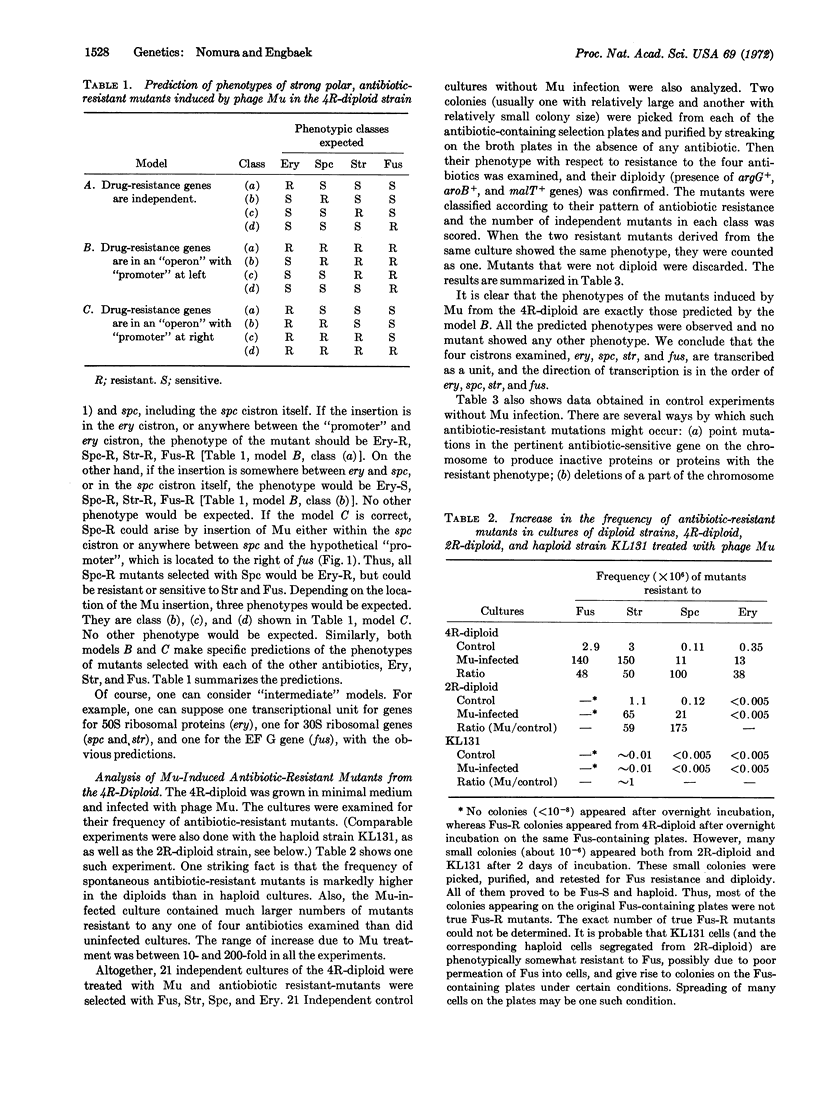
Abstract
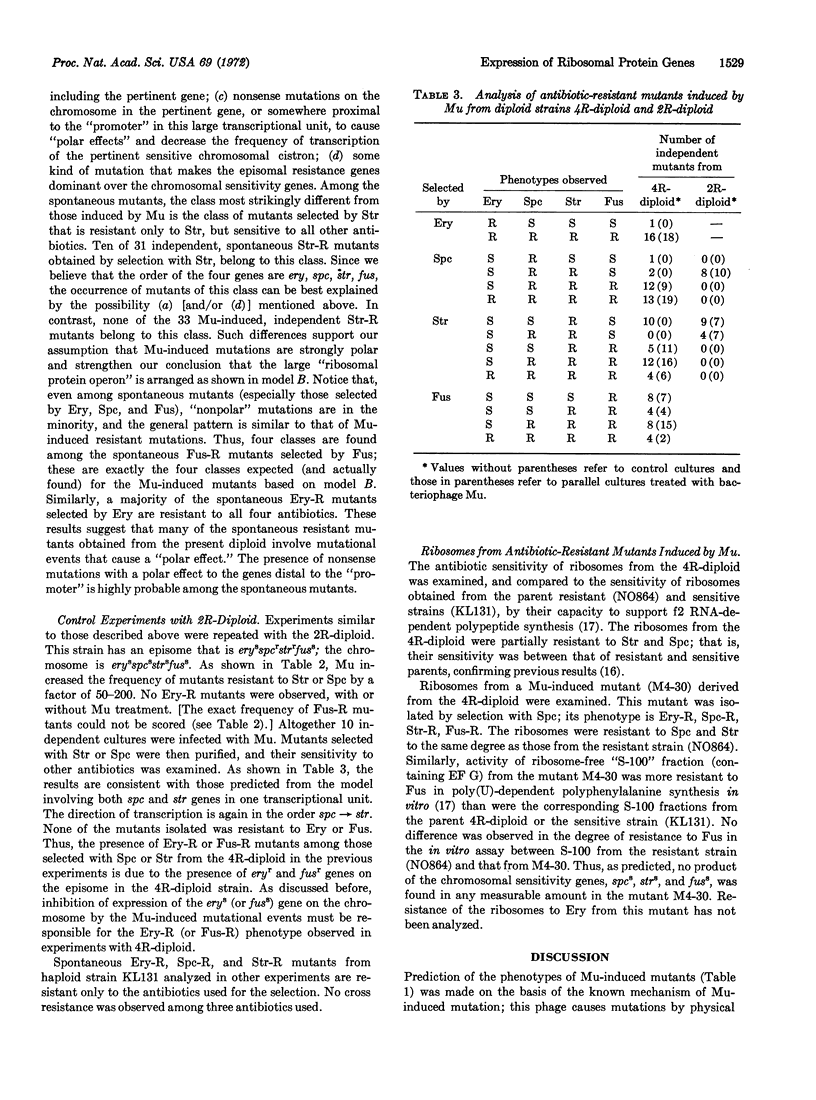
The organization of ribosomal protein genes and the gene (fus) for a protein chain elongation factor, EF G, in Escherichia coli were studied with a merodiploid strain that has an episome with genetic markers, eryr, spcr, strr, and fusr, and a chromosome with markers erys, spcs, strs, and fuss. The ery locus determines a 50S ribosomal protein and the spc and str loci determine 30S ribosomal proteins. The phenotype of the diploid strain is sensitive to all of the four antibiotics, erythromycin (Ery), spectinomycin (Spc), streptomycin (Str), and fusidic acid (Fus). Analysis of antibiotic-resistant mutants induced by bacteriophage Mu in the diploid strain indicates that these four genes, and probably many other ribosomal protein genes linked to them, are transcribed as a single unit, and the direction of the transcription is in the order of ery, spc, str, and fus.
