Abstract
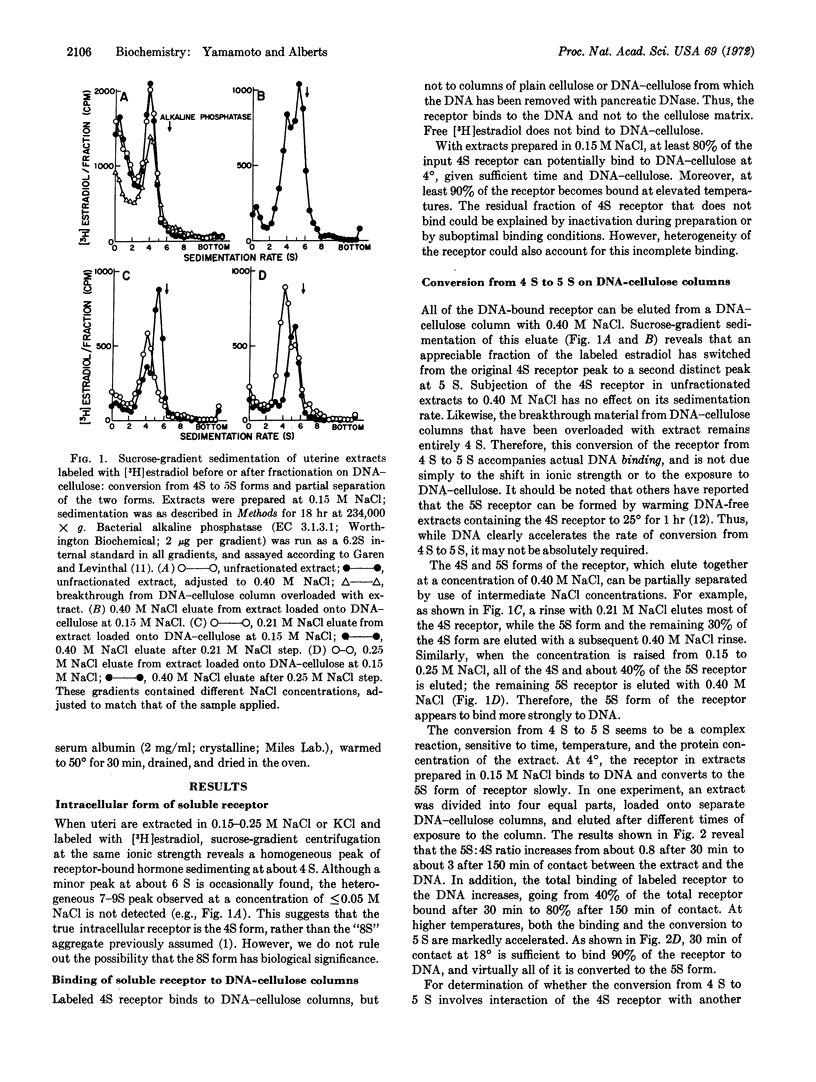
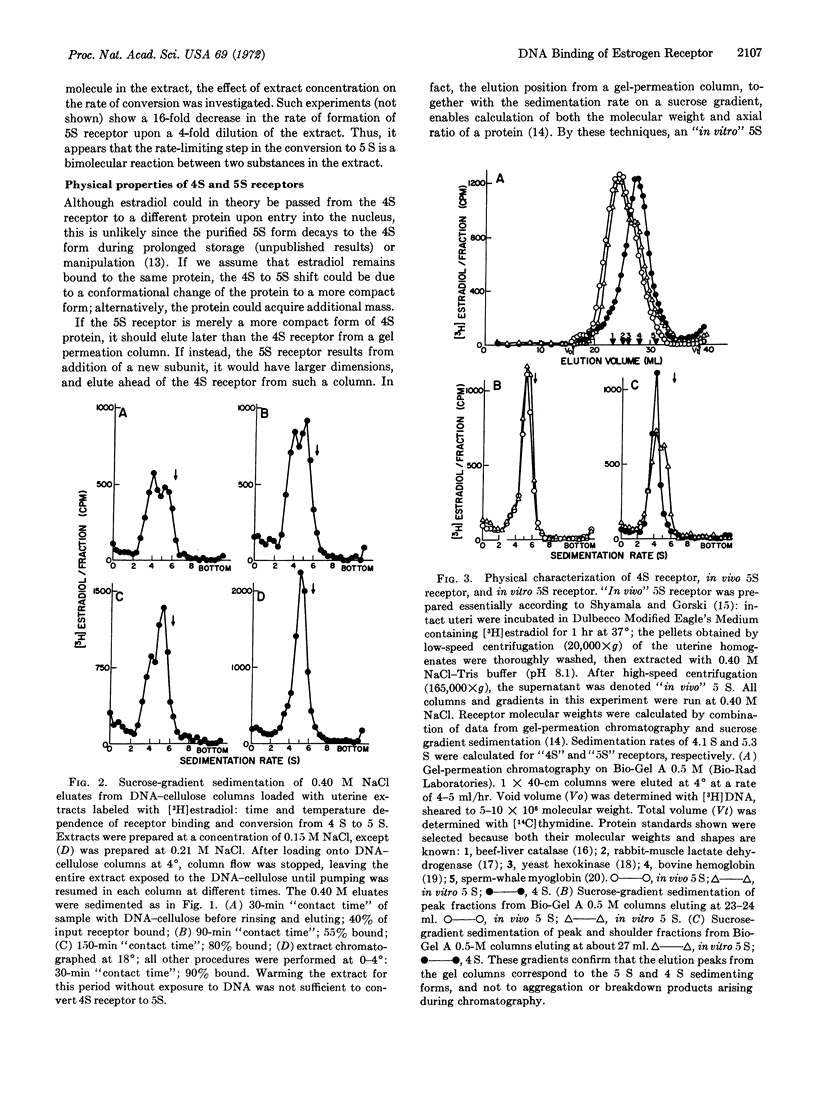
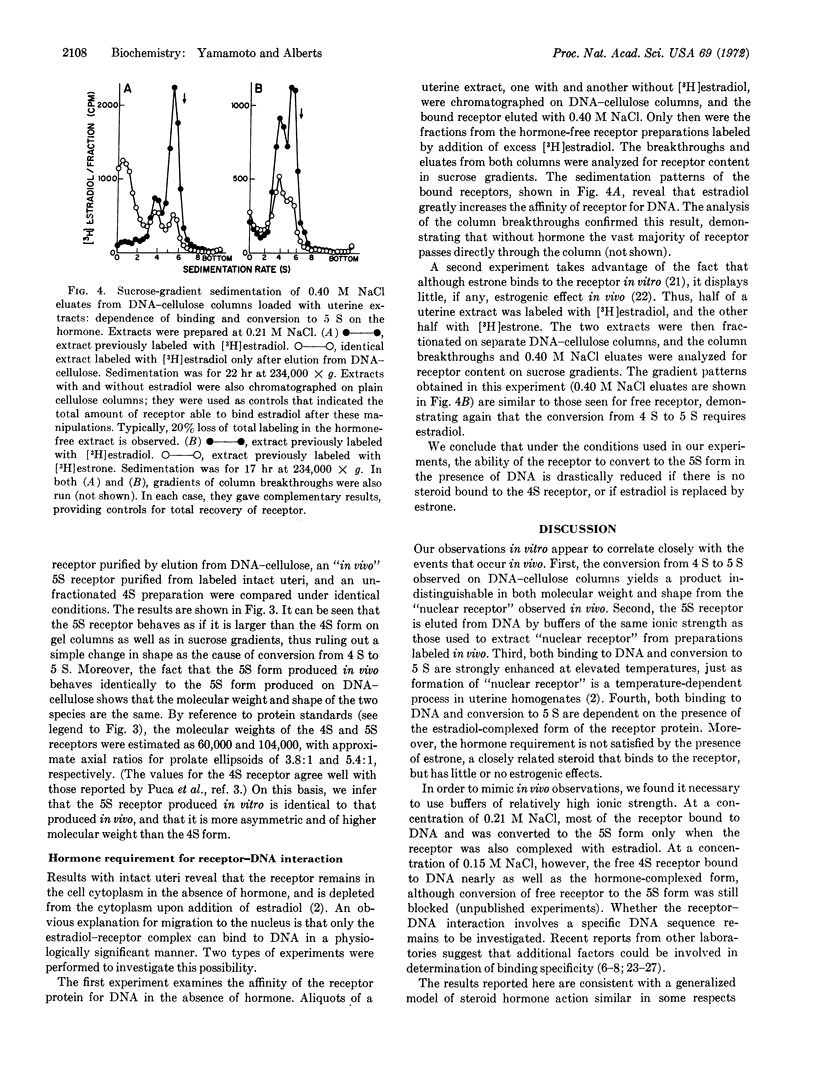
Early events in the action of 17-β-estradiol can be studied in soluble extracts of rat uterus by exposure of the estradiol-receptor protein to a DNA-cellulose matrix. After complexing with [3H]estradiol, the 4S receptor protein binds to the DNA, and it can be eluted with buffer of high ionic strength as a more tightly binding, 5S form. This parallels the in vivo situation, where migration of the receptor to the nucleus follows addition of hormone and is concomitant with a similar increase in sedimentation rate to 5 S. In both cases, the formation of a 5S receptor requires the presence of 17-β-estradiol. The rate at which 5S receptor forms is sensitive to extract concentration in a way that suggests that this receptor is a complex created by addition of a second subunit to the hormone-binding 4S component; physical studies on both in vivo and in vitro 5S receptors also support this view. These results are interpreted in terms of a model for action of estrogen in which the hormone potentiates binding of receptor to DNA, and in turn, the DNA-binding process triggers the cell response.
