Abstract
First reported in remote villages of Africa in the 1970s, the Ebolavirus was originally believed to be transmitted to people from wild animals. Ebolavirus (EBOV) causes a severe, frequently fatal hemorrhagic syndrome in humans. Each outbreak of the Ebolavirus over the last three decades has perpetuated fear and economic turmoil among the local and regional populations in Africa. Until now it has been considered a tragic malady confined largely to the isolated regions of the African continent, but it is no longer so. The frequency of outbreaks has increased since the 1970s. The 2014 Ebola outbreak in Western Africa has been the most severe in history and was declared a public health emergency by the World Health Organization. Given the widespread use of modern transportation and global travel, the EBOV is now a risk to the entire Global Village, with intercontinental transmission only an airplane flight away. Clinically, symptoms typically appear after an incubation period of approximately 11 days. A flu-like syndrome can progress to full hemorrhagic fever with multiorgan failure, and frequently, death. Diagnosis is confirmed by detection of viral antigens or Ribonucleic acid (RNA) in the blood or other body fluids. Although historically the mortality of this infection exceeded 80%, modern medicine and public health measures have been able to lower this figure and reduce the impact of EBOV on individuals and communities. The treatment involves early, aggressive supportive care with rehydration. Core interventions, including contact tracing, preventive initiatives, active surveillance, effective isolation and quarantine procedures, and timely response to patients, are essential for a successful outbreak control. These measures, combined with public health education, point-of-care diagnostics, promising new vaccine and pharmaceutical efforts, and coordinated efforts of the international community, give new hope to the Global effort to eliminate Ebola as a public health threat. Here we present a review of EBOV infection in an effort to further educate medical and political communities on what the Ebolavirus disease entails, and what efforts are recommended to treat, isolate, and eventually eliminate it.
Keywords: Containment, Ebolavirus, Epidemic, Outbreak, Global response, Government response system, Global Health Security Agenda, Virus transmission
INTRODUCTION
There have been multiple Ebola transmission events[1,2,3] and more than 20 Ebola outbreaks since the 1970s.[4,5] In August 2014, the largest, most sustained, and widespread Ebola outbreak in history was declared a Public Health Emergency of International Concern (PHEIC) by the World Health Organization (WHO).[6,7] The WHO was initially notified of the outbreak in March 2014,[8] after a febrile illness cluster associated with a high case fatality rate in the area of Gueckedou, Guinea, attracted international attention, and was subsequently identified as the viral zoonosis Ebola (EBOV), formerly known as Zaire Ebolavirus (ZEBV).[7,9,10,11] This deadly member of the family Filoviridae, an enveloped, negative single-stranded RNA virus, is the most virulent of the five family members.[12] The other members of the Ebolavirus family are Sudan (SUDV), Tai Forest (TAFV), Bundibugyo (BDBV), and Reston (RESV) sub-types.[13,14] The sequencing data showed that the 2014 outbreak in West Africa was due to infections with a strain of ZEBV, which differed from the viral strains identified in the earlier outbreaks.[15,16] For the sake of clarity and uniformity, we will refer to Ebolavirus as EBOV throughout the remainder of this manuscript, unless the mention of specific viral subtype is mandated.
Regarding the current EBOV outbreak, it is hypothesized that the index case most likely originated via animal — human contact (e.g., ingestion of undercooked ‘bush meat’, animal bite, or inadvertent contact with body fluids or blood from an animal).[17] Following the index transmission event, the predominant mode of the subsequent viral transmission is human-to-human.[18] This is consistent with the previous observations and characteristics of human-to-human transmission.[19] Late in the spring of 2014, the number of reported cases declined, causing medical investigators to believe that the course of this outbreak followed the trajectory of previous outbreaks and that the outbreak's ‘burnout’ phase had begun.[9] However, within a period of a few months, sporadic cases were being diagnosed beyond Guinea, including Liberia, Sierra Leone, Senegal, Mali, Nigeria, and most recently in the United States and Spain.[9,20,21,22,23,24] Some of the reported cases were clearly associated with transmission following a history of travel to the affected regions of Africa.[9,20,21,23] In West Africa, the number of new EBOV cases was increasing at an accelerating rate, with a number of factors contributing to this phenomenon, including poorly functioning healthcare, under-developed water and waste management systems;[25] a degree of international complacency;[26] population movement within the affected geographic areas (including rural-to-urban migrations);[27,28] increasing urban population density;[29] local cultural factors (e.g., burial customs);[30] widespread poverty;[27] and a lack of responsiveness from the local and national governments.[6,31,32] To make things worse, there was a shortage of physicians in West Africa.[33] For example, before the outbreak, fewer than a 100 physicians were providing healthcare for 4.3 million people in Liberia.[34] The fact that numerous healthcare workers were themselves becoming infected with Ebola (including over a 100 healthcare workers who died as of late August 2014) further complicated the already critical situation.[35,36] At the time of this manuscript's initial submission (November 14, 2014) the Ebola outbreak has been contained in Nigeria and Senegal, and there have been no further reported cases in the United States or Spain.[37,38] However, a new outbreak in Mali has just been announced.[39,40]
It has been noted that the global response to the current epidemic was initially slow, disorganized, financially constrained, and poorly planned and executed.[6,41] As it confronts the possibility of as many as 10,000 new cases per week,[42] the international medical community must realize that the confluence of circumstances and factors beyond human control may not always be in the society's favor, as it may have been within the last decade, with Influenza H1N1, Influenza H5N1, Hantavirus, or the Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS).[43,44] In the face of easy movement across relatively porous borders (intercontinental travel) in an age of super highways, fast rail, and air travel, all ‘corners’ of the planet have become reachable in a matter of hours, making cities such as Lagos, New York, Tokyo or New Delhi, with populations exceeding 12 million, easily vulnerable.[45,46,47,48] In fact, a recently ‘imported’ case of Ebola in New York City should serve as a wakeup call and a global stimulus for both local and global coordinated action.[49]
Until late August, most of the scientific journals and media reports advocated that the risk of Ebola is very low in the United States.[50] Although it remains so, a recent diagnosis of a patient in Dallas, Texas, with Ebolavirus disease (EVD), who had traveled from Liberia and ultimately died despite intensive efforts, has made Western countries wary.[51,52] It is important to note that initial care in the first documented US case of Ebola may have been delayed due to poor recognition of the patient's disease symptoms.[53] The diagnosis of two healthcare workers from the same hospital and the possible threat of spread of infection to people who had been in close contact with these subsequent cases has threatened a chain of transmission events.[54,55,56] This chain included a number of potentially exposed individuals on a commercial airline flight from Ohio to Texas on which an individual possibly experiencing early symptoms of Ebola may have traveled.[54,55,56]
EPIDEMIOLOGY
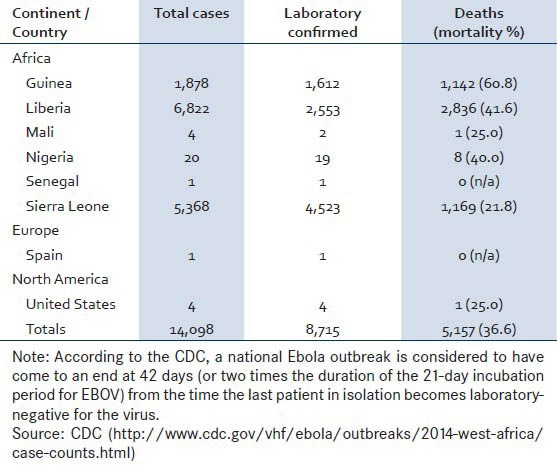
The initial documented episodes of filovirus hemorrhagic fever were seen in the late1960s, in nonhuman primates, which were being transported to Germany for vaccine development.[57,58] At that time, workers of the vaccine industry who handled non-human primates were also affected.[59] In 1976, reappearance of hemorrhagic fever outbreaks were noted to affect people in south Sudan and Zaire, which were caused by a distinct species of the Filoviridae family.[60,61] The Ebolavirus is named after the Ebola river, a tributary of the Congo River and an area where the first documented modern case of infection was identified, in 1976.[62] Of interest, some researchers have suggested that EBOV outbreaks may be related to certain confluences of environmental and climatic conditions.[63] The frequency of the recognizable outbreaks has been on the rise since 1990, involving many locations in sub-Saharan Africa.[64,65] The 2014 event has been the largest documented outbreak of Ebola thus far. Nearly 14,100 cases have been reported worldwide, killing almost 5,200 people — an overall mortality of 37% [Table 1]. The outbreak has been most intense in Guinea, Liberia and Sierra Leone, which together account for over 99% of all cases and nearly all the recorded deaths.[66]
Table 1.
The 2014 outbreak: Report of Ebola cases by country (data as of November 12, 2014)
VIRUS TRANSMISSION
Fruit bats are considered to be the primary reservoirs of filoviruses [Figure 1] and are thought to contribute to the viral transmission, to both non-human primates and humans.[67] According to the Centers for Disease Control (CDC), the modes of Ebola transmission include the following — contact with blood or body fluids of a person who is sick with or has died from Ebola, coming in contact with contaminated objects like needles and touching infected animals, their blood or other body fluids, or bush meat.[68] Reproduction rate (R0) of EBOV is low (1 to 4). Ebolavirus rarely spreads through the respiratory route.[69] Of interest, persistence of the Ebola viral RNA in convalescing individuals has been reported, likely due to replicating intracellular nucleocapsids.[70]
Figure 1.
