Abstract
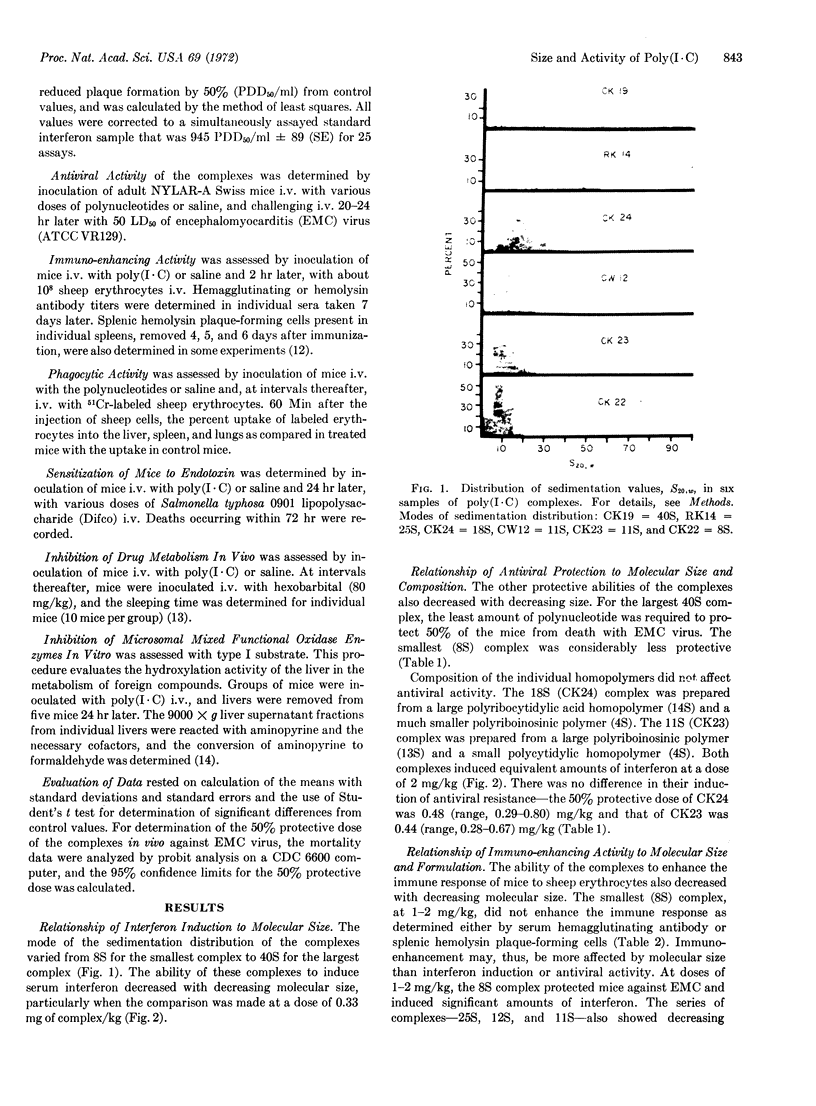
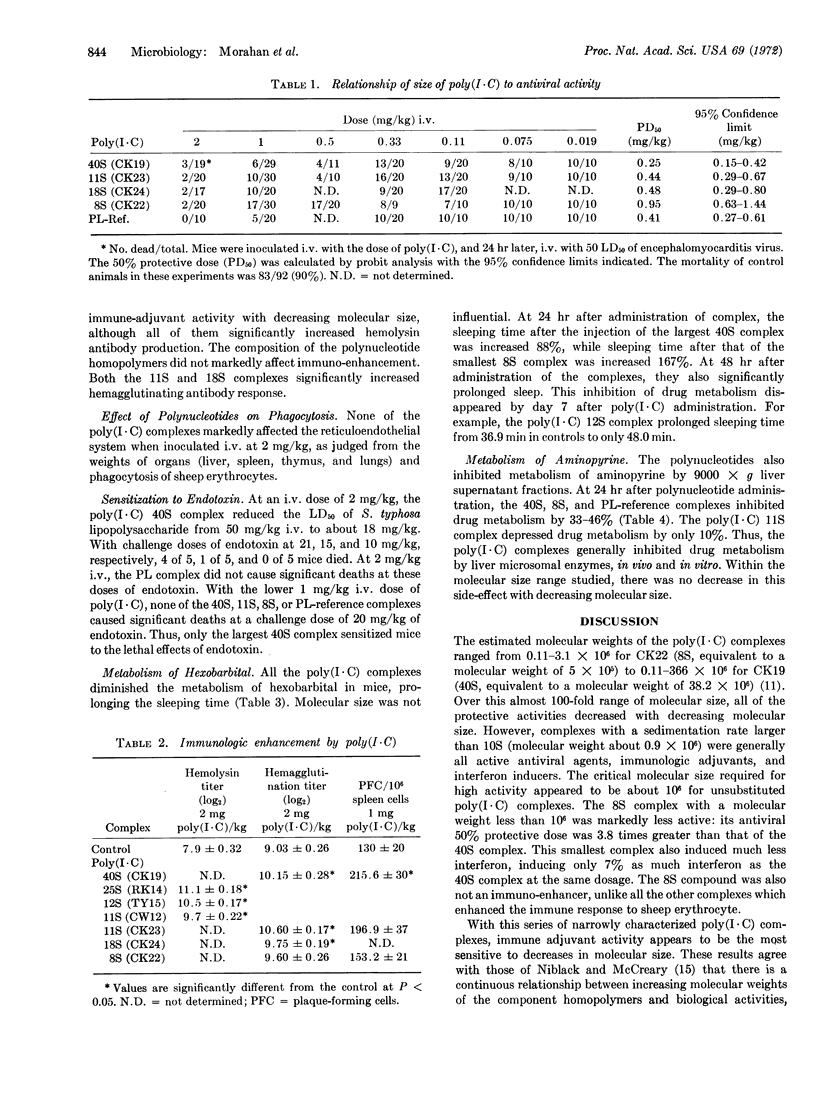
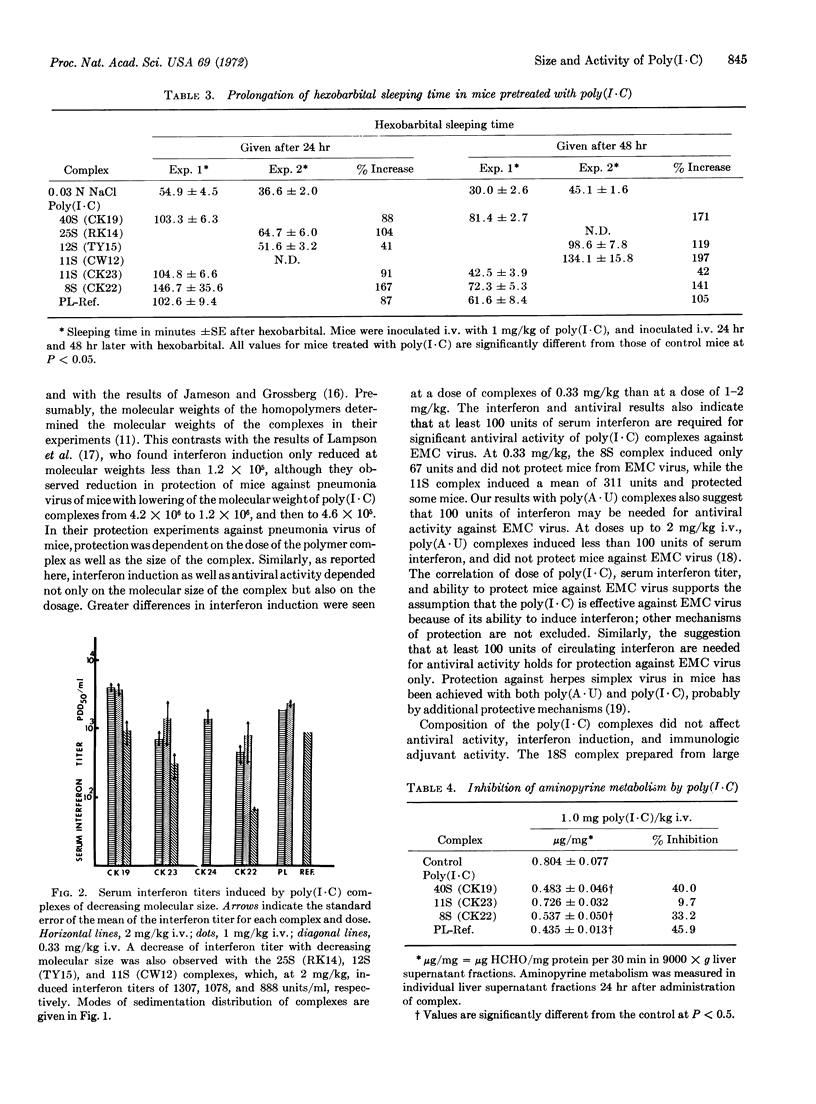
The decrease of the molecular size of poly(I·C) to less than 106 decreases its ability to induce interferon, protect mice against virus, or enhance the immune response. Immune adjuvant activity appeared more sensitive to molecular weight than the other protective activities. The composition of the complex—the molecular size of the individual homopolymers when one was large and the other small—did not affect antiviral activity; the activity of a complex made from large poly(I) and small poly(C) was similar to one made from small poly(I) and large poly(C). Molecular size of the complex did not profoundly alter the side effects of poly(I·C). At 2 mg/kg, none of the complexes markedly altered phagocytic function. Only the largest complex sensitized the mouse to endotoxin. However, all of the complexes studied profoundly inhibited drug metabolism by the liver microsomal enzymes between 24 and 72 hr after their inoculation. Decreasing the molecular weight did not alter this inhibition.
