The large variety of microbial species in the human microbiome plays an important role in human health by affecting tissue differentiation, modulation of the immune system, as well as the general response against infectious pathogens. The aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) contributes to immune homeostasis as having an antimicrobial role on the one hand – owing to AhR-dependent IL-22 transcription – and, on the other, an anti-inflammatory role in that it mediates the differentiation of regulatory T cells (Tregs). Here, we have examined the multifaceted physiological role of AhR as resulting from the vast array of recently described AhR ligands and of the multiplicity of AhR-expressing cells in host-microbial symbiosis in mammals.
The Promiscuous Nature of AhR Agonists
Aryl hydrocarbon receptor is a ligand-dependent transcription factor activated by a variety of synthetic and natural molecules. In particular, ligands of AhR include hydrocarbons, heterocyclic amines, and indole-derived compounds. Dioxin (2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin; TCDD) represents the prototypical environmental and most potent AhR ligand known (1). In addition, a variety of herbal extracts – such as ginseng, licorice, and gingko biloba – stimulate AhR DNA binding and the downstream transcription of numerous genes, thus indicating that AhR might have evolved to respond to mainly dietary products to which animals and humans are chronically exposed (2). Interestingly, ginseng, saponins (gingenosides) have been defined as potent AhR agonists or antagonists (3, 4). Despite the ability of environmental chemicals or other products in diet to bind and subsequently activate AhR, former studies have also shown that natural endogenous ligands may bind and mediate AhR-dependent downstream effects as well (5). Thus the evolution of the AhR – some 450 million years ago – underlies the concept that the original AhR ligands emerged prior to the anthropogenic introduction of polyaromatic hydrocarbons (2). In addition, AhR has an exceptionally promiscuous ligand-binding pocket, which explains the extreme variety of molecules binding AhR with agonist or antagonistic activity (6). Indeed, it has been shown that both bilirubin and biliverdin represent good examples of endogenous ligands in liver with agonist activity for AhR (7, 8). The induction of AhR in the liver by those ligands induces upregulation of Ugt1a1 to prevent jaundice in neonates and to regulate antioxidant AhR effects in the adult liver (9). The intricacies of AhR activation also relate to the mode of application of a ligand and not only to its nature. Thus systemic administration of 6-formylindolo [3,2-b]carbazole (FICZ) reduced clinical signs in a murine model of encephalomyelitis (EAE), while local injection of FICZ, incorporated into the antigen emulsion for induction of EAE, seemed to more directly target and promote Th17 cells, thereby exacerbating pathology in EAE (10).