Keywords: E. coli, episome, merodiploid, antibiotics, operon
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Austin S. J., Tittawella I. P., Hayward R. S., Scaife J. G. Amber mutations of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. Nat New Biol. 1971 Aug 4;232(31):133–136. doi: 10.1038/newbio232133a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernardi A., Leder P. Protein biosynthesis in Escherichia coli. Purification and characteristics of a mutant G factor. J Biol Chem. 1970 Sep 10;245(17):4263–4268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bollen A., Davies J., Ozaki M., Mizushima S. Ribosomal Protein Conferring Sensitivity to the Antibiotic Spectinomycin in Escherichia coli. Science. 1969 Jul 4;165(3888):85–86. doi: 10.1126/science.165.3888.85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boram W., Abelson J. Bacteriophage Mu integration: on the mechanism of Mu-induced mutations. J Mol Biol. 1971 Nov 28;62(1):171–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90137-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fahnestock S. R., Nomura M. Activity of ribosomes containing 5S RNA with a chemically modified 3'-terminus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Feb;69(2):363–365. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.2.363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. Regulation of the in vivo synthesis of the polypeptide chain elongation factors in Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1970 Feb 17;9(4):912–917. doi: 10.1021/bi00806a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan E., Saedler H., Starlinger P. O0 and strong-polar mutations in the gal operon are insertions. Mol Gen Genet. 1968;102(4):353–363. doi: 10.1007/BF00433726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuwano M., Schlessinger D. G factor mutants of Escherichia coli: map location and properties. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Feb 5;42(3):441–444. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90390-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEDERBERG J. Streptomycin resistance; a genetically recessive mutation. J Bacteriol. 1951 May;61(5):549–550. doi: 10.1128/jb.61.5.549-550.1951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leder P., Skogerson L. E., Nau M. M. Translocation of mRNA codons. I. The preparation and characteristics of a homogeneous enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Feb;62(2):454–460. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.2.454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low B. Formation of merodiploids in matings with a class of Rec- recipient strains of Escherichia coli K12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 May;60(1):160–167. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.1.160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura M. Bacterial ribosome. Bacteriol Rev. 1970 Sep;34(3):228–277. doi: 10.1128/br.34.3.228-277.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otaka E., Teraoka H., Tamaki M., Tanaka K., Osawa S. Ribosomes from erythromycin-resistant mutants of Escherichia coli Q13. J Mol Biol. 1970 Mar;48(3):499–510. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90061-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozaki M., Mizushima S., Nomura M. Identification and functional characterization of the protein controlled by the streptomycin-resistant locus in E. coli. Nature. 1969 Apr 26;222(5191):333–339. doi: 10.1038/222333a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparling P. F., Modolell J., Takeda Y., Davis B. D. Ribosomes from Escherichia coli merodiplods heterozygous for resistance to streptomycin and to spectinomycin. J Mol Biol. 1968 Nov 14;37(3):407–421. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90111-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAYLOR A. L. BACTERIOPHAGE-INDUCED MUTATION IN ESCHERICHIA COLI. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Dec;50:1043–1051. doi: 10.1073/pnas.50.6.1043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka N., Kawano G., Kinoshita T. Chromosomal location of a fusidic acid resistant marker in Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Feb 5;42(3):564–567. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90408-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toussaint A. Insertion of phage Mu. 1 within prophage lambda. A new approach for studying the control of the late functions in bacteriophage lambda. Mol Gen Genet. 1969;106(1):89–92. doi: 10.1007/BF00332824. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittmann H. G., Stöfflet G., Hindennach I., Kurland C. G., Birge E. A., Randall-Hazelbauer L., Nomura M., Kaltschmidt E., Mizushima S., Traut R. R. Correlation of 30S ribosomal proteins of Escherichia coli isolated in different laboratories. Mol Gen Genet. 1971;111(4):327–333. doi: 10.1007/BF00569784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]