Abstract
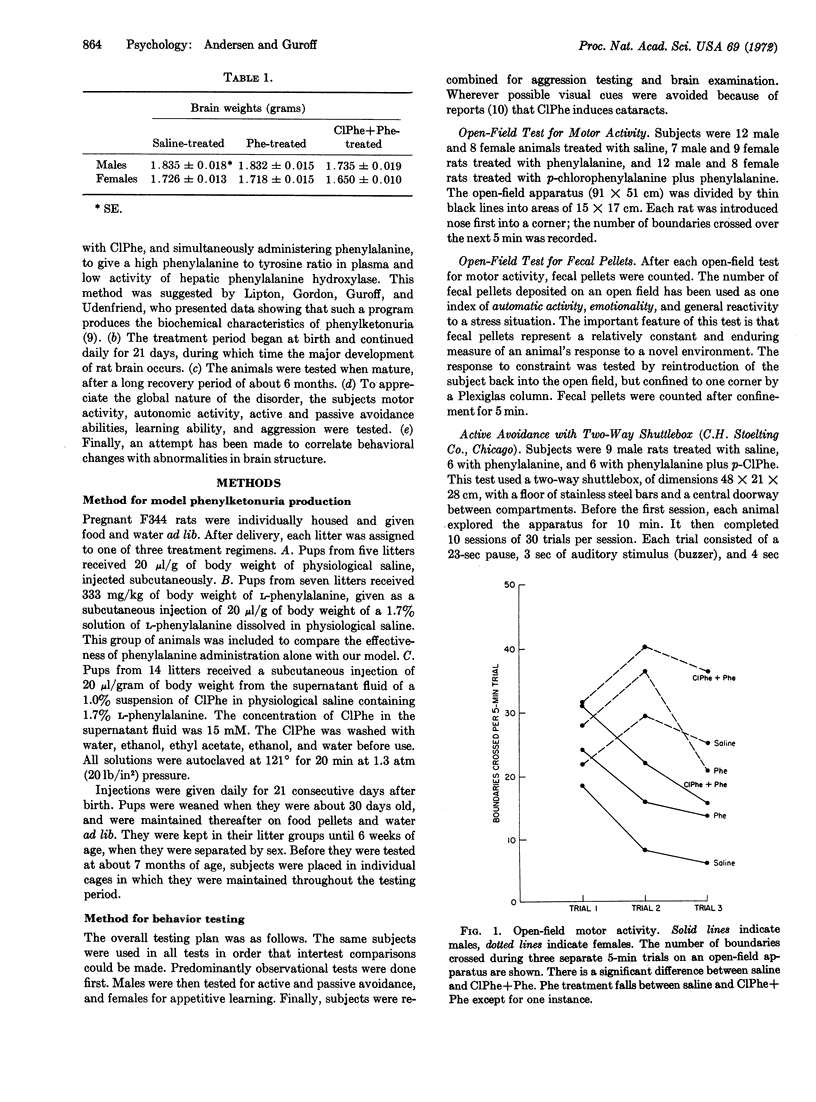
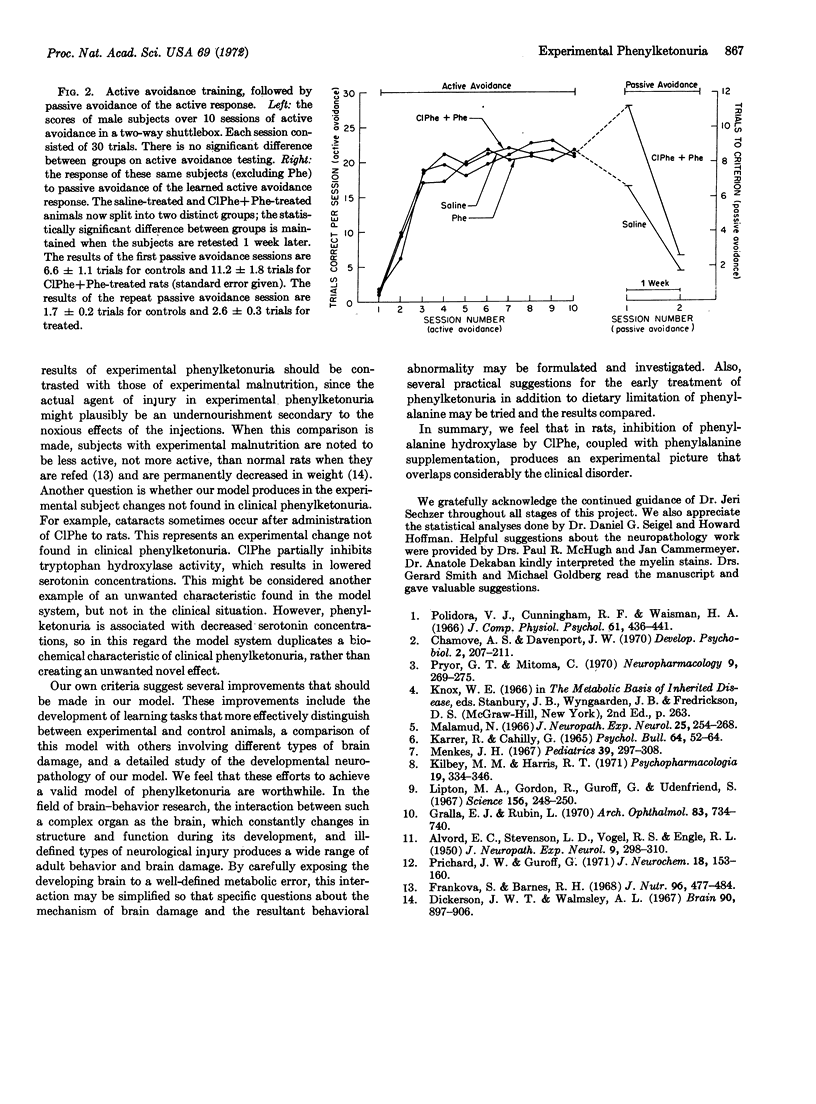
Several criticisms of past attempts to produce experimental phenylketonuria are discussed, and a model that appears to meet these criticisms is presented. This model uses inhibition in rats of phenylalanine hydroxylase (EC 1.14.3.1) by p-chlorophenylalanine and supplementation with phenylalanine to produce a high ratio of phenylalanine to tyrosine in their blood. By this method, an experimental subject is produced whose behavioral, neurological, and biochemical characteristics are similar to those of clinical patients with phenylketonuria.
Keywords: phenylalanine to tyrosine ratio, p-chlorophenylalanine, disease model, learning ability, brain structure
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALVORD E. C., Jr, STEVENSON L. D., VOGEL F. S., ENGLE R. L., Jr Neuropathological findings in phenyl-pyruvic oligophrenia (phenyl-ketonuria). J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1950 Jul;9(3):298–310. doi: 10.1097/00005072-195007000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamove A. S., Davenport J. W. Differential reinforcement of latency (DRL) in phenylketonuric monkeys. Dev Psychobiol. 1970;2(4):207–211. doi: 10.1002/dev.420020405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickerson J. W., Walmsley A. L. The effect of undernutrition and subsequent rehabilitation on the growth and composition of the central nervous system of the rat. Brain. 1967 Dec;90(4):897–906. doi: 10.1093/brain/90.4.897. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franková S., Barnes R. H. Influence of malnutrition in early life on exploratory behavior of rats. J Nutr. 1968 Dec;96(4):477–484. doi: 10.1093/jn/96.4.477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gralla E. J., Rubin L. Ocular studies with para-chlorophenylalanine in rats and monkeys. Arch Ophthalmol. 1970 Jun;83(6):734–740. