Abstract
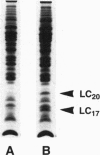
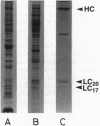
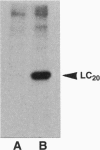
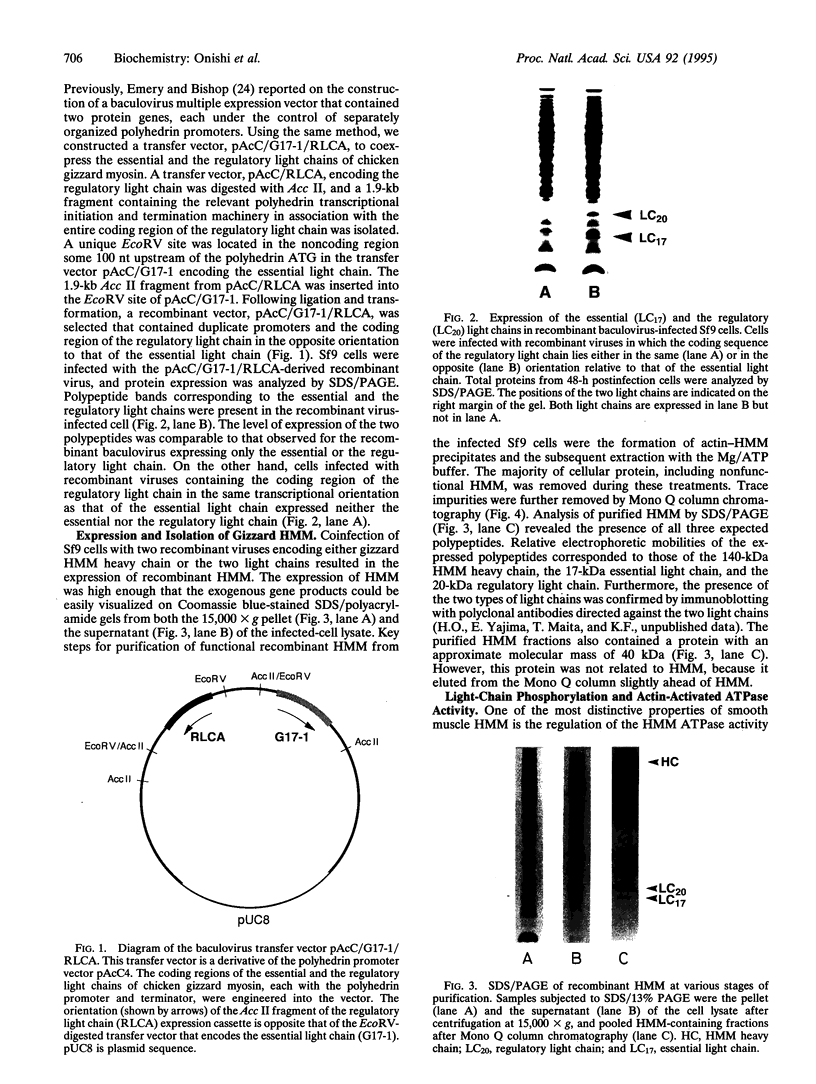
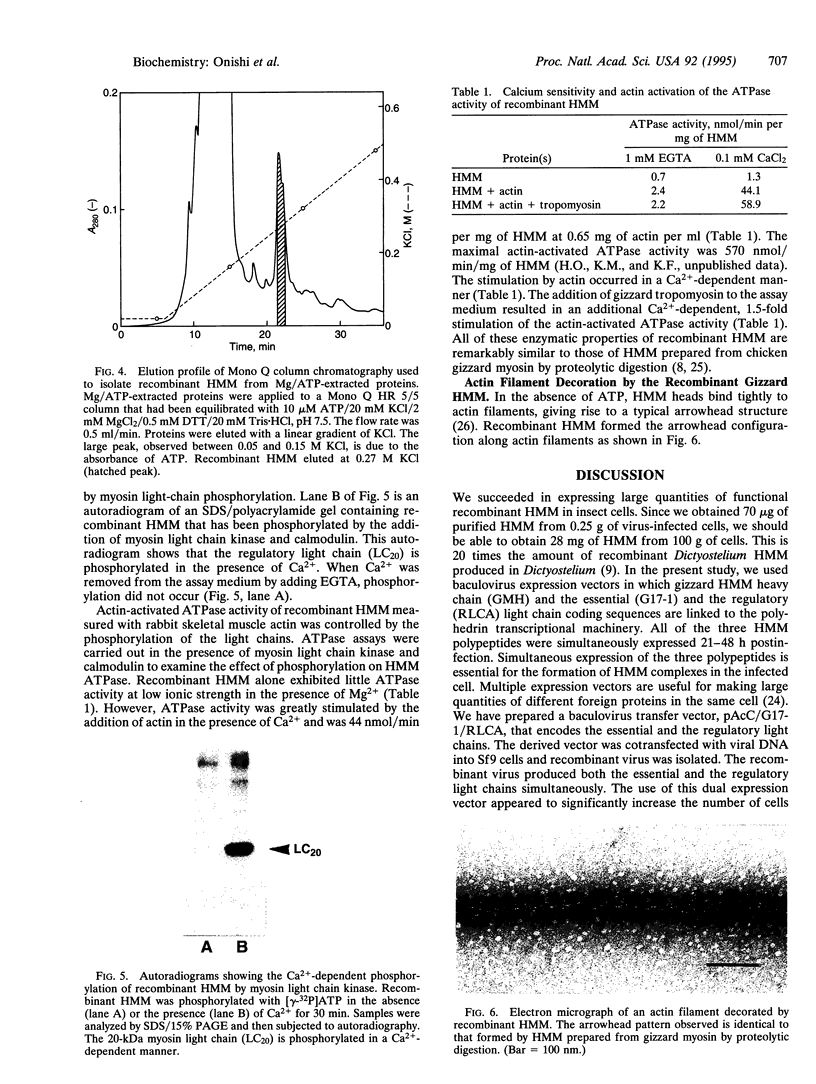
The heavy chain and the essential and the regulatory light chains of chicken gizzard heavy meromyosin (HMM) were coexpressed in Spodoptera frugiperda (fall armyworm) cells infected with a mixture of two recombinant Autographa californica baculoviruses. Soluble HMM consisting of the heavy chain and the two types of light chains was obtained. The recombinant HMM was purified from the virus-infected cells and characterized. The regulatory light chain of the isolated recombinant HMM was phosphorylated by myosin light chain kinase in the presence of calmodulin in a Ca(2+)-dependent manner. The ATPase of the recombinant HMM was activated by rabbit skeletal muscle actin when myosin light chain kinase, calmodulin, and Ca2+ were present in the reaction medium. Chicken gizzard tropomyosin enhanced the actin-activated ATPase activity. The recombinant HMM decorated actin filaments, displaying the characteristic arrowhead pattern along the filaments. This report on a functional recombinant double-headed smooth muscle myosin fragment opens the way to detailed studies on the molecule.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adelstein R. S., Eisenberg E. Regulation and kinetics of the actin-myosin-ATP interaction. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:921–956. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.004421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adelstein R. S., Klee C. B. Purification and characterization of smooth muscle myosin light chain kinase. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 25;256(14):7501–7509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emery V. C., Bishop D. H. The development of multiple expression vectors for high level synthesis of eukaryotic proteins: expression of LCMV-N and AcNPV polyhedrin protein by a recombinant baculovirus. Protein Eng. 1987 Aug-Sep;1(4):359–366. doi: 10.1093/protein/1.4.359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold L. Expression of heterologous proteins in Escherichia coli. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:11–14. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85004-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartshorne D. J., Siemankowski R. F. Regulation of smooth muscle actomyosin. Annu Rev Physiol. 1981;43:519–530. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.43.030181.002511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huxley H. E. The mechanism of muscular contraction. Science. 