Abstract
Prostaglandins, especially prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), and COX-2 play an important role in carcinogenesis of many tumors including bladder cancer (BCA). The PGE2 receptors EP1-4 regulate tumor cell growth, invasion and migration in different tumor entities but EP expression in BCA remains to be determined. In the present study we examined the expression of EP1-4 in non-muscle invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC), muscle invasive bladder cancer (MIBC) and normal urothelial tissue (NU) using immunohistochemistry. Nuclear and cytoplasmic EP1-4 expression was correlated with clinicopathological parameters and survival of BCA patients. EP1, EP2 and EP3 were significantly less expressed in the cytoplasm und nucleus of NMIBC and MIBC than in NU; EP4 cytoplasmic staining in MIBC was significantly higher compared to NU. The cytoplasmic staining was significantly more abundant in MIBC than in NMIBC in all investigated receptors except EP2. The level of EP staining in NMIBC was correlated with staging and grading, especially cytoplasmic EP1. Nuclear staining of EP1 was an independent predictor of BCA recurrence-free survival in NMIBC patients. EP receptors are dysregulated in BCA. The increase of EP1 may be used as prognostic parameter in NMIBC patients and its dysregulation could be targeted by specific EP1 inhibitors.
Keywords: Bladder cancer, EP1, EP2, EP3, EP4, prostaglandin receptors, immunohistochemistry
Introduction
In 2014, there are 74,690 new cases of urinary bladder cancer (BCA) and 15,580 BCA deaths expected in the USA; thus BCA is the most common malignancy of the urinary tract [1]. Major problems for non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC) include recurrence and progression to muscle-invasive bladder cancer (MIBC). Risk factors associated with progression to MIBC include the depth of invasion of the lamina propria, simultaneous presence of carcinoma in situ (CIS), tumor grade and size, multiple tumors and recurrence of NMIBC [2]. For MIBC patients, lymph node metastasis, tumor stage and grade, lymphovascular involvement and histological features are main predictors of outcome; in addition time from diagnosis to surgery, patient age and sex contribute to patients prognosis [2]. Some promising molecular markers [i.e. cathepsin E, Plk1 (polo-like kinase 1), maspin, survivin, ezrin membrane expression, FGFR3 (fibroblast growth factor receptor 3) mutation status] [3-5] of prognostic value have been described, but none of them is used in daily routine to predict the risk of recurrence/progression and accordingly to optimize the clinical management of BCA patients.
COX (cyclooxygenase), the key enzyme in prostaglandin synthesis from arachidonic acid, exists in two isoforms, COX-1 and COX-2. COX-1 is constitutively expressed in many organs, whereas COX-2 is induced by a variety of mediators including inflammatory cytokines, hormones, growth factors and tumor promoters [6]. PGE2 (prostaglandin E2), a lipid compound and the end product of eicosanoid synthesis by both isoforms of COX, has many physiological effects such as stimulating cell proliferation, motility and tumor angiogenesis, while inhibiting apoptosis and immune surveillance [6]. Both, prostaglandins and COX-2 play an important role in the carcinogenesis of many tumors including BCA [7]. Non-selective (indomethacin) and selective (celecoxib) COX inhibitors have been shown to act antineoplastic [8,9]. However, long-term inhibition of COX-2 increases the risk of cardiovascular events [10]. The PGE2 receptors EP1-4 (also termed PTGER1-4) have been considered as alternative pharmacological target [11].
PGE2 binds with different affinities to four receptors (EP1-4), which belong to a family of seven transmembrane G protein coupled rhodopsin-type receptors, with distinct signal-transduction properties [12]. The effects of PGE2 on cell growth depend on receptor-ligand affinity, ligand concentration, as well as target cell EP receptor expression [13]. EP receptors are localized on many different cells including tumor cells, stromal cells and immune effector cells. There are also perinuclear and/or nuclear localized EP receptors which influence the cell differently, probably by posttranslational modifications [14] and yet undefined, different signaling pathways [15].
Even though the four EP receptors have structural and sequence similarities, they are linked to different, but interacting intracellular signaling pathways [15]. The EP1 receptor is coupled to Gq protein and upregulates the level of intracellular Ca2+ through phospholipase C and phosphatidylinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) [16]. EP2 and EP4 are coupled to a stimulatory G protein (Gs), activating adenylate cyclase, resulting in an increase in cAMP (cyclic adenosine monophosphate), followed by protein kinase A (PKA) activity [17]. EP3, which is mainly coupled to Gαi protein, decreases the formation of intracellular cAMP [18]. Furthermore, alternative splice products of EP3 have stimulatory and inhibitory effects on adenylate cyclase [19].
EP1-4 receptors are dysregulated in many human malignancies [16,20-27], and its expression levels may indicate prognosis of patients (nuclear EP1 expression: breast cancer [28,29]; EP4: upper urinary tract cancer [30]). They are involved in invasion, migration, and growth of carcinoma cells from various tumor entities including breast, colon and kidney cancer [13,22,25,26]. Pharmacological manipulation of EP receptors may be feasible: an EP1 antagonist was protective against colon, breast and skin cancer [31-33], and an EP4 antagonist reduced tumor growth, angiogenesis and metastasis in a breast cancer model [17].
So far, EP receptor expression in BCA remains unknown. We therefore studied the expression of nuclear and cytoplasmic EP1-4 using tissue microarrays in 186 NMIBC and 210 MIBC specimens as well as 51 normal urothelial tissue samples to explore the role of EP receptors in BCA.
