Abstract
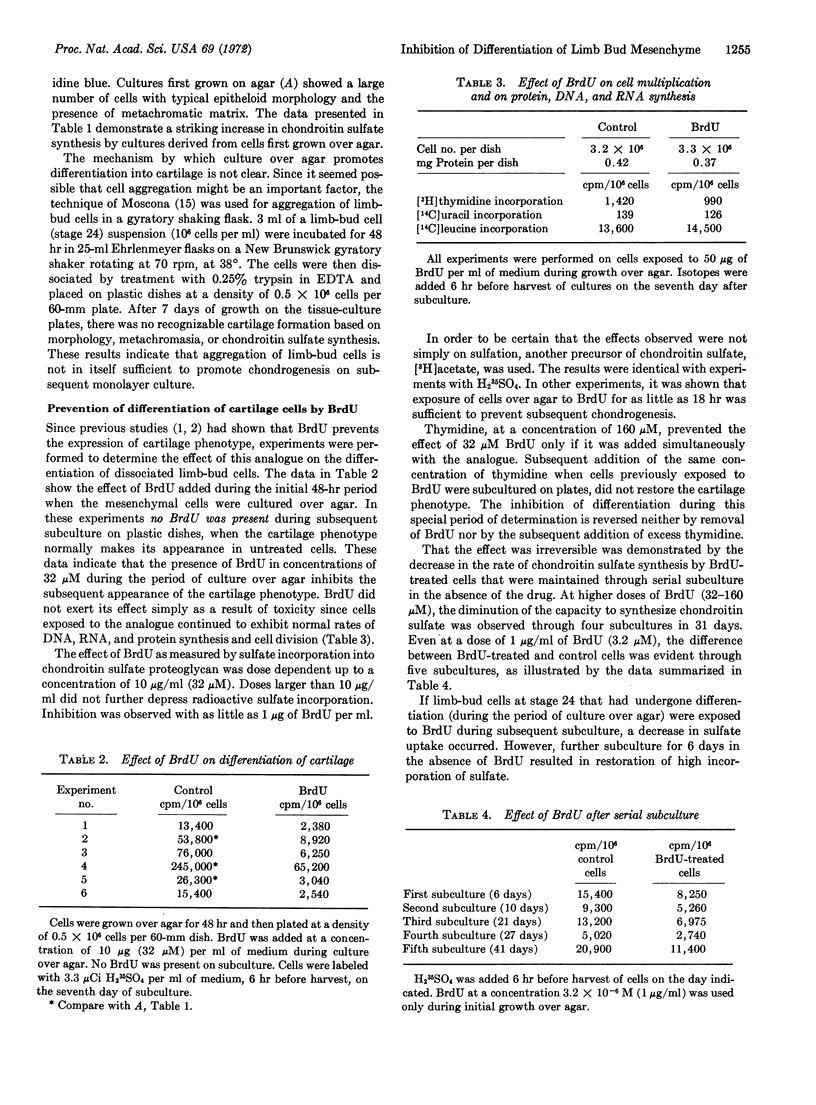
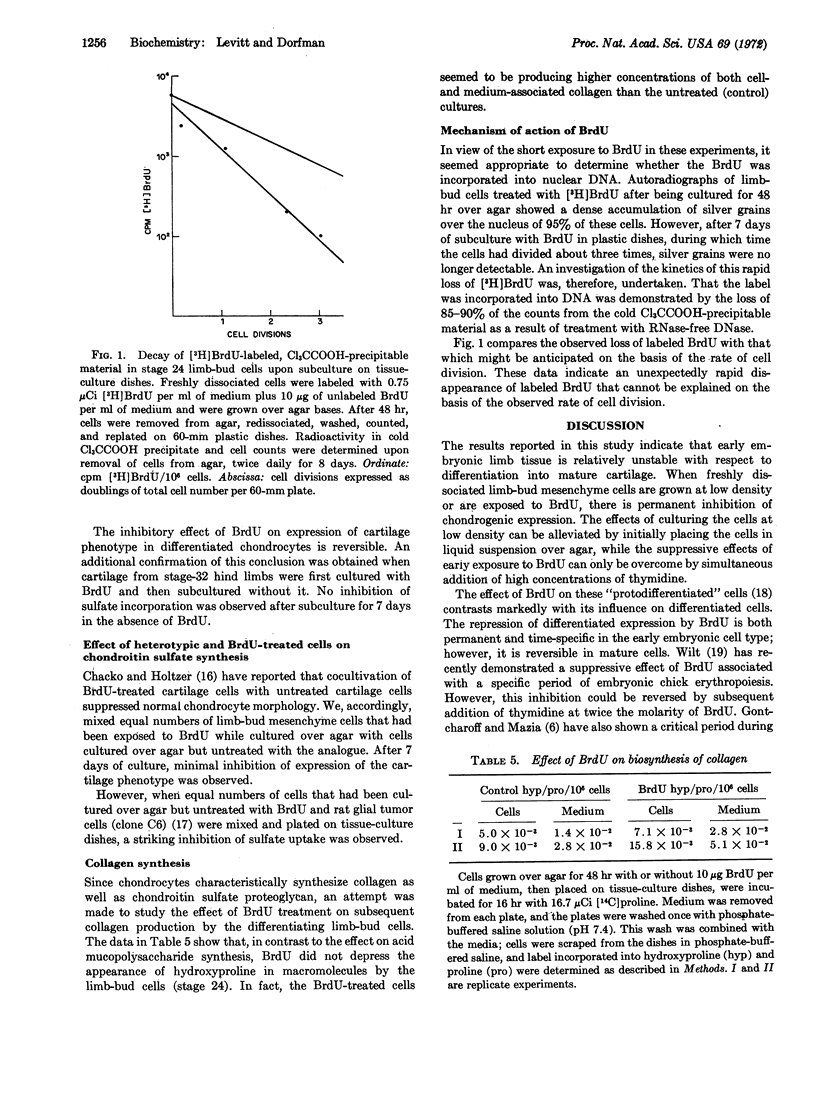
Growing freshly dissociated chick-limb bud cells (stage 24) over agar for 48 hr permits differentiation into cartilage upon monolayer culture even when initial plating and subculture densities are well below confluency. Addition of 5-bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU) during the initial (48-hr) period over agar irreversibly inhibits chondrogenic differentiation, as characterized by morphology, metachromasia, and sulfate incorporation into acid mucopolysaccharide. Simultaneous, but not subsequent, addition of excess thymidine will prevent the effect of the analogue. Collagen synthesis is not depressed in BrdU-treated cells. Radioautographic studies demonstrate the specific localization of BrdU in the nucleus. Treatment of trichloroacetic acid-precipitable material containing tritiated bromodeoxyuridine with deoxyribonuclease solubilizes 90% of the radioactivity. The loss of the analogue from this precipitable material upon prolonged culture of limb-bud cells is more rapid than can be expected from cell division alone. 5-Bromodeoxyuridine may affect a fraction of DNA involved in stabilization of the differentiated cell phenotype.