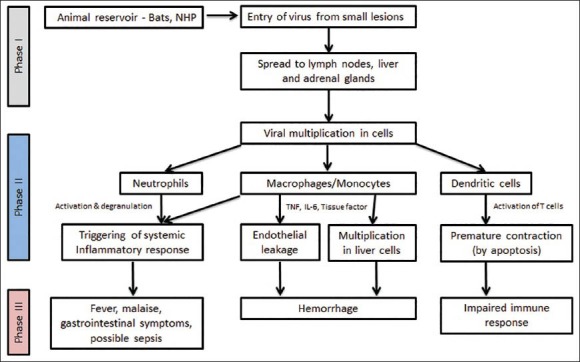
Diagram demonstrating the pathogenesis of Ebolavirus infection. Phase I can be characterized as the transfer of EBOV from an animal carrying the virus to a human, usually via small cutaneous lesions. Similar principles apply in human-to-human transmission during Ebola outbreaks. Phase II can be characterized as the early symptomatic stage — usually between days four and ten — where symptoms of a viral illness appear and gradually progress toward more advanced manifestations of the disease. Finally, Phase III represents the advanced Ebolavirus disease, with hemorrhagic manifestations, impaired immunity, and end-organ failure. Adapted from Feldmann H, Geisbert TW Ebola hemorrhagic fever. Lancet 2011;377:849-862. Legend: NHP = nonhuman primate; TNF = Tumor necrosis factor; IL = Interleukin
PATHOGENESIS
The pathophysiology of Ebola is not yet fully understood, however, most studies report that the incubation period varies depending on the type of exposure (i.e., six days for percutaneous and ten days for contact exposure).[71,72] The WHO Ebola response team's findings have documented that the mean incubation period was 11.4 days, which did not vary by country.[8] Following viral transmission, symptoms usually appear in approximately eight to ten days (range, 2-21 days).[8]
After EBOV enters the human body, macrophages and dendritic cells are generally considered as the first cells to be infected [Figure 1].[73] The virus then proliferates rapidly within these cells, releasing multiple new copies into the extracellular fluid.[74,75] Spread of the virus into the regional lymph nodes amplifies the viral load in the body, causing further viral dissemination to the lymphoid and vascular tissues.[74] Subsequently, a systemic inflammatory response is initiated, resulting in cytokine and chemokine release from the infected macrophages and other cells. This constellation of innate host responses is considered to be responsible for the prodromal symptoms.[74,75]
The coagulation defects are attributable to the synthesis of the cell surface tissue factor from viral infected macrophages.[74] The ensuing hepatic injury also leads to decreased synthesis of coagulation factors from the liver.[76] The appearance of hemorrhagic symptoms is associated with a worse prognosis, as outlined in the subsequent paragraphs.
CLINICAL FEATURES AND DIAGNOSTIC TESTING
The clinical presentation of Ebola patients progresses from non-specific ‘flu-like’ symptoms to multiorgan failure.[77] The mean time from the onset of symptoms to hospitalization is approximately five days.[8] After admission, the mean length of stay in the hospital, the mean time to death, and the mean time to discharge are 6.4 days, 4.2 days, and 11.8 days, respectively.[8] With regard to the symptoms, the fevers may be mild during the initial phase of illness, but may evolve to become more abrupt and high-grade, with associated chills and rigors. Non-specific prodromal symptoms are almost always present comprising mainly of malaise, weakness, anorexia, severe headache, and pain in the truncal and lower back muscles.[78] High fever with relative bradycardia mimicking the presentation of typhoid fever has also been reported.[79,80] Progressive, diffuse, erythematous, nonpruritic, maculopapular rash around the face, neck, trunk, and arms usually appears by the end of the first week.
As the disease progresses, gastrointestinal symptoms such as diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain begin to develop.[78] Although bleeding is not seen in the early phase, there may be a gradual appearance of petechiae, ecchymoses, prolonged bleeding from the venipuncture sites, and mucosal hemorrhage, as the disease progresses. Patients who recover from Ebola infection have been reported to show clinical improvement by the middle of the second week. As outlined in Figure 2a-d, the clinical outcomes may depend on the appearance and the subsequent management of the symptoms and signs associated with increased mortality (i.e., impending septic shock, hemorrhagic manifestations, and multiorgan failure).[72]
Figure 2a.
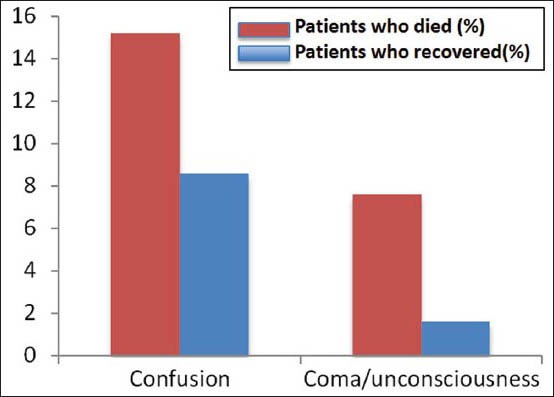
Neurological symptoms, including confusion, loss of consciousness or coma were more frequently seen in patients who died. Values shown on the y-axis represent percentages. Source: WHO Ebola Response Team. Ebolavirus disease in West Africa — The first nine months of the epidemic and forward projections. New Engl J Med 2014;371: 1481-1495.
Figure 2d.
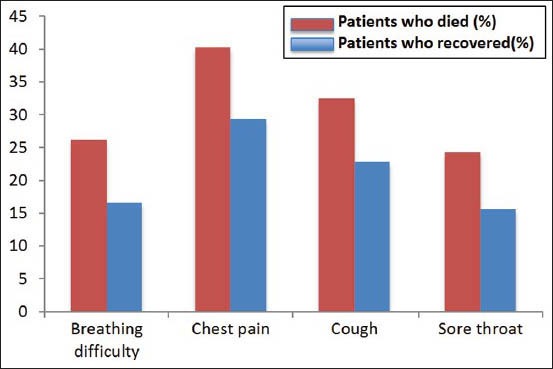
A number of miscellaneous symptoms — including difficulty breathing, chest pain, cough, and sore throat — were more frequently seen among non-survivors. Source: WHO Ebola Response Team. Ebola virus disease in West Africa — The first nine months of the epidemic and forward projections. New Engl J Med 2014;371: 1481-1495.
Figure 2b.
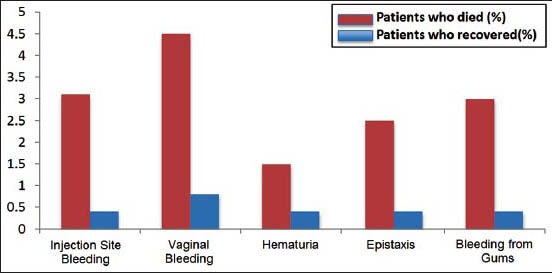
Hematological symptoms, including injection site bleeding, vaginal bleeding, hematuria, epistaxis, and bleeding from the gums were more frequently seen in patients who died. Values shown on the y-axis represent percentages. Source: WHO Ebola Response Team. Ebolavirus disease in West Africa — The first nine months of the epidemic and forward projections. New Engl J Med 2014;371: 1481-1495.
On the basis of the observed patient outcomes, the WHO Ebola Outbreak Team has compared the signs and symptoms that were more likely to be present in patients who died. Neurological symptoms (i.e., confusion, coma, unconsciousness); hematological symptoms (i.e., bleeding gums, bloody nose, bleeding from venipuncture sites, vaginal bleeding); and other selected symptoms (i.e., chest pain, cough, difficulty breathing, and sore throat), were associated with greater observed mortality.[8] Except for difficulty in swallowing, the presence of gastrointestinal symptoms (i.e., diarrhea, abdominal pain, loss of appetite) did not appear to be associated with increased mortality [Figure 2c]. A detailed summary of the clinical symptoms and signs in survivors and non-survivors is provided in Figure 2a-d. Of note, Towner et al.[81] demonstrated that patients who died were found to have higher viral loads.
Figure 2c.
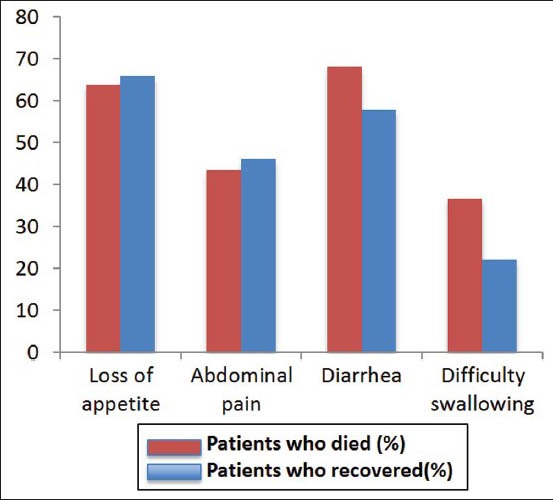
Gastrointestinal signs/symptoms of Ebola. Except for difficulty swallowing, gastrointestinal symptoms (i.e., loss of appetite, abdominal pain, and diarrhea) were seen at approximately similar rates in survivors and non-survivors of Ebola. Values shown on y-axis represent percentages. Source: WHO Ebola Response Team. Ebola virus disease in West Africa — The first nine months of the epidemic and forward projections. New Engl J Med 2014;371: 1481-1495.
Various derangements in the hematological profile characterized by leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, elevated transaminases, proteinuria, and elevated prothrombin, and thromboplastin times can be seen, and are associated with worse prognosis.[8] The confirmatory diagnosis for Ebola involves detection of the viral antigens or RNA in the blood or other body fluids.[81] Until recently, testing could only be performed in specialized laboratories, and relied on detection of the RNA sequence by reverse-transcription polymerase chain (RT-PCR) reaction or viral antigens by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) within three to ten days of onset of symptoms.[11] However, newer rapid diagnostic methods are quickly evolving,[82,83] and are expected to be available for deployment in the near future.