Patients and methods
Patients
We prepared tissue microarrays (TMAs) with samples of NMIBC (n=186) and MIBC (n=210) from formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue specimens (Table 1 for clinicopathological characteristics). Histologically confirmed normal urothelium (NU) (n=51) was obtained from patients undergoing surgery for BCA. A representative image of the tumor was achieved by aligning three tissue cores per patient using a manual device (Lika Electronic, Varré, Italy). The tumor tissues were chosen from the archival files of the Department of Pathology at the University Hospital Bonn based on tissue availability and were not selected according to preoperative or prognostic factors. The specimens were obtained from patients undergoing transurethral resection of the bladder (TURB; NMIBC, n=162; MIBC n=24) or radical cystectomy (RC; NMIBC, n=36; MIBC, n=174) at the Department of Urology at the University Hospital Bonn and the Waldkrankenhaus Bad Godesberg between 1988 and 2012. All cases were reviewed by an experienced pathologist (D.G.). Stage and grade were assigned according to the WHO classification from 1977. Follow-up information was available for 321 patients (81%): 103 NMIBC-patients suffered from disease recurrence and 7 died from BCA during a mean (median; range) follow-up period of 69 (55; 0-233) months. For patients with MIBC the mean (median, range) follow-up period was 28 (9; 0-172) months; 87 patients developed metastases and cancer-related deaths occurred in 53 patients. The study was approved by the ethic committee of the University Hospital Bonn (ethic vote 330/11).
Table 1.
Clinicopathological characteristics of patients with non-muscle invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC), muscle invasive bladder cancer (MIBC) and normal urothelium (NU)
| NMIBC (%) | MIBC (%) | NU (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
|
| |||
| n=186 | n=210 | n=51 | |
| Sex | |||
| Male | 150 (80.6) | 153 (72.9) | 29 (56.9) |
| Female | 36 (19.4) | 57 (27.1) | 22 (43.1) |
| Smoking status | |||
| Current | 43 (23.1) | 60 (28.6) | 1 (2) |
| Never | 78 (41.9) | 60 (28.6) | 5 (9.8) |
| Former | 9 (4.8) | 9 (4.3) | 6 (11.8) |
| Unknown | 55 (29.6) | 81 (38.6) | 45 (88.2) |
| Tumor stage | |||
| Ta | 101 (54.3) | 0 | n.a. |
| Tis | 33 (17.7) | 0 | n.a. |
| T1 | 52 (28.0) | 0 | n.a. |
| T2 | 0 | 77 (36.7) | n.a. |
| T3 | 0 | 96 (45.7) | n.a. |
| T4 | 0 | 37 (17.6) | n.a. |
| Grading | |||
| G1 | 62 (33.3) | 1 (0.5) | n.a. |
| G2 | 71 (38.7) | 59 (28.1) | n.a. |
| G3 | 49 (26.3) | 147 (70) | n.a. |
| G4 | 1 (0.5) | 1 (0.5) | n.a. |
| n.a. | 2 (1) | ||
| Lymph node metastasis | |||
| pN0 | 160 (86) | 103 (59) | n.a. |
| pN+ | 1 (0.5) | 69 (32.9) | n.a. |
| pNx | 38 (18.1) | n.a. | |
| Distant metastasis | |||
| M0 | 150 (80.6) | 119 (56.7) | n.a. |
| M1 | 0 (0) | 5 (2.4) | n.a. |
| n.a. | 36 (19.4) | 86 (41.0) | n.a. |
| Age | |||
| Mean | 67.01 | 67.72 | 65.96 |
| Median | 67 | 69 | 66 |
| Range | 30-92 | 38-94 | 43-84 |
Abbreviations: NMIBC=non-muscle invasive bladder cancer; MIBC=muscle invasive bladder cancer; NU=normal urothelium; n.a.=not applicable.
Immunohistochemistry
Immunohistochemistry was carried out as described by Oll et al [34]. Paraffin sections, 5 µm thick, were cut from the TMA block and transferred onto slides for staining. After deparaffinization with xylene and rehydration with isopropyl alcohol, the slides were placed in target retrieval solution (10 mM citrate buffer, pH 6.0) and boiled for 20 min using a microwave. After cooling for 30 min and exchanging citrate buffer against running tap water for 15 min, the endogenous peroxidase activity was blocked by treatment with 3% H2O2 for 10 min. The slides were incubated in Tris-buffered saline for 5 min. Then, EP1 (dilution 1:2000; Cayman Chemical; Ann Arbor, MI, USA; Item No. 101740; Lot No. 0419161-1); EP2 (dilution 1:100; Cayman Chemical; Ann Arbor, MI, USA; Item No. 101750; Lot No. 0434213-1); EP3 (dilution 1:100; Cayman Chemical; Ann Arbor, MI, USA; Item No. 101760; Lot No. 0424527-1), and EP4 (dilution 1:100; Cayman Chemical; Ann Arbor, MI, USA; Item No. 101775; Lot No. 0415476-1) antibodies were applied overnight at 4°C. Immunohistochemical staining was visualized using Dako Envision+ System-HRP staining technique (Dako No. K4002; Glostrup, Denmark). After incubated for 30 min with the secondary antibody at room temperature, the peroxidase was developed with aminoethylcarbazole (AEC) system (Dako No. K696). The slides were finally counterstained with hematoxylin and mounted. Identical TMAs with rabbit immunoglobulin (dilution 1:3750; Dako No. X0936; Glostrup, Denmark) were used as negative controls. The slides were scanned using the Panoramic Midi (3D HISTECH Kft, Budapest, Hungary), and high resolution images were virtually evaluated using the Panoramic Viewer (Version 1.15.2; 3DHistech Ltd.).
