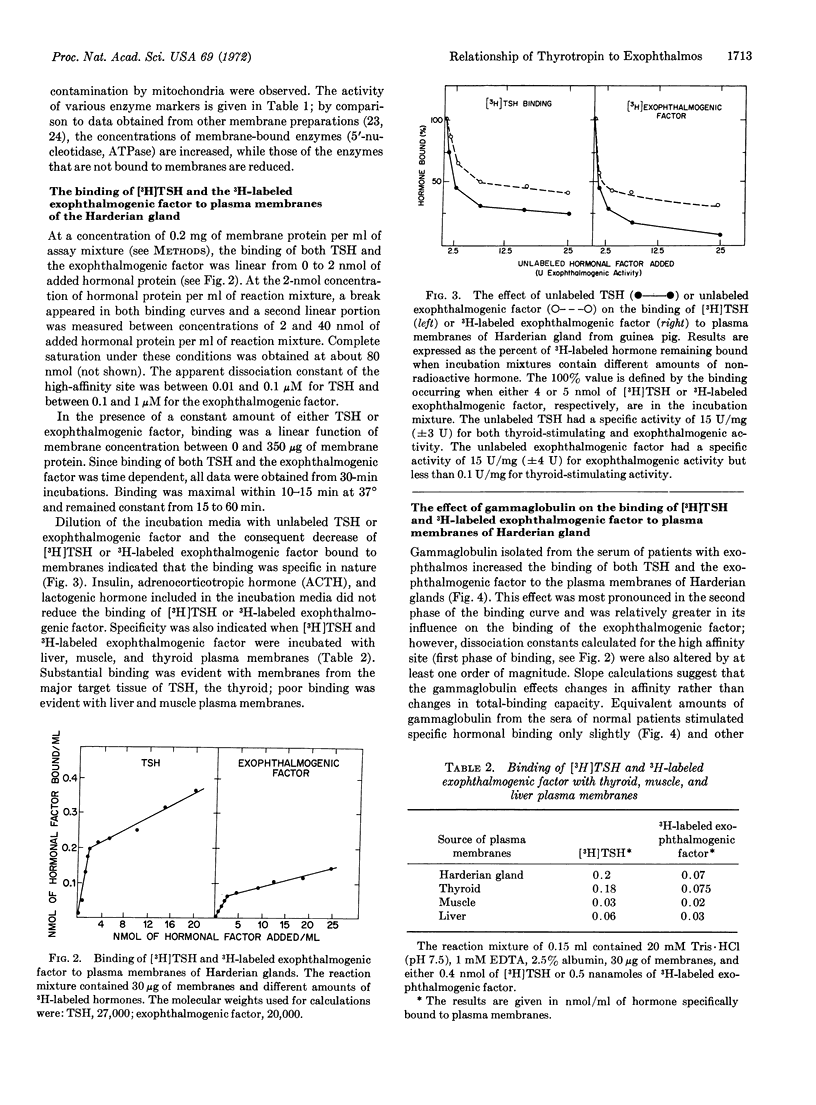
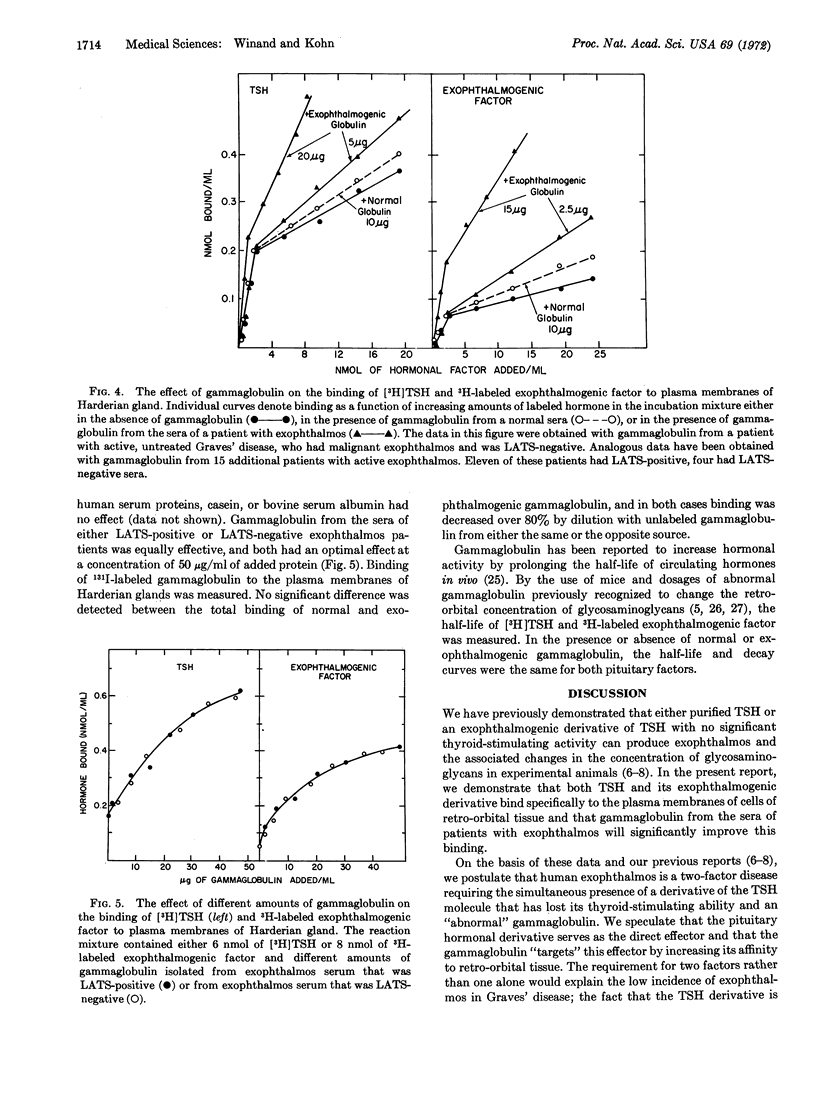
Abstract
Plasma membranes of cells from retroorbital tissue have been prepared from the Harderian glands of guinea pigs and have been characterized as being reasonably free of other subcellular structures by electron microscopy and by enzyme-marker analyses. Both bovine thyrotropin and a proteolytic derivative of bovine thyrotropin with exophthalmogenic activity but without thyroid-stimulating activity specifically bind to these membranes. Gammaglobulin from the sera of patients with malignant exophthalmos increases the binding of both pituitary factors, whereas binding is not similarly increased by gammaglobulin from the sera of individuals who are not exophthalmic. The increased binding caused by the gammaglobulin from exophthalmic patients is the same whether the sera are positive or negative for the long-acting thyroid stimulator. Present binding experiments do not indicate a direct interaction between the gammaglobulin and the plasma membranes of the cells from Harderian glands. A mechanism for the pathogenesis of human exophthalmos is proposed on the basis of these data.
