diets similarly increased body mass index (BMI). Increasing meal frequency significantly increased IHTG (HFHS mean relative increase of 45%; P = 0.016 and HS mean relative increase of 110%; P = 0.047), whereas increasing meal size did not (2-way analysis of variance [ANOVA] size versus frequency P = 0.03). Abdominal fat increased in the HFHS-frequency group (+63.3 ± 42.8 mL; P = 0.004) and tended to increase in the HS-frequency group (+46.5 ± 50.7 mL; P = 0.08). Hepatic insulin sensitivity tended to decrease in the HFHS-frequency group while peripheral insulin sensitivity was not affected. Conclusion: A hypercaloric diet with high meal frequency increased IHTG and abdominal fat independent of caloric content and body weight gain, whereas increasing meal size did not. This study suggests that snacking, a common feature in the Western diet, independently contributes to hepatic steatosis and obesity. (Trial registration: http://www.forestplots.net; nr.NCT01297738.) (Hepatology 2014;60:545–553)
Obesity is a worldwide health problem and associated with hepatic steatosis and intra-abdominal fat accumulation. Although obesity and hepatic steatosis often coincide, hepatic steatosis can be present in lean subjects and is not present in all obese humans,1 suggesting that factors besides obesity contribute to fat accumulation in the liver. An obvious candidate to be involved is the diet. Caloric content2 and individual macronutrients are associated with hepatic steatosis. Short-term high-fat diets increase intrahepatic triglyceride content (IHTG) in lean and obese humans3,4 and induce robust hepatic steatosis in rodents5 and dietary glucose and fructose stimulate de novo lipogenesis (DNL)6 and increase IHTG, even in lean subjects.7,8 Moreover, cross-sectional studies have identified the consumption of sugar-sweetened soft drinks as a dietary factor predicting hepatic steatosis.9 Recent human studies, however, showed that overfeeding resulted in accumulation of IHTG without a differential effect of fructose, glucose, or fat.10,11 This suggests that macronutrient composition is not the only determining dietary factor in IHTG accumulation. A factor less often considered is the frequency and timing of food intake. This is remarkable, since up to 27% of U.S. children's daily calories come from snacks12 and also in obese women excessive caloric intake mainly comes from snacks between meals.13 Interestingly, when provided with the choice to consume saturated fat and liquid sugar separate from their balanced chow pellets, rats increase their meal frequency, show persistent hyperphagia, and become obese.14 Whether snacking specifically affects IHTG is unknown.
Hepatic steatosis increases the risk for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), fibrosis, and cirrhosis and is associated with insulin resistance.15,16 How hepatic steatosis interferes with insulin sensitivity in humans is only in part elucidated. We recently showed in patients with familial hypobetalipoproteinemia, which is characterized by massive IHTG accumulation, that hepatic steatosis per se is not associated with insulin resistance.17 Interference of lipid metabolites with insulin signaling is a general concept in obesity-associated insulin resistance, and macronutrients themselves are able to modulate glucose production and insulin sensitivity independent of obesity.18,19 Rats snacking fat and sugar develop insulin resistance within 1 week,20 and female adolescents who reported consumption of frequent snacks throughout the day have a higher homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) compared to nonsnacking controls.21 Randomized controlled studies on the effect of increasing meal frequency or meal size with different macronutrient combinations on insulin sensitivity and IHTG are currently unavailable and was the aim of this study. We hypothesized that increasing meal frequency, representing a snacking eating pattern, negatively affects IHTG and insulin sensitivity.
Materials and Methods
Study Participants
We recruited 37 Caucasian, lean men (age 22 [19-27] years, body mass index [BMI] 22.5 [19.5-24.5] kg/m2) by way of local advertisements. Participants were healthy, had no family history of type 2 diabetes (T2DM) and a normal oral glucose tolerance test.22 Other exclusion criteria were use of medication, substance abuse (nicotine or drugs, alcohol >2 units/day), history of eating or psychiatric disorders, exercise >3 hours/week, and an unhealthy ad libitum diet. A healthy diet contained balanced macronutrient composition following the Dutch guidelines.23 Self-reported body weight was stable in the 6 months before study participation, thereby excluding a hypocaloric or hypercaloric state. The study protocol conformed to the ethical guidelines of the 1975 Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of the AMC Amsterdam. Written informed consent was obtained from all study participants before the start of study participation.
Study Design
A schematic overview of the study design is presented in Fig. 1. After inclusion subjects started the 1-week run-in phase: they reported their ad libitum intake on an online diet journal (eetmeter.voedingscentrum.nl). Body weight before and after this week had to be similar; the consumed amount of calories was then considered adequate for weight maintenance, i.e., eucaloric. Subjects were then randomized into one of four hypercaloric diet groups (n = 8/group) or a control group (n = 5). The control group underwent all measurements but continued the weight maintaining ad libitum diet. The diet was followed for 6 consecutive weeks. Subjects visited the research unit weekly for measurement of body weight and resting energy expenditure (REE) and diet monitoring; subjects daily reported their ad libitum intake online. When ad libitum caloric intake was lower than caloric need (1.4 × REE), subjects were instructed to increase their ad libitum intake. After the intervention, subjects were monitored until they returned to their baseline body weight. The baseline characteristics, study design, and changes in body weight have previously been reported.24
Figure 1.
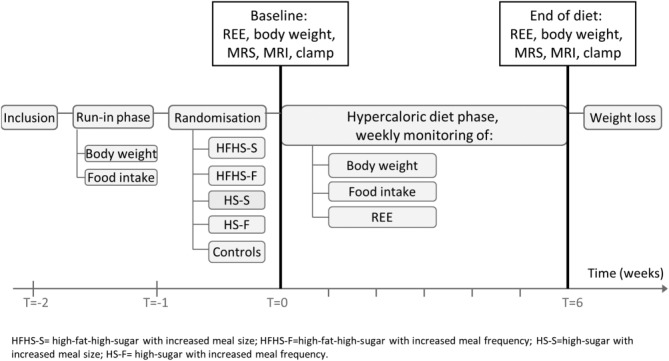
Study design.