The immunostaining results were recorded semiquantitatively, blinded to clinical outcome and evaluating cytoplasm and nucleus separately. The percentage of urothelial cells showing nuclear or cytoplasmic staining was estimated individually for each core and scaled: 0, no positive cells; 1, 1-25% positive cells; 2, 26-50% positive cells; 3, 51-75% positive cells; and 4, 76-100% positive cells. These scores were multiplied with an intensity scale (0, negative; 1, weak; 2, moderate; and 3, intensive staining). The results were presented as the mean of the three core samples. Multiple positive controls (liver, colon, skin and renal tissue) were included in each tissue microarray.
Statistical analysis
The Mann-Whitney U test was used to evaluate differences between the clinicopathological variables and each EP receptor. The EP receptors were correlated with using the Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient. The Kaplan-Meier method was used to calculate survival functions, and the significance was evaluated using the log-rank statistic. Cut-offs for a staining score of 6 turned out to be the best discriminator for both bladder-cancer progression and survival. Univariate and multivariate survival analyses were done using the Cox proportional hazard regression model. P values lower 0.05 were considered to show statistical significance; all tests were two-sided. Statistical analyses were performed using IBM® SPSS® Statistics v21.
Results
Levels of cytoplasmic as well as nuclear staining of EP1, EP2 and EP3 are different in NU tissue and BCA tissue
EP1-3 expression was observed in the cytoplasm and nucleus. EP4 nuclear staining was virtually undetectable in all samples (Figure 1 for representative photographs). Using the Mann-Whitney U Test we analyzed whether EP1-4 expression was different in NU and BCA tissue. EP1, EP2 and EP3 were significantly less present in the cytoplasm und nucleus of NMIBC and MIBC than in NU, whereas cytoplasmic staining of EP4 in MIBC compared to NU was significantly higher. The cytoplasmic staining was significantly more abundant in MIBC than in NMIBC in all investigated receptors except EP2 (p=0.120). On the contrary, the nuclear staining decreased from NMIBC to MIBC in all receptors except for EP4 (not detected in any BCA sample). See Table 2 and Figure 2. Nuclear and cytoplasmic expression of EP1, EP2 and EP3 was highly correlated to each other (p<0.001).
Figure 1.
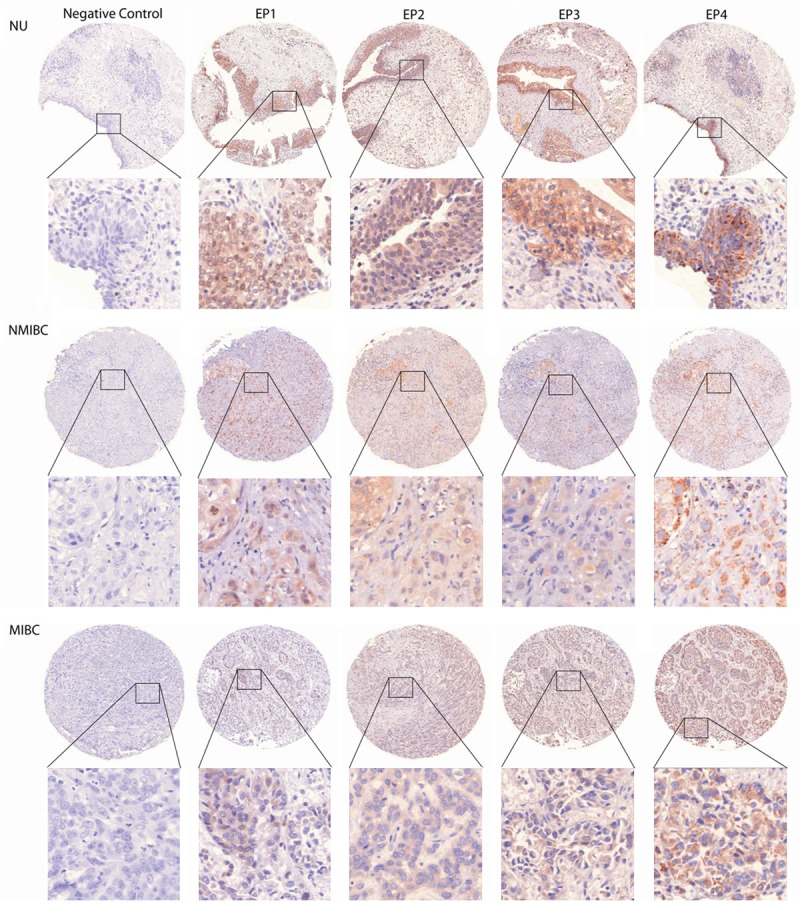
Representative photographs of EP1-4 and rabbit immunoglobulin in a sample of NU, NMIBC, MIBC. Cores represent the most frequent staining intensity of each antibody in the cytoplasm as well as the nucleus. Original x5, insets x40.
Table 2.
Levels of staining of prostaglandin receptors EP1-4 are different in NU, NMIBC and MIBC determined using the Mann-Whitney U test
| EP1 (c) | EP1 (n) | EP2 (c) | EP2 (n) | EP3 (c) | EP3 (n) | EP4 (c) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NU vs BCA | <0.001*↓ | <0.001 *↓ | <0.001 *↓ | <0.001 *↓ | 0.001 *↓ | <0.001 *↓ | 0.914 |
| NU vs NMIBC | 0.003 *↓ | <0.001 *↓ | <0.001 *↓ | <0.001 *↓ | 0.009 *↓ | <0.001 *↓ | 0.117 |
| NU vs MIBC | <0.001 *↓ | <0.001 *↓ | <0.001 *↓ | <0.001 *↓ | <0.001 *↓ | <0.001 *↓ | 0.037 *↑ |
| NMIBC vs MIBC | <0.001*↑ | 0.071 | 0.120 | 0.004 *↓ | 0.010 *↑ | 0.015 *↓ | <0.001 *↑ |
indicates positive correlation;
indicates negative correlation.
