Abstract
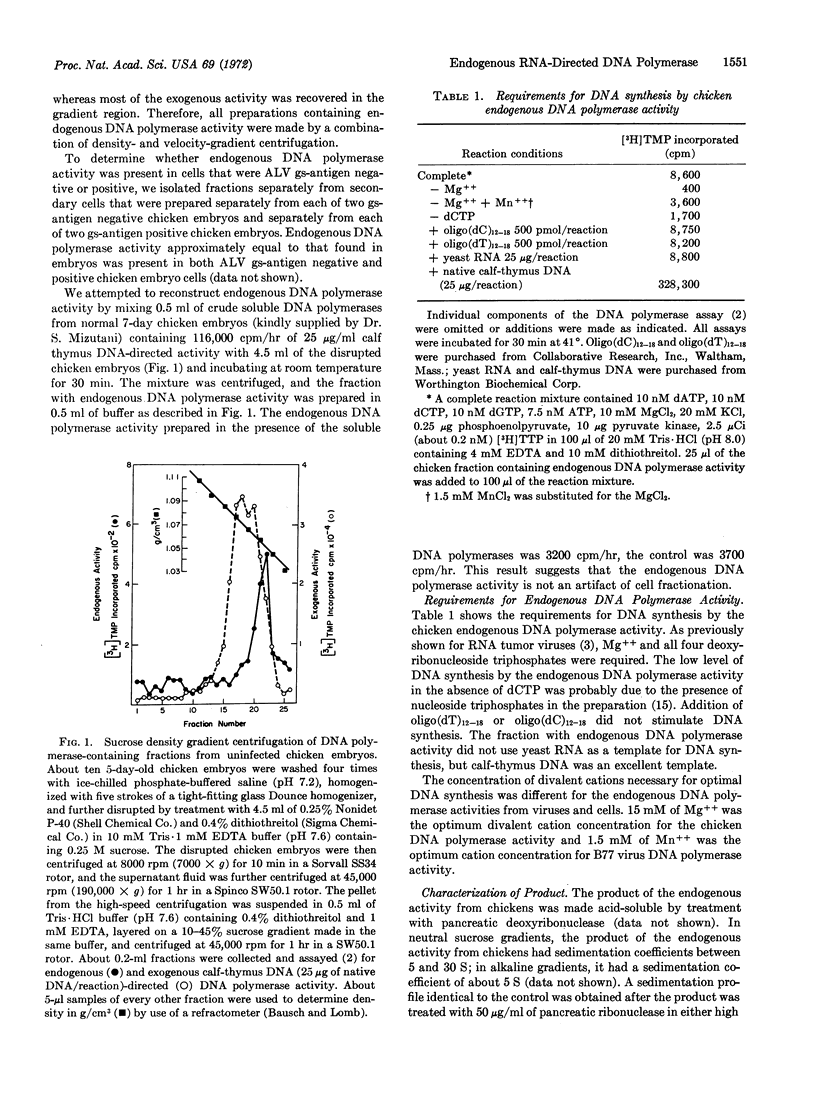
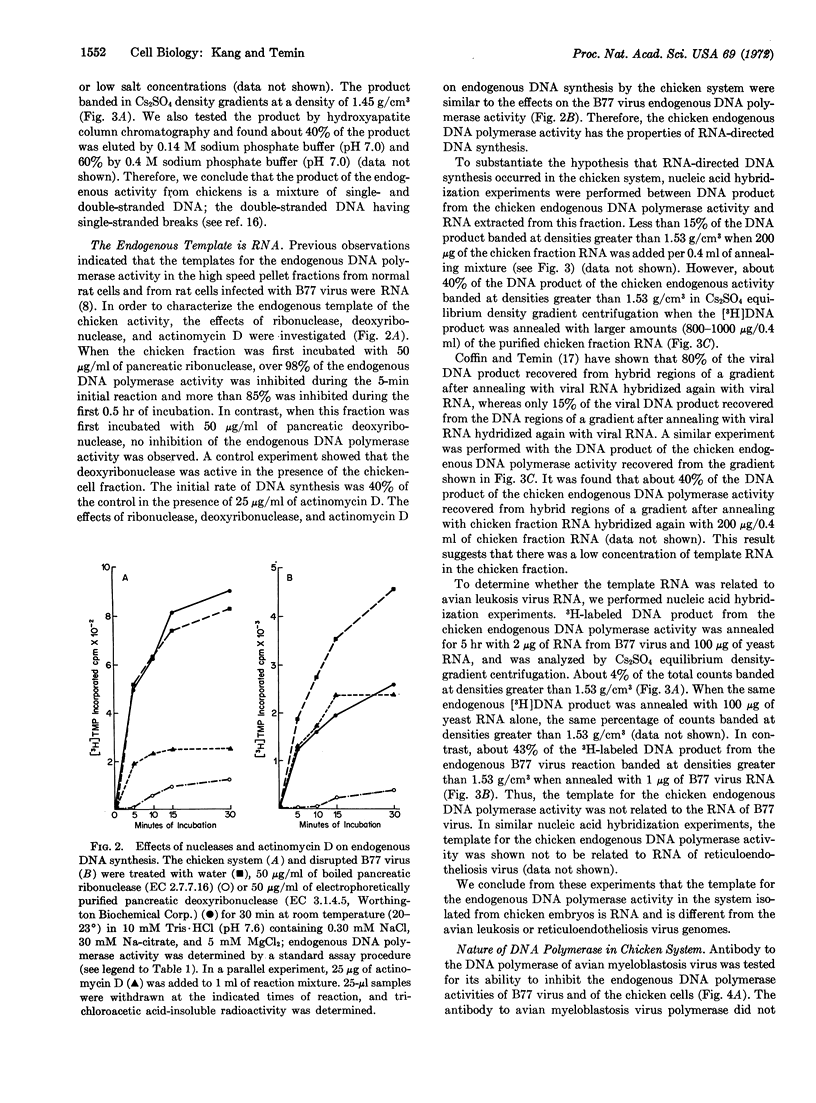
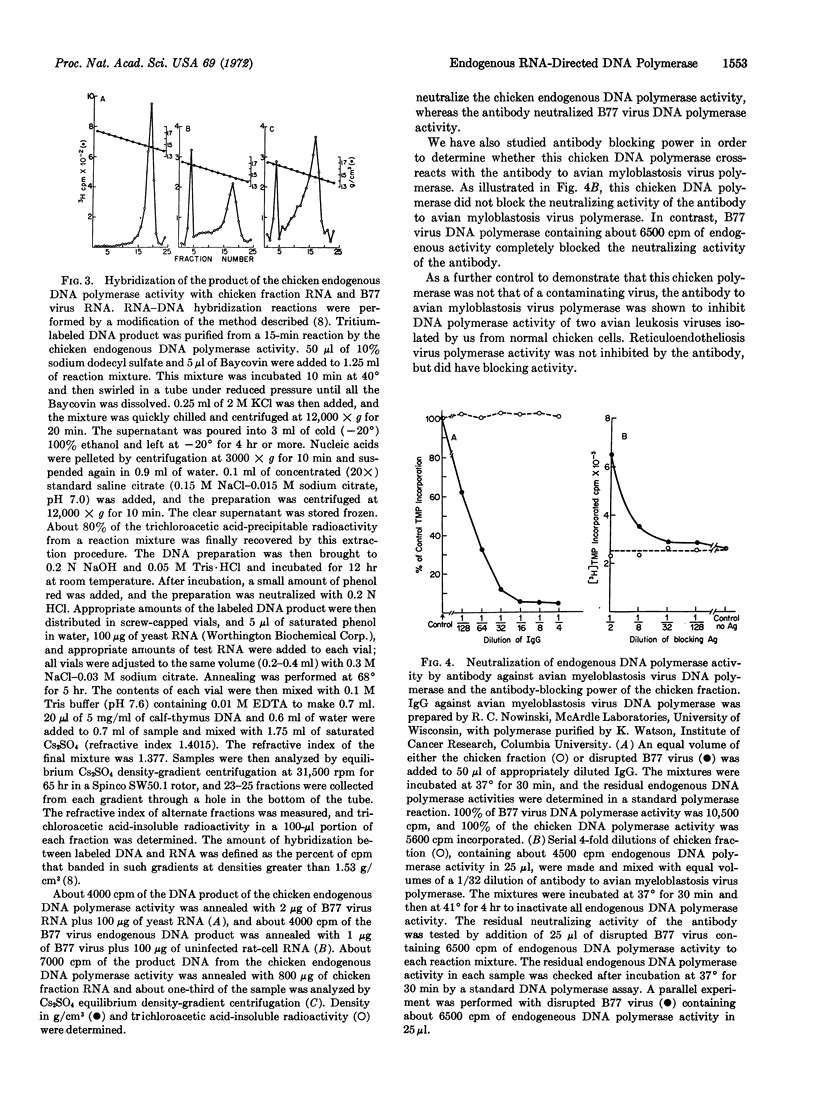
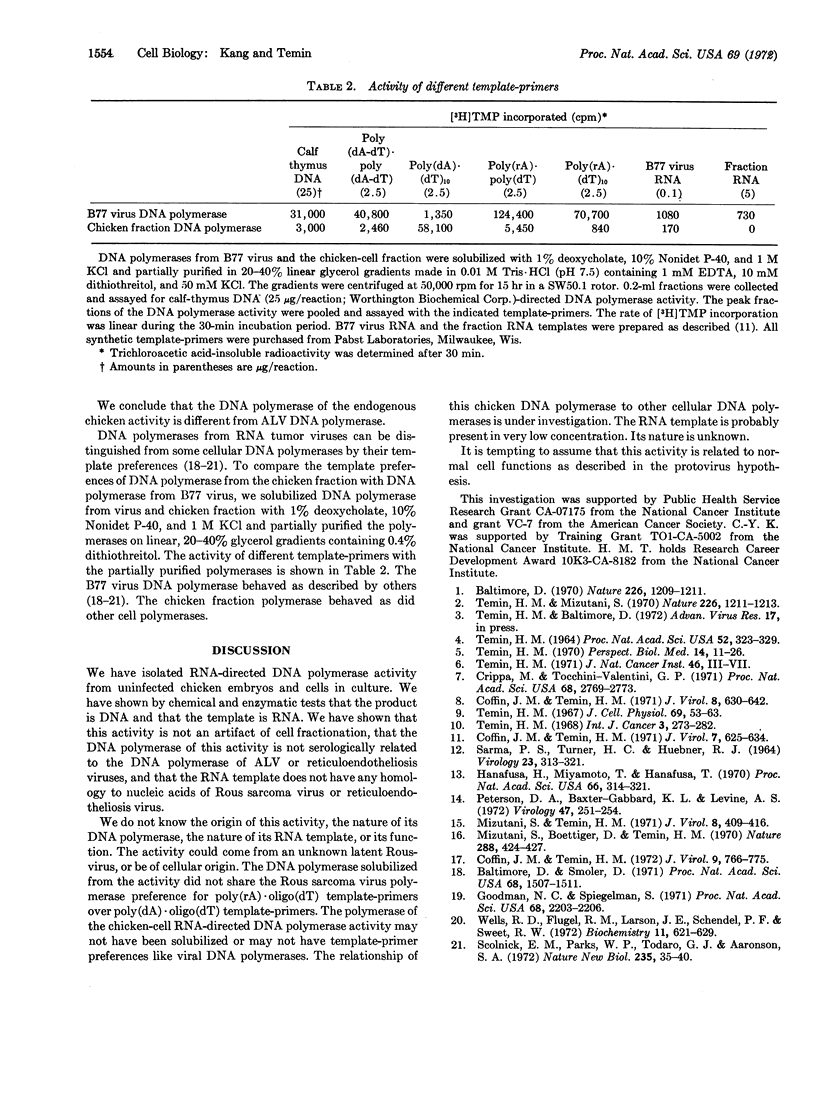
Early chicken embryos that are either positive or negative for group-specific antigens of avian leukosis viruses contained endogenous RNA-directed DNA polymerase activity. This endogenous DNA polymerase activity was not increased after mixture of soluble DNA polymerases isolated from chicken embryos with disrupted chicken embryo cells. The endogenous activity was resistant to treatment with deoxyribonuclease, and the initial rate of DNA synthesis was partially resistant to actinomycin D. In contrast, over 90% of the endogenous polymerase activity was destroyed by ribonuclease in medium with high salt concentration. The DNA product of the endogenous DNA polymerase activity from chicken embryos did not hybridize with RNA of Rous sarcoma virus or reticuloendotheliosis virus, whereas about 40% of this DNA product hybridized with the RNA from the same chicken-cell fraction. Antibody against DNA polymerase of avian myeloblastosis virus did not neutralize the chicken endogenous DNA polymerase activity. These results demonstrate that uninfected chicken embryo cells contain endogenous RNA-directed DNA polymerase activity that is not derived from avian leukosis or reticuloendotheliosis viruses.