Hypercaloric Diets
All diets consisted of a 40% caloric surplus on top of the ad libitum weight-maintaining diet (calculated as 1.4 × REE). The hypercaloric diet groups were:
HFHS-size group: high-fat-high-sugar (HFHS) diet using Nutridrink Compact three times a day, consumed together with the three daily main meals.
HFHS-frequency group: HFHS diet using Nutridrink Compact three times a day, consumed 2-3 hours after each meal.
HS-size group: high-sugar (HS) diet using commercially available sucrose-sweetened beverages three times a day, consumed together with the three daily main meals.
HS-frequency group: HS diet using commercially available sucrose-sweetened beverages three times a day, consumed 2-3 hours after each meal.
Nutridrink Compact (Nutricia Advanced Medical Nutrition; Zoetermeer, the Netherlands) is a liquid meal with nutritive value of 240 kcal/100 mL; 16 energy% protein (mainly casein), 49 energy% carbohydrates (mainly maltose and polysaccharides) and 35 energy% fat (mainly unsaturated fat). As HS liquid, subjects consumed commercially available sucrose-sweetened (=50% glucose/50% fructose) soft drinks. The soft drinks contained no fat or protein. Participants chose their beverage from a list of soft drinks with comparable nutritive value. Soft drinks contained 43.3 (range 36-49) kcal/100 mL and 10.3 (range 9-12) g/100 mL of sucrose. Participants consumed on average 1,000 mL 3 times per day.
Measurements and Calculations
REE
REE was measured using indirect calorimetry. VO2 and VCO2 were measured in the supine position for 20 minutes using a ventilated hood system (Vmax Encore 29; SensorMedics, Anaheim, CA). REE was calculated as described previously.25 The abbreviated Weir equation was used to calculate 24-hour energy expenditure.
IHTG Measurement Using Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (MRS)
1H-MRS measurements were performed on a clinical 3.0T Philips Intera scanner (Philips Healthcare, Best, The Netherlands). After performing T1-weighted coronal and axial localizer images of the abdomen, a voxel of 20 × 20 × 20 mm was positioned in the right hepatic lobe, avoiding inclusion of the diaphragm and edges of the liver, as well as vascular and biliary structures. Voxel size and acquisition times were standardized for all subjects. Spectra were acquired using first-order iterative shimming, a PRESS sequence with relaxation time/echo time (TR/TE) 2,000/35 ms and 64 signal acquisitions during free breathing.26 1H-MRS data were processed using jMRUI software. The water nonsuppressed spectra were used to quantify the lipid signal resonances. Relative fat content was expressed as a ratio of the fat peak area over the cumulative water and fat peak areas (1.3 ppm / (1.3 ppm + 4.65 ppm)). Calculated peak areas of water and fat were corrected for T2 relaxation. Percentage IHTG was calculated as previously described.26
Abdominal Fat Quantification Using MRI
We performed abdominal fat measurements in abdominal MRIs acquired on a clinical 3.0T Philips Intera scanner (Philips Healthcare) at baseline and after the diet period. The abdominal MRIs were bias field-corrected27 and then automatically segmented with in-house developed software, written in MatLab (MathWorks, Natick, MA). In short, subcutaneous fat was segmented using snakes, after which visceral fat was segmented by intensity thresholding. The data were then manually corrected by one well-trained researcher blinded for the randomization with ITK-SNAP 2.2 software. We analyzed abdominal fat in 10 consecutive slices at the level of lumbar vertebrae L3/L4, which has been shown to be representative for total abdominal fat.28
Two-Step Hyperinsulinemic Euglycemic Clamp
Insulin sensitivity was measured with a two-step hyperinsulinemic euglycemic clamp after an overnight fast in supine position as described previously.29 Additional details are given in the Supporting Material.
Laboratory Analyses
Plasma glucose concentrations were measured with a glucose oxidase method (EKF Diagnostics, Barleben/Magedeburg, Germany). Insulin and cortisol were determined on an IMMULITE 2000 system (Siemens Healthcare Diagnostics, Breda, The Netherlands). Free fatty acids (FFA) were measured by an enzymatic method (Nefac; Wako Chemicals, Richmond, VA). Leptin and glucagon were determined by radioimmunoassay (Millipore, Billerica, MA). [6,6-2H2] glucose enrichment was measured with gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Additional details are provided in the Supporting Material.
Sample Size
We based our sample size calculations on a previous study in which we showed that a hypercaloric diet increased HOMA-IR (measure for insulin sensitivity) by 0.46 ± 0.17.30 HOMA-IR has been shown previously to be associated with clamp-derived insulin sensitivity measures.31 We calculated the sample size with a significance level α = 0.05, power = 80% and effect size = 0.46. To determine significant differences in insulin sensitivity we needed seven subjects per group.
Randomization Process
Subjects were randomly allocated to one of the four hypercaloric diet groups or the control group. Randomization was not blinded. We performed simple, nonstratified randomization by drawing lots.
Calculations and Statistics
Endogenous glucose production (EGP) and peripheral glucose uptake (rate of disappearance, Rd) were calculated using modified versions of the Steele equations for the nonsteady-state and expressed as micromoles/kilograms/minute as described previously.32,33 We calculated caloric intake/day as the mean of the complete diet period of 6 weeks. When normality tests showed normal distribution, data before and after the diet within the groups were compared using a paired Student t test. Otherwise, the Wilcoxon matched pairs test was used. Between-group differences were analyzed using a two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with a post-hoc Bonferroni for multiple comparisons.
Results
Recruitment and Baseline Characteristics
After 37 subjects completed the study protocol, we excluded two subjects from the analyses because of uncertain diet compliance. We furthermore excluded one subject because of excessive alcohol consumption during the last hypercaloric intervention week. Two subjects were replaced by newly recruited participants. Baseline characteristics of the subjects are presented in Table1. Subjects were lean and had normal insulin sensitivity and IHTG. Control subjects consumed more carbohydrate and less fat at baseline compared to the four hypercaloric groups, but intake was similar between the four hypercaloric groups (Table1).
Table 1.