Keywords: Graves' disease, pretibial myxedema, LATS, thyroid, Harderian gland
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BROUHON-MASSILLON L. CONTRIBUTION 'A L''ETUDE EXP'ERIMENTALE DE L'EXOPHTALMIE ENDOCRINIENNE. Doc Ophthalmol. 1963;17:249–302. doi: 10.1007/BF00573526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dedman M. L., Fawcett J. S., Morris C. J. The exophthalmogenic activity of bovine thyrotrophic preparations. J Endocrinol. 1967 Oct;39(2):197–205. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0390197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodfriend T. L., Webster M. E., McGuire J. S. Complex effects of antibodies to polypeptide hormones. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1970 May;30(5):565–572. doi: 10.1210/jcem-30-5-565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNTER W. M., GREENWOOD F. C. Preparation of iodine-131 labelled human growth hormone of high specific activity. Nature. 1962 May 5;194:495–496. doi: 10.1038/194495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohn L. D., Winand R. J. Relationship of thyrotropin to exophthalmos-producing substance. Formation of an exophthalmos-producing substance by pepsin digestion of pituitary glycoproteins containing both thyrotropic and exophthalmogenic activity. J Biol Chem. 1971 Nov;246(21):6570–6575. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kriss J. P., Pleshakov V., Rosenblum A. L., Holderness M., Sharp G., Utiger R. Studies on the pathogenesis of the ophthalmopathy of Graves' disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1967 Apr;27(4):582–593. doi: 10.1210/jcem-27-4-582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUDWIG A. W., BOAS N. F., SOFFER L. J. Role of mucopolysaccharides in pathogenesis of experimental exophthalmos. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1950 Jan;73(1):137-40, illust. doi: 10.3181/00379727-73-17604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKENZIE J. M. The bioassay of thyrotropin in serum. Endocrinology. 1958 Sep;63(3):372–382. doi: 10.1210/endo-63-3-372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenzie J. M. Humoral factors in the pathogenesis of Graves' disease. Physiol Rev. 1968 Jan;48(1):252–310. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1968.48.1.252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenzie J. M., McCullagh E. P. Observations against a causal relationship between the long-acting thyroid stimulator and ophthalmopathy in Graves' disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1968 Aug;28(8):1177–1182. doi: 10.1210/jcem-28-8-1177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEVILLE D. M., Jr The isolation of a cell membrane fraction from rat liver. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1960 Oct;8:413–422. doi: 10.1083/jcb.8.2.413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pohl S. L., Birnbaumer L., Rodbell M. The glucagon-sensitive adenyl cyclase system in plasma membranes of rat liver. I. Properties. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 25;246(6):1849–1856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray T. K. A modified method for the isolation of the plasma membrane from rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Jan 6;196(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(70)90159-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodbell M., Krans H. M., Pohl S. L., Birnbaumer L. The glucagon-sensitive adenyl cyclase system in plasma membranes of rat liver. 3. Binding of glucagon: method of assay and specificity. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 25;246(6):1861–1871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SOBER H. A., PETERSON E. A. Protein chromatography on ion exchange cellulose. Fed Proc. 1958 Dec;17(4):1116–1126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh S. P., McKenzie J. M. The influence of thyrotropin on harderian gland glycosaminoglycans of the mouse. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1970 Nov;135(2):478–482. doi: 10.3181/00379727-135-35078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sisson J. C., Miles M. Acid mucopolysaccharide alterations in experimental exophthalmos. Endocrinology. 1967 May;80(5):931–937. doi: 10.1210/endo-80-5-931. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilfong R. F., Neville D. M., Jr The isolation of a brush border membrane fraction from rat kidney. J Biol Chem. 1970 Nov 25;245(22):6106–6112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winand R. J., Kohn L. D. Relationships of thyrotropin to exophthalmic-producing substance. Purification of homogeneous glycoproteins containing both activities from [3H]-labeled pituitary extracts. J Biol Chem. 1970 Mar 10;245(5):967–975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]