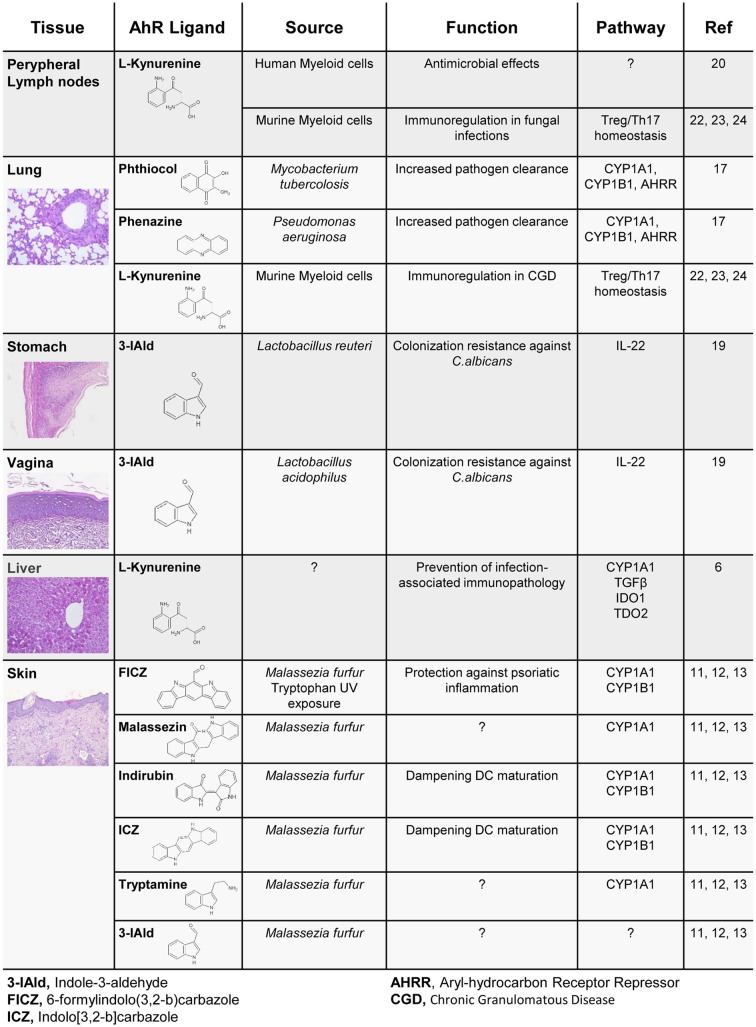
Recently, many studies have shown that the microbiome represents a consistent source of AhR endogenous ligands with disparate effects on immune homeostasis (Figure 1). Thus, moving to the context of the microbiota, the nature of both ligands and target cells vary consistently according to the microbe niche, providing a more complex scenario of AhR’s impact on immune homeostasis. In the human skin, commensals such as Malassezia yeasts secrete AhR agonists, such as indirubin, FICZ, indolo[3,2-b]carbazole (ICZ), malassezin, pityriacitrin, and tryptamine, which are all potent AhR ligands (11). When skin extracts are isolated from patients with ongoing skin infection, AhR is potently activated, and an increased concentration of AhR ligands in the skin has been linked to the development of Malassezia-associated skin diseases. Interestingly, some of the isolated molecules are able to convert to other AhR ligands such as ICZ, which is released under conversion of malassezin (12). Therefore, Malassezia-derived AhR ligands may have a significant impact on skin homeostatic immune mechanisms and disease development. Indeed, indirubin and ICZ significantly augmented AhR-mediated Cyp1a1 and Cyp1b1 gene expression in dendritic cells, while reducing Toll-like receptor (TLR)-induced dendritic cell maturation and T-lymphocyte proliferation (13). In line with this finding, FICZ has been used to dampen the inflammatory response in both mouse and human skin (14). Through the activation of AhR in non-hematopoietic skin cells, administration of FICZ ameliorated the inflammatory profile of psoriasiform human and murine skin specimens. Of interest, a key aspect of tryptophan-derived metabolites is related to their molecular dynamics of interconversion. For example, tryptamine serves as a proligand for AhR, and its activation depends mainly on monoamine oxidases (15), which eventually convert tryptamine to other AhR ligands, such as the indole-3-aldehyde (3-IAld) and eventually by spontaneous dimerization to FICZ (15). Importantly, intestinal microbiota will also convert tryptophan to tryptamine by decarboxylation. In doing so, and by modulating the colonic ion secretion, tryptamine affects the transit of food particles and bacterial cells through the gut lumen (16). More recently, Pseudomonas aeruginosa as well as Mycobacterium tuberculosis showed an ability to activate AhR in the lung through the release of pigmented virulence factors, such as phenazines and phthiocol, respectively, pointing to AhR as a sensor of a new class of pathogen-associated molecular patterns. Upon AhR binding, an AhR-controlled metabolic circuit was activated and the virulence factors degraded with consequent pathogen clearance (17).
Figure 1.
Tryptophan-derived AhR activating molecules with antimicrobial activity.