Abbreviations: NU=normal urothelium; BCA=bladder cancer; NMIBC=non-muscle invasive bladder cancer; MIBC=muscle invasive bladder cancer; (c)=cytoplasmic; (n)=nuclear; significant values are shown in bold.
Figure 2.
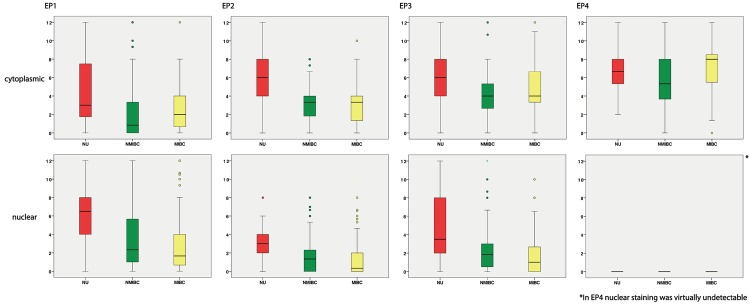
Distribution of the level of staining intensity in patients with NU, NMIBC and MIBC separated in nuclear and cytoplasmic staining.
EP expression is correlated with advanced stage and grade in BCA patients, and predicts patients outcome following surgery
The EP expression level in NMIBC was correlated with staging and grading: For example, cytoplasmic EP1 expression increased with the pT stage in NMBIC (pTa vs pT1, p=0.001; pTa vs pTis, p<0.001) and grading (G1 vs G2, p=0.002; G1 vs G3, p<0.001; G2 vs G3, p=0.040). Furthermore, EP2 in the cytoplasm was increased in pT1 compared to pTa and pTis (pTa vs pT1, p=0.001; pTis vs pT1, p<0.001). In contrast, pT stage in MIBC patients was negatively correlated with EP1 (pT2 vs pT3, p<0.001; pT2 vs pT4, p=0.029), EP2 (pT2 vs pT3, p<0.001; pT2 vs pT4, p<0.001) and EP3 (pT2 vs pT3, p<0.001; pT2 vs pT4, p=0.001) nuclear expression. See Table 3 for a detailed summary.
Table 3.
Differences between EP1-4 expression for different pathological stages and grades in patients with NMIBC and MIBC
| EP1 (c) | EP1 (n) | EP2 (c) | EP2 (n) | EP3 (c) | EP3 (n) | EP4 (c) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NMIBC | |||||||
| pTa vs pT1 | 0.001*↑ | 0.004 *↑ | 0.001 *↑ | <0.001 *↑ | 0.237 | 0.192 | 0.102 |
| pTa vs pTis | <0.001 *↑ | 0.182 | 0.038*↓ | 0.516 | 0.614 | 0.751 | 0.053 |
| pTis vs pTa | 0.266 | 0.368 | <0.001 *↑ | 0.001 *↑ | 0.690 | 0.262 | 0.245 |
| G1 vs G2 | 0.002 *↑ | 0.685 | 0.238 | 0.745 | 0.078 | 0.252 | 0.010 *↑ |
| G1 vs G3 | <0.001 *↑ | 0.067 | 0.055 | 0.354 | 0.388 | 0.894 | 0.004 *↑ |
| G2 vs G3 | 0.040 *↑ | 0.147 | 0.006*↓ | 0.459 | 0.670 | 0.387 | 0.400 |
| MIBC | |||||||
| pT2 vs pT3 | 0.156 | <0.001 *↓ | 0.980 | <0.001 *↓ | 0.062 | <0.001 *↓ | 0.025 *↑ |
| pT2 vs pT4 | 0.348 | 0.029 *↓ | 0.947 | <0.001 *↓ | 0.689 | 0.001 *↓ | 0.855 |
| pT3 vs pT4 | 0.791 | 0.054 | 0.972 | 0.128 | 0.027 *↑ | 0.640 | 0.031 *↓ |
| pN0 vs pN+ | 0.001 *↑ | 0.433 | 0.089 | 0.103 | 0.601 | 0.115 | 0.005 *↑ |
| cM0 vs cM+ | 0.058 | 0.673 | 0.126 | 0.904 | 0.271 | 0.561 | 0.140 |
| G2 vs G3 | 0.351 | 0.674 | 0.891 | 0.611 | 0.496 | 0.819 | 0.019 *↑ |
indicates positive correlation;
indicates negative correlation.
Abbreviations: NMIBC=non-muscle invasive bladder cancer; MIBC=muscle invasive bladder cancer; (c)=cytoplasmic; (n)=nuclear; significant values are shown in bold.
In addition, we used Cox proportional hazard models to evaluate whether EP expression predicts patients’ outcome: Increased nuclear expression of EP1 (p=0.028, hazard ratio [HR] 1.075) and decreased cytoplasmic expression of EP2 (p=0.019, HR 0.873) were correlated to recurrence-free survival. Nuclear EP1 expression was also predictive for cancer recurrence (p=0.020, HR 1.083) in a multivariate analysis (Table 4; Figure 3). EP expression was not correlated to cancer specific survival in NMIBC patients. Higher cytoplasmic EP1 levels were correlated to cancer specific mortality in a univariate analysis (p=0.027, HR 1.142; Figure 3), but lost its predictive value in a multivariate model including pT stage, lymph node metastasis and metastasis (p=0.167, HR 1.150). EP1-4 expression was not associated with recurrence-free survival in MIBC patients; see Table 5.