Baseline Characteristics of Study Participants
| Controls | HFHS-S | HFHS-F | HS-S | HS-F | P | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | 5 | 8 | 8 | 7 | 8 | |
| Age (y) | 23.0 ± 3.1 | 22.6 ± 2.9 | 21.5 ± 1.9 | 22.0 ± 2.5 | 21.9 ± 2.8 | 0.84 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 22.6 ± 2.3 | 22.3 ± 1.0 | 22.5 ± 1.5 | 21.7 ± 1.1 | 22.6 ± 1.8 | 0.90 |
| Weight (kg) | 76.6 ± 7.7 | 78.0 ± 5.6 | 81.3 ± 8.1 | 77.4 ± 7.9 | 81.0 ± 8.8 | 0.70 |
| Waist circumference (cm) | 79.9 ± 5.4 | 80.7 ± 3.1 | 83.3 ± 3.3 | 79.0 ± 4.9 | 82.4 ± 3.2 | 0.25 |
| Leptin (ng/ml) | 2.8 ± 1.7 | 3.0 ± 1.5 | 3.3 ± 1.4 | 1.9 ± 0.2 | 3.7 ± 1.4 | 0.14 |
| Resting energy expenditure (kCal/kg) | 23.7 ± 1.8 | 23.9 ± 2.6 | 24.1 ± 2.0 | 22.4 ± 2.5 | 24.5 ± 2.6 | 0.12 |
| Caloric intake (kCal/day) | 2490 ± 262 | 2566 ± 317 | 2616 ± 323 | 2353 ± 503 | 2456 ± 292 | 0.64 |
| Carbohydrate intake (% of total kCal) | 51 ± 8 | 45 ± 4 | 45 ± 5 | 45 ± 4 | 40 ± 5 | 0.02 |
| Fat intake (% of total kCal) | 29 ± 4 | 31 ± 5 | 35 ± 5 | 32 ± 6 | 39 ± 5 | 0.006 |
| Protein intake (% of total kCal) | 15 ± 3 | 15 ± 2 | 16 ± 2 | 16 ± 2 | 16 ± 2 | 0.48 |
| Glucose (mmol/L) | 4.8 ± 0.4 | 4.7 ± 0.3 | 4.7 ± 0.2 | 4.7 ± 0.1 | 4.9 ± 0.2 | 0.61 |
| Insulin (pmol/L) | 45.0 ± 13.4 | 40.1 ± 8.6 | 55.0 ± 21.5 | 37.0 ± 11.4 | 57.7 ± 28.7 | 0.21 |
| HOMA-IR | 1.4 ± 0.4 | 1.2 ± 0.3 | 1.7 ± 0.6 | 1.1 ± 0.3 | 1.7 ± 0.9 | 0.19 |
| Plasma TG (mmol/L) | 0.73 ± 0.29 | 0.70 ± 0.49 | 0.56 ± 0.20 | 0.60 ± 0.21 | 0.70 ± 0.37 | 0.90 |
| Free fatty acids (mmol/L) | 0.60 ± 0.27 | 0.33 ± 0.09 | 0.54 ± 0.23 | 0.48 ± 0.20 | 0.68 ± 0.28 | 0.09 |
| Hepatic TAG Content (%) | 1.34 ± 0.54 | 0.86 ± 0.34 | 0.98 ± 0.91 | 0.80 ± 0.49 | 1.49 ± 0.95 | 0.13 |
Data are presented as mean ± SD. Glucose, insulin, triglycerides (TG) and free fatty acids were determined in the fasting state.
Control Subjects
In the control group, BMI remained stable between the T = 0 weeks and T = 6 weeks measurements (22.3 ± 2.1 versus 22.2 ± 2.2 kg/m2; P = 0.37). Caloric intake and intake of specific macronutrients were stable during the observational period (data not shown). IHTG (1.34 ± 0.54 versus 1.15 ± 0.26%; P = 0.50), abdominal fat (0.57 ± 0.25 versus 0.56 ± 0.11 liter; P = 0.92), insulin-mediated suppression of EGP (75.0 ± 7.1 versus 73.0 ± 14.7%; P = 0.81), and peripheral rate of disappearance of glucose (64.8 ± 8.7 versus 68.3 ± 5.1 μmol/kg/min; P = 1.00) did not change after the observational period. Control subjects were included to show reproducibility of the measurements only and are therefore not further analyzed.
Caloric Intake
Food intake and macronutrient composition during the hypercaloric interventions are presented in Table2 and Fig. 2A. In summary, ad libitum nutrient intake was similar between the four diet groups. There was no difference in carbohydrate and fat intake between both HS groups or between both HFHS groups. There were no side effects or adverse events reported by subjects on any of the four diets.
Table 2.
Food Intake per Randomization Group During the Hypercaloric Diet
| Post-hoc | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HFHS-S | HFHS-F | HS-S | HS-F | P | Between HFHS | Between HS | |
| Total caloric intake (kCal) | 3747 ± 137 | 3987 ± 218 | 3474 ± 694 | 3614 ± 381 | 0.11 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Ad libitum caloric intake (kCal) | 2640 ± 141 | 2886 ± 171 | 2565 ± 469 | 2633 ± 216 | 0.13 | 0.49 | 1.00 |
| Caloric surplus (kCal) | 1106 ± 132 | 1101 ± 141 | 909 ± 239 | 982 ± 262 | 0.18 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Total carbohydrate intake (g) | 437 ± 33 | 444 ± 38 | 507 ± 118 | 511 ± 81 | 0.10 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Ad libitum carbohydrate intake (g) | 300 ± 33 | 308 ± 31 | 278 ± 68 | 263 ± 27 | 0.16 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Excess carbohydrate intake (g) | 137 ± 16 | 136 ± 17 | 229 ± 60 | 248 ± 66 | <0.001 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Total fat intake (g) | 143 ± 16 | 155 ± 6 | 102 ± 19 | 115 ± 11 | <0.001 | 0.64 | 0.42 |
| Ad libitum fat intake (g) | 100 ± 17 | 112 ± 4 | 102 ± 19 | 115 ± 11 | 0.11 | 0.61 | 0.46 |
| Excess fat intake (g) | 43 ± 5 | 43 ± 6 | 0 | 0 | <0.001 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Total protein intake (g) | 142 ± 13 | 151 ± 5 | 106 ± 24 | 108 ± 6 | <0.001 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Ad libitum protein intake (g) | 98 ± 11 | 106 ± 7 | 106 ± 24 | 108 ± 6 | 0.48 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Excess protein intake (g) | 44 ± 5 | 44 ± 6 | 0 | 0 | <0.001 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Relative carbohydrate intake (% of total kCal)* | 47 ± 4 | 46 ± 2 | 58 ± 3 | 56 ± 4 | <0.001 | 0.45 | 0.35 |
| Relative fat intake (% of total kCal)* | 35 ± 3 | 36 ± 1 | 27 ± 4 | 29 ± 3 | <0.001 | 0.43 | 0.26 |
| Relative protein intake (% of total kCal)* | 15 ± 1 | 15 ± 1 | 12 ± 2 | 12 ± 2 | <0.001 | 0.74 | 0.74 |
Data are presented as [mean ± SD] food intake per day over the complete 6-week diet period.
