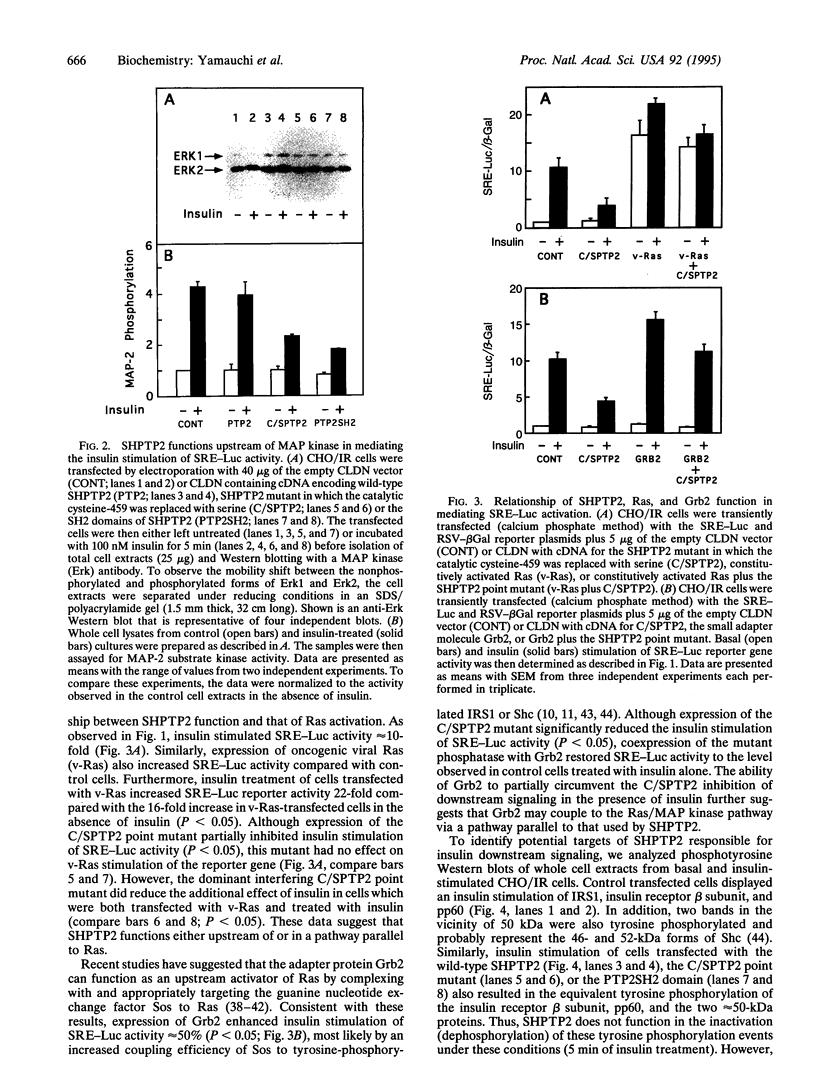
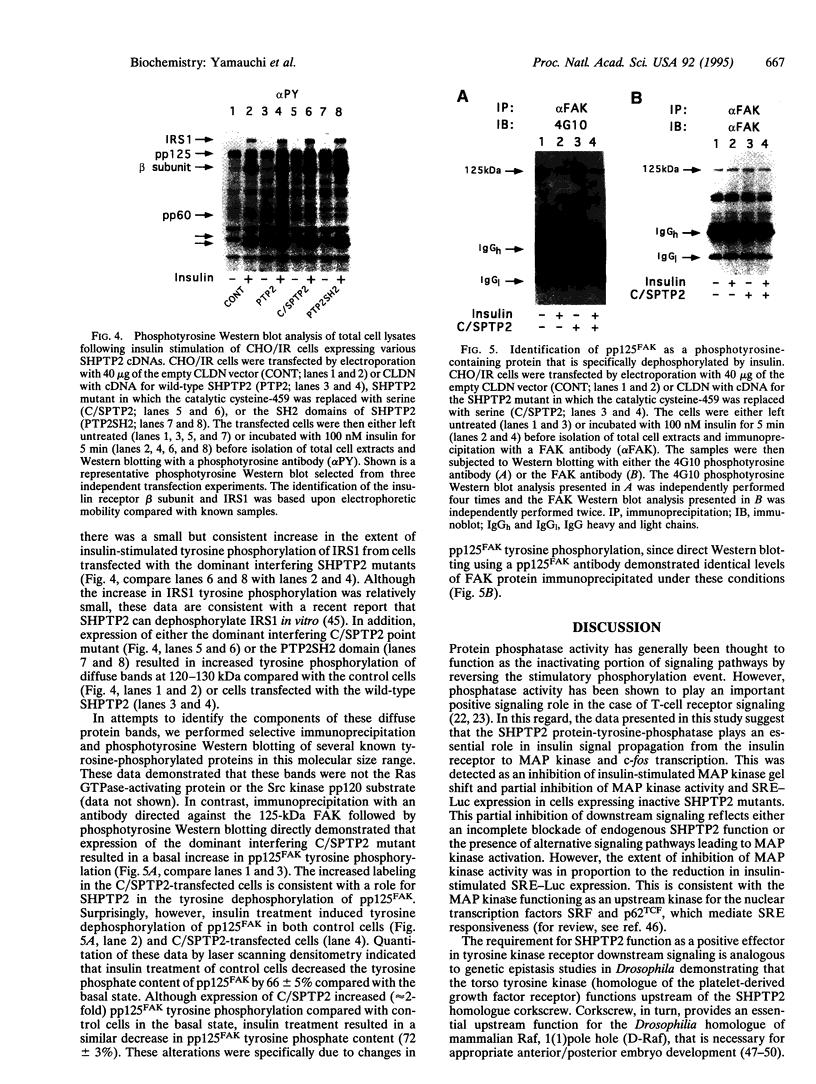
Abstract
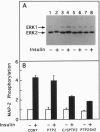
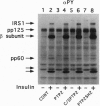
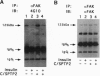
SHPTP2 is a ubiquitously expressed tyrosine-specific protein phosphatase that contains two amino-terminal Src homology 2 (SH2) domains responsible for its association with tyrosine-phosphorylated proteins. In this study, expression of dominant interfering mutants of SHPTP2 was found to inhibit insulin stimulation of c-fos reporter gene expression and activation of the 42-kDa (Erk2) and 44-kDa (Erk1) mitogen-activated protein kinases. Cotransfection of dominant interfering SHPTP2 mutants with v-Ras or Grb2 indicated that SHPTP2 regulated insulin signaling either upstream of or in parallel to Ras function. Furthermore, phosphotyrosine blotting and immunoprecipitation identified the 125-kDa focal adhesion kinase (pp125FAK) as a substrate for insulin-dependent tyrosine dephosphorylation. These data demonstrate that SHPTP2 functions as a positive regulator of insulin action and that insulin signaling results in the dephosphorylation of tyrosine-phosphorylated pp125FAK.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adachi M., Sekiya M., Miyachi T., Matsuno K., Hinoda Y., Imai K., Yachi A. Molecular cloning of a novel protein-tyrosine phosphatase SH-PTP3 with sequence similarity to the src-homology region 2. FEBS Lett. 1992 Dec 21;314(3):335–339. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)81500-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad S., Banville D., Zhao Z., Fischer E. H., Shen S. H. A widely expressed human protein-tyrosine phosphatase containing src homology 2 domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 15;90(6):2197–2201. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.6.2197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ambrosio L., Mahowald A. P., Perrimon N. Requirement of the Drosophila raf homologue for torso function. Nature. 1989 Nov 16;342(6247):288–291. doi: 10.1038/342288a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Backer J. M., Myers M. G., Jr, Shoelson S. E., Chin D. J., Sun X. J., Miralpeix M., Hu P., Margolis B., Skolnik E. Y., Schlessinger J. Phosphatidylinositol 3'-kinase is activated by association with IRS-1 during insulin stimulation. EMBO J. 1992 Sep;11(9):3469–3479. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05426.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltensperger K., Kozma L. M., Cherniack A. D., Klarlund J. K., Chawla A., Banerjee U., Czech M. P. Binding of the Ras activator son of sevenless to insulin receptor substrate-1 signaling complexes. Science. 1993 Jun 25;260(5116):1950–1952. doi: 10.1126/science.8391166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blenis J. Signal transduction via the MAP kinases: proceed at your own RSK. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):5889–5892. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.5889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buday L., Downward J. Epidermal growth factor regulates p21ras through the formation of a complex of receptor, Grb2 adapter protein, and Sos nucleotide exchange factor. Cell. 1993 May 7;73(3):611–620. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90146-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casanova J., Struhl G. Localized surface activity of torso, a receptor tyrosine kinase, specifies terminal body pattern in Drosophila. Genes Dev. 1989 Dec;3(12B):2025–2038. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.12b.2025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chardin P., Camonis J. H., Gale N. W., van Aelst L., Schlessinger J., Wigler M. H., Bar-Sagi D. Human Sos1: a guanine nucleotide exchange factor for Ras that binds to GRB2. Science. 1993 May 28;260(5112):1338–1343. doi: 10.1126/science.8493579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. J. The mitogen-activated protein kinase signal transduction pathway. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 15;268(20):14553–14556. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egan S. E., Giddings B. W., Brooks M. W., Buday L., Sizeland A. M., Weinberg R. A. Association of Sos Ras exchange protein with Grb2 is implicated in tyrosine kinase signal transduction and transformation. Nature. 1993 May 6;363(6424):45–51. doi: 10.1038/363045a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng G. S., Hui C. C., Pawson T. SH2-containing phosphotyrosine phosphatase as a target of protein-tyrosine kinases. Science. 1993 Mar 12;259(5101):1607–1611. doi: 10.1126/science.8096088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman R. M., Jr, Plutzky J., Neel B. G. Identification of a human src homology 2-containing protein-tyrosine-phosphatase: a putative homolog of Drosophila corkscrew. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 1;89(23):11239–11243. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.23.11239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiraga A., Munakata H., Hata K., Suzuki Y., Tsuiki S. Purification and characterization of a rat liver protein-tyrosine phosphatase with sequence similarity to src-homology region 2. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Oct 1;209(1):195–206. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb17277.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh T., Kaibuchi K., Masuda T., Yamamoto T., Matsuura Y., Maeda A., Shimizu K., Takai Y. A protein factor for ras p21-dependent activation of mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase through MAP kinase kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Feb 1;90(3):975–979. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.3.975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazlauskas A., Feng G. S., Pawson T., Valius M. The 64-kDa protein that associates with the platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta subunit via Tyr-1009 is the SH2-containing phosphotyrosine phosphatase Syp. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Aug 1;90(15):6939–6943. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.15.6939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koretzky G. A., Picus J., Schultz T., Weiss A. Tyrosine phosphatase CD45 is required for T-cell antigen receptor and CD2-mediated activation of a protein tyrosine kinase and interleukin 2 production. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 15;88(6):2037–2041. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.6.2037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koretzky G. A., Picus J., Thomas M. L., Weiss A. Tyrosine phosphatase CD45 is essential for coupling T-cell antigen receptor to the phosphatidyl inositol pathway. Nature. 1990 Jul 5;346(6279):66–68. doi: 10.1038/346066a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhné M. R., Pawson T., Lienhard G. E., Feng G. S. The insulin receptor substrate 1 associates with the SH2-containing phosphotyrosine phosphatase Syp. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 5;268(16):11479–11481. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhné M. R., Zhao Z., Rowles J., Lavan B. E., Shen S. H., Fischer E. H., Lienhard G. E. Dephosphorylation of insulin receptor substrate 1 by the tyrosine phosphatase PTP2C. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jun 3;269(22):15833–15837. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lechleider R. J., Freeman R. M., Jr, Neel B. G. Tyrosyl phosphorylation and growth factor receptor association of the human corkscrew homologue, SH-PTP2. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 25;268(18):13434–13438. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lechleider R. J., Sugimoto S., Bennett A. M., Kashishian A. S., Cooper J. A., Shoelson S. E., Walsh C. T., Neel B. G. Activation of the SH2-containing phosphotyrosine phosphatase SH-PTP2 by its binding site, phosphotyrosine 1009, on the human platelet-derived growth factor receptor. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 15;268(29):21478–21481. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leevers S. J., Marshall C. J. Activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase, ERK2, by p21ras oncoprotein. EMBO J. 1992 Feb;11(2):569–574. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05088.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li N., Batzer A., Daly R., Yajnik V., Skolnik E., Chardin P., Bar-Sagi D., Margolis B., Schlessinger J. Guanine-nucleotide-releasing factor hSos1 binds to Grb2 and links receptor tyrosine kinases to Ras signalling. Nature. 1993 May 6;363(6424):85–88. doi: 10.1038/363085a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milarski K. L., Zhu G., Pearl C. G., McNamara D. J., Dobrusin E. M., MacLean D., Thieme-Sefler A., Zhang Z. Y., Sawyer T., Decker S. J. Sequence specificity in recognition of the epidermal growth factor receptor by protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B. J Biol Chem. 1993 Nov 5;268(31):23634–23639. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers M. G., Jr, Backer J. M., Sun X. J., Shoelson S., Hu P., Schlessinger J., Yoakim M., Schaffhausen B., White M. F. IRS-1 activates phosphatidylinositol 3'-kinase by associating with src homology 2 domains of p85. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 1;89(21):10350–10354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.21.10350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers M. G., Jr, White M. F. The new elements of insulin signaling. Insulin receptor substrate-1 and proteins with SH2 domains. Diabetes. 1993 May;42(5):643–650. doi: 10.2337/diab.42.5.643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Rahilly S., Moller D. E. Mutant insulin receptors in syndromes of insulin resistance. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1992 Feb;36(2):121–132. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.1992.tb00945.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pang L., Decker S. J., Saltiel A. R. Bombesin and epidermal growth factor stimulate the mitogen-activated protein kinase through different pathways in Swiss 3T3 cells. Biochem J. 1993 Jan 1;289(Pt 1):283–287. doi: 10.1042/bj2890283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne D. M., Rossomando A. J., Martino P., Erickson A. K., Her J. H., Shabanowitz J., Hunt D. F., Weber M. J., Sturgill T. W. Identification of the regulatory phosphorylation sites in pp42/mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAP kinase). EMBO J. 1991 Apr;10(4):885–892. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08021.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelech S. L. Networking with protein kinases. Curr Biol. 1993 Aug 1;3(8):513–515. doi: 10.1016/0960-9822(93)90043-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins L. A., Larsen I., Perrimon N. corkscrew encodes a putative protein tyrosine phosphatase that functions to transduce the terminal signal from the receptor tyrosine kinase torso. Cell. 1992 Jul 24;70(2):225–236. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90098-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pronk G. J., McGlade J., Pelicci G., Pawson T., Bos J. L. Insulin-induced phosphorylation of the 46- and 52-kDa Shc proteins. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 15;268(8):5748–5753. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozakis-Adcock M., Fernley R., Wade J., Pawson T., Bowtell D. The SH2 and SH3 domains of mammalian Grb2 couple the EGF receptor to the Ras activator mSos1. Nature. 1993 May 6;363(6424):83–85. doi: 10.1038/363083a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruderman N. B., Kapeller R., White M. F., Cantley L. C. Activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase by insulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(4):1411–1415. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.4.1411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skolnik E. Y., Batzer A., Li N., Lee C. H., Lowenstein E., Mohammadi M., Margolis B., Schlessinger J. The function of GRB2 in linking the insulin receptor to Ras signaling pathways. Science. 1993 Jun 25;260(5116):1953–1955. doi: 10.1126/science.8316835. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skolnik E. Y., Lee C. H., Batzer A., Vicentini L. M., Zhou M., Daly R., Myers M. J., Jr, Backer J. M., Ullrich A., White M. F. The SH2/SH3 domain-containing protein GRB2 interacts with tyrosine-phosphorylated IRS1 and Shc: implications for insulin control of ras signalling. EMBO J. 1993 May;12(5):1929–1936. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05842.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprenger F., Stevens L. M., Nüsslein-Volhard C. The Drosophila gene torso encodes a putative receptor tyrosine kinase. Nature. 1989 Apr 6;338(6215):478–483. doi: 10.1038/338478a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stumpo D. J., Stewart T. N., Gilman M. Z., Blackshear P. J. Identification of c-fos sequences involved in induction by insulin and phorbol esters. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 5;263(4):1611–1614. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun X. J., Rothenberg P., Kahn C. R., Backer J. M., Araki E., Wilden P. A., Cahill D. A., Goldstein B. J., White M. F. Structure of the insulin receptor substrate IRS-1 defines a unique signal transduction protein. Nature. 1991 Jul 4;352(6330):73–77. doi: 10.1038/352073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor R. Insulin action 1991. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1991 Feb;34(2):159–171. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.1991.tb00287.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R. The serum response element. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Oct;17(10):423–426. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90013-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VanRenterghem B., Gibbs J. B., Maller J. L. Reconstitution of p21ras-dependent and -independent mitogen-activated protein kinase activation in a cell-free system. J Biol Chem. 1993 Sep 25;268(27):19935–19938. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel W., Lammers R., Huang J., Ullrich A. Activation of a phosphotyrosine phosphatase by tyrosine phosphorylation. Science. 1993 Mar 12;259(5101):1611–1614. doi: 10.1126/science.7681217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White M. F., Kahn C. R. The insulin signaling system. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 7;269(1):1–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White M. F., Maron R., Kahn C. R. Insulin rapidly stimulates tyrosine phosphorylation of a Mr-185,000 protein in intact cells. Nature. 1985 Nov 14;318(6042):183–186. doi: 10.1038/318183a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood K. W., Sarnecki C., Roberts T. M., Blenis J. ras mediates nerve growth factor receptor modulation of three signal-transducing protein kinases: MAP kinase, Raf-1, and RSK. Cell. 1992 Mar 20;68(6):1041–1050. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90076-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamauchi K., Holt K., Pessin J. E. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase functions upstream of Ras and Raf in mediating insulin stimulation of c-fos transcription. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 15;268(20):14597–14600. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamauchi K., Pessin J. E. Enhancement or inhibition of insulin signaling by insulin receptor substrate 1 is cell context dependent. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jul;14(7):4427–4434. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.7.4427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zachary I., Rozengurt E. Focal adhesion kinase (p125FAK): a point of convergence in the action of neuropeptides, integrins, and oncogenes. Cell. 1992 Dec 11;71(6):891–894. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90385-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vries-Smits A. M., Burgering B. M., Leevers S. J., Marshall C. J., Bos J. L. Involvement of p21ras in activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 2. Nature. 1992 Jun 18;357(6379):602–604. doi: 10.1038/357602a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]