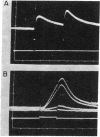
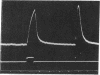
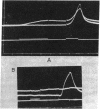
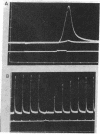
Abstract
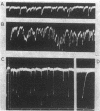
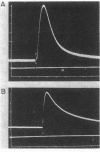
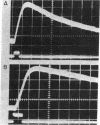
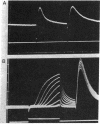
Cholinergic compounds, protein oxidizing agents, heavy metal ions, and organic mercurials were microelectrophoretically (or electro-osmotically) applied to the innervated surface of the isolated electroplax of Electrophorus electricus. Phasic potential changes, resembling those observed under similar conditions in frog muscle, followed not only pulses of the common cholinergic drugs, but were also elicited by o-iodosobenzoate, p-chloromercuribenzoate, and Hg++ ions. These results suggest that cholinergic receptors of both the electroplax and amphibian endplates behave in essentially the same manner. The discrepancies previously observed can be attributed mainly to the different techniques of drug application.
Keywords: acetylcholine, o-iodosobenzoate, p-chloromercuribenzoate, Mg++, electro-osmotic technique
Full text
PDF
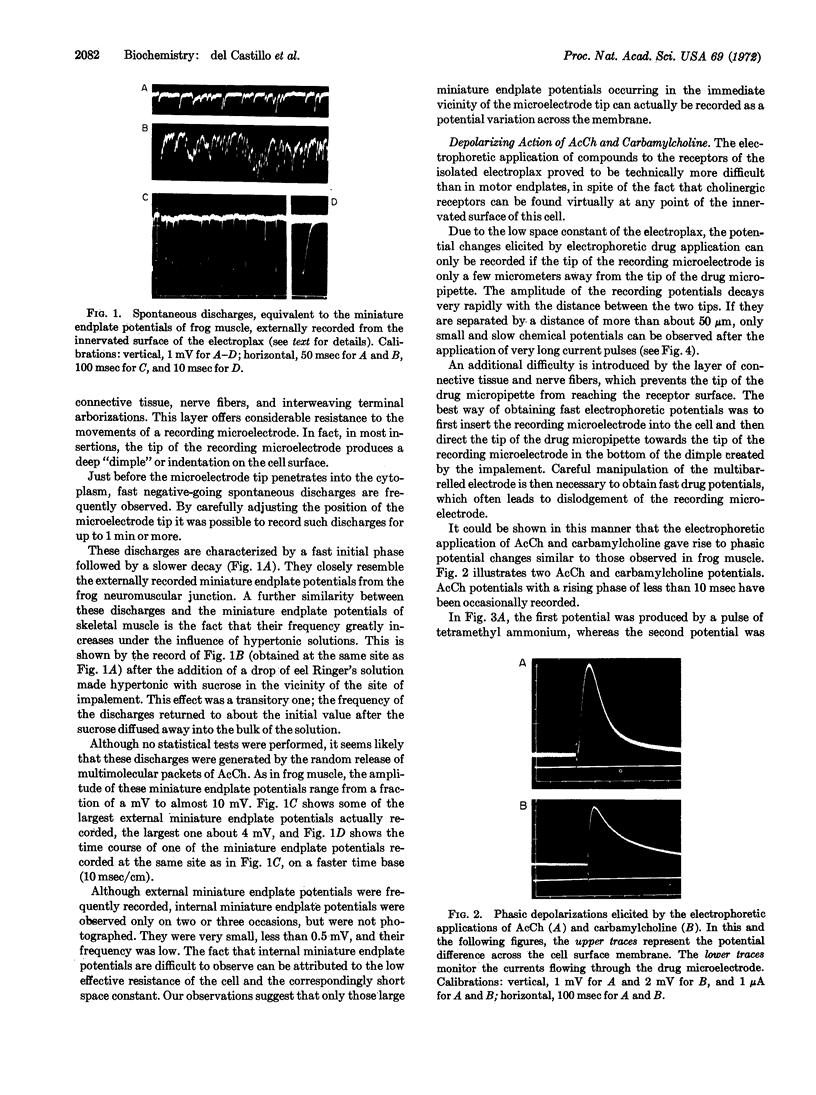
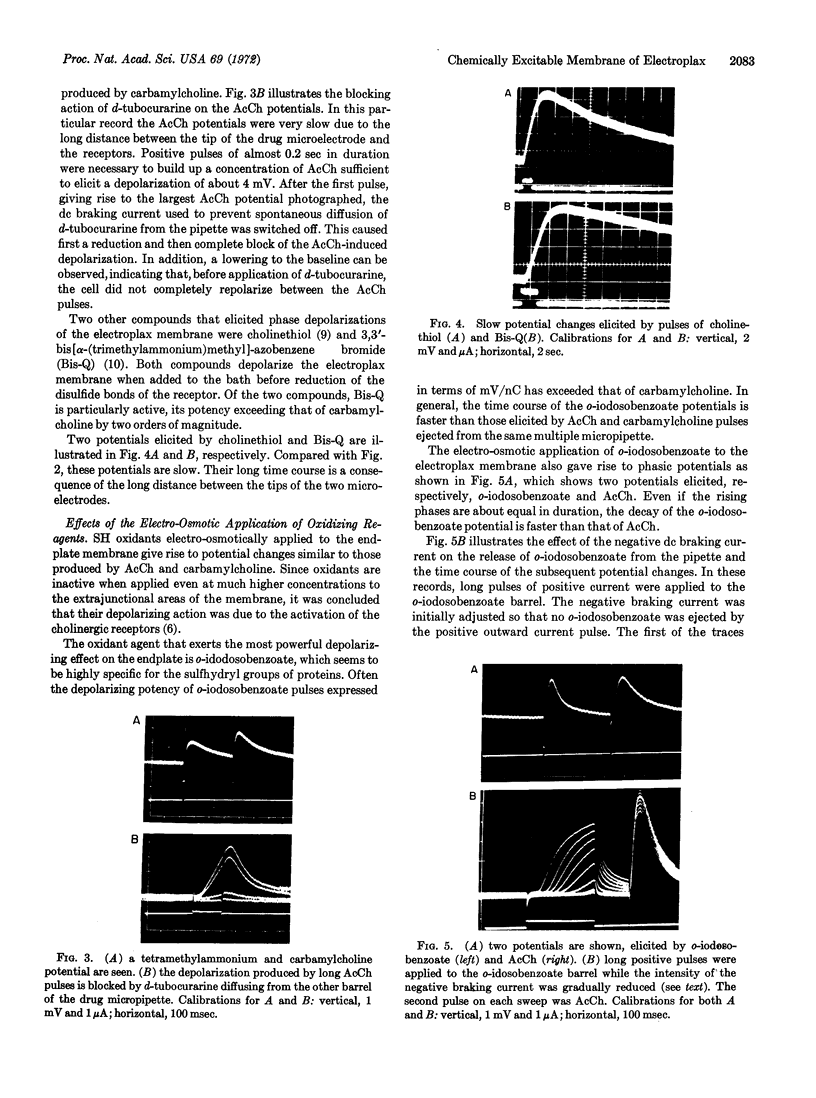


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bartels E., Deal W., Karlin A., Mautner H. G. Affinity oxidation of the reduced acetylcholine receptor. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Jun 2;203(3):568–571. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(70)90193-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartels E., Wassermann N. H., Erlanger B. F. Photochromic activators of the acetylcholine receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Aug;68(8):1820–1823. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.8.1820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEL CASTILLO J., KATZ B. Electrophoretic application of acetylcholine to the two sides of the end-plate membrane. J Physiol. 