Relative intake data are approximations due to used assumptions on converting grams to calories: 1g carb = 4 kCal; 1g fat = 9 kCal; 1g protein = 4 kCal.
Figure 2.
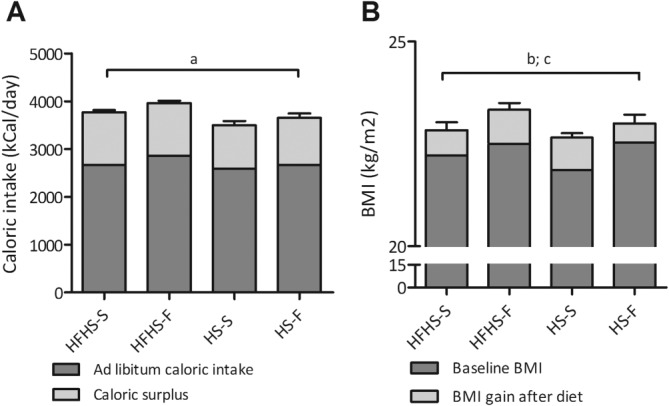
(A) Ad libitum caloric intake and surplus caloric intake during the diet interventions. Data are presented as mean and SEM, average of the 6-week diet period. (a) ANOVA of total caloric intake: P = 0.11, F = 2.24. (B) Baseline BMI and BMI gain after the hypercaloric diets. Data are presented as mean and SEM group averages. (b) ANOVA BMI gain: P = 0.42, F = 0.97; (c) ANOVA BMI after the diet: P = 0.81, F = 0.32.
BMI and REE
Subjects gained 2.5 ± 1.7 kg within the 6 weeks. All hypercaloric diet interventions resulted in an increase in BMI (Table3) with no differences between the diet groups (Fig. 2B). REE did not change in any of the diet groups (Table3).
Table 3.
Intervention Data
| HFHS-S | HFHS-F | HS-S | HS-F | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | End diet | P | Baseline | End diet | P | Baseline | End diet | P | Baseline | End diet | P | |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 22.2 ± 1.0 | 22.8 ± 1.1 | 0.016 | 22.5 ± 1.5 | 23.4 ± 1.3 | 0.001 | 21.9 ± 1.1 | 22.7 ± 1.1 | <0.001 | 22.6 ± 1.8 | 23.1 ± 2.2 | 0.070 |
| REE (kCal/day) | 1898 ± 187 | 1946 ± 115 | 0.442 | 1948 ± 157 | 1985 ± 123 | 0.273 | 1794 ± 167 | 1892 ± 245 | 0.175 | 1925 ± 140 | 1904 ± 145 | 0.774 |
| Fasting glucose (mmol/L) | 4.8 ± 0.3 | 4.7 ± 0.2 | 0.935 | 4.7 ± 0.2 | 4.8 ± 0.2 | 0.644 | 4.7 ± 0.1 | 4.6 ± 0.4 | 0.516 | 4.9 ± 0.2 | 5.0 ± 0.2 | 0.685 |
| Fasting insulin (pmol/L) | 41 ± 8 | 48 ± 15 | 0.398 | 55 ± 22 | 60 ± 20 | 0.207 | 36 ± 11 | 48 ± 13 | 0.028 | 55 ± 28 | 53 ± 15 | 0.889 |
| Fasting cortisol (nmol/L) | 346 ± 195 | 281 ± 81 | 0.575 | 247 ± 81 | 281 ± 115 | 0.575 | 186 ± 46 | 196 ± 73 | 0.612 | 347 ± 150 | 274 ± 164 | 0.161 |
| Fasting glucagon (ng/L) | 68.6 ± 20.8 | 58.6 ± 13.8 | 0.401 | 74.1 ± 16.0 | 78.0 ± 17.6 | 0.496 | 67.2 ± 10.3 | 78.6 ± 20.0 | 0.248 | 70.8 ± 18.6 | 62.9 ± 16.1 | 0.779 |
| Fasting leptin (ng/ml) | 2.9 ± 1.5 | 3.7 ± 1.9 | 0.030 | 3.3 ± 1.4 | 5.0 ± 2.6 | 0.028 | 1.9 ± 0.2 | 2.7 ± 0.9 | 0.028 | 3.5 ± 1.4 | 4.9 ± 2.4 | 0.075 |
| Fasting triglyceride (mmol/L) | 0.69 ± 0.45 | 0.78 ± 0.35 | 0.647 | 0.56 ± 0.21 | 0.84 ± 0.32 | 0.012 | 0.66 ± 0.24 | 0.83 ± 0.40 | 0.176 | 0.68 ± 0.35 | 0.85 ± 0.38 | 0.233 |
| Fasting FFA (mmol/L) | 0.35 ± 0.11 | 0.37 ± 0.10 | 0.574 | 0.54 ± 0.23 | 0.41 ± 0.11 | 0.208 | 0.48 ± 0.18 | 0.31 ± 0.17 | 0.108 | 0.65 ± 0.28 | 0.45 ± 0.26 | 0.093 |
| Basal EGP (μmol/kg.min) | 12.1 ± 0.8 | 12.1 ± 1.7 | 0.899 | 11.7 ± 1.0 | 11.9 ± 1.1 | 0.610 | 11.8 ± 1.2 | 11.8 ± 1.0 | 0.964 | 11.9 ± 1.1 | 12.2 ± 1.4 | 0.341 |
| Suppression of EGP (%) | 72.7 ± 5.9 | 78.9 ± 5.7 | 0.166 | 84.6 ± 10.9 | 75.2 ± 7.2 | 0.083 | 80.2 ± 7.8 | 75.3± 7.3 | 0.248 | 71.9 ± 15.3 | 73.3 ± 6.7 | 0.527 |
| Rd (μmol/kg.min) | 67.3 ± 7.2 | 65.7 ± 8.1 | 1.000 | 65.3 ± 11.8 | 65.1 ± 9.6 | 0.779 | 62.4 ± 10.9 | 59.7 ± 9.1 | 0.310 | 57.3 ± 5.9 | 54.9 ± 7.7 | 0.263 |
| Step 1 Plasma Insulin (pmol/L) | 128 ± 25 | 144 ± 46 | 0.122 | 160 ± 40 | 169 ± 38 | 0.342 | 146 ± 32 | 142 ± 35 | 0.629 | 134 ± 35 | 150 ± 43 | 0.238 |