Table 4.
Cox proportional hazard analysis of EP1-4 and pathological features in correlation to cancer-specific survival (CSS) and bladder-cancer recurrence in patients with NMIBC
| Recurrence-free survival univariate analysis | CSS univariate analysis | Recurrence-free survival multivariate analysis | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| |||||||||
| p | SE | HR (95% CI) | p | SE | HR (95% CI) | p | SE | HR (95% CI) | |
| EP1 (c) | 0.374 | 0.045 | 0.961 (0.897-1.050) | 0.741 | 0.180 | 0.942 (0.663-1.340) | |||
| EP1 (n) | 0.028 | 0.033 | 1.075 (1.008-1.146) | 0.331 | 0.112 | 1.115 (0.895-1.388) | 0.020 | 0.034 | 1.083 (1.012-1.157) |
| EP2 (c) | 0.019 | 0.058 | 0.873 (0.780-0.978) | 0.585 | 0.220 | 0.887 (0.576-1.365) | 0.111 | 0.068 | 0.897 (0.786-1.025) |
| EP2 (n) | 0.955 | 0.054 | 0.997 (0.897-1.108) | 0.245 | 0.385 | 0.639 (0.300-1.359) | |||
| EP3 (c) | 0.231 | 0.054 | 0.937 (0.842-1.042) | 0.729 | 0.200 | 0.933 (0.631-1.380) | |||
| EP3 (n) | 0.394 | 0.050 | 0.958 (0.869-1.057) | 0.870 | 0.167 | 1.028 (0.741-1.424) | |||
| EP4 (c) | 0.381 | 0.034 | 0.970 (0.907-1.038) | 0.842 | 0.118 | 0.977 (0.775-1.232) | |||
| pTstage | 0.289 | 0.116 | 0.884 (0.704-1.110) | 0.689 | 0.456 | 0.833 (0.341-2.037) | |||
| Grade | 0.715 | 0.133 | 1.050 (0.809-1.361) | 0.350 | 0.502 | 1.598 (0.598-4.271) | |||
Abbreviations: CSS=cancer-specific survival; (c)=cytoplasmic; (n)=nuclear; p = p-value, SE=standard error, HR=hazard ratio; significant values are shown in bold.
Figure 3.
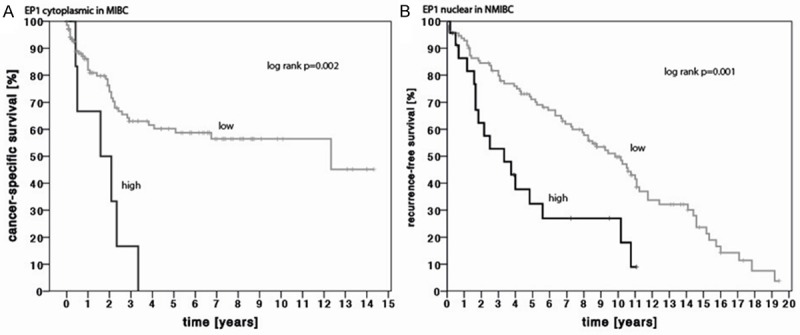
Kaplan-Meier estimates of A) cytoplasmic EP1 expression for the prediction of cancer-specific survival in patients with MIBC (log rank p=0.002) and B) nuclear EP1 expression for the prediction of recurrence-free survival in patients with NMIBC (log rank p=0.001). EP1 Expression was grouped into low (staining score ≤ 6) and high (staining score > 6).
Table 5.
Cox proportional hazard analysis of EP1-4 and pathological features in correlation to cancer-specific survival (CSS) and bladder-cancer recurrence in patients with MIBC
| Recurrence-free survival univariate analysis | CSS univariate analysis | CSS multivariate analysis | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| |||||||||
| p | SE | HR (95% CI) | p | SE | HR (95% CI) | p | SE | HR (95% CI) | |
| EP1 (c) | 0.325 | 0.053 | 1.054 (0.950-1.169) | 0.027 | 0.060 | 1.142 (1.015-1.286) | 0.167 | 0.101 | 1.150 (0.943-1.403) |
| EP1 (n) | 0.154 | 0.040 | 1.059 (0.979-1.147) | 0.110 | 0.052 | 1.087 (0.981-1.203) | |||
| EP2 (c) | 0.171 | 0.060 | 0.922 (0.820-1.036) | 0.331 | 0.076 | 0.929 (0.800-1.078) | |||
| EP2 (n) | 0.390 | 0.081 | 0.933 (0.796-1.093) | 0.404 | 0.106 | 0.915 (0.743-1.127) | |||
| EP3 (c) | 0.660 | 0.046 | 0.980 (0.895-1.073) | 0.945 | 0.060 | 0.996 (0.885-1.120) | |||
| EP3 (n) | 0.950 | 0.067 | 0.996 (0.872-1.137) | 0.595 | 0.086 | 1.047 (0.884-1.240) | |||
| EP4 (c) | 0.868 | 0.047 | 0.992 (0.904-1.086) | 0.475 | 0.061 | 1.044 (0.927-1.176) | |||
| pTstage | 0.076 | 0.050 | 1.092 (0.991-1.205) | 0.022 | 0.065 | 1.160 (1.022-1.318) | 0.017 | 0.091 | 1.242 (1.040-1.483) |
| Grade | 0.539 | 0.226 | 0.870 (0.559-1.355) | 0.068 | 0.338 | 1.853 (0.955-3.598) | |||
| pNstage | 0.396 | 0.131 | 1.118 (0.864-1.447) | 0.049 | 0.153 | 1.351 (1.002-1.823) | 0.896 | 0.212 | 1.028 (0.679-1.557) |
| cMstage | 0.236 | 1.022 | 3.355 (0.453-24.858) | 0.000 | 0.561 | 9.879 (3.250-29.972) | 0.001 | 0.697 | 9.421 (2.406-36.899) |
Abbreviations: CSS=cancer-specific survival; (c)=cytoplasmic; (n)=nuclear; P=p-value; SE=standard error; HR=hazard ratio; significant values are shown in bold.