TREATMENT
In the past, mortality associated with Ebola infection was as high as 50-80%.[84,85,86] More recently, the mortality rate of Ebolavirus is reported to be between 20 and 60% [Table 1], due mainly to the prompt and more effective clinical management of infected patients.[84] Most of the care that is being offered to infected patients is comprised of supportive measures such as hydration, nutritional support, and replacement of electrolytes.[87,88] As of now, there is no specific immunization or treatment for the Ebolavirus disease that has been validated in humans,[89,90] although survivors may exhibit immunity.[91] Of interest, both nurses who became infected while caring for the Dallas, Texas patient, were declared free of the virus.[92,93] Passive immunity associated with plasma transfusion from an Ebola survivor, Dr Kent Brantley, may have played a role in one of those cases[94] and has some support in the historical experiences from a 1995 Ebola outbreak in Kikwit, Democratic Republic of Congo.[95]
Other than the above-mentioned supportive therapy, there is no proven treatment for Ebola. Some have suggested that anti-retroviral agents may have some effectiveness against EBOV,[96] but at this time these claims remain both unproven and controversial. As mentioned previously, passive immunity may be helpful in attenuating the severity of the disease, as suggested by the relatively quick recovery of one of the Dallas, Texas nurses following plasma transfusion from an Ebola survivor.[94] An experimental drug called ZMapp (Mapp Biopharmaceutical, San Diego, California, USA), is also based on the concept of passive immunotherapy, and combines three humanized monoclonal anti-EBOV antibodies that are synthesized in Nicotiana benthamiana plants.[97] Administration of ZMapp in rhesus macaque primates who were inoculated with virulent Ebola strains may have attenuated the disease severity.[97] The drug has also shown some promise after it was administered, with permission from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA),[98] to several infected individuals; however, its scarcity and lack of substantiating data make it challenging for the agent to reach those most in need.[97] Another drug, TKM-Ebola (Tekmira Pharmaceuticals, British Columbia, Canada), has also been approved for selective use by the FDA, along with ZMapp.[99] Finally, Brincidofovir (Chimerix, Durham, North Carolina), a broad-spectrum antiviral drug, has been shown to have in vitro activity against Ebola,[100] and has reportedly been administered to patients with EVD in the United States.[101]
There are currently two notable Ebola vaccine efforts. The first is cAd3-ZEBOV developed by GlaxoSmithKline and tested by the US National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID).[102,103] The second is the rVSV tested by the New Link Genetics Corporation after being licensed from the Public Health Agency of Canada.[103,104] Both vaccines demonstrated promising rates of efficacy in nonhuman primates, but the translation of these results to human subjects has not yet been accomplished.[90]
PERSONAL PROTECTIVE EQUIPMENT FOR HEALTH WORKERS
With regard to healthcare worker protection and prevention of healthcare-related transmission of Ebola, many opportunities for improvement have been identified, based on the previous outbreaks.[84,105,106,107] It is critical that the medical community learns from the previous mistakes so that emphasis in the fight against Ebola can shift toward preparing healthcare systems and organizations, establishing better disease surveillance systems, and restoring the trust in health services across affected communities.[108,109]
Patients infected with EBOV, who seek emergency care, expose ‘front-line’ healthcare workers to significant risk of contracting the infection.[36,110,111] Considering the highly contagious nature of the body fluids from individuals with symptomatic infection, dealing with Ebola mandates that healthcare workers follow standard safety precautions rigorously in order to safeguard themselves and the people with whom they interact.[109] The critical nature of the personal protective equipment (PPE) in cases of Ebola and the risk of transmission despite taking apparently adequate precautions is exemplified by the two cases of patient-to-nurse viral transmission in Dallas, Texas,[112] one case in Spain,[113] and the recently diagnosed case in New York City.[114] It is important to note that special circumstances requiring heightened vigilance regarding personal protection equipment may arise when caring for patients with Ebola, including the performance of emergency surgery in this population.
An example of the personal protective equipment used by healthcare workers when caring for patients with Ebola is shown in Figure 3. Detailed illustrated guidelines have been provided by the WHO regarding the use of protective equipment and handling of potentially infectious Ebola samples.[115] Any biological specimens or samples obtained from EBOV patients should be collected using adequate personal protective equipment, using closed vacuum containers.[115] The samples should be transported in leak-proof containers and kept separately from other patient samples. For blood work of patients suspected with EBOV, under no circumstances should manual pipetting and open centrifugation be considered. After the laboratory tests are concluded, disinfectants with a higher potency (preferably, 10% chlorine solution) to kill the virus should be used. Elimination of all infectious materials should be conducted according to the prevailing/approved local protocols, rules, and regulations.[116,117] It is important to note that the actual approach to biohazardous waste disposal has to take into consideration specific economic-based realities and circumstances across different geographic areas. Pertaining to this, it is critical that adequate training of the medical transportation personnel is conducted, to ensure safe and transmission-free transit of the infected patients and/or infectious materials.[118]
Figure 3.
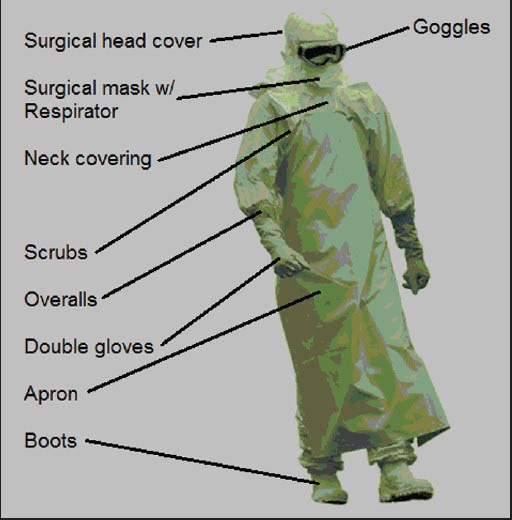
A pictorial representation of the protective equipment used by healthcare personnel in the setting of direct contact with actively symptomatic individuals, their blood, or body fluids. Ebolavirus can be contracted by such contact and is capable of infecting via very small defects in the human skin. Although Ebola cannot be transmitted via airborne droplets, the surgical mask and the respirator assist in completely covering the face and preventing larger fluid droplets from entering the upper respiratory passages. Whole-body coverage also makes it less likely for the healthcare worker to accidentally make contact between gloves or other surfaces directly exposed to the virus and any uncovered skin surfaces. For that reason, it is also important that workers be decontaminated before taking off the protective equipment, and that another person observes the removal of the said equipment, to ensure that none of the exposed external surfaces come in direct contact with the healthcare worker's skin during the process
More recently, potential technological solutions designed to reduce human exposure to EBOV were introduced. Among those, the most prominent one was the idea of a robotic device that could help assist in the care of Ebola patients by delivering supplies, disinfecting, and transporting hazardous specimens, among other functionalities.[119,120] Another important consideration is the possibility of creating volunteer teams of Ebola survivors, who could help in the direct care of the exposed and acutely ill cases so that the overall risk of viral exposure and acute illness would be minimized for other ‘front-line’ healthcare workers.[121,122,123]
SCREENING AND ACTIVE SURVEILLANCE
There is an ongoing debate about the screening of individuals from Ebola-affected countries, who are traveling abroad,[124,125,126,127] with some experts questioning the usefulness of routine traveler screening.[128] Although there are no available statistics to support the effectiveness of screening methods used in the current Ebola epidemic, data from the SARS epidemic airport screening in Canada demonstrated that of the 677,494 who completed the screening questionnaire, 2,478 answered with a ‘yes’ to one or more questions, and among those, none went on to develop SARS.[129] Six major airports installed thermal scanners and screened 467,870 people, of whom 95 suspected ‘positives’ were further assessed. None of them went on to develop SARS. The total cost of the program was 17 million Canadian dollars.[125,130]
From the Ebola case in Texas, it has been recognized that a delay in diagnosis was sufficient enough to create a ‘near-panic’ situation.[131] Employing adequate screening protocols and ensuring that the ‘front-line’ personnel are familiar with pertinent policies is of special importance. In order to contain the spread of Ebola, it is of paramount importance to ensure that the medical staff in the Emergency Departments is prepared, that appropriate screening and isolation policies are in place, and that vigilance and clinical suspicion are sufficient enough to readily identify individuals who have recently traveled to EBOV-affected areas or who may have been in contact with an actively symptomatic Ebola patient, keeping in mind the pertinent incubation periods and other key information about the characteristics of the virus. Despite the significant resources needed to institute such efforts, the societal benefits of limiting or arresting the spread of Ebola outbreak(s) will far outweigh the costs of such concerted initiatives.[36,132]
Active surveillance is a public health approach that consists of the ongoing, systematic collection, analysis, and interpretation of key clinical data, closely integrated with a prompt dissemination of such data to officials responsible for control and prevention of disease.[133] In case of Ebola, active surveillance consists of close supervision by health officials, with systematic collection of vital signs, and monitoring of key clinical symptoms associated with the early course of clinical infection.[134] The use of active surveillance is critical for containing the outbreaks of Ebola, especially in the densely populated urban settings where human-to-human transmission predominates.[135] It has been recommended that the coordinated response to Ebola outbreaks should include sufficiently funded national and regional interdisciplinary surveillance response systems that incorporate early warning capabilities.[136]
QUARANTINE AND ISOLATION
By definition, quarantine is a procedure wherein a healthy person exposed to a communicable disease undergoes a period of close observation in order to prevent disease transmission during the incubation period, and isolation is the restriction of an infected person during their time of communicability.[137,138] The use of quarantine is highly controversial and is usually viewed as an unjust measure, always invoking the consideration of fairness and distributive justice.[139] Herein lies the clash between personal liberty and the public's health.[140] The use of quarantine and isolation of the infectious individual was a basic pillar of public health in seaports in centuries past.[141] However, its use as an effective tool since the latter part of the twentieth century has come into question. There is probably less resistance by professionals and politicians in this Ebola epidemic to the isolation of infected patients, as compared to the use of quarantine for healthy exposed individuals, although it must be acknowledged that isolation itself can be an emotionally traumatic experience.[142] In a modern, free society, the use of quarantine and isolation is likely to face legal challenges by the affected individuals.[143,144]
