Abstract
Aryl hydrocarbon hydroxylase activity is inducible in mouse 3T3 fibroblasts by benz[α]anthracene, whereas no detectable basal or inducible levels of this enzyme occur in rat-hepatoma tissue culture cells. Conversely, tyrosine aminotransferase activity is inducible in hepatoma cells by dexamethasone, whereas only low noninducible levels of this enzyme exist in 3T3 cells. In hybrids formed by fusion of these two parent lines, levels of inducible hydroxylase activity range from the same as, to more than 20-fold greater than, that in the 3T3 parent; aminotransferase levels remain very low and noninducible in all of these same hybrids. A majority of the 1S-chromosomal complement from each parent is retained in most of these hybrids. The kinetics of hydroxylase induction and degradation, responses of hydroxylase induction to actinomycin D and cycloheximide, and the relative thermolability of the control and induced activities are similar in the 3T3 parent and in the hybrids. Failure to inactivate any of the aminotransferase activity in the hybrids with antibody specific for the rat enzyme indicates that all of the basal noninducible aminotransferase activity is derived from the mouse 3T3 parent.
Keywords: cell fusion, cell culture, enzyme induction
Full text
PDF
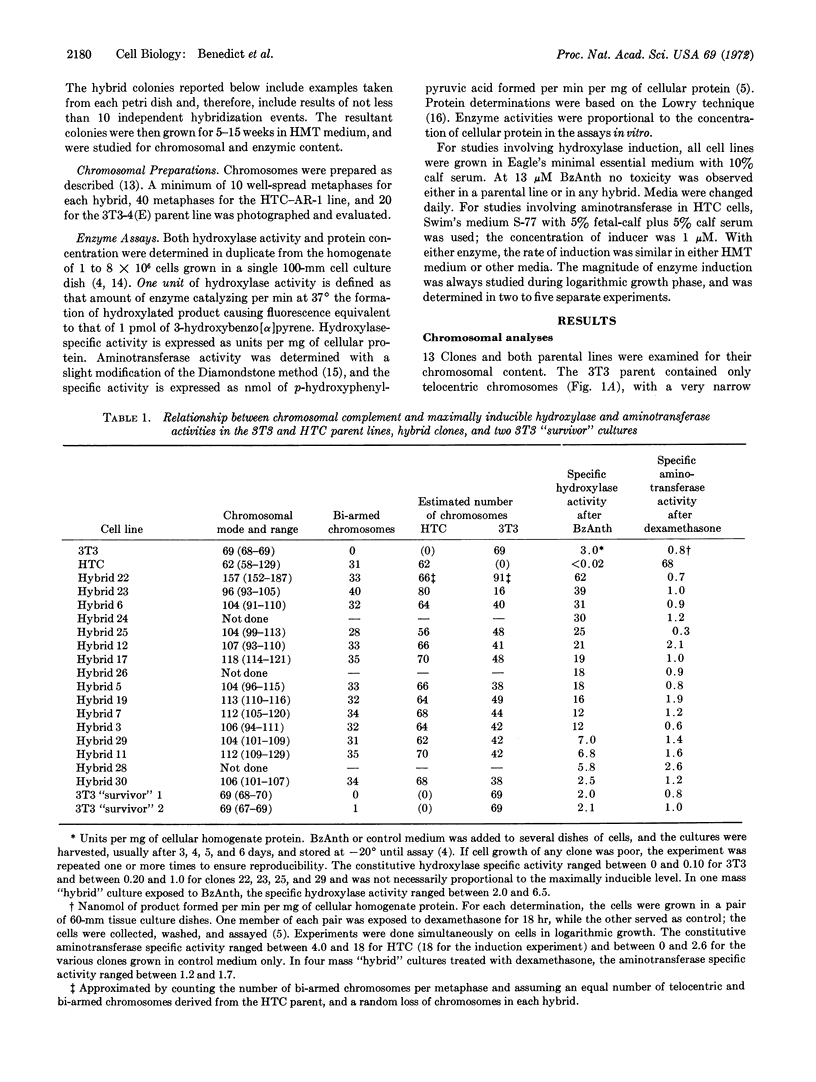



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Basilico C., Matsuya Y., Green H. The interaction of polyoma virus with mouse-hamster somatic hybrid cells. Virology. 1970 Jun;41(2):295–305. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90082-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benedict W. F., Gielen J. E., Nebert D. W. Polycyclic hydrocarbon-produced toxicity, transformation, and chromosomal aberrations as a function of aryl hydrocarbon hydroxylase activity in cell cultures. Int J Cancer. 1972 Mar 15;9(2):435–451. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910090223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conney A. H. Pharmacological implications of microsomal enzyme induction. Pharmacol Rev. 1967 Sep;19(3):317–366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson R. L. Regulation of gene expression in somatic cell hybrids: a review. In Vitro. 1971 May-Jun;6(6):411–426. doi: 10.1007/BF02616043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estabrook R. W., Franklin M. R., Cohen B., Shigamatzu A., Hildebrandt A. G. Biochemical and genetic factors influencing drug metabolism. Influence of hepatic microsomal mixed function oxidation reactions on cellular metabolic control. Metabolism. 1971 Feb;20(2):187–199. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(71)90091-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GARREN L. D., HOWELL R. R., TOMKINS G. M., CROCCO R. M. A PARADOXICAL EFFECT OF ACTINOMYCIN D: THE MECHANISM OF REGULATION OF ENZYME SYNTHESIS BY HYDROCORTISONE. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Oct;52:1121–1129. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.4.1121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gielen J. E., Goujon F. M., Nebert D. W. Genetic regulation of aryl hydrocarbon hydroxylase induction. II. Simple Mendelian expression in mouse tissues in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1972 Feb 25;247(4):1125–1137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gielen J. E., Nebert D. W. Aryl hydrocarbon hydroxylase induction in mammalian liver cell culture. I. Stimulation of enzyme activity in nonhepatic cells and in hepatic cells by phenobarbital, polycyclic hydrocarbons, and 2,2-bis(p-chlorophenyl)-1,1,1-trichloroethane. J Biol Chem. 1971 Sep 10;246(17):5189–5198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris H. Behaviour of differentiated nuclei in heterokaryons of animal cells from different species. Nature. 1965 May 8;206(984):583–588. doi: 10.1038/206583a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu A. Y., Kuntzman R., West S., Conney A. H. Reconstituted liver microsomal enzyme system that hydroxylates drugs, other foreign compounds and endogenous substrates. I. Determination of substrate specificity by the cytochrome P-450 and P-448 fractions. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Mar 19;42(6):1200–1206. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90033-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuya Y., Green H. Somatic cell hybrid between the established human line D98 (presumptive HeLa) and 3T3. Science. 1969 Feb 14;163(3868):697–698. doi: 10.1126/science.163.3868.697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nebert D. W., Bausserman L. L. Aryl hydrocarbon hydroxylase induction in cell culture as a function of gene expression. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1971 Jul 6;179:561–579. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1971.tb46933.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nebert D. W., Bausserman L. L. Fate of inducer during induction of aryl hydrocarbon hydroxylase activity in mammalian cell culture. II. Levels of intracellular polycyclic hydrocarbon during enzyme induction and decay. Mol Pharmacol. 1970 Jul;6(4):304–314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nebert D. W., Gelboin H. V. Substrate-inducible microsomal aryl hydroxylase in mammalian cell culture. II. Cellular responses during enzyme induction. J Biol Chem. 1968 Dec 10;243(23):6250–6261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nebert D. W., Gelboin H. V. The in vivo and in vitro induction of aryl hydrocarbon hydroxylase in mammalian cells of different species, tissues, strains, and developmental and hormonal states. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Oct;134(1):76–89. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90253-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nebert D. W., Gielen J. E. Aryl hydrocarbon hydroxylase induction in mammalian liver cell culture. II. Effects of actinomycin D and cycloheximide on induction processes by phenobarbital or polycyclic hydrocarbons. J Biol Chem. 1971 Sep 10;246(17):5199–5206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PUCK T. T., MARCUS P. I., CIECIURA S. J. Clonal growth of mammalian cells in vitro; growth characteristics of colonies from single HeLa cells with and without a feeder layer. J Exp Med. 1956 Feb 1;103(2):273–283. doi: 10.1084/jem.103.2.273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHIMKE R. T., SWEENEY E. W., BERLIN C. M. THE ROLES OF SYNTHESIS AND DEGRADATION IN THE CONTROL OF RAT LIVER TRYPTOPHAN PYRROLASE. J Biol Chem. 1965 Jan;240:322–331. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEVER J. L., CASTELLANO G. A., PELON W., HUEBNER R. J., WOLMAN F. INACTIVATION OF THE INFECTIVITY OF VIRAL HEMAGGLUTINATING ANTIGENS WITH THE USE OF BETAPRONE. J Lab Clin Med. 1964 Dec;64:983–988. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider J. A., Weiss M. C. Expression of differentiated functions in hepatoma cell hybrids. I. Tyrosine aminotransferase in hepatoma-fibroblast hybrids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jan;68(1):127–131. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.1.127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson E. B., Gelehrter T. D. Expression of tyrosine aminotransferase activity in somatic-cell heterokaryons: evidence for negative control of enzyme expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Oct;68(10):2589–2593. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.10.2589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson E. B., Granner D. K., Tomkins G. M. Superinduction of tyrosine aminotransferase by actinomycin D in rat hepatoma (HTC) cells. J Mol Biol. 1970 Dec 14;54(2):159–175. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90424-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomkins G. M., Gelehrter T. D., Granner D., Martin D., Jr, Samuels H. H., Thompson E. B. Control of specific gene expression in higher organisms. Expression of mammalian genes may be controlled by repressors acting on the translation of messenger RNA. Science. 1969 Dec 19;166(3912):1474–1480. doi: 10.1126/science.166.3912.1474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss M. C., Chaplain M. Expression of differentiated functions in hepatoma cell hybrids: reappearance of tyrosine aminotransferase inducibility after the loss of chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Dec;68(12):3026–3030. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.12.3026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