| Step 2 Plasma Insulin (pmol/L) | 424 ± 79 | 445 ± 102 | 0.349 | 522 ± 103 | 489 ± 73 | 0.262 | 468 ± 91 | 445 ± 107 | 0.359 | 445 ± 81 | 492 ± 95 | 0.184 |
| Step 1 FFA suppression (%) | 90.2 ± 7.8 | 90.2 ± 5.8 | 0.889 | 92.1 ± 6.3 | 87.5 ± 6.7 | 0.036 | 95.0 ± 2.8 | 89.5 ± 8.1 | 0.128 | 92.8 ± 3.7 | 91.6 ± 5.7 | 0.735 |
| Step 2 FFA suppression (%) | 97.8 ± 3.2 | 95.7 ± 4.3 | 0.465 | 96.1 ± 4.0 | 96.1 ± 3.4 | 0.463 | 98.3 ± 3.1 | 98.7 ± 3.6 | 0.655 | 98.9 ± 2.1 | 98.2 ± 3.1 | 0.686 |
| Intra-abdominal adipose tissue (liter) | 0.45 ± 0.09 | 0.45 ± 0.06 | 0.907 | 0.53 ± 0.20 | 0.59 ± 0.19 | 0.004 | 0.39 ± 0.14 | 0.44 ± 0.10 | 0.303 | 0.50 ± 0.14 | 0.55 ± 0.16 | 0.051 |
| Subcutaneous adipose tissue (liter) | 0.25 ± 0.06 | 0.23 ± 0.06 | 0.393 | 0.29 ± 0.14 | 0.33 ± 0.14 | 0.007 | 0.19 ± 0.07 | 0.22 ± 0.06 | 0.151 | 0.26 ± 0.08 | 0.29 ± 0.09 | 0.020 |
| Visceral adipose tissue (liter) | 0.20 ± 0.06 | 0.21 ± 0.05 | 0.177 | 0.24 ± 0.08 | 0.26 ± 0.08 | 0.074 | 0.22 ± 0.12 | 0.21 ± 0.05 | 0.565 | 0.24 ± 0.08 | 0.27 ± 0.08 | 0.175 |
IHTG
IHTG significantly increased in the HFHS-frequency (0.98 ± 0.91% versus 1.38 ± 1.26% [mean relative increase 45%]; P = 0.018) and the HS-frequency (1.49 ± 0.95% versus 3.10 ± 2.16% [mean relative increase 110%]; P = 0.043) groups (Fig. 3). The increase in IHTG tended to be higher in the HS-frequency group (P = 0.07). In the two groups with increased meal size, IHTG did not change (HFHS-size 0.85 ± 0.32% versus 1.05 ± 0.57%, P = 0.208; HS-size 0.80 ± 0.45% versus 0.93 ± 1.04%, P = 0.917) (Fig. 3). Two-way ANOVA analysis of the four hypercaloric diet groups showed an overall effect of size versus frequency (P = 0.03, F = 5.435) but not of HFHS versus HS (P = 0.13, F = 2.418).
Figure 3.
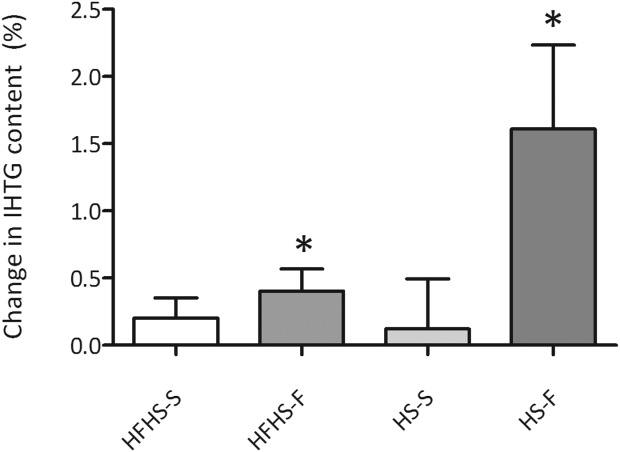
Change in IHTG (%) by the different hypercaloric interventions *P < 0.05. Data are presented as mean and SEM.
Abdominal Fat
Total abdominal fat significantly increased in the HFHS-frequency group and tended to increase in the HS-frequency group. In the HFHS-size and HF-size group abdominal fat did not change (Table3). The increase in abdominal fat was not different between the two frequency groups (P = 0.50). The increase in total abdominal fat was mainly caused by an increase in subcutaneous fat in both frequency groups (Table3). Fat in the visceral compartment tended to increase in the HFHS-frequency group and was unchanged in all other groups (Table3).
Glucose Metabolism
Fasting glucose and EGP did not change upon the diet interventions. Fasting insulin levels slightly but significantly increased in the HS-S group only (Table3). Hepatic insulin sensitivity expressed as percent insulin-mediated suppression of baseline EGP tended to decrease in the HFHS-frequency group (Table3) but not in the other groups. Peripheral insulin sensitivity did not change in any of the hypercaloric diet groups (Table3). In the HFHS-frequency group insulin-mediated suppression of FFA significantly decreased (Table3).
Glucoregulatory Hormones, Leptin, and Plasma Lipids
Plasma leptin concentrations increased in all diet intervention groups (Table3). Glucoregulatory hormones did not change. Fasting plasma concentrations of triglycerides (TG) increased upon the HFHS-frequency diet only.