1954 Jul 28;125(1):16–7P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Del Castillo J., Escobar I., Gijón E. Effects of the electrophoretic application of sulfhydryl reagents to the end-plate receptors. Int J Neurosci. 1971 Feb;1(3):199–209. doi: 10.3109/00207457109146971. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIGMAN H. B., PODLESKI T. R., BARTELS E. APPARENT DISSOCIATION CONSTANTS BETWEEN CARBAMYLCHOLINE, DELTA-TUBOCURARINE AND THE RECEPTOR. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Sep 24;75:187–193. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)90597-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlin A., Bartels E. Effects of blocking sulfhydryl groups and of reducing disulfide bonds on the acetylcholine-activated permeability system of the electroplax. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Nov 8;126(3):525–535. doi: 10.1016/0926-6585(66)90010-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mautner H. G., Bartels E., Webb G. D. Sulfur and selenium isologs related to acetycholine. and choline IV. Activity in the electroplax preparation. Biochem Pharmacol. 1966 Feb;15(2):187–193. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(66)90059-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHOFFENIELS E. An isolated single electroplax preparation. II. Improved preparation for studying ion flux. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1957 Dec;26(3):585–596. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(57)90106-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHOFFENIELS E., NACHMANSOHN D. An isolated single electroplax preparation. I. New data on the effect of acetylcholine and related compounds. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1957 Oct;26(1):1–15. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(57)90047-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]