Abstract
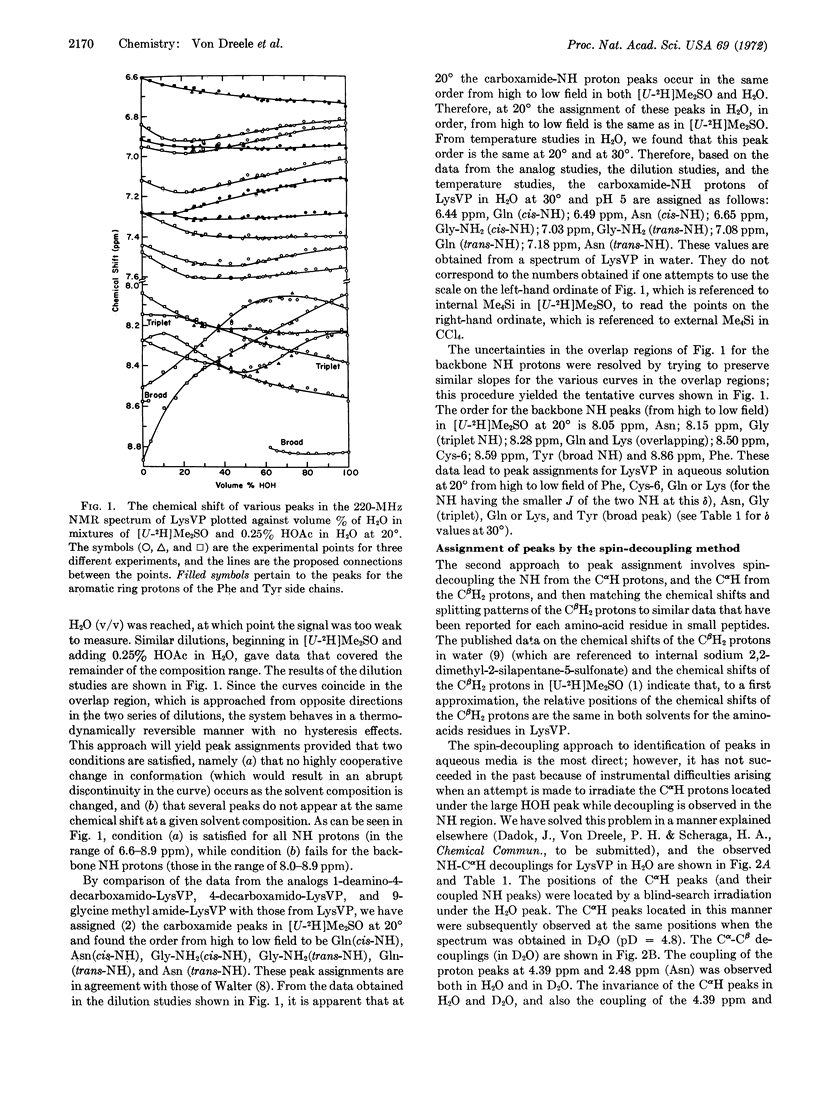
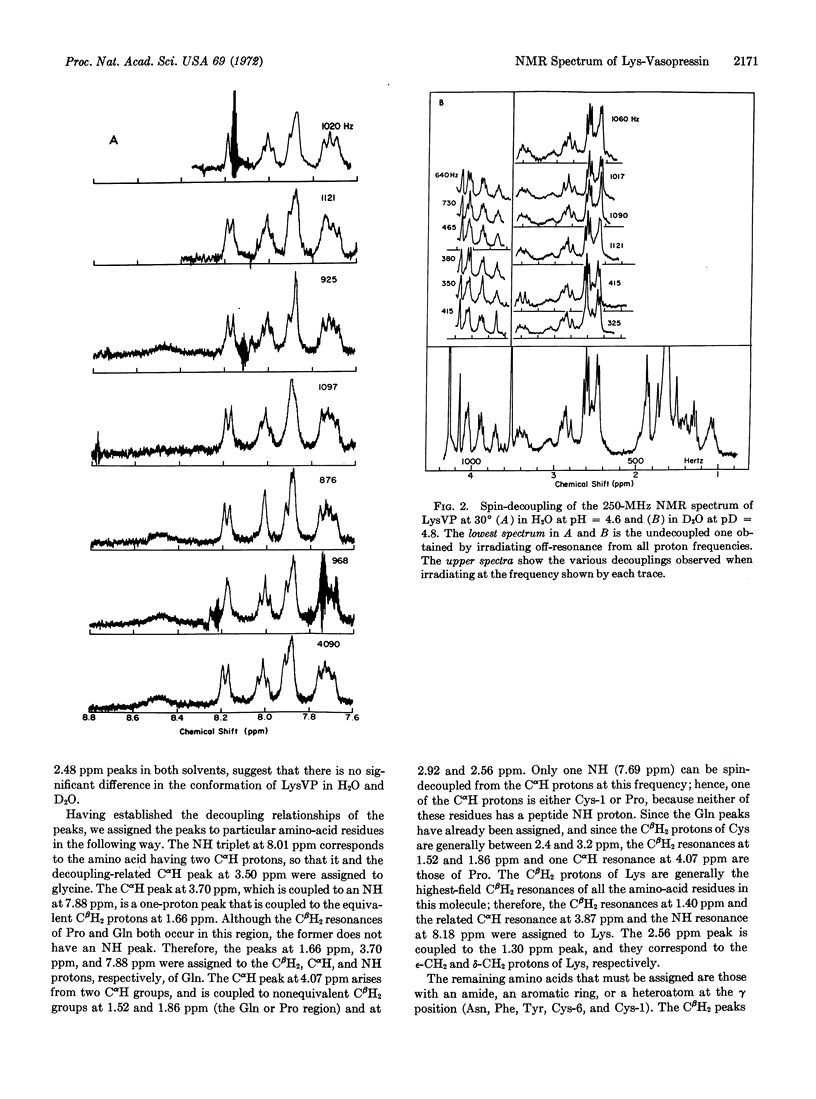
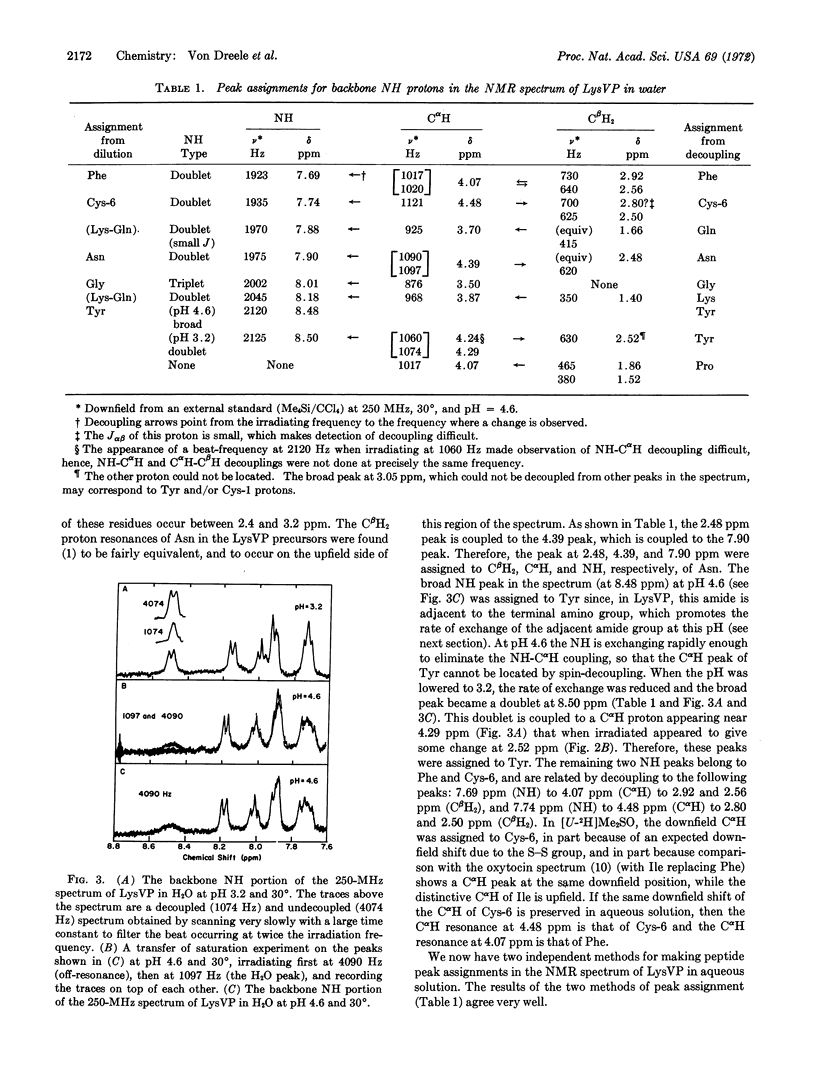
The peaks in the proton NMR spectrum of lysine-vasopressin in aqueous solution at pH 3-5 were assigned to particular amino-acid residues by the use of the results of dilution studies and NH-CαH and CαH-CβH decoupling experiments. The conformation of lysine-vasopressin in water differs from its conformation in dimethylsulfoxide.
Keywords: proton assignments, dimethylsulfoxide, peptide, conformation, amino acids
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Deslauriers R., Smith I. C. Evidence from proton magnetic resonance data for the stacking of aromatic amino acids in lysine-vasopressin: comparison with oxytocin derivatives and related dipeptides. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Jul 13;40(1):179–185. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)91063-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feeney J., Roberts G. C., Rockey J. H., Burgen A. S. Conformational studies of oxytocin and lysine vasopressin in aqueous solution using high resolution NMR spectroscopy. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jul 28;232(30):108–110. doi: 10.1038/newbio232108a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson L. F., Schwartz I. L., Walter R. Oxytocin and neurohypophyseal peptides: spectral assignment and conformational analysis by 220 MHz nuclear magnetic resonance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Dec;64(4):1269–1275. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.4.1269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald C. C., Phillips W. D. Proton magnetic resonance spectra of proteins in random-coil configurations. J Am Chem Soc. 1969 Mar 12;91(6):1513–1521. doi: 10.1021/ja01034a039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molday R. S., Englander S. W., Kallen R. G. Primary structure effects on peptide group hydrogen exchange. Biochemistry. 1972 Jan 18;11(2):150–158. doi: 10.1021/bi00752a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheinblatt M. Nuclear magnetic resonance study of the protolysis kinetics of the peptide hydrogens of triglycine. J Am Chem Soc. 1966 May 20;88(10):2123–2126. doi: 10.1021/ja00962a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Von Dreele P. H., Brewster A. I., Bovey F. A., Scheraga H. A., Ferger M. F., Du Vigneaud V. Nuclear magnetic resonance studies of lysine-vasopressin: structural constraints. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Dec;68(12):3088–3091. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.12.3088. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Von Dreele P. H., Brewster A. I., Scheraga H. A., Ferger M. F., Du Vigneaud V. Nuclear magnetic resonance spectrum of lysine-vasopressin and its structural implications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 May;68(5):1028–1031. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.5.1028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



