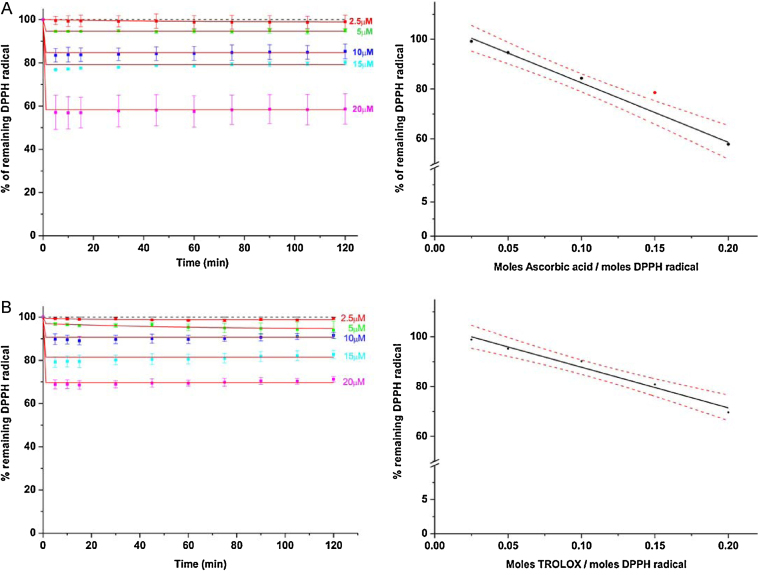
Fig. 3.
Time course of 100 μM DPPH radical reduction following addition of different concentrations of control antioxidants ascorbic acid and TROLOX at pH 3. The reaction mixture (1.0 ml) in 0.3% Triton X-100/0.1 M citrate phosphate buffer contained DPPH (100 μM) alone or in the presence of increasing concentrations of ascorbic acid (A) or TROLOX (B). For better comparison, each absorbance is displayed as percentage of the control absorbance with 100 μM DPPH in the respective buffer (short-dashed line). Data were fitted to an exponential decay using the function y = A1*exp(−x/t1) + A2*exp(−x/t2) + y0. Concentrations of the control antioxidants (in mole per mole DPPH radical) were plotted against the percentage of remaining DPPH radical after 30 min reaction time and extrapolated to obtain the EC50 value of ascorbic acid and TROLOX in the new buffer system (right panel in A and B). EC50 values were calculated from the fitted curve and represent the molar ratio of antioxidant to DPPH radical needed to decrease the initial DPPH concentration by 50%. Analysis of lower and upper confidence levels (95%) and linear or exponential correlation tests were determined using Origin 8.