Abstract
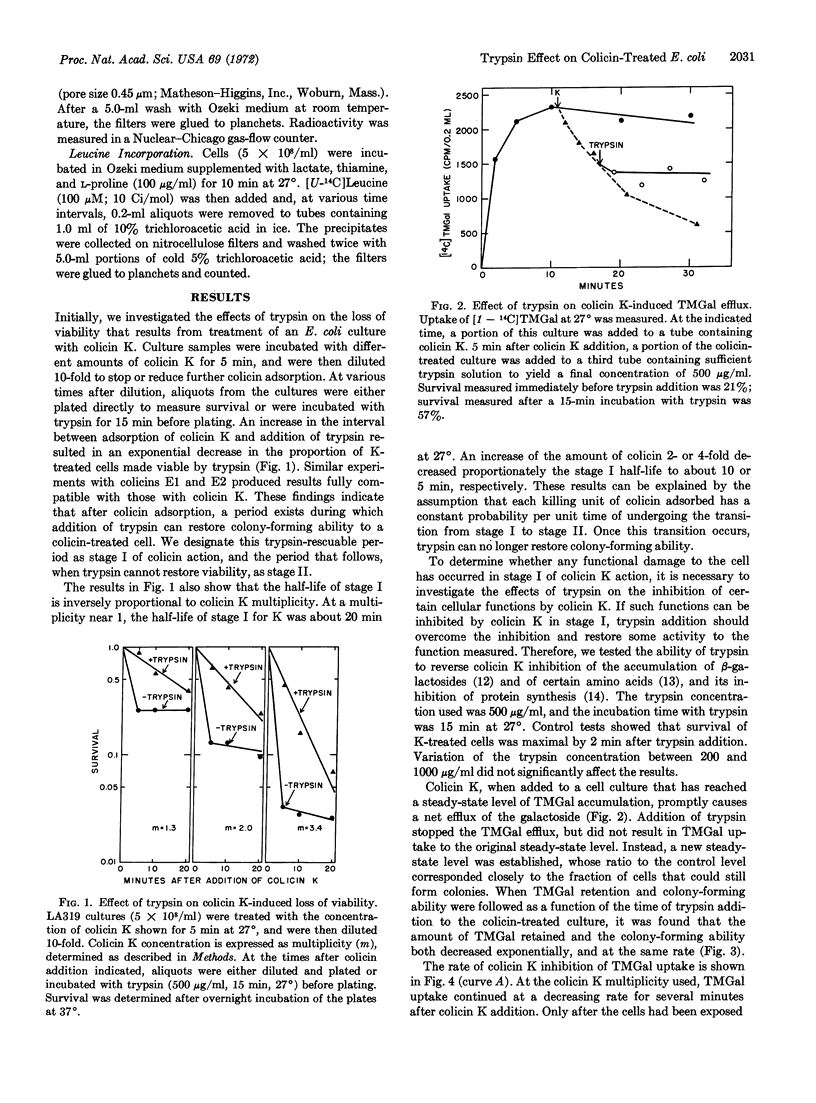
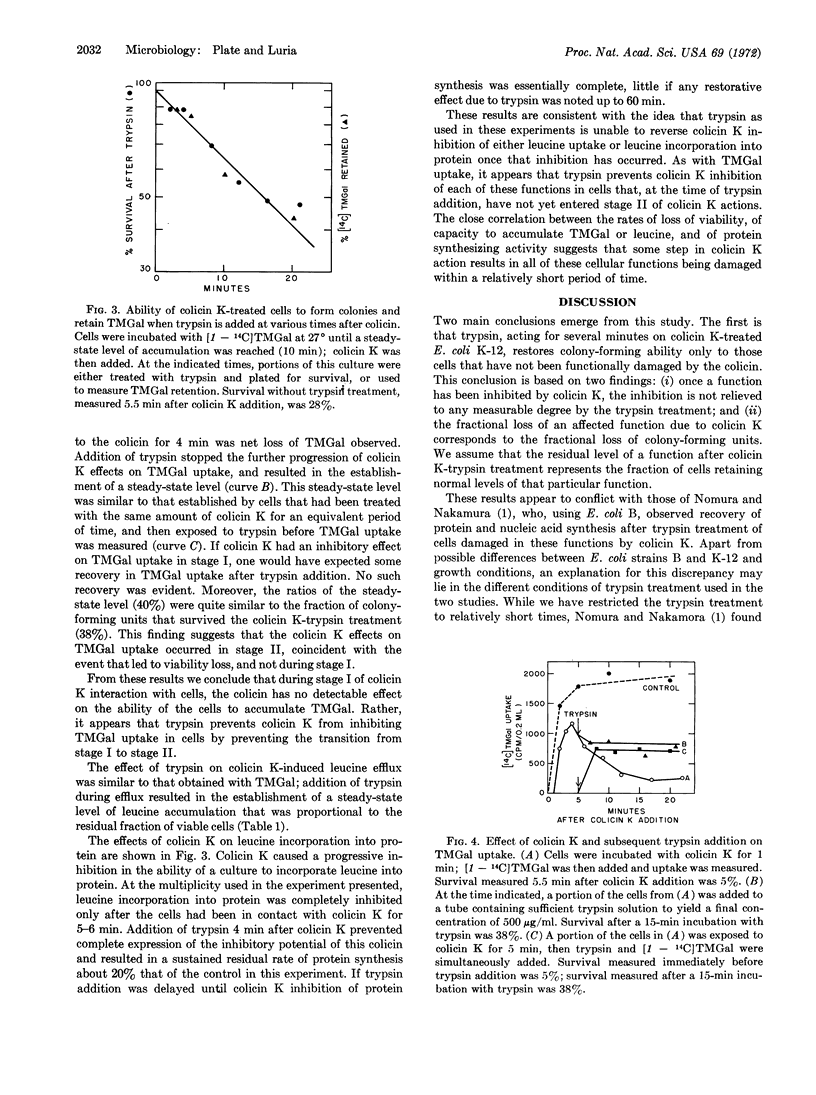
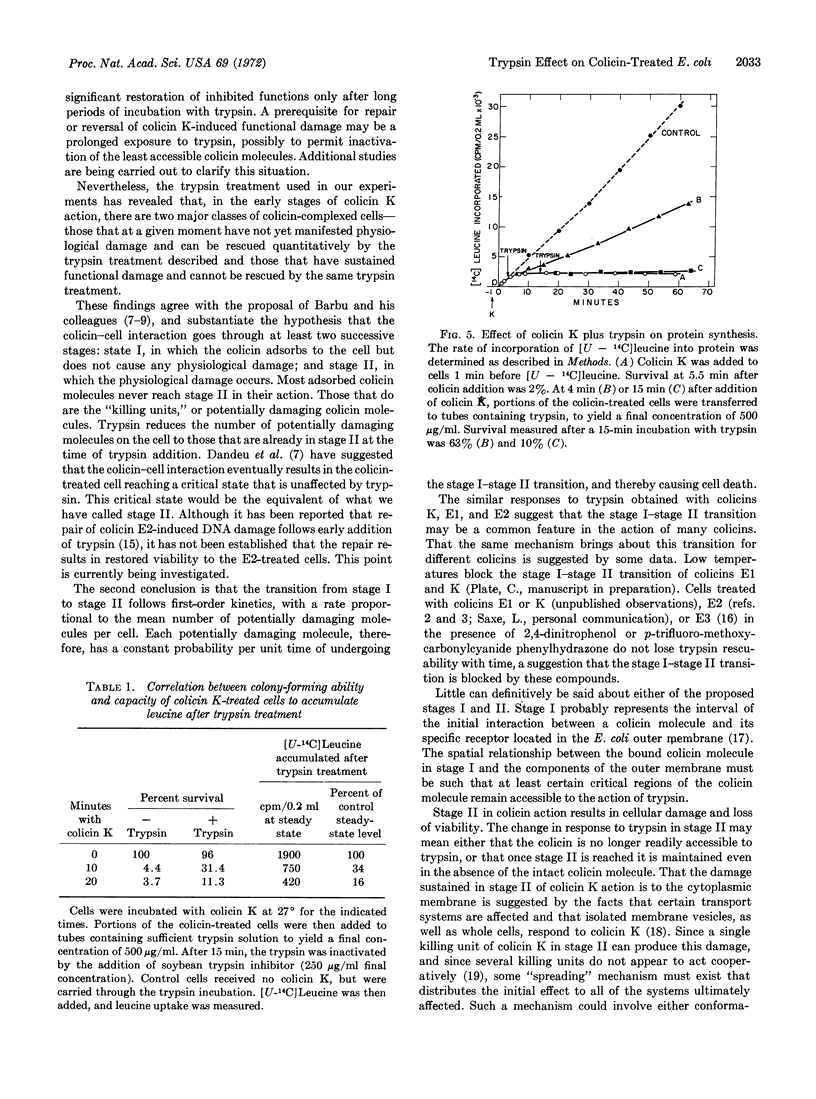
The effects of trypsin on Escherichia coli cells that have been treated with colicins have been examined. By the use of trypsin, it has been possible to demonstrate that the action of several colicins (E1, E2, and K) proceeds through at least two stages. Stage I is a period after colicin adsorption when trypsin can restore colony-forming ability to a colicin-treated cell. Stage I is followed by a period when trypsin is unable to restore colony-forming ability (stage II). The transition between stage I and stage II follows first-order kinetics, with a rate proportional to the number of killing units of colicin adsorbed.