Overall Effects of Increasing Meal Size Versus Meal Frequency
In Table4 the differences between pooled data from the meal size (HS-S and HFHS-S) and meal frequency (HS-F and HFHS-F) hypercaloric diet groups are shown. While BMI significantly increases in both groups, only increasing meal frequency significantly increases IHTG and abdominal (subcutaneous and visceral) fat and reduces insulin-mediated suppression of circulating fatty acids.
Table 4.
Increased Meal Size vs. Increased Meal Frequency
| Increased Meal Size | Increased Meal Frequency | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | After diet | P | Baseline | After diet | P | |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 22.05 ± 0.98 | 22.75 ± 1.04 | < 0.001 | 22.5 ± 1.5 | 23.2 ± 1.6 | < 0.001 |
| Basal EGP (μmol/kg.min) | 11.9 ± 1.0 | 11.9 ± 1.3 | 0.94 | 11.8 ± 1.0 | 12.1 ± 1.3 | 0.29 |
| Suppression of EGP (%) | 76.5 ± 7.7 | 77.1 ± 6.6 | 0.84 | 78.3 ± 14.0 | 74.7 ± 6.6 | 0.28 |
| Rd (μmol/kg.min) | 64.2 ± 9.0 | 62.7 ± 8.9 | 0.54 | 61.3 ± 9.9 | 60.0 ± 9.9 | 0.45 |
| Step 1 FFA suppression (%) | 92.4 ± 6.3 | 89.9 ± 6.7 | 0.31 | 92.5 ± 5.0 | 89.6 ± 6.4 | 0.04 |
| Step 2 FFA suppression (%) | 97.9 ± 3.1 | 97.2 ± 4.1 | 0.51 | 97.5 ± 3.4 | 97.2 ± 3.3 | 0.68 |
| Intra-abdominal adipose tissue (L) | 0.421 ± 0.112 | 0.444 ± 0.075 | 0.35 | 0.515 ± 0.167 | 0.581 ± 0.171 | < 0.001 |
| Visceral adipose tissue (L) | 0.196 ± 0.068 | 0.215 ± 0.041 | 0.18 | 0.239 ± 0.073 | 0.266 ± 0.077 | 0.02 |
| Subcutaneous adipose tissue (L) | 0.225 ± 0.069 | 0.228 ± 0.056 | 0.83 | 0.276 ± 0.111 | 0.315 ± 0.115 | < 0.001 |
| Intrahepatic triglyceride content (%) | 0.83 ± 0.38 | 1.00 ± 0.77 | 0.35 | 1.22 ± 0.93 | 2.18 ± 1.90 | 0.01 |
Discussion
We show that a 6-week hypercaloric snacking diet increases IHTG and abdominal fat in lean men while increasing meal size does not. Moreover, we show that this was irrespective of the macronutrients in the diet, as both snacking sugar and snacking fat and sugar resulted in IHTG and abdominal fat accumulation. However, the increase in IHTG tended to be higher in the HS-frequency group, indicating that the frequent snacking of sugar leads to the most profound accumulation of IHTG. Although frequent consumption of snacks has been linked to obesity,13,14 we are the first to provide evidence that overeating by consuming frequent meals, and not large meals, contributes to fat accumulation in liver independent of body weight gain. It has been shown that consumption of excessive carbohydrates above caloric need substantially increases fractional DNL34 and glycogen synthesis.11 The trend we demonstrated for a higher increase in IHTG in the HS-frequency group compared to the HFHS-frequency group (which consumed fewer carbohydrates) is in line with this hypothesis, although subjects in the size groups also consumed excessive carbohydrates but spread over three meals. Snacking of mono- and polysaccharides seems to exert the same effect on IHTG, as our HS diets contained monosaccharides, whereas our HFHS diets contained polysaccharides.
The underlying molecular mechanisms remain to be elucidated. Continuous delivery of nutrients through the portal vein might yield a different metabolic response compared to a pattern of fasting and feeding cycles. Our data suggest that a continuous flow of nutrients to hepatocytes stimulates DNL either through induction of carbohydrate responsive transcription factors like CHREBP or insulin-mediated induction of SREBP1c, PPARγ, or LXR.35,36 Besides the nutrients, an increased flux of portal FFA might stimulate DNL37 since it has been reported that the plasma FFA pool accounts for 60% of IHTG in humans with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).6 Lipolysis rates from abdominal adipose tissue were not directly measured in our study, but insulin-mediated suppression of plasma FFA, a marker of insulin sensitivity of adipose tissue, was reduced in the HFHS-, but not HS-, frequency group. A reduction in β-oxidation is another possible mechanism since in obesity-related hepatic steatosis both increased DNL and decreased β-oxidation have been shown in rodents.38 The mechanisms of excessive storage of liver TGs might be different when subjects are exposed to high-sugar versus high-fat-high-sugar diets. Increased IHTG and abdominal fat are risk factors for insulin resistance and T2DM and our data imply that a long-term hypercaloric snacking diet increases the risk for perturbed glucose metabolism independently of obesity. A reduction in hepatic insulin sensitivity was observed in the HFHS-frequency group compared to the HFHS-size group, suggesting that fat and sugar when consumed in excess and as between-meal snacks independently affect hepatic glucose metabolism. However, the effect was relatively modest. Although some studies show an association between dietary sugar consumption and insulin resistance and the prevalence of diabetes,10,19,39 it is difficult to discern whether this is a direct effect of carbohydrates overconsumption or secondary to the induction of obesity. Moreover, the eating pattern was not always monitored in those studies. We did not observe changes in peripheral insulin sensitivity in any of the diet groups studied. We previously showed that a period of 4-7 weeks of a hypercaloric diet significantly decreased insulin sensitivity.30 However, in that study subjects were older, had a higher baseline BMI, and gained more body weight.
Limitations
The study was conducted under free-living conditions with a risk of noncompliance. However, weekly visits and intensive phone and email contact with the participants ensured good compliance with the diets, confirmed by a steady weekly increase in body weight. Furthermore, this study was conducted in healthy, young, Caucasian, male volunteers. Therefore, the results might be different in older subjects, female subjects, and subjects from different ethnicities. Therefore, the results of this study cannot be extrapolated to the general population. Because our intervention was a short-term diet, results might be different during long-term exposure to hypercaloric diets. We did not include a high-fat-only group and therefore the specific effect of a high-fat high-frequency diet remains unknown. The total increase in IHTG in our subjects was relatively modest and might be different in other populations.