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1970.00990030734012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KARRER R., CAHILLY G. EXPERIMENTAL ATTEMPTS TO PRODUCE PHENYLKETONURIA IN ANIMALS: A CRITICAL REVIEW. Psychol Bull. 1965 Jul;64:52–64. doi: 10.1037/h0022025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilbey M. M., Harris R. T. Behavioral, biochemical and maturation effects of early DL-para-chlorophenylalanine treatment. Psychopharmacologia. 1971;19(4):334–346. doi: 10.1007/BF00404378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipton M. A., Gordon R., Guroff G., Udenfriend S. p-Chlorophenylalanine-induced chemical manifestations of phenylketonuria in rats. Science. 1967 Apr 14;156(3772):248–250. doi: 10.1126/science.156.3772.248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malamud N. Neuropathology of phenylketonuria. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1966 Apr;25(2):254–268. doi: 10.1097/00005072-196604000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menkes J. H. The pathogenesis of mental retardation in phenylketonuria and other inborn errors of amino acid metabolism. Pediatrics. 1967 Feb;39(2):297–308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polidora V. J., Cunningham R. F., Waisman H. A. Dosage parameters of a behavioral deficit associated with phenylketonuria in rats. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1966 Jun;61(3):436–441. doi: 10.1037/h0023257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prichard J. W., Guroff G. Increased cerebral excitability caused by p-chlorophenylalanine in young rats. J Neurochem. 1971 Jan;18(1):153–160. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1971.tb00177.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pryor G. T., Mitoma C. Use of p-chlorophenylalanine to induce a phenylketonuric-like condition in rats. Neuropharmacology. 1970 May;9(3):269–275. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(70)90076-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