There have been calls from many professionals to ‘honor’ workers returning from the Ebola front in West Africa, while at the same time they criticize the intervention of public officials/politicians to pursue the quarantine of those same workers.[145] What is ironic is that during the SARS outbreak in 2003, the decision was made by scientific experts that quarantine should be put into place because no one knew, at least initially, how the disease was effectively spread and how quickly it could spread across the globe.[146] After the SARS outbreak, there was great concern about how and why quarantine measures were put into place, with Bensimon et al.[146] stating that, “It is, therefore, incumbent on us to recognize and legitimize a broader notion of effectiveness (of quarantine) — one that transcends the dominant conception that it derives from a set of proven and verifiable data to one that gives a voice to nonscientific, nontechnical perspectives, experiences, preferences, and cultural commitments. Such efforts are essential and not accidental”.[146]
However, in the current Ebola outbreak, as opposed to the SARS event, with regard to the United States, the public health authorities/scientific experts, who know much more about the modes of transmission, effectiveness of counter measures, and the number of individuals one person could infect (1 to 4), and so on, did not make the call to ‘quarantine’ the exposed, but healthy, individuals.[147,148] In this case it was the political leaders who ordered/recommended the quarantine (New York and New Jersey) instead of the scientific establishment. The governors were the non-technical voices that many citizens felt needed to be heard. There is a basis to state that the fear of Ebola in 2014 seems to be greater than that of SARS in 2003.[149] However, there is evidence from quarantines carried out for the SARS epidemic that quarantine is the most effective, ‘when it is voluntary, home-based, and accompanied by extensive outreach, communication, and education efforts’.[150] This outbreak is not the first, nor will it be the last, to pit individual civil liberties against the utilitarianism of the general public's health. To add further perspective to the above argument, it appears thus far that Nigeria was able to contain the outbreak by utilizing an immediate and aggressive response to the very first report of Ebola on its soil,[151] while Guinea and Sierra Leone have experienced a resurgence of cases amid claims of complacency.[152] Faced with the most recent outbreak in Mali, government officials are responding with quarantine orders for dozens of potentially exposed individuals.[40]
ETHICAL AND CULTURAL ISSUES
There have been a lot of controversies related to Ebola in the context of cultural and religious influences.[84,153,154] As much as it is important for containing the infection, the fact that a patient's life has come to an end needs to be dealt with equal empathy. Preparing for a funeral in a respectful yet safe way can be done following a few guidelines. First, it is acceptable to bury patients who died from Ebola without washing the bodies. Second, it is acceptable to offer prayers for people who have died from Ebola and bury them while avoiding direct contact with the body and limiting the burial attendance to family and close friends. Third, religious leaders should be intimately involved in the process of containing the outbreak and should work with the local authorities and the community so that appropriate and safe actions are taken with regard to disposition of the bodies.[153,155] Finally, governments need to do more to clamp down on the illegal practices of bribing health facility workers in order to recover highly infectious bodies of relatives so that a private burial (as opposed to a cremation or burial in designated public sites) can take place.[156]
COLLABORATIVE GLOBAL EFFORTS: STEPS FOR THE FUTURE
As Ebola has managed to spread outside of West Africa, it is imperative to diligently contain the infection in all affected localities.[27,157] During earlier Ebola outbreaks, a combination of core interventions has been effective in containing the disease — exhaustive case and contact tracing, preventive interventions, and an effective and timely response to patients and the community.[27,157,158,159] However, given the massive scale of the current EBOV outbreak, new and more effective approaches are required.[43] On account of the magnitude of the current events, it will be very difficult to effectively and simultaneous implement all of the above-mentioned measures in very under-resourced medical systems. This is further exacerbated by the delayed and underfunded early international response and increased mobility of patients and/or their contacts, who can readily reach large population centers through improved highways, rail systems, and air travel. Finally, there is a relative lack of trust by local populations toward the authorities,[160] which is further exacerbated by the incompatibility between local social customs, the biology of the virus, and the rules of outbreak containment.[84,153,154] The traditional outbreak approaches used during earlier, smaller Ebola outbreaks will probably not work and will require massive International supplementation. The global community will need to augment local roads, hospitals, supply medical and support personnel, pharmaceuticals, and accelerate vaccine efforts.[32,36,103,161,162,163,164] This needs to be accompanied by a social/media thrust to explain this disease to the affected inhabitants and to ‘win their hearts and minds.’ In other words, while significant scientific and medical initiatives are needed to stop the outbreak, these efforts will likely be less effective without population-based education and trust-building efforts. Finally, population-based prevention and treatment strategies are desperately needed, involving (among other things) the development of new pharmaceutical agents and vaccines, better diagnostic point-of-care tools that are both rapid and inexpensive, the encouragement of out-of-the-box thinking with regard to enhanced surveillance methods, as well as the concept of readily deployable international rapid medical response teams.[103,157,165] It is incumbent on the international medical community to not only establish a rapid and effective global response capability to large-scale epidemics and natural disasters, but also to realize the necessity and acceptance of the concept of Global Responsibility and Security for all nations that cannot fend off calamities on their own.[162,166]
Failure to act in a timely and coordinated fashion as a global community has brought us to a position where we simply must act together or face the full wrath of an out-of-control Ebola outbreak.[167] Although strategic actions needed for the management of an epidemic remain the same for any disease, there are a few essential issues in the context of the Global Health Security Agenda [Table 2] that need to be addressed in order to effectively combat Ebola. Although the likelihood of Ebola becoming an epidemic in high-income countries is very low, there are many reasons for supporting the ongoing efforts in countries of West Africa, the most prominent among which are the duty to provide humanitarian assistance to the people affected, the obligation of global justice and fairness, and the ethical code of conduct inherent to the above.[168] Equally important is the need to minimize Ebola's spread to other potentially vulnerable geographic areas including the densely populated regions in other parts of Africa, East Asia, and the Central and South Americas.[169,170] Some have suggested, for example, that an Ebola outbreak in Central America and Asia may be as difficult to manage as the current outbreak in West Africa,[169,170] with some government officials openly concerned about lack of resources to effectively deal with Ebola.[171] In fact, some countries in Central America are already reacting to the possibility of Ebola importation, by imposing travel bans and restrictions.[171]
Table 2.
Key elements of the global health security agenda

EBOLA: ECONOMICS OF THE OUTBREAK
The Human Development Index ranked Liberia, Guinea, and Sierra Leone one hundred and seventy-fifth, one hundred and seventy-ninth, and one hundred and eighty-third, from a total of 187 countries, in 2014.[172] Even as Guinea is exceptionally and chronically underdeveloped, Liberia and Sierra Leone have had recent civil wars. Over 20% of the populace lives in poverty and these countries are woefully understaffed in regard to medical personnel.[173] In recent times, a World Bank Report indicated that if Ebola spreads to nearby countries, the global cost of this epidemic may reach $32 billion over the next two years.[174] With a forecast of 550,000-1,400,000 cases by early next year these countries will suffer immeasurably.[167] The outbreak may cost Sierra Leone as much as $163 million (3.3% of its Gross National Product, or GDP), with a loss of up to 8.9% of GDP, in 2015. Liberia may expend as much as $234 million (12% of GDP), and Guinea will spend approximately $142 million (2.3% of GDP) as a result of this outbreak.[174]
Agriculture, which constitutes a significant portion of the regional economy, will be most specifically affected, reducing not only farm productivity, but also threatening local food security.[175] Sierra Leone reported that its economy has deflated by approximately 30% because of Ebola.[175] Additionally, a significant proportion of the GDP of Guinea, Liberia, and Sierra Leone is attributable to mining operations and services, all of which will experience a negative impact from the Ebola epidemic.[176] The World Bank report leaves the reader with a serious warning-if 800 SARS deaths between 2002 and 2004 cost an estimated $40 billion, what will happen, not only to the West African, but also to the World's economy, if the total cases exceed the predicted 1,400,000 mark in 2015, or the outbreak spreads to other geographic regions?[157,158,159] Contrast the possible aftershocks to the estimated $1 billion needed right now to contain the current outbreak of Ebola.[177]
CONTROVERSIES
Despite our growing knowledge of Ebola and outbreak dynamics, many unanswered questions and controversies remain. For example, it is not known what the optimal decontamination procedures should be. Likewise, there is lack of agreement on what constitutes the best personal protective equipment when treating patients suffering from Ebola infection. Furthermore, we do not yet have a complete picture of the virus’ ability to survive extracorporeally under a variety of physical conditions.[178,179] Better understanding is needed of why there is a variable host response to the infection, with some patients experiencing a more severe clinical course than others.[81] Finally, should patients with Ebola be treated at local hospitals or should they be transferred to highly specialized referral centers that are better equipped to handle the logistics and complexities of the care involved?[180,181,182]
CONCLUSION
Successfully combating the current outbreak of Ebola involves coordinated global action. Aggressive investment for early containment efforts is the wisest and the least expensive of all approaches and the global community should come together at this time of crisis to implement a uniform, well-coordinated strategy to prevent catastrophic human and economic losses that may result from inaction. One of the reasons the current outbreak has been more difficult to contain than the earlier Ebola outbreaks is the spread of the disease to areas of high population density, as opposed to the previously seen rural area incidents, where isolation is easier. This may also be a harbinger of what may happen if the virus were to spread to other developing countries with large cities, where millions of low-income residents live in very densely populated areas (i.e., Bangkok in Thailand, Cairo in Egypt, Dhaka in Bangladesh, Lagos in Nigeria, or Mumbai in India). As part of the global health security strategy, the key preventive interventions must include meticulous infection control in healthcare settings, creating awareness and community support for implementation of containment measures, rigorous enforcement of the existing public health protocols, and ample resources to investigate and document any new chain of transmission. Although isolation of suspected cases is likely to be ineffective or impossible under many circumstances, voluntary quarantine and active surveillance can prove helpful. Given all of the above considerations, the time is now for humanity to act as one unified front, against Ebola.
Footnotes
Source of Support: Nil.
Conflict of Interest: None declared.