Keywords: cartilage, metachromasia, agar, acid mucopolysaccharides
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abbott J., Holtzer H. The loss of phenotypic traits by differentiated cells, V. The effect of 5-bromodeoxyuridine on cloned chondrocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Apr;59(4):1144–1151. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.4.1144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell E. I-DNA: Its packaging into I-somes and its relation to protein synthesis during differentiation. Nature. 1969 Oct 25;224(5217):326–328. doi: 10.1038/224326a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benda P., Lightbody J., Sato G., Levine L., Sweet W. Differentiated rat glial cell strain in tissue culture. Science. 1968 Jul 26;161(3839):370–371. doi: 10.1126/science.161.3839.370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bischoff R. Acid mucopolysaccharide synthesis by chick amnion cell cultures. Inhibition by 5-bromodeoxyuridine. Exp Cell Res. 1971 May;66(1):224–236. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4827(71)80032-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caplan A. I. Effects of the nicotinamide-sensitive teratogen3-acetylpyridine on chick limb cells in culture. Exp Cell Res. 1970 Oct;62(2):341–355. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(70)90564-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman A. W., Coleman J. R., Kankel D., Werner I. The reversible control of animal cell differentiation by the thymidine analog, 5-bromodeoxyuridine. Exp Cell Res. 1970 Feb;59(2):319–328. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(70)90606-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorfman A., Ho P. L. Synthesis of acid mucopolysaccharides by glial tumor cells in tissue culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jun;66(2):495–499. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.2.495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gontcharoff M., Mazia D. Developmental consequences of introduction of bromouracil into the DNA of sea urchin embryos during early division stages. Exp Cell Res. 1967 May;46(2):315–327. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(67)90069-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz A. L., Dorfman A. The growth of cartilage cells in soft agar and liquid suspension. J Cell Biol. 1970 May;45(2):434–438. doi: 10.1083/jcb.45.2.434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUKENS L. N. EVIDENCE FOR THE NATURE OF THE PRECURSOR THAT IS HYDROXYLATED DURING THE BIOSYNTHESIS OF COLLAGEN HYDROXYPROLINE. J Biol Chem. 1965 Apr;240:1661–1669. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner R. A., Meinke W., Goldstein D. A. Membrane-associated DNA in the cytoplasm of diploid human lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jun;68(6):1212–1216. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.6.1212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levenson G. E. The effect of ascorbic acid on monolayer cultures of three types of chondrocytes. Exp Cell Res. 1969 May;55(2):225–228. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(69)90484-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOSCONA A. Rotation-mediated histogenetic aggregation of dissociated cells. A quantifiable approach to cell interactions in vitro. Exp Cell Res. 1961 Jan;22:455–475. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(61)90122-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medoff J. Enzymatic events during cartilage differentiation in the chick embryonic limb bud. Dev Biol. 1967 Aug;16(2):118–143. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(67)90020-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEARLS R. L. AN AUTORADIOGRAPHIC STUDY OF THE UPTAKE OF S35-SULFATE DURING THE DIFFERENTIATION OF LIMB BUD CARTILAGE. Dev Biol. 1965 Apr;11:155–168. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(65)90054-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Searls R. L., Janners M. Y. The stabilization of cartilage properties in the cartilage-forming mesenchyme of the embryonic chick limb. J Exp Zool. 1969 Mar;170(3):365–375. doi: 10.1002/jez.1401700313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Searls R. L. The role of cell migration in the development of the embryonic chick limb bud. J Exp Zool. 1967 Oct;166(1):39–49. doi: 10.1002/jez.1401660105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silagi S., Bruce S. A. Suppression of malignancy and differentiation in melanotic melanoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 May;66(1):72–78. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.1.72. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turkington R. W., Majumder G. C., Riddle M. Inhibition of mammary gland differentiation in vitro by 5-bromo-2'-deoxyuridine. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 25;246(6):1814–1819. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


