Abstract
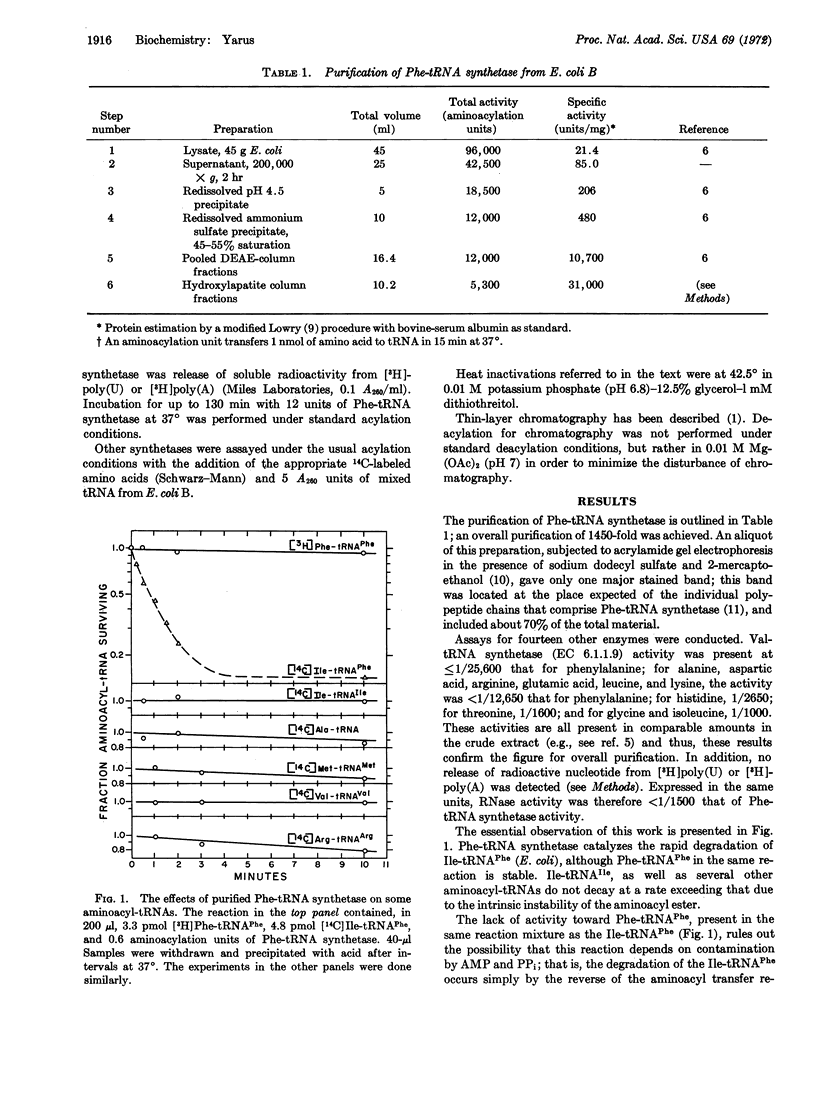
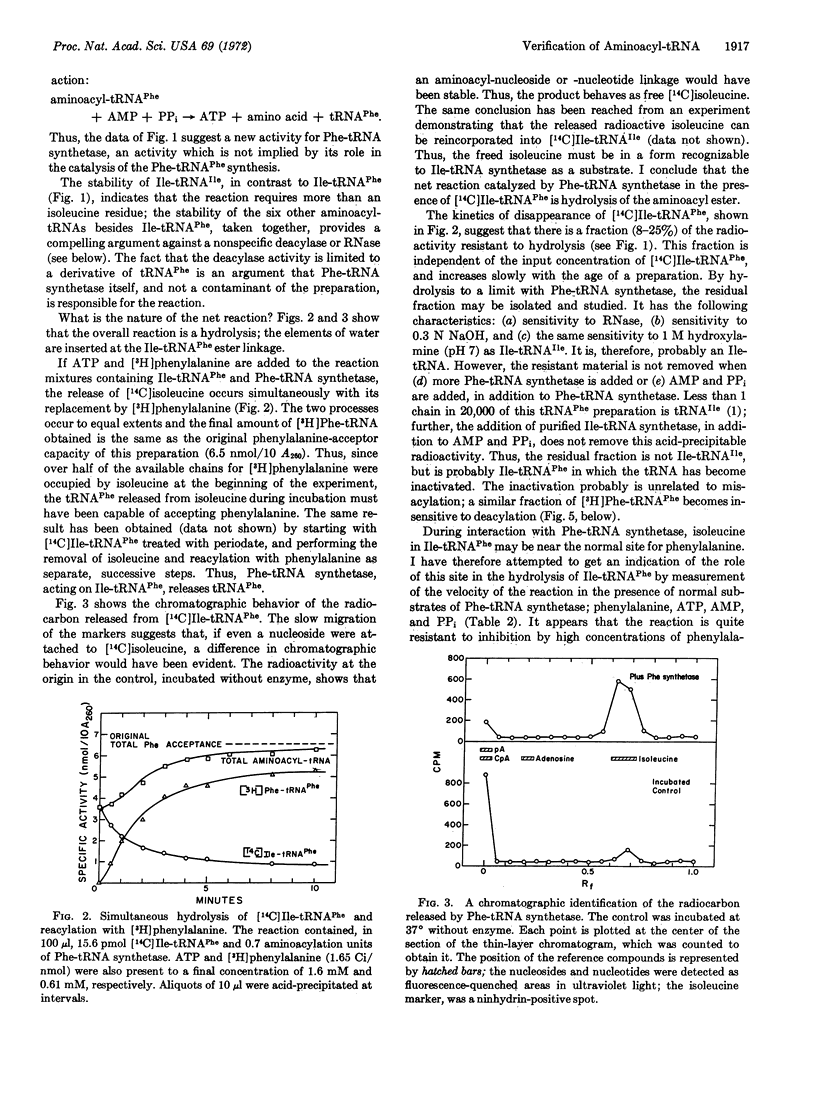
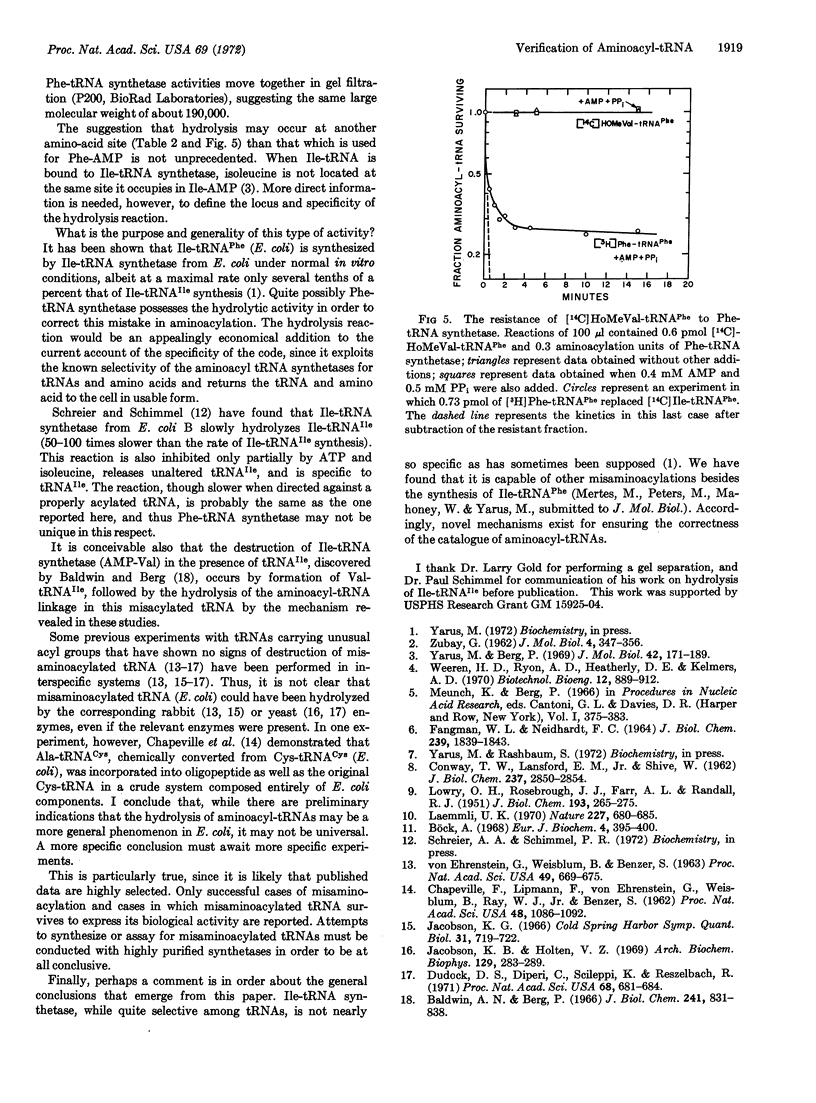
The synthesis of isoleucyl-tRNAPhe (Escherichia coli) proceeds at an appreciable rate under normal in vitro conditions in the presence of isoleucyl-tRNA synthetase (EC 6.1.1.5) from E. coli. The misacylated product is shown here to be hydrolyzed by highly purified phenylalanyl-tRNA synthetase from E. coli, with release of isoleucine and active tRNAPhe. Thus, phenylalanyl-tRNA synthetase possesses a previously unrecognized activity, which deacylates a mistakenly acylated tRNAPhe; the enzyme is inactive toward correctly matched aminoacyl tRNAs. Such a mechanism could serve to verify aminoacyl-tRNAs, deacylating those that are misacylated. Thus, a common generalization needs to be modified: an amino acid is not necessarily committed to a given (incorrect) anticodon when it is incorporated into aminoacyl-tRNA. It may be possible to correct it thereafter.
Keywords: misaminoacylation, coding, recognition
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baldwin A. N., Berg P. Purification and properties of isoleucyl ribonucleic acid synthetase from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1966 Feb 25;241(4):831–838. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böck A. Relation between subunit structure and temperature-sensitivity of mutant phenylalanyl RNA synthetases of Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1968 Apr;4(3):395–400. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1968.tb00225.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHAPEVILLE F., LIPMANN F., VON EHRENSTEIN G., WEISBLUM B., RAY W. J., Jr, BENZER S. On the role of soluble ribonucleic acid in coding for amino acids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Jun 15;48:1086–1092. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.6.1086. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CONWAY T. W., LANSFORD E. M., Jr, SHIVE W. Purification and substrate specificity of a phenylalanine-activating enzyme from Escherichia coli 9723. J Biol Chem. 1962 Sep;237:2850–2854. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudock B., DiPeri C., Scileppi K., Reszelbach R. The yeast phenylalanyl-transfer RNA synthetase recognition site: the region adjacent to the dihydrouridine loop. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Mar;68(3):681–684. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.3.681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrenstein G., Weisblum B., Benzer S. THE FUNCTION OF sRNA AS AMINO ACID ADAPTOR IN THE SYNTHESIS OF HEMOGLOBIN. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 May;49(5):669–675. doi: 10.1073/pnas.49.5.669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FANGMAN W. L., NEIDHARDT F. C. DEMONSTRATION OF AN ALTERED AMINOACYL RIBONUCLEIC ACID SYNTHETASE IN A MUTANT OF ESCHERICHIA COLI. J Biol Chem. 1964 Jun;239:1839–1843. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holten V. Z., Jacobson K. B. Studies on the aminoacylation of valine- and alanine-specific transfer RNA of Escherichia coli by aminoacyl transfer RNA synthetases from Neurospora crassa and E. coli. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Jan;129(1):283–289. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90177-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson K. B. A test of tRNA as amino acid adaptor in hemoglobin synthesis. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1966;31:719–722. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1966.031.01.092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeren H. O., Ryon A. D., Heatherly D. E., Kelmers A. D. Gram-scale purification of arginine, formylmethionione, glutamic acid and the nylalanine transfer ribonucleic acids from E. coli K-12MO7. Biotechnol Bioeng. 1970 Nov;12(6):889–912. doi: 10.1002/bit.260120604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarus M., Berg P. Recognition of tRNA by isoleucyl-tRNA synthetase. Effect of substrates on the dynamics of tRNA-enzyme interaction. J Mol Biol. 1969 Jun 14;42(2):171–189. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90037-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