REFERENCES
- 1.Leroy EM, Rouquet P, Formenty P, Souquière S, Kilbourne A, Froment JM, et al. Multiple Ebolavirus transmission events and rapid decline of central African wildlife. Science. 2004;303:387–90. doi: 10.1126/science.1092528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Chowell G, Nishiura H. Transmission dynamics and control of Ebolavirus disease (EVD): A review. BMC Med. 2014;12:196. doi: 10.1186/s12916-014-0196-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Nishiura H, Chowell G. Euro Surveill 2014. Vol. 19. West Africa: 2014. March to August. Early transmission dynamics of Ebolavirus disease (EVD) p. 20894. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Towner JS, Sealy TK, Khristova ML, Albariño CG, Conlan S, Reeder SA, et al. Newly discovered Ebolavirus associated with hemorrhagic fever outbreak in Uganda. PLoS Pathog. 2008;4:e1000212. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Klompas M, Diekema DJ, Fishman NO, Yokoe DS. Ebola Fever: Reconciling Ebola Planning With Ebola Risk in U.S. Hospitals. Ann Intern Med. 2014 doi: 10.7326/M14-1918. In Press. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Farrar JJ, Piot P. The Ebola Emergency — Immediate Action, Ongoing Strategy. N Engl J Med. 2014;371:1545–6. doi: 10.1056/NEJMe1411471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Briand S, Bertherat E, Cox P, Formenty P, Kieny MP, Myhre JK, et al. The international Ebola emergency. N Engl J Med. 2014;371:1180–3. doi: 10.1056/NEJMp1409858. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.WHO Ebola Response Team. Ebolavirus Disease in West Africa — The First 9 Months of the Epidemic and Forward Projections. N Engl J Med. 2014;371:1481–95. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1411100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Baden LR, Kanapathipillai R, Campion EW, Morrissey S, Rubin EJ, Drazen JM. Ebola--an ongoing crisis. N Engl J Med. 2014;371:1458–9. doi: 10.1056/NEJMe1411378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Feldmann H, Geisbert TW. Ebola haemorrhagic fever. Lancet. 2011;377:849–62. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60667-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Del Rio C, Mehta AK, Lyon Iii GM, Guarner J. Ebola Hemorrhagic Fever in 2014: The Tale of an Evolving Epidemic. Ann Intern Med. 2014 doi: 10.7326/M14-1880. In Press. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Wauquier N, Becquart P, Padilla C, Baize S, Leroy EM. Human fatal zaire Ebolavirus infection is associated with an aberrant innate immunity and with massive lymphocyte apoptosis. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2010;4pii:e837. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0000837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Sullivan NJ, Geisbert TW, Geisbert JB, Shedlock DJ, Xu L, Lamoreaux L, et al. Immune protection of nonhuman primates against Ebolavirus with single low-dose adenovirus vectors encoding modified GPs. PLoS Med. 2006;3:e177. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.0030177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Peterson AT, Bauer JT, Mills JN. Ecologic and geographic distribution of filovirus disease. Emerg Infect Dis. 2004;10:40–7. doi: 10.3201/eid1001.030125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Prevention, C.f.D.C.a. Outbreaks chronology: Ebola hemorrhagic fever. [Last accessed on 2014 Oct 13]. Available from: http://www.cdc.gov/vhf/ebola/resources/outbreak-table.html .
- 16.Baize S, Pannetier D, Oestereich L, Rieger T, Koivogui L, Magassouba N, et al. Emergence of Zaire Ebolavirus disease in Guinea. N Engl J Med. 2014;371:1418–25. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1404505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.CDC. Ebola (Ebolavirus Disease) Transmission. [Last accessed on 2014 Oct 17]. Available from: http://www.cdc.gov/vhf/ebola/transmission/
- 18.Gire SK, Goba A, Andersen KG, Sealfon RS, Park DJ, Kanneh L, et al. Genomic surveillance elucidates Ebolavirus origin and transmission during the 2014 outbreak. Science. 2014;345:1369–72. doi: 10.1126/science.1259657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Feldmann H, Wahl-Jensen V, Jones SM, Ströher U. Ebolavirus ecology: A continuing mystery. Trends Microbiol. 2004;12:433–7. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2004.08.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Organization WH. Ebola Response Roadmap situation report 1. 2014. [Last accessed on 2014]. Available from: http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/131974/1/roadmapsitrep1_eng.pdf?ua=1)
- 21.WHO. Mali confirms its first case of Ebola. [Last accessed on 2014 Oct 28]. Available from: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/news/ebola/24-october-2014/en/
- 22.McCarthy M. Texas healthcare worker is diagnosed with Ebola. BMJ. 2014;349:g6200. doi: 10.1136/bmj.g6200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.McCarthy M. Liberian man being treated for Ebola in Texas dies. BMJ. 2014;349:g6145. doi: 10.1136/bmj.g6145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Euronews. Spanish nursing assistant's husband who overcame Ebola leaves hospital. [Last accessed on 2014 Oct 28]. Available from: http://www.euronews.com/2014/10/27/spanishnursing-assistant-s-husband-who-overcame-ebola-leaves-hospital/
- 25.Flynn L, Bery R, Kaitano AE. Emerging infectious diseases and impact assessments. [Last accessed on 2014 Nov 6]. Available from: http://www.iaia.org/conferences/iaia13/proceedings/Final%20papers%20review%20process%2013/Emerging%20Infectious%20Diseases%20and%20Impact%20Assessments.pdf?AspxAutoDetectCookieSupport=1 .
- 26.House T. Epidemiological dynamics of Ebola outbreaks. Elife. 2014;3:e03908. doi: 10.7554/eLife.03908. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Chan M. Ebolavirus disease in West Africa--no early end to the outbreak. N Engl J Med. 2014;371:1183–5. doi: 10.1056/NEJMp1409859. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Alirol E, Getaz L, Stoll B, Chappuis F, Loutan L. Urbanisation and infectious diseases in a globalised world. Lancet Infect Dis. 2011;11:131–41. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(10)70223-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Daszak P, Cunningham AA, Hyatt AD. Emerging infectious diseases of wildlife - Threats to biodiversity and human health. Science. 2000;287:443–9. doi: 10.1126/science.287.5452.443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Hewlett BS, Amola RP. Cultural contexts of Ebola in northern Uganda. Emerg Infect Dis. 2003;9:1242–8. doi: 10.3201/eid0910.020493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Philips M, Markham A. Ebola: A failure of international collective action. Lancet. 2014;384:1181. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)61606-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Halliday J, Daborn C, Auty H, Mtema Z, Lembo T, Bronsvoort BM, et al. Bringing together emerging and endemic zoonoses surveillance: Shared challenges and a common solution. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2012;367:2872–80. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2011.0362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Mills EJ, Kanters S, Hagopian A, Bansback N, Nachega J, Alberton M, et al. The financial cost of doctors emigrating from sub-Saharan Africa: Human capital analysis. BMJ. 2011;343:d7031. doi: 10.1136/bmj.d7031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Boozary AS, Farmer PE, Jha AK. The Ebola Outbreak, Fragile Health Systems, and Quality as a Cure. JAMA. 2014;312:1859–60. doi: 10.1001/jama.2014.14387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.WHO. Unprecedented number of medical staff infected with Ebola. [Last accessed on 2014 Oct 28]. Available from: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/news/ebola/25-august-2014/en/
- 36.Youde J. The Ebola outbreak in Guinea, Liberia, and Sierra Leone. E-International relations. [Last accessed on 2014 Nov 10]. Available from: http://www.e-ir.info/2014/07/26/the-ebola-outbreak-in-guinea-liberia-and-sierra-leone/
- 37.News B. Ebola contained in Nigeria, Senegal - US health officials. [Last accessed on 2014 Nov 9]. Available from: http://www.bbc.com/news/world-africa-29436851 .
- 38.AFP. Spain Ebola-free in two weeks if no new case. [Last accessed on 2014 Nov 9]. Available from: http://www.thelocal.es/20141013/spain-to-be-ebola-free-by-oct-27th-if-no-newcases .
- 39.Smith D, Hoije K. Mali races to head off Ebola outbreak after second death. [Last accessed on 2014 Nov 12]. Available from: http://www.theguardian.com/global-development/2014/Nov/12/mali-ebola-outbreak-second-death .
- 40.Penney J. Mali quarantines dozens as second Ebola outbreak spreads in country. [Last accessed on 2014 Nov 12]. Available from: http://www.reuters.com/article/2014/11/12/us-health-ebola-mali-idUSKCN0IW12C20141112 .
- 41.Grady D. US scientists see long fight against Ebola. [Last accessed on 2014 Nov 6]. Available from: http://www.nytimes.com/2014/09/13/world/africa/us-scientists-see-long-fightagainst-ebola.html .
- 42.Sengupta S. New Ebola cases may soon reach 10,000 a week, officials predict. [Last accessed on 2014 Nov 9]. Available from: http://www.nytimes.com/2014/10/15/world/africa/ebolaepidemic-who-west-africa.html?_r=0 .
- 43.Farrar JJ, Piot P. The Ebola emergency--immediate action, ongoing strategy. N Engl J Med. 2014;371:1545–6. doi: 10.1056/NEJMe1411471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.CDC. Outbreak of Hantavirus Infection in Yosemite National Park. 2012. 2014. Oct 17, [Last accessed on 2014 Oct 17]. Available from: http://www.cdc.gov/hantavirus/outbreaks/yosemite-national-park-2012.html .
- 45.Shane AL, Roels TH, Goldoft M, Herikstad H, Angulo FJ. Foodborne disease in our global village: A multinational investigation of an outbreak of Salmonella serotype Enteritidis phage type 4 infection in Puerto Vallarta, Mexico. Int J Infect Dis. 2002;6:98–102. doi: 10.1016/s1201-9712(02)90068-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Boyer ME. Service to “our emerging global village”. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1993;202:1817–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Evans G. Health and security in the global village. World Health Forum. 1993;14:133–5. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Wilson ME. Infectious diseases in the era of the global village. Salud Publica Mex. 1992;34:352–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Mogul F. New York's disease detectives hit the street in search of Ebola. [Last accessed on 2014 Oct 28]. Available from: http://www.npr.org/blogs/health/2014/10/27/359323578/newyorks-disease-detectives-hit-the-street-in-search-of-ebola .
- 50.Stephenson J. CDC: Ebola risk to US patients is low, but clinicians should be on alert. JAMA. 2014;312:686. doi: 10.1001/jama.2014.10528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Buchanan L, Copeland B, Yourish K, Trahan Martinez M, et al. Retracing the steps of the Dallas Ebola patient. [Last accessed on 2014 Oct 17]. Available from: http://www.nytimes.com/interactive/2014/10/01/us/retracing-the-steps-of-the-dallas-ebolapatient.html?_r=0 .
- 52.Botelho G, Wilson J. Thomas Eric Duncan: First Ebola death in U.S. [Last accessed on 2014 Oct 17]. Available from: http://www.edition.cnn.com/2014/10/08/health/thomaseric-duncan-ebola/
- 53.Jonsson P. First US Ebola case: Why the delayed diagnosis? [Last accessed on 2014 Oct 31]. Available from: http://www.csmonitor.com/USA/2014/1001/First-US-Ebola-case-Whythe-delayed-diagnosis-video .