Discussion
BCA is a highly immunogenic malignancy and inflammation is a critical component of tumor progression [35]. A preoperative systemic inflammatory response is an independent predictor of poor cancer specific survival in patients with BCA [36]. Prostaglandins play a prominent role in inflammatory processes, and the expression of COX-2 is associated with BCA progression [7]. So far, knowledge about EP receptors in urothelial cancer is limited to upper urinary tract cancer [30,37], and we thus determined systematically EP1-4 expression in NU, NMIBC and MIBC tissue.
The expression of cytoplasmic and nuclear EP1-4 was decreased in BCA compared to NU. Furthermore, we observed lower levels of cytoplasmic EP1, EP3 and EP4 levels in MIBC compared to NMIBC, whereas nuclear EP3 was somewhat increased in NMIBC. This finding indicates a cumulative alteration of EP expression during BCA carcinogenesis. In a former study on urothelial cancer of the upper urinary tract, Miyata et al. did not investigate EP expression in normal urothelial tissue [37]. In other tumor entities, the expression of EP receptors was mostly increased in tumor samples: Shoji et. al. were able to show that EP1 mRNA were increased in colon cancer tissue [21]. EP2 is required for mammary epithelial hyperplasia and EP2 overexpression in mammary tumor leads to increased VEGF (vascular endothelial growth factor) production, a factor associated to carcinogenesis [22,23]. Furthermore, EP2 deficiency significantly decreases the growth, angiogenesis, and pulmonary metastasis of mammary tumors produced in mice [24]. Contrarily to these findings, Gustaffson et al [20] and Shoji et al [21] found the expression of EP2 mRNA to be significantly higher in normal colon tissue compared with tumor tissue. EP4 receptor protein expression was increased in colorectal cancer as well as adenomas compared to normal colonic epithelium using immunohistochemistry [25]. Furthermore, EP4 protein expression increased in malignant compared with benign human kidney cells [26]. Additionally, EP4 is upregulated in castration-resistant hormone-naive prostate cancer [27].
Even though EP levels were lower in tumor, we observed an increase of EP expression in patients with poor prognostic clinicopathological parameters: in NMIBC patients’ EP1 and EP2 expression was correlated with advanced pT-stage and less differentiated tumors. In MIBC patients nuclear EP1-4 expression was also negatively correlated with advanced pathological stage. Most importantly, high nuclear EP1 expression was an independent predictor of recurrence-free survival, so a marker of poor prognosis, following TURB in NMIBC patients. In addition, cytoplasmic EP2 was associated with disease recurrence predicting good prognosis in NMIBC patients and cytoplasmic EP1 was associated with cancer-specific survival, as a marker of poor prognosis in MIBC patients, although both markers lost its significance in the multivariate analysis. Interestingly, Miyata et al. found that co-expression of COX-2 and EP4 was associated with patients’ survival following nephroureterectomy for upper urinary tract urothelial cancer, whereas EP4 alone was not predictive for survival [30]. Upregulation of EP receptors was also determined as poor prognostic parameter in other tumor entities. Gustaffson et al., for example, showed that signaling via EP1-4 subtype receptors in colorectal cancer, particularly EP2, could predict poor survival [20]. Controversially, Thorat et al. reported that nuclear expression of EP1 correlates with good prognosis marker like node negative status and progesterone receptor expression in breast cancer [28]. Similar results were seen in a study by Ma et al. who determined that nuclear EP1 expression in invasive ductal carcinomas correlates with improved survival compared to women with no nuclear EP1 expression [29]. Earlier studies provided evidence that EP receptors promote invasion, migration and cell growth [13,22,25,26]. A number of pro-tumorigenic pathways have been identified. The induction of epithelial growth factors like amphiregulin in mammary cells by an EP2-specific agonist is one of them [22]. Additionally, renal cell invasion takes place through a pathway that encompasses EP4 and small GTPase Rap (guanosine triposphate) [26]. Moreover, PGE2 can inhibit apoptosis induced by staurosporine or anti-FAS antibody [13], to name only a few. The EP receptors are specifically pharmacologically targetable: EP1 (colon, breast and skin cancer [31-33]) and EP4 (breast cancer [17]) inhibition inhibited cancer growth.
Several limitations should be acknowledged: NU tissue was obtained from patients with BCA undergoing RC as collection of NU tissue from healthy individuals is for ethical reasons unfeasible. According to the cancer field effect it is not definitively possible to exclude molecular abnormalities in this normal tissue [38]. However, the significant differences of EP expression in BCA and NU tissue do not support a bias due to the cancer field effect. MIBC tissue was obtained from TURB as well as from RC specimen because residual tumor after TURB may be marginal and the TURB specimen seemed histologically better suitable for TMA construction in some cases; however, we did not observe differences in MIBC tissue from RC and TURB specimen (data not shown).
Conclusion
In conclusion, EP1 expression is predictive of BCA recurrence in NMIBC and cancer-specific survival in MIBC patients. Thus, its analysis may be helpful for the identification of patients benefitting from adjuvant therapy. Furthermore, targeting EP1 could be a novel pharmacological approach for BCA patients.
