Abstract
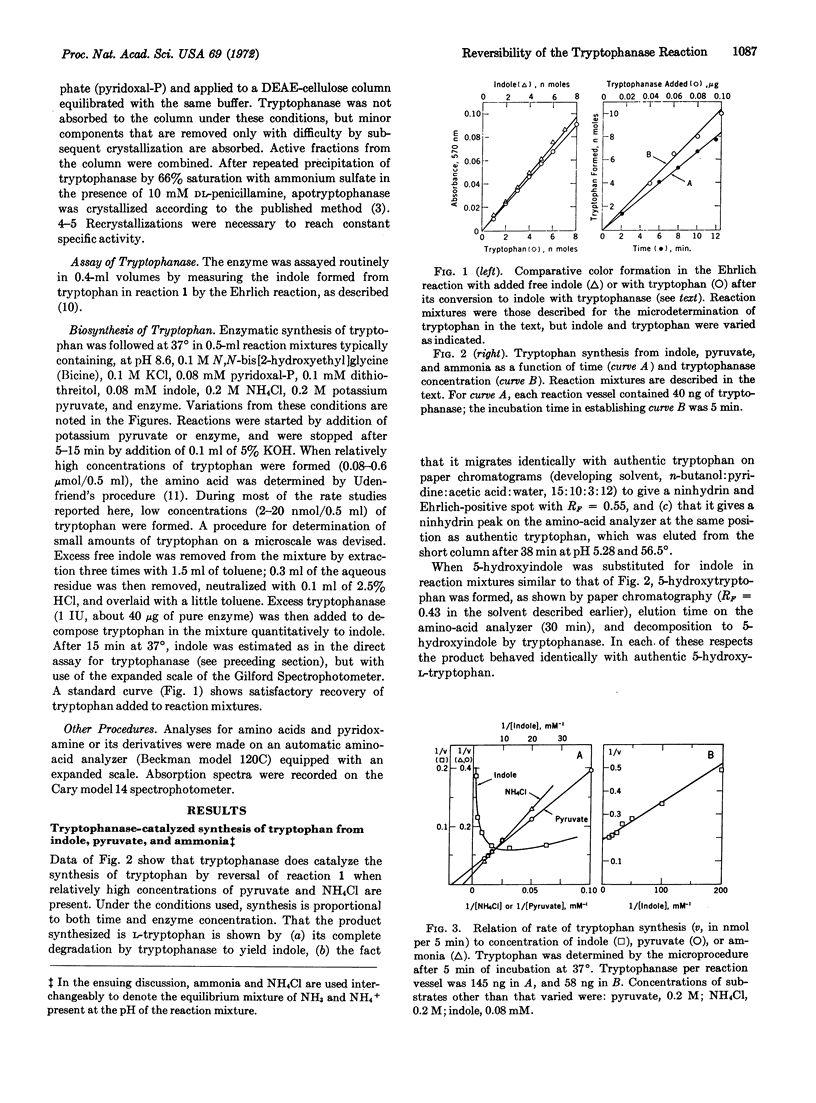
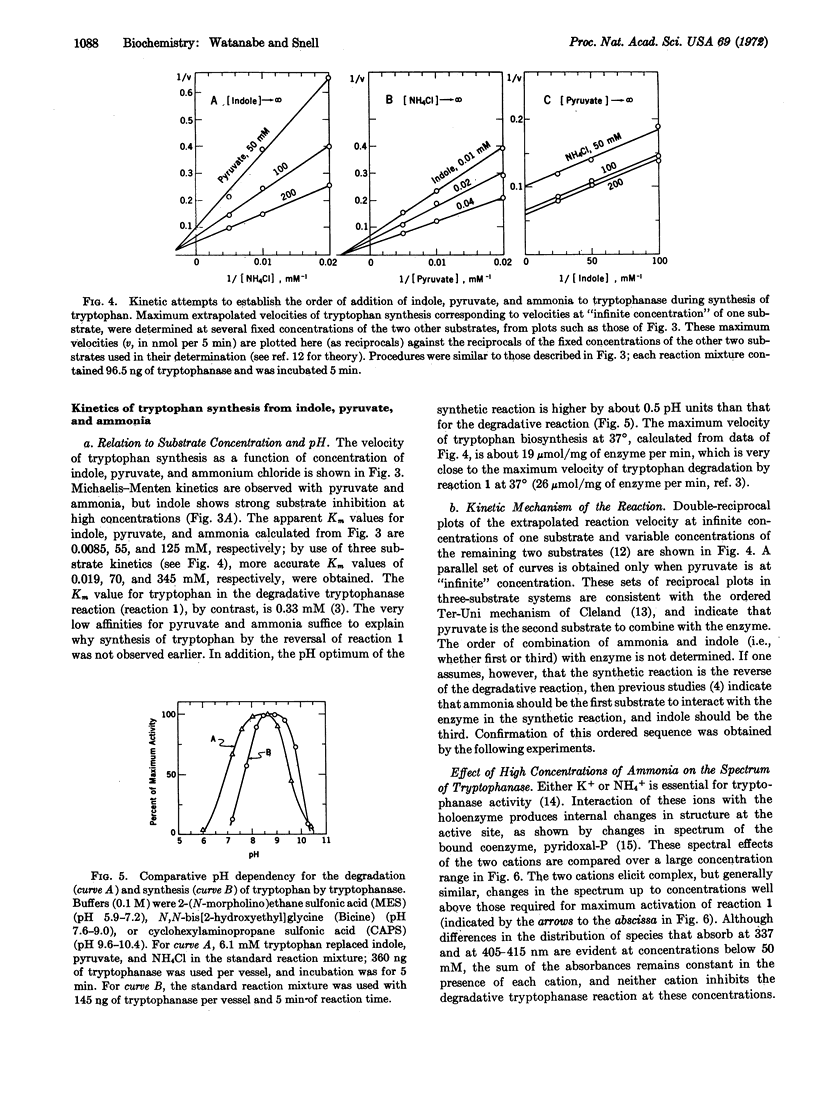
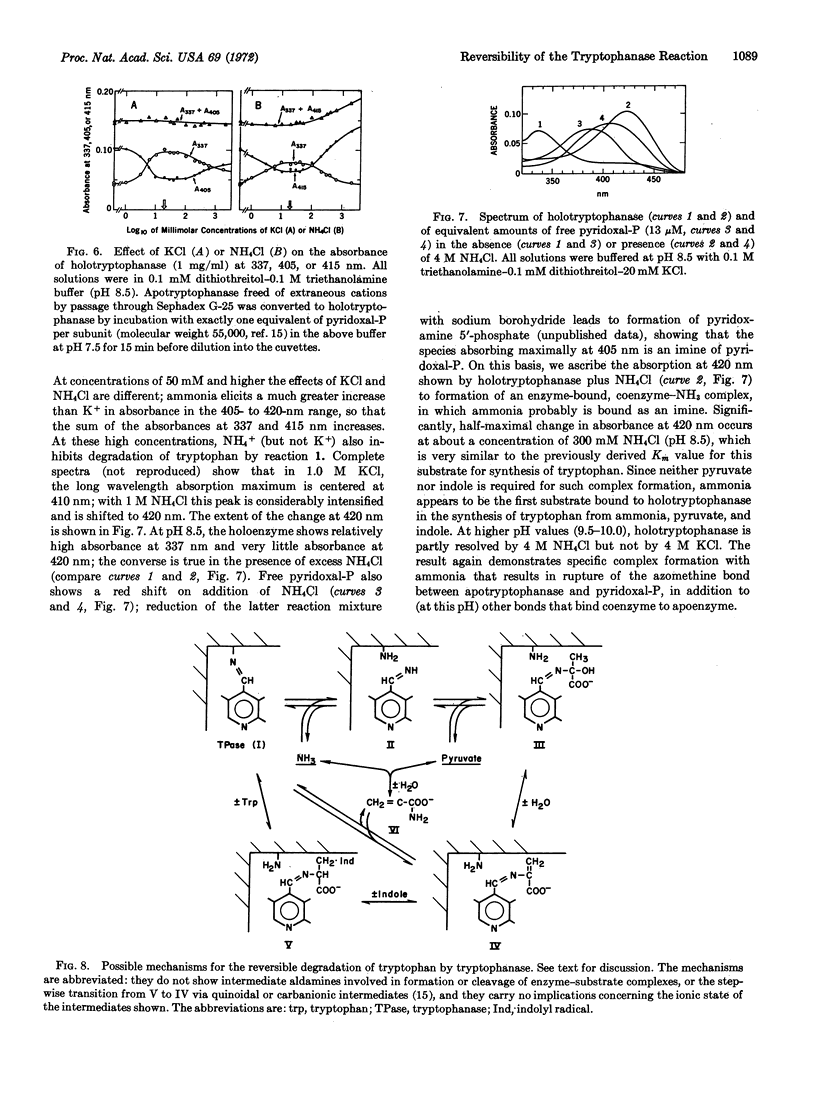
Degradation of tryptophan to indole, pyruvate, and ammonia by tryptophanase (EC 4....) from Escherichia coli, previously thought to be an irreversible reaction, is readily reversible at high concentrations of pyruvate and ammonia. Tryptophan and certain of its analogues, e.g., 5-hydroxytryptophan, can be synthesized by this reaction from pyruvate, ammonia, and indole or an appropriate derivative at maximum velocities approaching those of the degradative reactions. Concentrations of ammonia required for the synthetic reactions produce specific changes in the spectrum of tryptophanase that differ from those produced by K+ and indicate that ammonia interacts with bound pyridoxal 5′-phosphate to form an imine. Kinetic results indicate that pyruvate is the second substrate bound, hence indole must be the third. These results favor a modified mechanism for the multitude of tryptophanase-catalyzed reactions in which α-aminoacrylate, which functions as a common enzyme-bound intermediate in both synthetic and degradative reactions, is not released into the medium during the latter reactions, but is degraded to pyruvate and ammonia by sequential reversible steps via enzyme-bound intermediates.
Keywords: E. coli, α-aminoacrylate, Michaelis-Menten kinetics, pyridoxal 5′-phosphate