- 54.Botelho G. Nurse may have had symptoms of Ebola longer than first thought. [Last accessed on 2014 Oct 17]. Available from: http://www.edition.cnn.com/2014/10/16/health/us-ebola/
- 55.Bever L. Chain reaction: Concern about Ebola nurse's flight prompts school closings in two states. [Last accessed on 2014 Oct 17]. Available from: http://www.washingtonpost.com/news/morning-mix/wp/2014/10/16/afterconcern-about-ebola-patients-flight-schools-close-in-two-cities/
- 56.CBS. Comparison of contact between two sick nurses and Ebola patient. [Last accessed on 2014 Oct 17]. Available from: http://www.dfw.cbslocal.com/2014/10/15/comparisonof-contact-between-two-sick-nurses-ebola-patient/
- 57.Johnson-Delaney CA. Seattle, Wash., U.S.A. USA: Primate Information Center, Regional Primate Research Center, University of Washington; 1990. University of Washington. Primate Information Center., The filoviridae: Ebola, ebola-like, and marburg viruses in nonhuman primates: A selective bibliography, 1965-1990. Primate Information Center topical bibliographies. 1990; p. 10. [Google Scholar]
- 58.Fisher-Hoch SP. Lessons from nosocomial viral hemorrhagic fever outbreaks. Br Med Bull. 2005;73-74:123–37. doi: 10.1093/bmb/ldh054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Slenczka WG. The Marburg virus outbreak of 1967 and subsequent episodes. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1999;235:49–75. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-59949-1_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Ebola haemorrhagic fever in Zaire, 1976. Bull World Health Organ. 1978;56:271–93. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Bres P. The epidemic of Ebola haemorrhagic fever in Sudan and Zaire, 1976: Introductory note. Bull World Health Organ. 1978;56:245. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Cooper C. How the >Ebolavirus got its name adn how we caught it from animals. [Last accessed on 2014 Oct 17]. Available from: http://www.independent.co.uk/life-style/healthand-families/how-the-ebola-virus-got-its-name-and-how-we-caught-itfrom-animals-9770193.html .
- 63.Pinzon JE, Wilson JM, Tucker CJ, Arthur R, Jahrling PB, Formenty P. Trigger events: Enviroclimatic coupling of Ebola hemorrhagic fever outbreaks. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2004;71:664–74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Martini GA. Marburg agent disease: In man. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1969;63:295–302. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(69)90001-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Siegert R, Shu HL, Slenczka W, Peters D, Müller G. On the etiology of an unknown human infection originating from monkeys. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 1967;92:2341–3. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1106144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Times T.N.Y. Ebola Facts: How Many People Have Been Sent to Countries With Ebola by Doctors Without Borders? 2014. [Last accessed on 2014 Nov 15]. Available from: http://www.nytimes.com/interactive/2014/07/31/world/africa/ebola-virusoutbreak-qa.html?_r=1 .
- 67.Towner JS, Amman BR, Sealy TK, Carroll SA, Comer JA, Kemp A, et al. Isolation of genetically diverse Marburg viruses from Egyptian fruit bats. PLoS Pathog. 2009;5:e1000536. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Jin J. JAMA patient page: Ebolavirus Disease. JAMA. 2014;312:1942. doi: 10.1001/jama.2014.13759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.World Health Organization. Barriers to rapid containment of the Ebola outbreak. 2014. [Last accessed on 2014 Nov 15]. Available from: http://www.who.int/csr/disease/ebola/overview-august-2014/en/
- 70.Rodriguez LL, De Roo A, Guimard Y, Trappier SG, Sanchez A, Bressler D, et al. Persistence and genetic stability of Ebolavirus during the outbreak in Kikwit, Democratic Republic of the Congo, 1995. J Infect Dis. 1999;179(Suppl 1):S170–6. doi: 10.1086/514291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.World Health Organization. Travel and transport risk assessment: Guidance for public health authorities and transport sector. 2014. [Last accessed on 2014 Nov 15]. Available from: http://www.who.int/csr/resources/publications/ebola/travel-guidance/en/
- 72.Feldmann F, Geisbert TW. Ebola hemorrhagic fever. Lancet. 2011;377:849–62. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60667-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Ebolavirus Disease Information for Clinicians in U. S. Healthcare Settings. 2014. [Last accessed on 2014 Nov 15]. Available from: http://www.cdc.gov/vhf/ebola/hcp/clinician-information-us-healthcare-settings.html .
- 74.Bray M, Geisbert TW. Ebolavirus: The role of macrophages and dendritic cells in the pathogenesis of Ebola hemorrhagic fever. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2005:371560–6. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2005.02.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Mahanty S, Bray M. Pathogenesis of filoviral haemorrhagic fevers. Lancet Infect Dis. 2004;4:487–98. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(04)01103-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Geisbert TW, Young HA, Jahrling PB, Davis KJ, Larsen T, Kagan E, et al. Pathogenesis of Ebola hemorrhagic fever in primate models: Evidence that hemorrhage is not a direct effect of virus-induced cytolysis of endothelial cells. Am J Pathol. 2003;163:2371–82. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63592-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.United States Army Public Health Command. Ebolavirus Disease (Ebola) 2014. [Last accessed on 2014 Nov 15]. Available from: http://phc.amedd.army.mil/topics/discond/diseases/pages/EbolavirusDisease.aspx .
- 78.Bwaka MA, Bonnet MJ, Calain P, Colebunders R, De Roo A, Guimard Y, et al. Ebola hemorrhagic fever in Kikwit, Democratic Republic of the Congo: Clinical observations in 103 patients. J Infect Dis. 1999;179(Suppl 1):S1–7. doi: 10.1086/514308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Sureau PH. Firsthand clinical observations of hemorrhagic manifestations in Ebola hemorrhagic fever in Zaire. Rev Infect Dis. 1989;11(Suppl 4):S790–3. doi: 10.1093/clinids/11.supplement_4.s790. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Emond RT, Evans B, Bowen ET, Lloyd G. A case of Ebolavirus infection. Br Med J. 1977;2:541–4. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6086.541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Towner JS, Rollin PE, Bausch DG, Sanchez A, Crary SM, Vincent M, et al. Rapid diagnosis of Ebola hemorrhagic fever by reverse transcription-PCR in an outbreak setting and assessment of patient viral load as a predictor of outcome. J Virol. 2004;78:4330–41. doi: 10.1128/JVI.78.8.4330-4341.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Leonard S. Containing Ebola: 7 next-gen rapid diagnostic tests. [Last accessed on 2014 Nov 12]. Available from: http://www.mddionline.com/article/containing-ebola-7-next-genrapid-diagnostic-tests-11-07-14 .
- 83.Madore JT. Chembio diagnostics joining biotech firm to develop rapid test for Ebola. [Last accessed on 1014 Nov 12]. Available from: http://www.newsday.com/business/chembiodiagnostics-developing-rapid-test-for-ebola-1.9550864 .
- 84.Borchert M, Mutyaba I, Van Kerkhove MD, Lutwama J, Luwaga H, Bisoborwa G, et al. Ebola haemorrhagic fever outbreak in Masindi District, Uganda: Outbreak description and lessons learned. BMC Infect Dis. 2011;11:357. doi: 10.1186/1471-2334-11-357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Mupapa K, Mukundu W, Bwaka MA, Kipasa M, De Roo A, Kuvula K, et al. Ebola hemorrhagic fever and pregnancy. J Infect Dis. 1999;179(Suppl 1):S11–2. doi: 10.1086/514289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Francesconi P, Yoti Z, Declich S, Onek PA, Fabiani M, Olango J, et al. Ebola hemorrhagic fever transmission and risk factors of contacts, Uganda. Emerg Infect Dis. 2003;9:1430–7. doi: 10.3201/eid0911.030339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.de Lamballerie X. Co-ordinating the clinical management of imported human cases suspected of being infected with a highly pathogenic virus such as Ebola. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2014 doi: 10.1111/1469-0691.12792. In Press. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Roddy P, Howard N, Van Kerkhove MD, Lutwama J, Wamala J, Yoti Z, et al. Clinical manifestations and case management of Ebola haemorrhagic fever caused by a newly identified virus strain, Bundibugyo, Uganda, 2007-2008. PLoS One. 2012;7:e52986. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0052986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Joffe S. Evaluating novel therapies during the Ebola epidemic. JAMA. 2014;312:1299–300. doi: 10.1001/jama.2014.12867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Kanapathipillai R, Restrepo AM, Fast P, Wood D, Dye C, Kieny MP, et al. Ebola Vaccine - An Urgent International Priority. N Engl J Med. 2014 doi: 10.1056/NEJMp1412166. In Press. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Sobarzo A, Ochayon DE, Lutwama JJ, Balinandi S, Guttman O, Marks RS, et al. Persistent immune responses after Ebolavirus infection. N Engl J Med. 2013;369:492–3. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1300266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.McClam E. Dallas nurse Amber Vinson is Ebola-free, will leave hospital. [Last accessed on 2014 Oct 28]. Available from: http://www.nbcnews.com/storyline/ebola-virus-outbreak/dallas-nurse-amber-vinson-ebola-free-will-leave-hospital-n235316 .
- 93.Morse D. Nina Pham, nurse who contracted Ebola, is now free of virus and leaves NIH. [Last accessed on 2014 Oct 28]. Available from: http://www.washingtonpost.com/local/dallas-nurse-treated-for-ebola-at-nih-now-vir usfree/2014/10/24/91355cd2-5b8c-11e4-bd61-346aee66ba29_story.html .
- 94.Bacon J, Owens M. Infected Dallas nurse ID’d; gets transfusion from Ebola survivor. 2014. 2014. Oct 28, [Last accessed on 2014 Oct 28]. Available from: http://www.usatoday.com/story/news/nation/2014/10/13/ebola-nurse-who/17182599/
- 95.Mupapa K, Massamba M, Kibadi K, Kuvula K, Bwaka A, Kipasa M, et al. Treatment of Ebola hemorrhagic fever with blood transfusions from convalescent patients. International Scientific and Technical Committee. J Infect Dis. 1999;179(Suppl 1):S18–23. doi: 10.1086/514298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Saul H. Ebolavirus outbreak: Liberia doctor treating patients with HIV drugs reports success. 2014. 2014. Nov 9, [Last accessed on 2014 Nov 9]. Available from: http://www.independent.co.uk/news/world/africa/ebola-outbreak-liberia-doctortreating-patients-with-hiv-drugs-claims-13-out-of-15-survived-9759642.html .