Acknowledgements
We thank Mrs Doris Schmidt for technical assistance. Isabella Syring was supported by a Ferdinand Eisenberger Fellowship of the German Society of Urology (SYI1/FE-13).
Disclosure of conflict of interest
None.
References
- 1.Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 2014;64:9–29. doi: 10.3322/caac.21208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Di Pierro GB, Gulia C, Cristini C, Fraietta G, Marini L, Grande P, Gentile V, Piergentili R. Bladder cancer: a simple model becomes complex. Curr Genomics. 2012;13:395–415. doi: 10.2174/138920212801619232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Fristrup N, Ulhoi BP, Birkenkamp-Demtroder K, Mansilla F, Sanchez-Carbayo M, Segersten U, Malmstrom PU, Hartmann A, Palou J, Alvarez-Mugica M, Zieger K, Borre M, Orntoft TF, Dyrskjot L. Cathepsin E, maspin, Plk1, and survivin are promising prognostic protein markers for progression in non-muscle invasive bladder cancer. Am J Pathol. 2012;180:1824–1834. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2012.01.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Palou J, Algaba F, Vera I, Rodriguez O, Villavicencio H, Sanchez-Carbayo M. Protein expression patterns of ezrin are predictors of progression in T1G3 bladder tumours treated with nonmaintenance bacillus Calmette-Guerin. Eur Urol. 2009;56:829–836. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2008.09.062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Van Rhijn BW, van der Kwast TH, Liu L, Fleshner NE, Bostrom PJ, Vis AN, Alkhateeb SS, Bangma CH, Jewett MA, Zwarthoff EC, Zlotta AR, Bapat B. The FGFR3 mutation is related to favorable pT1 bladder cancer. J Urol. 2012;187:310–314. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2011.09.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Tanaka T, Miyazawa K, Tsukamoto T, Kuno T, Suzuki K. Pathobiology and chemoprevention of bladder cancer. J Oncol. 2011;2011:528353. doi: 10.1155/2011/528353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Yoshimura R, Sano H, Mitsuhashi M, Kohno M, Chargui J, Wada S. Expression of cyclooxygenase-2 in patients with bladder carcinoma. J Urol. 2001;165:1468–1472. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Castelao JE, Yuan JM, Gago-Dominguez M, Yu MC, Ross RK. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and bladder cancer prevention. Br J Cancer. 2000;82:1364–1369. doi: 10.1054/bjoc.1999.1106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Grubbs CJ, Lubet RA, Koki AT, Leahy KM, Masferrer JL, Steele VE, Kelloff GJ, Hill DL, Seibert K. Celecoxib inhibits N-butyl-N-(4-hydroxy-butyl)-nitrosamine-induced urinary bladder cancers in male B6D2F1 mice and female Fischer-344 rats. Cancer Res. 2000;60:5599–5602. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Bresalier RS, Sandler RS, Quan H, Bolognese JA, Oxenius B, Horgan K, Lines C, Riddell R, Morton D, Lanas A, Konstam MA, Baron JA Adenomatous Polyp Prevention on Vioxx (APPROVe) Trial Investigators. Cardiovascular events associated with rofecoxib in a colorectal adenoma chemoprevention trial. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:1092–1102. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa050493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Fulton AM, Ma X, Kundu N. Targeting prostaglandin E EP receptors to inhibit metastasis. Cancer Res. 2006;66:9794–9797. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-2067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Kiriyama M, Ushikubi F, Kobayashi T, Hirata M, Sugimoto Y, Narumiya S. Ligand binding specificities of the eight types and subtypes of the mouse prostanoid receptors expressed in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1997;122:217–224. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0701367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Hull MA, Ko SC, Hawcroft G. Prostaglandin EP receptors: targets for treatment and prevention of colorectal cancer? Mol Cancer Ther. 2004;3:1031–1039. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Zhu T, Gobeil F, Vazquez-Tello A, Leduc M, Rihakova L, Bossolasco M, Bkaily G, Peri K, Varma DR, Orvoine R, Chemtob S. Intracrine signaling through lipid mediators and their cognate nuclear G-protein-coupled receptors: a paradigm based on PGE2, PAF, and LPA1 receptors. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2006;84:377–391. doi: 10.1139/y05-147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Reader J, Holt D, Fulton A. Prostaglandin E2 EP receptors as therapeutic targets in breast cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2011;30:449–463. doi: 10.1007/s10555-011-9303-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Ma J, Chen M, Xia SK, Shu W, Guo Y, Wang YH, Xu Y, Bai XM, Zhang L, Zhang H, Zhang M, Wang YP, Leng J. Prostaglandin E2 promotes liver cancer cell growth by the upregulation of FUSE-binding protein 1 expression. Int J Oncol. 2013;42:1093–1104. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2013.1782. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Xin X, Majumder M, Girish GV, Mohindra V, Maruyama T, Lala PK. Targeting COX-2 and EP4 to control tumor growth, angiogenesis, lymphangiogenesis and metastasis to the lungs and lymph nodes in a breast cancer model. Lab Invest. 2012;92:1115–1128. doi: 10.1038/labinvest.2012.90. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Wu T. Cyclooxygenase-2 and prostaglandin signaling in cholangiocarcinoma. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2005;1755:135–150. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2005.04.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Kotani M, Tanaka I, Ogawa Y, Usui T, Mori K, Ichikawa A, Narumiya S, Yoshimi T, Nakao K. Molecular cloning and expression of multiple isoforms of human prostaglandin E receptor EP3 subtype generated by alternative messenger RNA splicing: multiple second messenger systems and tissue-specific distributions. Mol Pharmacol. 