Finally, the lack of an effect of the short-term hypercaloric diet intervention on insulin sensitivity might become apparent in other populations, since we showed previously that short-term hypercaloric diets in a somewhat older population affected whole body insulin sensitivity.30
Clinical Relevance
Reports estimate that American children consume up to 27% of calories from snacks12 and snacking is common in obese women.13 Our findings are therefore an actual reflection of eating habits in today's society and might in part be an explanation for the increased number of children and adults with hepatic steatosis and T2DM.40,41 Our data indicate that attention should be paid to diet patterns besides caloric intake in general in the treatment of subjects with hepatic steatosis and abdominal obesity. In obese subjects who presumably consume a hypercaloric diet, snacking should be strongly discouraged. In addition, one might hypothesize that consuming fewer meals might be beneficial in reducing hepatic and abdominal fat accumulation.
In conclusion, hypercaloric diets with increased meal frequency, representing snacking, increase IHTG and abdominal fat in lean men, whereas similar diets with increased meal size do not. This suggests that food intake pattern independent of caloric excess and weight gain contributes to the occurrence of hepatic steatosis and abdominal obesity. Besides, hypercaloric snacking of fat and sugar tended to reduce hepatic insulin sensitivity. Therefore, reducing snacking behavior and encouraging consuming 3 meals per day might have favorable metabolic consequences in the long term and might reduce the prevalence of NAFLD.
Glossary
- 1H-MRS
proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy
- HFHS
high-fat-high-sugar
- IHTG
intrahepatic triglyceride content
- MRI
magnetic resonance imaging
- REE
resting energy expenditure
Supporting Information
Additional Supporting Information may be found in the online version of this article at the publisher's website.
Supporting Information
References
- 1.Ong JP, Younossi ZM. Epidemiology and natural history of NAFLD and NASH. Clin Liver Dis. 2007;11:1–16, vii. doi: 10.1016/j.cld.2007.02.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Heilbronn LK, Coster AC, Campbell LV, Greenfield JR, Lange K, Christopher MJ, et al. Obesity. Vol. 21. (Silver Spring); 2013. The effect of short-term overfeeding on serum lipids in healthy humans; pp. E649–E659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.van der Meer RW, Hammer S, Lamb HJ, Frolich M, Diamant M, Rijzewijk LJ, et al. Effects of short-term high-fat, high-energy diet on hepatic and myocardial triglyceride content in healthy men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008;93:2702–2708. doi: 10.1210/jc.2007-2524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Westerbacka J, Lammi K, Hakkinen AM, Rissanen A, Salminen I, Aro A, et al. Dietary fat content modifies liver fat in overweight nondiabetic subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2005;90:2804–2809. doi: 10.1210/jc.2004-1983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Meli R, Mattace RG, Irace C, Simeoli R, Di PA, Paciello O, et al. High fat diet induces liver steatosis and early dysregulation of iron metabolism in rats. PLoS One. 2013;8:e66570. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0066570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Donnelly KL, Smith CI, Schwarzenberg SJ, Jessurun J, Boldt MD, Parks EJ. Sources of fatty acids stored in liver and secreted via lipoproteins in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J Clin Invest. 2005;115:1343–1351. doi: 10.1172/JCI23621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Maersk M, Belza A, Stodkilde-Jorgensen H, Ringgaard S, Chabanova E, Thomsen H, et al. Sucrose-sweetened beverages increase fat storage in the liver, muscle, and visceral fat depot: a 6-mo randomized intervention study. Am J Clin Nutr. 2012;95:283–289. doi: 10.3945/ajcn.111.022533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Le KA. Ith M. Kreis R. Faeh D. Bortolotti M. Tran C, et al. Fructose overconsumption causes dyslipidemia and ectopic lipid deposition in healthy subjects with and without a family history of type 2 diabetes. Am J Clin Nutr. 2009;89:1760–1765. doi: 10.3945/ajcn.2008.27336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Assy N, Nasser G, Kamayse I, Nseir W, Beniashvili Z, Djibre A, et al. Soft drink consumption linked with fatty liver in the absence of traditional risk factors. Can J Gastroenterol. 2008;22:811–816. doi: 10.1155/2008/810961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Lecoultre V, Egli L, Carrel G, Theytaz F, Kreis R, Schneiter P, et al. Obesity. Vol. 21. (Silver Spring); 2013. Effects of fructose and glucose overfeeding on hepatic insulin sensitivity and intrahepatic lipids in healthy humans; pp. 782–785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Johnston RD, Stephenson MC, Crossland H, Cordon SM, Palcidi E, Cox EF, et al. No difference between high-fructose and high-glucose diets on liver triacylglycerol or biochemistry in healthy overweight men. Gastroenterology. 2013;145:1016–1025. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2013.07.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Piernas C, Popkin BM. Trends in snacking among U.S. Children. Health Aff (Millwood) 2010;29:398–404. doi: 10.1377/hlthaff.2009.0666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Corbalan-Tutau MD, Madrid JA, Garaulet M. Timing and duration of sleep and meals in obese and normal weight women. Association with increase blood pressure. Appetite. 2012;59:9–16. doi: 10.1016/j.appet.2012.03.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.la Fleur SE, Luijendijk MC, van der Zwaal EM, Brans MA, Adan RA. The snacking rat as model of human obesity: effects of a free-choice high-fat high-sugar diet on meal patterns. Int J Obes (Lond) 2013 doi: 10.1038/ijo.2013.159. Epub ahead of print] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Fan JG, Li F, Cai XB, Peng YD, Ao QH, Gao Y. Effects of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease on the development of metabolic disorders. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007;22:1086–1091. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2006.04781.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Ortiz-Lopez C, Lomonaco R, Orsak B, Finch J, Chang Z, Kochunov VG, et al. Prevalence of prediabetes and diabetes and metabolic profile of patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) Diabetes Care. 2012;35:873–878. doi: 10.2337/dc11-1849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Visser ME, Lammers NM, Nederveen AJ, van der Graaf M, Heerschap A, Ackermans MT, et al. Hepatic steatosis does not cause insulin resistance in people with familial hypobetalipoproteinaemia. Diabetologia. 2011;54:2113–2121. doi: 10.1007/s00125-011-2157-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Dirlewanger M, Schneiter P, Jequier E, Tappy L. Effects of fructose on hepatic glucose metabolism in humans. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2000;279:E907–E911. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.2000.279.4.E907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Stanhope KL, Schwarz JM, Keim NL, Griffen SC, Bremer AA, Graham JL, et al. Consuming fructose-sweetened, not glucose-sweetened, beverages increases visceral adiposity and lipids and decreases insulin sensitivity in overweight/obese humans. J Clin Invest. 2009;119:1322–1334. doi: 10.1172/JCI37385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Diepenbroek C, Eggels L, Ackermans M, Fliers E, Serlie M, Kalsbeek A, et al. Obesogenic diets with fat and sugar reduce site specific sensitivity to insulin [Abstract] Appetite. 2011;57:13. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Sese MA, Jimenez-Pavon D, Gilbert CC, Gonzalez-Gross M, Gottrand F, de HS, et al. Eating behaviour, insulin resistance and cluster of metabolic risk factors in European adolescents. The HELENA study. Appetite. 2012;59:140–147. doi: 10.1016/j.appet.2012.04.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Report of the expert committee on the diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 2003;26(1):S5–20. doi: 10.2337/diacare.26.2007.s5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Guidelines for a Healthy Diet 2006. The Hague, Netherlands: 2006. Health Council of the Netherlands. [Google Scholar]
- 24.Koopman KE, Booij J, Fliers E, Serlie MJ, la Fleur SE. Diet-induced changes in the lean brain: hypercaloric high-fat-high-sugar snacking decreases serotonin transporters in the human hypothalamic region. Mol Metab. 2013;2:417–422. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2013.07.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Frayn KN. Calculation of substrate oxidation rates in vivo from gaseous exchange. J Appl Physiol. 1983;55:628–634. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1983.55.2.628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.van Werven JR, Hoogduin JM, Nederveen AJ, van Vliet AA, Wajs E, Vandenberk P, et al. Reproducibility of 3.0 Tesla magnetic resonance spectroscopy for measuring hepatic fat content. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2009;30:444–448. doi: 10.1002/jmri.21837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Tustison NJ, Avants BB, Cook PA, Zheng Y, Egan A, Yushkevich PA, et al. N4ITK: improved N3 bias correction. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2010;29:1310–1320. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2010.2046908. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Siegel MJ, Hildebolt CF, Bae KT, Hong C, White NH. Total and intra-abdominal fat distribution in preadolescents and adolescents: measurement with MR imaging. Radiology. 2007;242:846–856. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2423060111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Ackermans MT, Pereira Arias AM, Bisschop PH, Endert E, Sauerwein HP, Romijn JA. The quantification of gluconeogenesis in healthy men by (2)H2O and [2-(13)C]glycerol yields different results: rates of gluconeogenesis in healthy men measured with (2)H2O are higher than those measured with [2-(13)C]glycerol. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2001;86:2220–2226. doi: 10.1210/jcem.86.5.7383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Brands M, Swat M, Lammers NM, Sauerwein HP, Endert E, Ackermans MT, et al. Effects of a hypercaloric diet on beta-cell responsivity in lean healthy men. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 2013;78:217–225. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.2012.04364.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Yokoyama H, Emoto M, Fujiwara S, Motoyama K, Morioka T, Komatsu M, et al. Quantitative insulin sensitivity check index and the reciprocal index of homeostasis model assessment are useful indexes of insulin resistance in type 2 diabetic patients with wide range of fasting plasma glucose. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2004;89:1481–1484. doi: 10.1210/jc.2003-031374. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Finegood DT, Bergman RN, Vranic M. Estimation of endogenous glucose production during hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic glucose clamps. Comparison of unlabeled and labeled exogenous glucose infusates. Diabetes. 1987;36:914–924. doi: 10.2337/diab.36.8.914. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Steele R. Influences of glucose loading and of injected insulin on hepatic glucose output. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1959;82:420–430. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1959.tb44923.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Acheson KJ, Flatt JP, Jequier E. Glycogen synthesis versus lipogenesis after a 500 gram carbohydrate meal in man. Metabolism. 1982;31:1234–1240. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(82)90010-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Gao M, Bu L, Ma Y, Liu D. Concurrent activation of liver x receptor and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha exacerbates hepatic steatosis in high fat diet-induced obese mice. PLoS One. 2013;8:e65641. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0065641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Herman MA, Peroni OD, Villoria J, Schon MR, Abumrad NA, Bluher M, et al. A novel ChREBP isoform in adipose tissue regulates systemic glucose metabolism. Nature. 2012;484:333–338. doi: 10.1038/nature10986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Item F, Konrad D. Visceral fat and metabolic inflammation: the portal theory revisited. Obes Rev. 2012;13(2):30–39. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-789X.2012.01035.x. Suppl. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Tanaka S, Yamazaki T, Asano S, Mitsumoto A, Kobayashi D, Kudo N, et al. Increased lipid synthesis and decreased beta-oxidation in the liver of SHR/NDmcr-cp (cp/cp) rats, an animal model of metabolic syndrome. Lipids. 2013;48:1115–1134. doi: 10.1007/s11745-013-3839-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.InterAct Consortium. Consumption of sweet beverages and type 2 diabetes incidence in European adults: results from EPIC-InterAct. Diabetologia. 2013;56:1520–1530. doi: 10.1007/s00125-013-2899-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Danaei G, Finucane MM, Lu Y, Singh GM, Cowan MJ, Paciorek CJ, et al. National, regional, and global trends in fasting plasma glucose and diabetes prevalence since 1980: systematic analysis of health examination surveys and epidemiological studies with 370 country-years and 2.7 million participants. Lancet. 2011;378:31–40. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)60679-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Fagot-Campagna A, Pettitt DJ, Engelgau MM, Burrows NR, Geiss LS, Valdez R, et al. Type 2 diabetes among North American children and adolescents: an epidemiologic review and a public health perspective. J Pediatr. 2000;136:664–672. doi: 10.1067/mpd.2000.105141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Supporting Information