A quantitative comparison of the effects of colicin K on colony-forming ability and on several cellular processes indicates that colicin damage to these processes occurs in the stage II period of colicin action and is not subject to reversal by the trypsin treatment that restores viability to cell in stage I. The implications of these findings for an understanding of the mode of action of colicins are discussed.
Keywords: irreversible, protein synthesis, sugar transport, aminoacid uptake, viability
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almendinger R., Hager L. P. Role for endonuclease I in the transmission process of colicin E 2 . Nat New Biol. 1972 Feb 16;235(59):199–203. doi: 10.1038/newbio235199a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boon T. Inactivation of ribosomes in vitro by colicin E 3 . Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Oct;68(10):2421–2425. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.10.2421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowman C. M., Sidikaro J., Nomura M. Specific inactivation of ribosomes by colicin E3 in vitro and mechanism of immunity in colicinogenic cells. Nat New Biol. 1971 Dec 1;234(48):133–137. doi: 10.1038/newbio234133a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavard D., Marotel-Schirmann J., Barbu E. Réversion de la fixation des colicines. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1971 Sep 27;273(13):1167–1170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavard D., Rampini C., Barbu E., Polonovski J. Activité phospholipasique et autres modifications du métabolisme des phospholipides consécutives a l'action des colicines sur E. coli. Bull Soc Chim Biol (Paris) 1968 Dec;50(9):1455–1471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Changeux J. P., Thiéry J. On the mode of action of colicins: a model of regulation at the membrane level. J Theor Biol. 1967 Nov;17(2):315–318. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(67)90175-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dandeu J. P., Billault A., Barbu E. Action des colicines sur la vitesse de sortie du potassium intracellulaire. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1969 Nov 17;269(20):2044–2047. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields K. L., Luria S. E. Effects of colicins E1 and K on transport systems. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jan;97(1):57–63. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.1.57-63.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACOB F., SIMINOVITCH L., WOLLMAN E. Sur la biosynthèse d'une colicine et sur son mode d'action. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1952 Sep;83(3):295–315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LURIA S. E., ADAMS J. N., TING R. C. Transduction of lactose-utilizing ability among strains of E. coli and S. dysenteriae and the properties of the transducing phage particles. Virology. 1960 Nov;12:348–390. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(60)90161-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LURIA S. E. ON THE MECHANISMS OF ACTION OF COLICINS. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1964 Nov;107:SUPPL–SUPPL:73. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marotel-Schirmann J., Cavard D., Sandler L., Barbu E. Temps nécessaire à une colicine fixée sur une bactérie pour déclencher des processus irréversibles. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1970 Jan 5;270(1):230–233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOMURA M. MECHANISM OF ACTION OF COLICINES. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Dec;52:1514–1521. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.6.1514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOMURA M., NAKAMURA M. Reversibility of inhibition of nucleic acids and protein synthesis by colicin K. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1962 May 4;7:306–309. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(62)90196-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagel de Zwaig R., Luria S. E. Genetics and physiology of colicin-tolerant mutants of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1967 Oct;94(4):1112–1123. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.4.1112-1123.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS B. L., REEVES P. R. Some observations on the mode of action of colicin F. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1963 Apr 23;11:140–145. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(63)90081-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds B. L., Reeves P. R. Kinetics of adsorption of colicin CA42-E2 and reversal of its bactericidal activity. J Bacteriol. 1969 Oct;100(1):301–309. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.1.301-309.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ringrose P. Sedimentation analysis of DNA degradation products resulting from the action of colicin E2 on Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Aug 8;213(2):320–334. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(70)90040-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabet S. F., Schnaitman C. A. Localization and solubilization of colicin receptors. J Bacteriol. 1971 Oct;108(1):422–430. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.1.422-430.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scandella C. J., Kornberg A. A membrane-bound phospholipase A1 purified from Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1971 Nov 23;10(24):4447–4456. doi: 10.1021/bi00800a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer S. J., Nicolson G. L. The fluid mosaic model of the structure of cell membranes. Science. 1972 Feb 18;175(4023):720–731. doi: 10.1126/science.175.4023.720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smarda J. Some problems of the immediate action of colicines on susceptible bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (Bethesda) 1965;5:345–348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wendt L. Mechanism of colicin action: early events. J Bacteriol. 1970 Dec;104(3):1236–1241. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.3.1236-1241.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



