Abstract
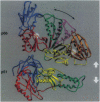
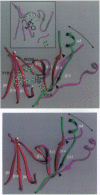
The crystal structure of the reverse transcriptase (RT) from the type 1 human immunodeficiency virus has been determined at 3.2-A resolution. Comparison with complexes between RT and the polymerase inhibitor Nevirapine [Kohlstaedt, L.A., Wang, J., Friedman, J.M., Rice, P.A. & Steitz, T.A. (1992) Science 256, 1783-1790] and between RT and an oligonucleotide [Jacobo-Molina, A., Ding, J., Nanni, R., Clark, A. D., Lu, X., Tantillo, C., Williams, R. L., Kamer, G., Ferris, A. L., Clark, P., Hizi, A., Hughes, S. H. & Arnold, E. (1993) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90, 6320-6324] reveals changes associated with ligand binding. The enzyme is a heterodimer (p66/p51), with domains labeled "fingers," "thumb," "palm," and "connection" in both subunits, and a ribonuclease H domain in the larger subunit only. The most striking difference between RT and both complex structures is the change in orientation of the p66 thumb (approximately 33 degrees rotation). Smaller shifts relative to the core of the molecule were also found in other domains, including the p66 fingers and palm, which contain the polymerase active site. Within the polymerase catalytic region itself, there are no rearrangements between RT and the RT/DNA complex. In RT/Nevirapine, the drug binds in the p66 palm near the polymerase active site, a region that is well-packed hydrophobic core in the unliganded enzyme. Room for the drug is provided by movement of a small beta-sheet within the palm domain of the Nevirapine complex. The rearrangement within the palm and thumb, as well as domain shifts relative to the enzyme core, may prevent correct placement of the oligonucleotide substrate when the drug is bound.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bacolla A., Shih C. K., Rose J. M., Piras G., Warren T. C., Grygon C. A., Ingraham R. H., Cousins R. C., Greenwood D. J., Richman D. Amino acid substitutions in HIV-1 reverse transcriptase with corresponding residues from HIV-2. Effect on kinetic constants and inhibition by non-nucleoside analogs. J Biol Chem. 1993 Aug 5;268(22):16571–16577. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debyser Z., Pauwels R., Andries K., Desmyter J., Kukla M., Janssen P. A., De Clercq E. An antiviral target on reverse transcriptase of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 revealed by tetrahydroimidazo-[4,5,1-jk] [1,4]benzodiazepin-2 (1H)-one and -thione derivatives. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1451–1455. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delarue M., Poch O., Tordo N., Moras D., Argos P. An attempt to unify the structure of polymerases. Protein Eng. 1990 May;3(6):461–467. doi: 10.1093/protein/3.6.461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobo-Molina A., Ding J., Nanni R. G., Clark A. D., Jr, Lu X., Tantillo C., Williams R. L., Kamer G., Ferris A. L., Clark P. Crystal structure of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase complexed with double-stranded DNA at 3.0 A resolution shows bent DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):6320–6324. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.6320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones T. A., Zou J. Y., Cowan S. W., Kjeldgaard M. Improved methods for building protein models in electron density maps and the location of errors in these models. Acta Crystallogr A. 1991 Mar 1;47(Pt 2):110–119. doi: 10.1107/s0108767390010224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohlstaedt L. A., Wang J., Friedman J. M., Rice P. A., Steitz T. A. Crystal structure at 3.5 A resolution of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase complexed with an inhibitor. Science. 1992 Jun 26;256(5065):1783–1790. doi: 10.1126/science.1377403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizrahi V., Lazarus G. M., Miles L. M., Meyers C. A., Debouck C. Recombinant HIV-1 reverse transcriptase: purification, primary structure, and polymerase/ribonuclease H activities. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1989 Sep;273(2):347–358. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(89)90493-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poch O., Sauvaget I., Delarue M., Tordo N. Identification of four conserved motifs among the RNA-dependent polymerase encoding elements. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3867–3874. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08565.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibanda B. L., Blundell T. L., Thornton J. M. Conformation of beta-hairpins in protein structures. A systematic classification with applications to modelling by homology, electron density fitting and protein engineering. J Mol Biol. 1989 Apr 20;206(4):759–777. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90583-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smerdon S. J., Jäger J., Wang J., Kohlstaedt L. A., Chirino A. J., Friedman J. M., Rice P. A., Steitz T. A. Structure of the binding site for nonnucleoside inhibitors of the reverse transcriptase of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Apr 26;91(9):3911–3915. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.9.3911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor P. B., Culp J. S., Debouck C., Johnson R. K., Patil A. D., Woolf D. J., Brooks I., Hertzberg R. P. Kinetic and mutational analysis of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase inhibition by inophyllums, a novel class of non-nucleoside inhibitors. J Biol Chem. 1994 Mar 4;269(9):6325–6331. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tramontano E., Cheng Y. C. HIV-1 reverse transcriptase inhibition by a dipyridodiazepinone derivative: BI-RG-587. Biochem Pharmacol. 1992 Mar 17;43(6):1371–1376. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(92)90515-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]