Abstract
By determination of the rheological flow curve of minute quantities of axoplasm drawn into a microcapillary tube connected to a high vacuum, extruded axoplasm was shown to behave as a pseudoplastic fluid with a viscosity of 106-times that of water and without significant signs of time-dependent thixotropic or viscoelastic properties. A theoretical analysis of peristaltic pumping of such pseudoplastic fluids by sinusoidal surface waves was combined with experimental studies of a mechanical model designed to simulate peristaltic drive. The correlation of the respective data permitted quantitative predictions for the peristaltic mechanism of axonal flow, with speed being a function of peristaltic wave geometry and fluid properties, yielding a theoretical mean value of 0.45 mm/day, i.e., of the same order as that observed in the living nerve fiber.
Keywords: neuroplasmic flow, model, viscosimetry, axoplasm
Full text
PDF

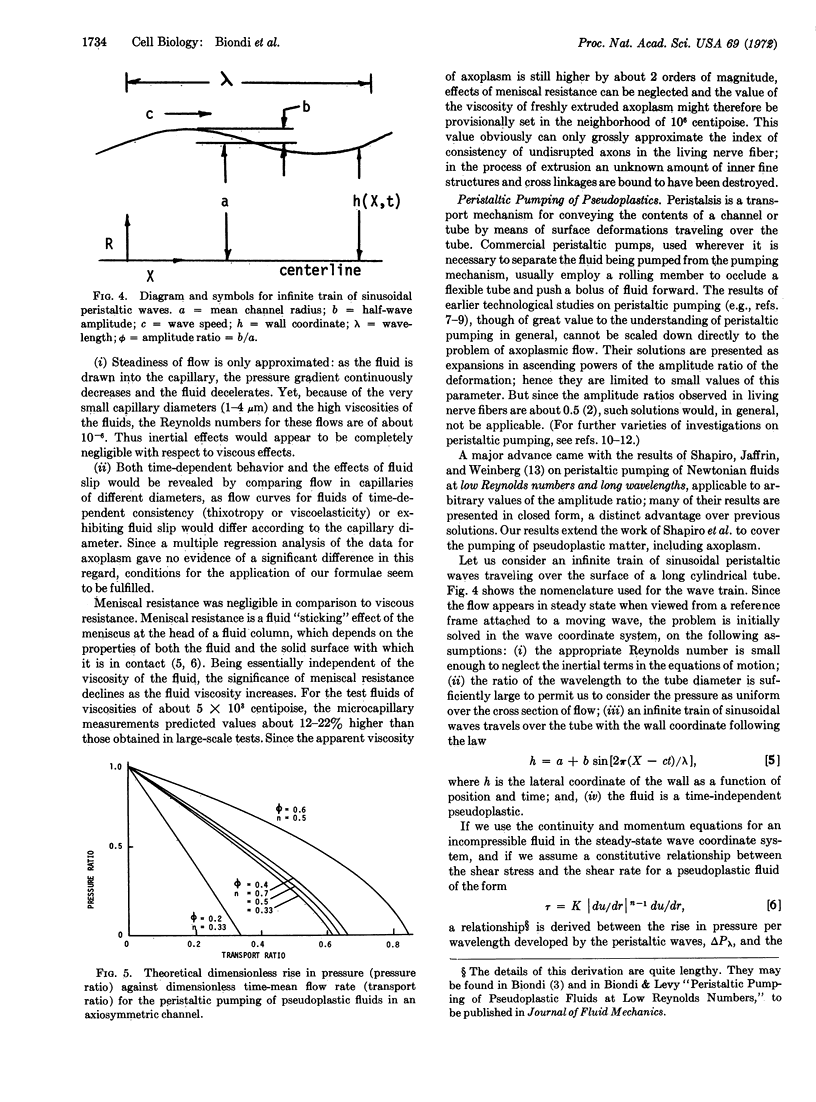
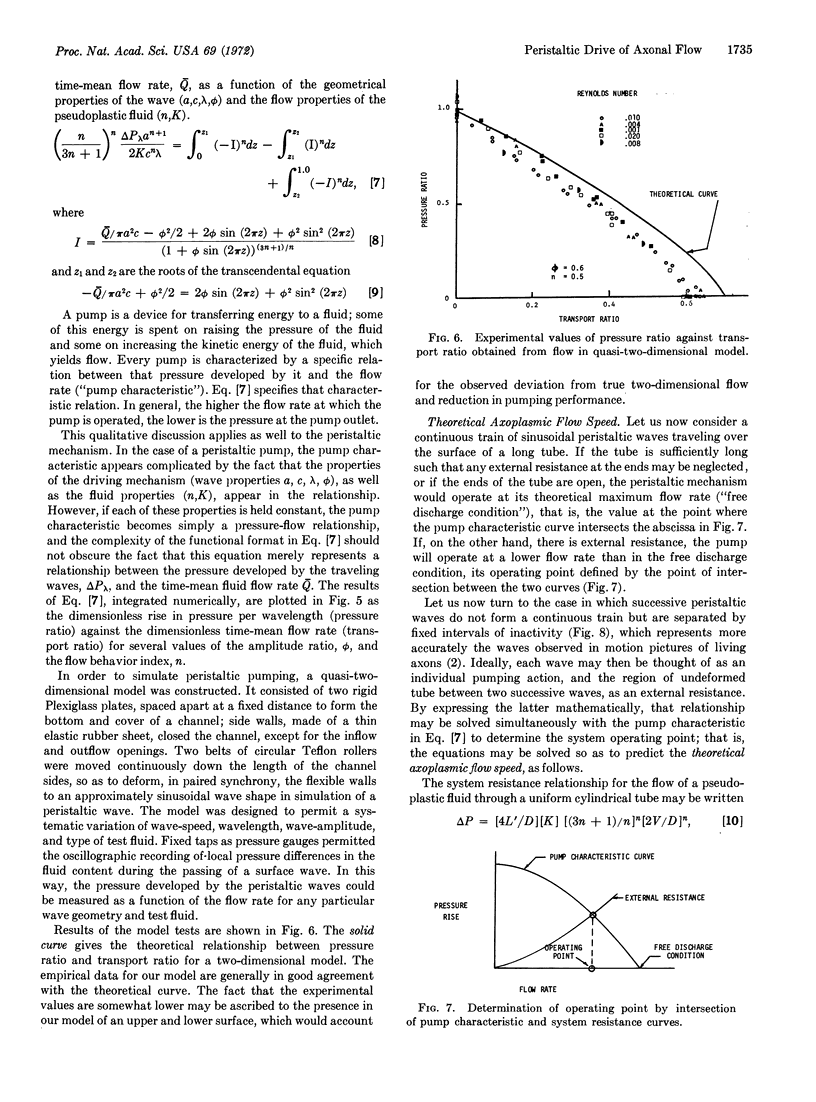

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barton C., Raynor S. Peristaltic flow in tubes. Bull Math Biophys. 1968 Dec;30(4):663–680. doi: 10.1007/BF02476682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mardles E. W. The flow of liquids through fine capillaries and narrow channels: the meniscus resistance (Jamin effect). Biorheology. 1969 Apr;6(1):1–10. doi: 10.3233/bir-1969-6101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss P. A., Mayr R. Organelles in neuroplasmic ("axonal") flow: neurofilaments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Apr;68(4):846–850. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.4.846. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss P. A. Neuronal dynamics and axonal flow. V. The semisolid state of the moving axonal column. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Mar;69(3):620–623. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.3.620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss P. A. Neuronal dynamics and axonal flow: axonal peristalsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 May;69(5):1309–1312. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.5.1309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