1969 Jun 20;164(3886):1356–1365. doi: 10.1126/science.164.3886.1356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikebe M., Tonomura Y., Onishi H., Watanabe S. Elementary steps in the F-actin activated Mg2+-ATPase reaction of gizzard H-meromysin: effects of phosphorylation of the light-chain subunit. J Biochem. 1981 Jul;90(1):61–77. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a133470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamisoyama H., Araki Y., Ikebe M. Mutagenesis of the phosphorylation site (serine 19) of smooth muscle myosin regulatory light chain and its effects on the properties of myosin. Biochemistry. 1994 Jan 25;33(3):840–847. doi: 10.1021/bi00169a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley C. A., Takahashi M., Yu J. H., Adelstein R. S. An insert of seven amino acids confers functional differences between smooth muscle myosins from the intestines and vasculature. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 15;268(17):12848–12854. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kodama T., Fukui K., Kometani K. The initial phosphate burst in ATP hydrolysis by myosin and subfragment-1 as studied by a modified malachite green method for determination of inorganic phosphate. J Biochem. 1986 May;99(5):1465–1472. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowey S., Slayter H. S., Weeds A. G., Baker H. Substructure of the myosin molecule. I. Subfragments of myosin by enzymic degradation. J Mol Biol. 1969 May 28;42(1):1–29. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90483-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messer N., Kendrick-Jones J. Chimaeric myosin regulatory light chains: sub-domain switching experiments to analyse the function of the N-terminal EF hand. J Mol Biol. 1991 Apr 20;218(4):825–835. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90270-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabeshima Y., Nabeshima Y., Nonomura Y., Fujii-Kuriyama Y. Nonmuscle and smooth muscle myosin light chain mRNAs are generated from a single gene by the tissue-specific alternative RNA splicing. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 5;262(22):10608–10612. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onishi H., Watanabe S. Chicken gizzard heavy meromyosin that retains the two light-chain components, including a phosphorylatable one. J Biochem. 1979 Feb;85(2):457–472. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a132352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruppel K. M., Egelhoff T. T., Spudich J. A. Purification of a functional recombinant myosin fragment from Dictyostelium discoideum. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1990;582:147–155. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1990.tb21675.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidel J. C. Fragmentation of gizzard myosin by alpha-chymotrypsin and papain, the effects on ATPase activity, and the interaction with actin. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 10;255(9):4355–4361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sellers J. R., Eisenberg E., Adelstein R. S. The binding of smooth muscle heavy meromyosin to actin in the presence of ATP. Effect of phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 10;257(23):13880–13883. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smillie L. B. Preparation and identification of alpha- and beta-tropomyosins. Methods Enzymol. 1982;85(Pt B):234–241. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(82)85023-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudich J. A., Watt S. The regulation of rabbit skeletal muscle contraction. I. Biochemical studies of the interaction of the tropomyosin-troponin complex with actin and the proteolytic fragments of myosin. J Biol Chem. 1971 Aug 10;246(15):4866–4871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trybus K. M., Chatman T. A. Chimeric regulatory light chains as probes of smooth muscle myosin function. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 25;268(6):4412–4419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagisawa M., Hamada Y., Katsuragawa Y., Imamura M., Mikawa T., Masaki T. Complete primary structure of vertebrate smooth muscle myosin heavy chain deduced from its complementary DNA sequence. Implications on topography and function of myosin. J Mol Biol. 1987 Nov 20;198(2):143–157. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90302-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yazawa M., Sakuma M., Yagi K. Calmodulins from muscles of marine invertebrates, scallop and sea anemone. J Biochem. 1980 May;87(5):1313–1320. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a132869. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zavodny P. J., Petro M. E., Kumar C. C., Dailey S. H., Lonial H. K., Narula S. K., Leibowitz P. J. The nucleotide sequence of chicken smooth muscle myosin light chain two. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 11;16(3):1214–1214. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.3.1214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]