We found that highly adaptive lactobacilli in the gut, in particular Lactobacillus reuteri, by switching from sugar to tryptophan as an energy source, were expanded and produced an AhR ligand, 3-IAld, active in innate lymphoid cells (ILCs) where it would contribute to mucosal resistance against the opportunistic pathogen Candida albicans. IL-22 is the main downstream product of AhR activation upon 3-IAld stimulation in ILCs, regulating the release of antimicrobial peptides in the gut epithelia. Of notice, IL-22+ ILCs are also able to limit segmented filamentous bacteria colonization in the gut (18). A similar effect was found in the murine vaginal tissue, where Lactobacillus acidophilus will degrade tryptophan to 3-IAld and protect mice from C. albicans vaginitis (19). Pivotally, these antimicrobial effects were more evident under conditions of higher tryptophan availability in mucosal tissues, as it occurs in mice fed with a tryptophan-enriched diet or in mice bearing deficiency of a tryptophan catabolic enzyme.
In addition to microbial derived ligands, mammalian cells in the liver, as well as in peripheral lymph nodes, activate enzymes such as tryptophan-2,3-dioxygenase (TDO2) and indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase 1 (IDO1), able to generate tryptophan derivatives such as kynurenines, which also notably act as ligands for AhR (6). Kynurenines have long been known for their ability to exert specific antimicrobial activities (20). Thus, the recent findings provide mechanistic insight into the interplay between IDO1-dependent metabolism and AhR activation in colonization resistance and tolerance induction at the host/microbe interface (6) (Figure 1).
The IDO1-AhR-Treg Axis in Mammals: The Co-Evolution of a Tolerogenic Defense Strategy
Humans have evolved with microbes, and crucial factors for survival include prompt recognition of invading pathogens, acquisition of controlled immune response, fine-tuned pathogen eradication and return to homeostasis. Co-evolution with hosts had a particularly strong impact on the immune system, which needed to develop an ability to discriminate between resident microbes – maintaining a homeostatic balance – and invasive pathogens, which it must respond to. This complexity could be achieved by integrating two major immune defense mechanisms: infection resistance and disease tolerance (21). Induction of immune tolerance and the maintenance of homeostatic balance provide a series of benefits, including avoidance of tissue injury and para-inflammatory side effects, such as chronic infection and inflammation, which are major epigenetic and environmental factors that contribute to metabolic diseases and autoimmunity, and, in specific settings, to cancer. Conversely, the induction of immune resistance reflects opposite intents, such as the avoidance of infection and control of microbial burden (22, 23).
This paradigm has been epitomized in fungal commensalisms where immune protection must oppose fungal infectivity and ensure survival, while limiting collateral damage and restoring a homeostatic environment (also referred to as “protective tolerance”) (22, 24). Primordial resistance against fungi is mainly mediated by naturally occurring IL-22/IL-17A-producing cells, highly prevalent at mucosal sites, and activated by AhR (19, 25). The tryptophan metabolic pathway appeared to play a key and decisive role in fostering tolerance by means of IDO1 activation, tryptophan starvation, the production of immunomodulatory kynurenines, and the activation of Tregs that are strictly required for the generation of protective tolerance to fungi (26, 27). As AhR activation leads to the activation of IDO1 (25), the regulatory loop involving AhR and IDO1 may have driven the co-evolution of commensal fungi with the mammalian immune system and the microbiota, to the benefit of host survival and fungal commensalism.
More recently, the cross-regulatory circuit between IDO1 and AhR has been elegantly shown to mediate disease tolerance (6). Among IDO1 secondary metabolites, l-kynurenine has been identified as an AhR ligand (6). In turn, the AhR-associated Src activity was responsible for IDO1 phosphorylation, TGF-β production, and Treg cell expansion, thus allowing for endotoxin tolerance to occur. Importantly, the activation of the IDO-AhR-Treg axis prevented Salmonella typhimurium infection and significantly reduced clinical signs of Streptococcus arthritis (6).