1995;48:869–879. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Gustafsson A, Hansson E, Kressner U, Nordgren S, Andersson M, Wang W, Lonnroth C, Lundholm K. EP1-4 subtype, COX and PPAR gamma receptor expression in colorectal cancer in prediction of disease-specific mortality. Int J Cancer. 2007;121:232–240. doi: 10.1002/ijc.22582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Shoji Y, Takahashi M, Kitamura T, Watanabe K, Kawamori T, Maruyama T, Sugimoto Y, Negishi M, Narumiya S, Sugimura T, Wakabayashi K. Downregulation of prostaglandin E receptor subtype EP3 during colon cancer development. Gut. 2004;53:1151–1158. doi: 10.1136/gut.2003.028787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Chang SH, Ai Y, Breyer RM, Lane TF, Hla T. The prostaglandin E2 receptor EP2 is required for cyclooxygenase 2-mediated mammary hyperplasia. Cancer Res. 2005;65:4496–4499. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-0129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Chang SH, Liu CH, Wu MT, Hla T. Regulation of vascular endothelial cell growth factor expression in mouse mammary tumor cells by the EP2 subtype of the prostaglandin E2 receptor. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2005;76:48–58. doi: 10.1016/j.prostaglandins.2004.12.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Tian M, Schiemann WP. PGE2 receptor EP2 mediates the antagonistic effect of COX-2 on TGF-beta signaling during mammary tumorigenesis. FASEB J. 2010;24:1105–1116. doi: 10.1096/fj.09-141341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Chell SD, Witherden IR, Dobson RR, Moorghen M, Herman AA, Qualtrough D, Williams AC, Paraskeva C. Increased EP4 receptor expression in colorectal cancer progression promotes cell growth and anchorage independence. Cancer Res. 2006;66:3106–3113. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-3702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Wu J, Zhang Y, Frilot N, Kim JI, Kim WJ, Daaka Y. Prostaglandin E2 regulates renal cell carcinoma invasion through the EP4 receptor-Rap GTPase signal transduction pathway. J Biol Chem. 2011;286:33954–33962. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.187344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Terada N, Shimizu Y, Kamba T, Inoue T, Maeno A, Kobayashi T, Nakamura E, Kamoto T, Kanaji T, Maruyama T, Mikami Y, Toda Y, Matsuoka T, Okuno Y, Tsujimoto G, Narumiya S, Ogawa O. Identification of EP4 as a potential target for the treatment of castration-resistant prostate cancer using a novel xenograft model. Cancer Res. 2010;70:1606–1615. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-2984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Thorat MA, Morimiya A, Mehrotra S, Konger R, Badve SS. Prostanoid receptor EP1 expression in breast cancer. Mod Pathol. 2008;21:15–21. doi: 10.1038/modpathol.3800970. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Ma X, Kundu N, Ioffe OB, Goloubeva O, Konger R, Baquet C, Gimotty P, Reader J, Fulton AM. Prostaglandin E receptor EP1 suppresses breast cancer metastasis and is linked to survival differences and cancer disparities. Mol Cancer Res. 2010;8:1310–1318. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-10-0003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Miyata Y, Kanda S, Nomata K, Eguchi J, Kanetake H. Expression of cyclooxygenase-2 and EP4 receptor in transitional cell carcinoma of the upper urinary tract. J Urol. 2005;173:56–60. doi: 10.1097/01.ju.0000148272.77539.2d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Watanabe K, Kawamori T, Nakatsugi S, Ohta T, Ohuchida S, Yamamoto H, Maruyama T, Kondo K, Ushikubi F, Narumiya S, Sugimura T, Wakabayashi K. Role of the prostaglandin E receptor subtype EP1 in colon carcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 1999;59:5093–5096. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Kawamori T, Uchiya N, Nakatsugi S, Watanabe K, Ohuchida S, Yamamoto H, Maruyama T, Kondo K, Sugimura T, Wakabayashi K. Chemopreventive effects of ONO-8711, a selective prostaglandin E receptor EP(1) antagonist, on breast cancer development. Carcinogenesis. 2001;22:2001–2004. doi: 10.1093/carcin/22.12.2001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Tober KL, Wilgus TA, Kusewitt DF, Thomas-Ahner JM, Maruyama T, Oberyszyn TM. Importance of the EP(1) receptor in cutaneous UVB-induced inflammation and tumor development. J Invest Dermatol. 2006;126:205–211. doi: 10.1038/sj.jid.5700014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Oll M, Baumann C, Behbahani TE, von Ruecker A, Muller SC, Ellinger J. Identification of prostaglandin receptors in human ureters. BMC Urol. 2012;12:35. doi: 10.1186/1471-2490-12-35. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Gakis G. The role of inflammation in bladder cancer. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2014;816:183–196. doi: 10.1007/978-3-0348-0837-8_8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Qayyum T, McArdle P, Hilmy M, Going J, Orange C, Seywright M, Horgan P, Underwood M, Edwards J. A prospective study of the role of inflammation in bladder cancer. Curr Urol. 2013;6:189–193. doi: 10.1159/000343537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Miyata Y, Ohba K, Kanda S, Nomata K, Eguchi J, Hayashi T, Kanetake H. Pathological function of prostaglandin E2 receptors in transitional cell carcinoma of the upper urinary tract. Virchows Arch. 2006;448:822–829. doi: 10.1007/s00428-006-0198-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Takahashi T, Habuchi T, Kakehi Y, Mitsumori K, Akao T, Terachi T, Yoshida O. Clonal and chronological genetic analysis of multifocal cancers of the bladder and upper urinary tract. Cancer Res. 1998;58:5835–5841. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