Keywords: RNA tumor viruses
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baltimore D. RNA-dependent DNA polymerase in virions of RNA tumour viruses. Nature. 1970 Jun 27;226(5252):1209–1211. doi: 10.1038/2261209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltimore D., Smoler D. Primer requirement and template specificity of the DNA polymerase of RNA tumor viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jul;68(7):1507–1511. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.7.1507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffin J. M., Temin H. M. Comparison of Rous sarcoma virus-specific deoxyribonucleic acid polymerases in virions of Rous sarcoma virus and in Rous sarcoma virus-infected chicken cells. J Virol. 1971 May;7(5):625–634. doi: 10.1128/jvi.7.5.625-634.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffin J. M., Temin H. M. Hybridization of Rous sarcoma virus deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase product and ribonucleic acids from chicken and rat cells infected with Rous sarcoma virus. J Virol. 1972 May;9(5):766–775. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.5.766-775.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffin J. M., Temin H. M. Ribonuclease-sensitive deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase activity in uninfected rat cells and rat cells infected with Rous sarcoma virus. J Virol. 1971 Nov;8(5):630–642. doi: 10.1128/jvi.8.5.630-642.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crippa M., Tocchini-Valentini G. P. Synthesis of amplified DNA that codes for ribosomal RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Nov;68(11):2769–2773. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.11.2769. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman N. C., Spiegelman S. Distinguishing reverse transcriptase of an RNA tumor virus from other known DNA polymerases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Sep;68(9):2203–2206. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.9.2203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanafusa H., Miyamoto T., Hanafusa T. A cell-associated factor essential for formation of an infectious form of Rous sarcoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jun;66(2):314–321. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.2.314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizutani S., Boettiger D., Temin H. M. A DNA-depenent DNA polymerase and a DNA endonuclease in virions of Rous sarcoma virus. Nature. 1970 Oct 31;228(5270):424–427. doi: 10.1038/228424a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizutani S., Temin H. M. Enzymes and nucleotides in virions of Rous sarcoma virus. J Virol. 1971 Oct;8(4):409–416. doi: 10.1128/jvi.8.4.409-416.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson D. A., Baxter-Gabbard K. L., Levine A. S. Avian reticuloendotheliosis virus (strain T): V. DNA polymerase. Virology. 1972 Jan;47(1):251–254. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90259-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SARMA P. S., TURNER H. C., HUEBNER R. J. AN AVIAN LEUCOSIS GROUP-SPECIFIC COMPLEMENT FIXATION REACTION. APPLICATION FOR THE DETECTION AND ASSAY OF NON-CYTOPATHOGENIC LEUCOSIS VIRUSES. Virology. 1964 Jul;23:313–321. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(64)90253-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scolnick E. M., Parks W. P., Todaro G. J., Aaronson S. A. Immunological characterization of primate C-type virus reverse transcriptases. Nat New Biol. 1972 Jan 12;235(54):35–40. doi: 10.1038/newbio235035a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TEMIN H. M. HOMOLOGY BETWEEN RNA FROM ROUS SARCOMA VIROUS AND DNA FROM ROUS SARCOMA VIRUS-INFECTED CELLS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Aug;52:323–329. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.2.323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Temin H. M. Malignant transformation of cells by viruses. Perspect Biol Med. 1970 Autumn;14(1):11–26. doi: 10.1353/pbm.1970.0006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Temin H. M., Mizutani S. RNA-dependent DNA polymerase in virions of Rous sarcoma virus. Nature. 1970 Jun 27;226(5252):1211–1213. doi: 10.1038/2261211a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Temin H. M. Studies on carcinogenesis by avian sarcoma viruses. 8. Glycolysis and cell multiplication. Int J Cancer. 1968 Mar 15;3(2):273–282. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910030213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells R. D., Flügel R. M., Larson J. E., Schendel P. F., Sweet R. W. Comparison of some reactions catalyzed by deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase from avian myeloblastosis virus, Escherichia coli, and Micrococcus luteus. Biochemistry. 1972 Feb 15;11(4):621–629. doi: 10.1021/bi00754a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