More interestingly, the interaction between IDO1 and AhR may have important roles in the context of autoimmune diseases. Autoimmune diseases are indeed multifactorial, depending on intrinsic or environmental components, including diet, infections, and microbial exposure. The role of AhR in autoimmunity is even more interesting because of evidence on protection to EAE by TCDD, which exerts anti-inflammatory effects through induction of Tregs (1). In this context, it is interesting to note that FICZ also protects against EAE when systemically administered (10). Therefore, future studies are needed to elucidate the possible role of AhR ligands of microbial origin in protecting from autoimmune diseases.
In conclusion, the development of a highly specialized symbiosis requires iterative sets of mutual adaptation between and among symbionts and their hosts. This demands moving beyond surveys of microbial diversity to identify host/microbial metabolites that directly target the IDO1-AhR axis for the promotion of infection control and immune homeostasis.
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Specific Targeted Research Project FunMeta (ERC-2011-AdG-293714), the Italian Grant funded by the Italian Cystic Fibrosis Research Foundation (FFC#22/2014). We thank Dr. Cristina Massi Benedetti for editorial assistance.
References
- 1.Stockinger B, Di Meglio P, Gialitakis M, Duarte JH. The aryl hydrocarbon receptor: multitasking in the immune system. Annu Rev Immunol (2014) 32:403–32. 10.1146/annurev-immunol-032713-120245 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Hahn ME. Aryl hydrocarbon receptors: diversity and evolution. Chemico-Biol Interact (2002) 141:131–60. 10.1016/S0009-2797(02)00070-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Jeuken A, Keser BJ, Khan E, Brouwer A, Koeman J, Denison MS. Activation of the Ah receptor by extracts of dietary herbal supplements, vegetables, and fruits. J Agricul Food Chem (2003) 51:5478–87. 10.1021/jf030252u [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Hu Q, He G, Zhao J, Soshilov A, Denison MS, Zhang A, et al. Ginsenosides are novel naturally-occurring aryl hydrocarbon receptor ligands. PLoS One (2013) 8:e66258. 10.1371/journal.pone.0066258 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Heath-Pagliuso S, Rogers WJ, Tullis K, Seidel SD, Cenijn PH, Brouwer A, et al. Activation of the Ah receptor by tryptophan and tryptophan metabolites. Biochemistry (1998) 37:11508–15. 10.1021/bi980087p [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Bessede A, Gargaro M, Pallotta MT, Matino D, Servillo G, Brunacci C, et al. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor control of a disease tolerance defence pathway. Nature (2014) 511:184–90. 10.1038/nature13323 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Sinal CJ, Bend JR. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor-dependent induction of cyp1a1 by bilirubin in mouse hepatoma hepa 1c1c7 cells. Mol Pharmacol (1997) 52:590–9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Phelan D, Winter GM, Rogers WJ, Lam JC, Denison MS. Activation of the Ah receptor signal transduction pathway by bilirubin and biliverdin. Arch Biochem Biophys (1998) 357:155–63. 10.1006/abbi.1998.0814 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Togawa H, Shinkai S, Mizutani T. Induction of human UGT1A1 by bilirubin through AhR dependent pathway. Drug Metabol Lett (2008) 2:231–7. 10.2174/187231208786734120 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Duarte JH, Di Meglio P, Hirota K, Ahlfors H, Stockinger B. Differential influences of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor on Th17 mediated responses in vitro and in vivo. PLoS One (2013) 8:e79819. 10.1371/journal.pone.0079819 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Machowinski A, Kramer HJ, Hort W, Mayser P. Pityriacitrin – a potent UV filter produced by Malassezia furfur and its effect on human skin microflora. Mycoses (2006) 49:388–92. 10.1111/j.1439-0507.2006.01265.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Gaitanis G, Magiatis P, Stathopoulou K, Bassukas ID, Alexopoulos EC, Velegraki A, et al. AhR ligands, malassezin, and indolo[3,2-b]carbazole are selectively produced by Malassezia furfur strains isolated from seborrheic dermatitis. J. Invest Dermatol (2008) 128:1620–5. 