- 97.Zhang Y, Li D, Jin X, Huang Z. Fighting Ebola with ZMapp: Spotlight on plant-made antibody. Sci China Life Sci. 2014;57:987–8. doi: 10.1007/s11427-014-4746-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Till B. DARPA may have a way to stop Ebola in its tracks. [Last accessed on 2014 Nov 9]. Available from: http://www.newrepublic.com/article/119376/ebola-drug-zmapp-darpaprogram-could-get-it-africa .
- 99.Pollack A. Second drug is allowed for treatment of Ebola. [Last accessed on 2014 Nov 9]. Available from: http://www.nytimes.com/2014/08/08/health/second-experimental-drugallowed-for-treating-ebola.html?_r=0 .
- 100.Chimerix I. Chimerix's Brincidofovir has in vitro activity against Ebola. [Last accessed on 2014 Nov 12]. Available from: http://ir.chimerix.com/releasedetail.cfm?releaseid=868807 .
- 101.Kroll D. Cimerix's Brincidofovir given to Dallas, Nebraska Ebola patients. [Last accessed on 2014 Nov 12]. Available from: http://www.forbes.com/sites/davidkroll/2014/10/07/chimerixs-brincidofovir-given-to-dallas-nebraska-ebola-patients/
- 102.Phillip A. An Ebola vaccine was given to 10 volunteers, and there are ‘no red flags’ yet. [Last accessed on 2014 Nov 9]. Available from: http://www.washingtonpost.com/news/to-yourhealth/wp/2014/09/16/an-ebola-vaccine-was-given-to-10-volunteers-andthere-are-no-red-flags-yet/
- 103.Fox C. Two anti-Ebola vaccines in historic race. [Last accessed on 2014 Nov 9]. Available from: http://www.dddmag.com/articles/2014/09/two-anti-ebola-vaccines-historic-race .
- 104.Marketwired. FDA gives New Link Genetics approval to proceed to Phase I clinical studies of their Ebola vaccine. [Last accessed on 2014 Nov 9]. Available from: http://www.investors.linkp.com/releasedetail.cfm?releaseid=869082 .
- 105.Okware SI, Omaswa FG, Zaramba S, Opio A, Lutwama JJ, Kamugisha J, et al. An outbreak of Ebola in Uganda. Trop Med Int Health. 2002;7:1068–75. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-3156.2002.00944.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Heymann DL, Barakamfitiye D, Szczeniowski M, Muyembe-Tamfum JJ, Bele O, Rodier G. Ebola hemorrhagic fever: Lessons from Kikwit, Democratic Republic of the Congo. J Infect Dis. 1999;179(Suppl 1):S283–6. doi: 10.1086/514287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Hall RC, Hall RC, Chapman MJ. Chapman, The 1995 Kikwit Ebola outbreak: Lessons hospitals and physicians can apply to future viral epidemics. Gen Hosp Psychiatry. 2008;30:446–52. doi: 10.1016/j.genhosppsych.2008.05.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Gounder C. To combat Ebola, first build back trust in healthcare workers. [Last accessed on 2014 Nov 9]. Available from: http://www.blogs.reuters.com/great-debate/2014/07/30/efforts-against-ebola-outbreak-hampered-by-victims-lack-of-trust-inhealthcare-workers/
- 109.Wolz A. Face to face with Ebola-an emergency care center in Sierra Leone. N Engl J Med. 2014;371:1081–3. doi: 10.1056/NEJMp1410179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Kerstiëns B, Matthys F. Interventions to control virus transmission during an outbreak of Ebola hemorrhagic fever: Experience from Kikwit, Democratic Republic of the Congo, 1995. J Infect Dis. 1999;179(Suppl 1):S263–7. doi: 10.1086/514320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Baron RC, McCormick JB, Zubeir OA. Zubeir, Ebolavirus disease in southern Sudan: Hospital dissemination and intrafamilial spread. Bull World Health Organ. 1983;61:997–1003. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Shoichet CE. Ebola: 5 things nurses say the Texas hospital got wrong. [Last accessed on 2014 Oct 28]. Available from: http://www.cnn.com/2014/10/15/health/texas-ebolanurses-union-claims/
- 113.Greenheimer L. Ebola spread shows flaws in protective gear and procedures. 2014. 2014. Oct 28, [Last accessed on 2014 Oct 28]. Available from: http://www.scientificamerican.com/article/ebola-spread-shows-flaws-in-protective-gear-and-procedures/
- 114.Hartocollis A, Santora M. Plenty of hugs as craig spencer, recovered New York Ebola patient, goes home. 2014. 2014. Nov 12, [Last accessed on 2014 Nov 12]. Available from: http://www.nytimes.com/2014/11/12/nyregion/craig-spencer-new-yorkebola-patient-bellevue.html?_r=0 .
- 115.WHO. How to safely collect blood samples from persons suspected to be infected with highly infectious blood-borne pathogens (e.g. Ebola). 2014. 2014. Nov 9, [Last accessed on 2014 Nov 9]. Available from: http://www.who.int/csr/resources/publications/ebola/blood-collect-en.pdf .
- 116.Lippi G, Mattiuzzi C, Plebani M. Laboratory preparedness to face infectious outbreaks. Ebola and beyond. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2014;52:1681–4. doi: 10.1515/cclm-2014-0960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.CDC. Ebola-associated waste management. [Last accessed on 2014 Nov 5]. Available from: http://www.cdc.gov/vhf/ebola/hcp/medical-waste-management.html .
- 118.Christopher GW, Eitzen EM., Jr Air evacuation under high-level biosafety containment: The aeromedical isolation team. Emerg Infect Dis. 1999;5:241–6. doi: 10.3201/eid0502.990208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Martinez M, Vercammen P, Hannah J. Germ-zapping robot Gigi sets its sights on Ebola. [Last accessed on 2014 Nov 9]. Available from: http://www.cnn.com/2014/10/16/us/germ-zapping-robot-ebola/
- 120.Caywood T. WPI explores using robots to treat Ebola. [Last accessed on 2014 Nov 9]. Available from: http://www.telegram.com/article/20141109/NEWS/311099832/1246 .
- 121.Mulvihill J. Ebola's orphans: Survivors care for children left behind by disease. [Last accessed on 2014 Nov 10]. Available from: http://www.foxnews.com/health/2014/11/04/ebolas-orphans-survivors-care-for-children-left-behind-by-disease/
- 122.WHO. Liberia: Survivors help train health workers for Ebola care. [Last accessed on 2014 Nov 10]. Available from: http://www.who.int/features/2014/liberia-ebola-survivors/en/
- 123.UN. Ebola: Back from outbreak epicentre, UN offical says survivors now helping with care. [Last accessed on 2014 Nov 10]. Available from: http://www.un.org/apps/news/story.asp?NewsID=49108#.VGDVOMkfKQo .
- 124.Kumana CR, Cheung BM, Chan LS. Airport screening for Ebola: Current thermal scanning procedures are unreliable. BMJ. 2014;349:g6571. doi: 10.1136/bmj.g6571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Mabey D, Flasche S, Edmunds WJ. Airport screening for Ebola. BMJ. 2014;349:g6202. doi: 10.1136/bmj.g6202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Parkes-Ratanshi R, Elbireer A, Mbambu B, Mayanja F, Coutinho A, Merry C. Ebola outbreak response; Experience and development of screening tools for viral haemorrhagic fever (VHF) in a HIV center of excellence near to VHF epicentres. PLoS One. 2014;9:e100333. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0100333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.McCarthy M. US increases Ebola screening at five airports. BMJ. 2914;349:g6147. doi: 10.1136/bmj.g6147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Gulland A. Experts question usefulness of screening travellers to UK for Ebola. BMJ. 2014;349:g6199. doi: 10.1136/bmj.g6199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.St John RK, King A, de Jong D, Bodie-Collins M, Squires SG, Tam TW. Border screening for SARS. Emerg Infect Dis. 2005;11:6–10. doi: 10.3201/eid1101.040835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Pitman RJ, Cooper BS, Trotter CL, Gay NJ, Edmunds WJ. Entry screening for severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) or influenza: Policy evaluation. BMJ. 2005;331:1242–3. doi: 10.1136/bmj.38573.696100.3A. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Feldman J. Schools in Texas, Ohio close over Ebola panic. [Last accessed on 2014 Nov 9]. Available from: http://www.mediaite.com/online/schools-in%C2%A0texas-ohio-closeover-ebola-panic/
- 132.Luyten J. Mutual moral obligations in the preventin of infectious diseases, in Justice, Luck and Responsibility in Health Care. In: Denier Y, et al., editors. Springer Netherlands; 2014. pp. 85–100. [Google Scholar]
- 133.Thacker SB, Berkelman RL. Public health surveillance in the United States. Epidemiol Rev. 1988;10:164–90. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.epirev.a036021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134.CDC. CDC announces active post-arrival monitoring for travelers from impacted countries. 2014. 2014. Nov 12, [Last accessed on 2014 Nov 12]. Available from: http://www.cdc.gov/media/releases/2014/p1022-post-arrival-monitoring.html .