Keywords: DNA-cellulose chromatography, rat uterus
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baxter J. D., Rousseau G. G., Benson M. C., Garcea R. L., Ito J., Tomkins G. M. Role of DNA and specific cytoplasmic receptors in glucocorticoid action. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jul;69(7):1892–1896. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.7.1892. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fang S., Liao S. Androgen receptors. Steroid- and tissue-specific retention of a 17 beta-hydroxy-5 alpha-androstan-3-one-protein complex by the cell nuclei of ventral prostate. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jan 10;246(1):16–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GAREN A., LEVINTHAL C. A fine-structure genetic and chemical study of the enzyme alkaline phosphatase of E. coli. I. Purification and characterization of alkaline phosphatase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Mar 11;38:470–483. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)91282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GORSKI J. EARLY ESTROGEN EFFECTS ON THE ACTIVITY OF UTERINE RIBONUCLEIC ACID POLYMERASE. J Biol Chem. 1964 Mar;239:889–892. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gehring U., Tomkins G. M., Ohno S. Effect of the androgen-insensitivity mutation on a cytoplasmic receptor for dihydrotestosterone. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jul 28;232(30):106–107. doi: 10.1038/newbio232106a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton T. H. Control by estrogen of genetic transcription and translation. Binding to chromatin and stimulation of nucleolar RNA synthesis are primary events in the early estrogen action. Science. 1968 Aug 16;161(3842):649–661. doi: 10.1126/science.161.3842.649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris G. S. Nature of oestrogen specific binding sites in the nuclei of mouse uteri. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jun 23;231(25):246–248. doi: 10.1038/newbio231246a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen E. V., Numata M., Brecher P. I., Desombre E. R. Hormone-receptor interaction as a guide to biochemical mechanism. Biochem Soc Symp. 1971;32:133–159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen E. V., Suzuki T., Kawashima T., Stumpf W. E., Jungblut P. W., DeSombre E. R. A two-step mechanism for the interaction of estradiol with rat uterus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Feb;59(2):632–638. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.2.632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN R. G., AMES B. N. A method for determining the sedimentation behavior of enzymes: application to protein mixtures. J Biol Chem. 1961 May;236:1372–1379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurer H. R., Chalkley G. R. Some properties of a nuclear binding site of estradiol. J Mol Biol. 1967 Aug 14;27(3):431–441. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90049-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musliner T. A., Chader G. J. A role for DNA in the formation of nuclear estradiol-receptor complex in a cell-free system. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Nov;45(4):998–1003. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90436-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musliner T. A., Chader G. J., Villee C. A. Studies on estradiol receptors of the rat uterus. Nuclear uptake in vitro. Biochemistry. 1970 Oct 27;9(22):4448–4453. doi: 10.1021/bi00824a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Notides A., Gorski J. Estrogen-induced synthesis of a specific uterine protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Jul;56(1):230–235. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.1.230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Malley B. W. Hormonal regulation of nucleic acid and protein synthesis. Trans N Y Acad Sci. 1969 May;31(5):478–503. doi: 10.1111/j.2164-0947.1969.tb02930.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Malley B. W., Spelsberg T. C., Scharder W. T., Chytil F., Steggles A. W. Mechanisms of interaction of a hormone--receptor complex with the genome of a eukaryotic target cell. Nature. 1972 Jan 21;235(5334):141–144. doi: 10.1038/235141a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono S. Simplicity of mammalian regulatory systems inferred by single gene determination of sex phenotypes. Nature. 1971 Nov 19;234(5325):134–137. doi: 10.1038/234134a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PESCE A., MCKAY R. H., STOLZENBACH F., CAHN R. D., KAPLAN N. O. THE COMPARATIVE ENZYMOLOGY OF LACTIC DEHYDROGENASES. I. PROPERTIES OF THE CRYSTALLINE BEEF AND CHICKEN ENZYMES. J Biol Chem. 1964 Jun;239:1753–1761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pastan I., Perlman R. Cyclic adenosine monophosphate in bacteria. Science. 1970 Jul 24;169(3943):339–344. doi: 10.1126/science.169.3943.339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder W. A., Shelton J. R., Shelton J. B., Robberson B., Babin D. R. Amino acid sequence of the alpha-chain of bovine fetal hemoglobin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1967 Apr;120(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(67)90591-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel L. M., Monty K. J. Determination of molecular weights and frictional ratios of proteins in impure systems by use of gel filtration and density gradient centrifugation. Application to crude preparations of sulfite and hydroxylamine reductases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Feb 7;112(2):346–362. doi: 10.1016/0926-6585(66)90333-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spelsberg T. C., Steggles A. W., O'Malley B. W. Progesterone-binding components of chick oviduct. 3. Chromatin acceptor sites. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jul 10;246(13):4188–4197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steggles A. W., Spelsberg T. C., Glasser S. R., O'Malley B. W. Soluble complexes between steroid hormones and target-tissue receptors bind specifically to target-tissue chromatin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jul;68(7):1479–1482. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.7.1479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steitz T. A. Structure of yeast hexokinase-B. I. Preliminary x-ray studies and subunit structure. J Mol Biol. 1971 Nov 14;61(3):695–700. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90073-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toft D., Gorski J. A receptor molecule for estrogens: isolation from the rat uterus and preliminary characterization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Jun;55(6):1574–1581. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.6.1574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