10.1038/sj.jid.5701252 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Vlachos C, Schulte BM, Magiatis P, Adema GJ, Gaitanis G. Malassezia-derived indoles activate the aryl hydrocarbon receptor and inhibit Toll-like receptor-induced maturation in monocyte-derived dendritic cells. Br J Dermatol (2012) 167:496–505. 10.1111/j.1365-2133.2012.11014.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Di Meglio P, Duarte JH, Ahlfors H, Owens ND, Li Y, Villanova F, et al. Activation of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor dampens the severity of inflammatory skin conditions. Immunity (2014) 40:989–1001. 10.1016/j.immuni.2014.04.019 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Vikstrom Bergander L, Cai W, Klocke B, Seifert M, Pongratz I. Tryptamine serves as a proligand of the AhR transcriptional pathway whose activation is dependent of monoamine oxidases. Mol Endocrinol (2012) 26:1542–51. 10.1210/me.2011-1351 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Williams BB, Van Benschoten AH, Cimermancic P, Donia MS, Zimmermann M, Taketani M, et al. Discovery and characterization of gut microbiota decarboxylases that can produce the neurotransmitter tryptamine. Cell Host Microbe (2014) 16:495–503. 10.1016/j.chom.2014.09.001 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Moura-Alves P, Faé K, Houthuys E, Dorhoi A, Kreuchwig A, Furkert J, et al. AhR sensing of bacterial pigments regulates antibacterial defence. Nature (2014) 512:387–92. 10.1038/nature13684 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Qiu J, Guo X, Chen ZM, He L, Sonnenberg GF, Artis D, et al. Group 3 innate lymphoid cells inhibit T-cell-mediated intestinal inflammation through aryl hydrocarbon receptor signaling and regulation of microflora. Immunity (2013) 39:386–99. 10.1016/j.immuni.2013.08.002 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Zelante T, Iannitti RG, Cunha C, De Luca A, Giovannini G, Pieraccini G, et al. Tryptophan catabolites from microbiota engage aryl hydrocarbon receptor and balance mucosal reactivity via interleukin-22. Immunity (2013) 39:372–85. 10.1016/j.immuni.2013.08.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Niño-Castro A, Abdullah Z, Popov A, Thabet Y, Beyer M, Knolle P, et al. The IDO1-induced kynurenines play a major role in the antimicrobial effect of human myeloid cells against Listeria monocytogenes. Innate Immun (2014) 20:401–11. 10.1177/1753425913496442 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Raberg L, Sim D, Read AF. Disentangling genetic variation for resistance and tolerance to infectious diseases in animals. Science (2007) 318:812–4. 10.1126/science.1148526 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Romani L. Immunity to fungal infections. Nat Rev Immunol (2011) 11:275–88 10.1038/nri2939 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Zelante T, Iannitti R, De Luca A, Romani L. IL-22 in antifungal immunity. Eur J Immunol (2011) 41:270–5. 10.1002/eji.201041246 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Romani L, Puccetti P. Protective tolerance to fungi: the role of IL-10 and tryptophan catabolism. Trends Microbiol (2006) 14:183–9. 10.1016/j.tim.2006.02.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Romani L, Zelante T, Luca AD, Iannitti RG, Moretti S, Bartoli A, et al. Microbiota control of a tryptophan-AhR pathway in disease tolerance to fungi. Eur J Immunol (2014) 44(11):3192–200. 10.1002/eji.201344406 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Montagnoli C, Fallarino F, Gaziano R, Bozza S, Bellocchio S, Zelante T, et al. Immunity and tolerance to Aspergillus involve functionally distinct regulatory T cells and tryptophan catabolism. J Immunol. (2006) 176:1712–23. 10.4049/jimmunol.176.3.1712 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Romani L, Fallarino F, De Luca A, Montagnoli C, D’Angelo C, Zelante T, et al. Defective tryptophan catabolism underlies inflammation in mouse chronic granulomatous disease. Nature (2008) 451:211–5. 10.1038/nature06471 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]