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CLELAND W. W. The kinetics of enzyme-catalyzed reactions with two or more substrates or products. I. Nomenclature and rate equations. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Jan 8;67:104–137. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)91800-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAPPOLD F. C., STRUYVENBERG A. The activation of tryptophanase apo-enzyme by potassium, ammonium and rubidium ions. Biochem J. 1954 Nov;58(3):379–382. doi: 10.1042/bj0580379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagamiyama H., Matsubara H., Snell E. E. The chemical structure of tryptophanase from Escherichia coli. 3. Isolation and amino acid sequence of the tryptic peptides. J Biol Chem. 1972 Mar 10;247(5):1576–1586. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumagai H., Matsui H., Ohgishi H., Ogata K., Yamada H., Ueno T., Fukami H. Synthesis of 3,4-dihydroxyphenyl-L-alanine from L-tyrosine and pyrocatechol by crystalline beta-tyrosinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Feb 7;34(3):266–270. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90826-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumagai H., Yamada H., Matsui H., Ohkishi H., Ogata K. Tyrosine phenol lyase. I. Purification, crystallization, and properties. J Biol Chem. 1970 Apr 10;245(7):1767–1772. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morino Y., Snell E. E. A kinetic study of the reaction mechanism of tryptophanase-catalyzed reactions. J Biol Chem. 1967 Jun 25;242(12):2793–2799. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morino Y., Snell E. E. The relation of spectral changes and tritium exchange reactions to the mechanism of tryptophanase-catalyzed reactions. J Biol Chem. 1967 Jun 25;242(12):2800–2809. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEWTON W. A., MORINO Y., SNELL E. E. PROPERTIES OF CRYSTALLINE TRYPTOPHANASE. J Biol Chem. 1965 Mar;240:1211–1218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEWTON W. A., SNELL E. E. An inducible tryptophan synthetase in tryptophan auxotrophs of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Aug;48:1431–1439. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.8.1431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEWTON W. A., SNELL E. E. CATALYTIC PROPERTIES OF TRYPTOPHANASE, A MULTIFUNCTIONAL PYRIDOXAL PHOSPHATE ENZYME. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Mar;51:382–389. doi: 10.1073/pnas.51.3.382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueno T., Fukami H., Ohkishi H., Kumagai H., Yamada H. [Synthesis of 3,4-dihydro-3-amino-7-hydroxycoumarin from S-methyl-l-cysteine and resorcinol by crystalline-beta-tyrosinase]. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Jun 10;206(3):476–479. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(70)90163-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada H., Kumagai H., Kashima N., Torii H., Enei H., Okumura S. Synthesis of L-tyrosine from pyruvate, ammonia and phenol by crystalline tyrosine phenol lyase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Jan 31;46(2):370–374. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(72)80148-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