- 135.Allaranga Y, Kone ML, Formenty P, Libama F, Boumandouki P, Woodfill CJ, et al. Lessons learned during active epidemiological surveillance of Ebola and Marburg viral hemorrhagic fever epidemics in Africa. East Afr J Public Health. 2010;7:30–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136.Tambo E, Ugwu EC, Ngogang JY. Need of surveillance response systems to combat Ebola outbreaks and other emerging infectious diseases in African countries. Infect Dis Poverty. 2014;3:29. doi: 10.1186/2049-9957-3-29. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137.Gostin LO. Rev. and expanded. 2nd ed. Berkeley: California/Milbank Books on Health and the Public; 2008. Public health law: Power, duty, restraint. [Google Scholar]
- 138.Smith RE, editor. New York Milbank Memorial Fund. Quarantine and isolation. Br Med J. Vol. 2. New York: University of California Press; 1952. pp. 34–6. [Google Scholar]
- 139.Gostin LO. Milbank Memorial Fund. Berkeley New York: University of California Press; 2000. Public health law: Power, duty, restraint. California/Milbank series on health and the public; p. 491. [Google Scholar]
- 140.Markovits D. Quarantines and distributive justice. J Law Med Ethics. 2005;33:323–44. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-720x.2005.tb00497.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 141.Bostick NA, Levine MA, Sade RM. Ethical obligations of physicians participating in public health quarantine and isolation measures. Public Health Rep. 2008;123:3–8. doi: 10.1177/003335490812300102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 142.Gensini GF, Yacoub MH, Conti AA. The concept of quarantine in history: From plague to SARS. J Infect. 2004;49:257–61. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2004.03.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 143.Hawryluck L, Gold WL, Robinson S, Pogorski S, Galea S, Styra R. SARS control and psychological effects of quarantine, Toronto, Canada. Emerg Infect Dis. 2004;10:1206–12. doi: 10.3201/eid1007.030703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 144.Zernike K, Fitzsimmons EG. Threat of lawsuit could test Maine's quarantine policy. [Last accessed on 2014 Nov 10]. Available from: http://www.nytimes.com/2014/10/30/us/kacihickox-nurse-under-ebola-quarantine-threatens-lawsuit.html?_r=0 .
- 145.Gregg C. Ebola nurse forced into quarantine in N.J. contemplates civil rights lawsuit. [Last accessed on 2014 Nov 10]. Available from: http://philadelphia.cbslocal.com/2014/10/27/ebola-nurse-forced-into-quarantine-in-n-j-contemplates-civil-rightslawsuit/
- 146.Drazen JM, Kanapathipillai R, Campion EW, Rubin EJ, Hammer SM, Morrissey S, et al. Ebola and Quarantine. N Engl J Med. 2014 doi: 10.1056/NEJMe1413139. In Press. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 147.Bensimon CM, Upshur RE. Evidence and effectiveness in decisionmaking for quarantine. Am J Public Health. 2007;97(Suppl 1):S44–8. doi: 10.2105/AJPH.2005.077305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 148.Chowell G, Fuentes R, Olea A, Aguilera X, Nesse H, Hyman JM. The basic reproduction number R0 and effectiveness of reactive interventions during dengue epidemics: The 2002 dengue outbreak in Easter Island, Chile. Math Biosci Eng. 2013;10:1455–74. doi: 10.3934/mbe.2013.10.1455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 149.Legrand J, Grais RF, Boelle PY, Valleron AJ, Flahault A. Understanding the dynamics of Ebola epidemics. Epidemiol Infect. 2007;135:610–21. doi: 10.1017/S0950268806007217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 150.Mitman G. Ebola in a Stew of Fear. N Engl J Med. 2014;371:1763–5. doi: 10.1056/NEJMp1411244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 151.Wynia MK. Ethics and public health emergencies: Restrictions on liberty. Am J Bioeth. 2007;7:1–5. doi: 10.1080/15265160701577603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 152.Izadi E. Nigeria's Ebola outbreak may be coming to an end. [Last accessed on 2014 Nov 12]. Available from: http://www.washingtonpost.com/news/to-your-health/wp/2014/09/30/nigerias-ebola-outbreak-may-be-coming-to-an-end/
- 153.Murphy T. Ebola cases fall in Liberia, rise in Sierra Leone, and concerns persist. [Last accessed on 2014 Nov 12]. Available from: http://www.humanosphere.org/globalhealth/2014/11/calls-increased-efforts-amid-promising-worrying-progressebola/
- 154.Green A. Ebola emergency meeting establishes new control centre. Lancet. 2014;384:118. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(14)61147-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 155.Muyembe-Tamfum JJ, Kipasa M, Kiyungu C, Colebunders R. Ebola outbreak in Kikwit, Democratic Republic of the Congo: Discovery and control measures. J Infect Dis. 1999;179(Suppl 1):S259–62. doi: 10.1086/514302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 156.Bah SM, Aljoudi AS. Taking a religious perspective to contain Ebola. Lancet. 2014;384:951. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)61344-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 157.Charlton C. Bribery breaks out in battle against Ebola: Liberian victims’ families paying corrupt retrieval teams to keep bodies so they can give them traditional burials. [Last accessed on 2014 Oct 28]. Available from: http://www.dailymail.co.uk/news/article-2791911/bribery-breaks-battle-against-ebola-liberian-victimsfamilies-paying-corrupt-retrieval-teams-bodies-traditional-burials.html .
- 158.Lamunu M, Lutwama JJ, Kamugisha J, Opio A, Nambooze J, Ndayimirije N, et al. Containing a haemorrhagic fever epidemic: The Ebola experience in Uganda (October 2000-January 2001) Int J Infect Dis. 2004;8:27–37. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2003.04.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 159.Muyembe T, Kipasa M. Ebola haemorrhagic fever in Kikwit, Zaire. International Scientific and Technical Committee and WHO Collaborating Centre for Haemorrhagic Fevers. Lancet. 1995;345:1448. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(95)92640-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 160.Guimard Y, Bwaka MA, Colebunders R, Calain P, Massamba M, De Roo A, et al. Organization of patient care during the Ebola hemorrhagic fever epidemic in Kikwit, Democratic Republic of the Congo, 1995. J Infect Dis. 1999;179(Suppl 1):S268–73. doi: 10.1086/514315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 161.Harman S. Ebola and the politics of a global health crisis. [Last accessed on 2014 Nov 10]. Available from: http://www.e-ir.info/2014/10/20/ebola-and-the-politics-of-a-globalhealth-crisis/
- 162.Gomez DO. New international agencies for a global village. Salud Publica Mex. 2003;45:333–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 163.Inglesby T, Fischer JE. Moving ahead on the global health security agenda. Biosecur Bioterror. 2014;12:63–5. doi: 10.1089/bsp.2014.3314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 164.Pillai SK, Nyenswah T, Rouse E, Arwady MA, Forrester JD, Hunter JC, et al. Developing an incident management system to support ebola response — liberia, july-august 2014. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2014;63:930–3. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 165.Schneider P. Toward a global medical village. Healthc Inform. 1997;14:26–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 166.Stawicki SP, Stoltzfus JC, Aggarwal P, Bhoi S, Bhatt S, Kalra OP, et al. Academic College of Emergency Experts in India's INDO-US Joint Working Group and OPUS12 Foundation Consensus Statement on Creating A Coordinated, Multi-Disciplinary, Patient-Centered, Global Point-of-Care Biomarker Discovery Network. Int J Crit Illn Inj Sci. 2014;4:200–8. doi: 10.4103/2229-5151.141398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 167.Marchigiani R, Gordy S, Cipolla J, Adams RC, Evans DC, Stehly C, et al. Wind disasters: A comprehensive review of current management strategies. Int J Crit Illn Inj Sci. 2013;3:130–42. doi: 10.4103/2229-5151.114273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 168.Press A. CDC report predicts as many as 1.4 million cases of Ebola by January. 2014. 2014. Nov 10, [Last accessed on 2014 Nov 10]. Available from: http://www.foxnews.com/health/2014/09/23/who-forecasts-more-than-20000-ebola-cases-bynovember-2/
- 169.Rid A, Emanuel EJ. Why should high-income countries help combat Ebola? JAMA. 2014;312:1297–8. doi: 10.1001/jama.2014.12869. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 170.Bier J. General: If Ebola reaches Central America, ‘There will be mass migration into the U.S.’. [Last accessed on 2014 Nov 9]. Available from: http://www.weeklystandard.com/blogs/general-if-ebola-reaches-central-america-there-will-be-massmigration-us_810793.html .
- 171.Uhlmann C. Must stop Ebola from getting to Asia: Volunteer doctor. [Last accessed on 2014 Nov 10]. Available from: http://www.abc.net.au/news/2014-10-17/health-minister-defendsaustralias-ebola-response/5821036 .
- 172.Charles J, Wyss J. Ebola fears spur travel bans in Latin America, Caribbean. [Last accessed on 2014 Nov 9]. Available from: http://www.miamiherald.com/news/nation-world/world/americas/article3073953.html .
- 173.UN. United Nations Development Program. Sustaining human progress: Reducing vulnerabilities and building resilience. [Last accessed on 2014 Nov 10]. Available from: http://www.undp.org/content/undp/en/home/librarypage/hdr/2014-human-development-report.html .
- 174.Bausch DG, Schwarz L. Outbreak of Ebolavirus disease in Guinea: Where ecology meets economy. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2014;8:e3056. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0003056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 175.Kottasova I. World Bank: Cost of Ebola could top $32 billion. [Last accessed on 2014 Nov 5]. Available from: http://edition.cnn.com/2014/09/24/business/ebola-cost-warning/
- 176.Hamilton R. Ebola crisis: The economic impact. [Last accessed on 2014 Nov 10]. Available from: http://www.bbc.com/news/business-28865434 .
- 177.Mirzayev E. Ebola's economic impacts on Liberia, Sierra Leone and Guinea. [Last accessed on 2014 Nov 10]. Available from: http://www.investopedia.com/articles/investing/101314/ebolas-economic-impacts-liberia-sierra-leone-and-guinea.asp .
- 178.Schlein L. WHO: $1 billion needed to contain Ebola outbreak. [Last accessed on 2014 Nov 10]. Available from: http://www.voanews.com/content/ebola-outbreak-who-responseone-billion-dollars/2451347.html .
- 179.Burki TK. USA focuses on Ebola vaccine but research gaps remain. Lancet. 2011;378:389. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(11)61194-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 180.PHAC-ASPC. Pathogen safety data sheet - Infectious substances. [Last accessed on 2014 Nov 12]. Available from: http://www.phac-aspc.gc.ca/lab-bio/res/psds-ftss/ebola-eng.php .
- 181.News C. Ebola outbreak: Latest Texas patient taken to Atlanta hospital. [Last accessed on 2014 Nov 12]. Available from: http://www.cbsnews.com/news/ebola-outbreak-latest-texas-patient-tobe-transferred-to-atlanta-hospital/
- 182.Keneally M. Second nurse with Ebola arrives at Emory. [Last accessed on 2014 Nov 12]. pp. 180–182. Available from: http://abcnews.go.com/Health/nurse-ebola-arrives-emory/careinvolved?