Keywords: synthetic polynucleotide, interferon, antitumor agent, drug metabolism
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Absher M., Stinebring W. R. Toxic properties of a synthetic double-stranded RNA. Endotoxin-like properties of poly I. poly C, an interferon stimulator. Nature. 1969 Aug 16;223(5207):715–717. doi: 10.1038/223715a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun W. Relationships between the effects of poly I. poly C and endotoxin. Nature. 1969 Dec 6;224(5223):1024–1025. doi: 10.1038/2241024a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chester T. J., de Clercq E., Merigan T. C. Effect of Separate and Combined Injections of Poly rI: Poly rC and Endotoxin on Reticulo-endothelial Activity, Interferon, and Antibody Production in the Mouse. Infect Immun. 1971 Apr;3(4):516–520. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.4.516-520.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field A. K., Tytell A. A., Lampson G. P., Hilleman M. R. Inducers of interferon and host resistance. II. Multistranded synthetic polynucleotide complexes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Sep;58(3):1004–1010. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.3.1004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gram T. E., Wilson J. T., Fouts J. R. Some characteristics of hepatic microsomal systems which metabolize aminopyrine in the rat and rabbit. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1968 Jan;159(1):172–181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton L. D., Babcock V. I., Southam C. M. Inhibition of herpes simplex virus by synthetic double-stranded RNA (polyriboadenylic and polyribouridylic acids and polyriboinosinic and polyribocytidylic acids). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Nov;64(3):878–883. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.3.878. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampson G. P., Field A. K., Tytell A. A., Nemes M. M., Hilleman M. R. Relationship of molecular size of rIn:rCn (poly I:C) to induction of interferon and host resistance. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1970 Dec;135(3):911–916. doi: 10.3181/00379727-135-35169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy H. B., Law L. W., Rabson A. S. Inhibition of tumor growth by polyinosinic-polycytidylic acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Feb;62(2):357–361. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.2.357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy H. B., Riley F. The effect of polyinosinic:polycytidylic acid on tumor metabolism. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1970 Oct;135(1):141–145. doi: 10.3181/00379727-135-35006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindsay H. L., Trown P. W., Brandt J., Forbes M. Pyrogenicity of poly I. poly C in rabbits. Nature. 1969 Aug 16;223(5207):717–718. doi: 10.1038/223717a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niblack J. F., McCreary M. B. Relationship of biological activities of poly I-poly C to homopolymer molecular weights. Nat New Biol. 1971 Sep 8;233(36):52–53. doi: 10.1038/newbio233052a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips B. M., Hartnagel R. E., Kraus P. J., Tamayo R. P., Fonseca E. H., Kowalski R. L. Systemic toxicity of polyinosinic acid: polycytidylic acid in rodents and dogs. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1971 Jan;18(1):220–230. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(71)90330-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richmond J. Y., Hamilton L. D. Foot-and-mouth disease virus inhibition induced in mice by synthetic double-stranded RNA (polyriboinosinic and polyribocytidylic acids). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Sep;64(1):81–86. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.1.81. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tytell A. A., Lampson G. P., Field A. K., Nemes M. M., Hilleman M. R. Influence of size of individual homopolynucleotides on the physical and biological properties of complexed rIn:rCn (poly I:C). Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1970 Dec;135(3):917–921. doi: 10.3181/00379727-135-35170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wacker A., Singh A., Svec J., Lodemann E. Einfluss der Kettenlänge von Oligonucleotiden auf die Interferon-Induction. Naturwissenschaften. 1969 Dec;56(12):638–638. doi: 10.1007/BF01185750. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wooles W. R., Munson A. E. The effect of stimulants and depressants of reticuloendothelial activity on drug metabolism. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1971 Feb;9(2):108–119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]