Abstract
Pancreatic DNase I is used to probe the structure of chromatin isolated from synchronized HeLa cells. The degree to which DNA in chromatin is protected from DNase attack varies during the G1, S, and G2 phases of the cell cycle. In addition, the DNase sensitivity of chromatin from contact-inhibited African green monkey kidney cells differs from that of actively dividing, subconfluent cultures. These cell cycle-dependent chromatin changes were observed consistently at all enzyme concentrations (5000-fold range) and incubation times (15 min-2 hr) tested. The results indicate that the degree of complexing between DNA and chromosomal proteins changes during interphase, and they suggest that the chromosome coiling cycle of visible mitosis may extend in more subtle form over the entire cell cycle.
Keywords: DNase I, synchronized HeLa cells, monkey-kidney cells, contact inhibition
Full text
PDF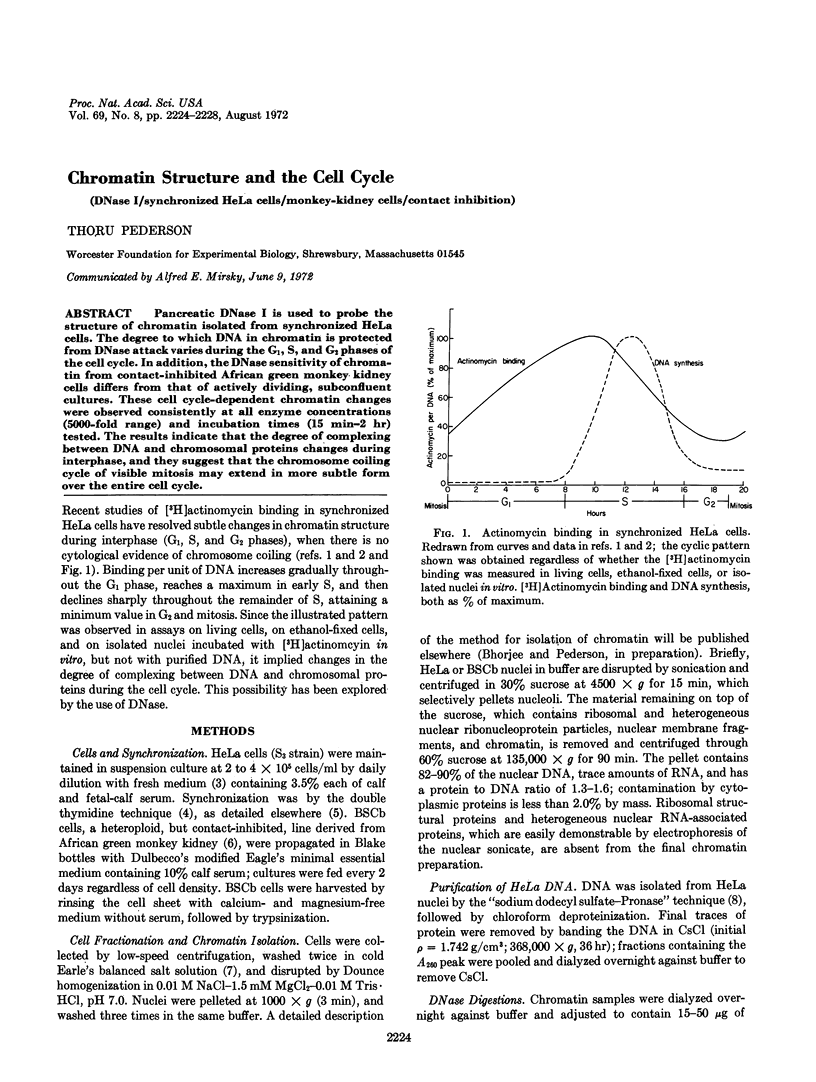

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLOCH D. P., GODMAN G. C. Evidence of differences in the desoxyribonucleoprotein complex of rapidly proliferating and non-dividing cells. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1955 Nov 25;1(6):531–550. doi: 10.1083/jcb.1.6.531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balhorn R., Bordwell J., Sellers L., Granner D., Chalkley R. Histone phosphorylation and DNA synthesis are linked in synchronous cultures of HTC cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Feb 16;46(3):1326–1333. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(72)80120-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balhorn R., Chalkley R., Granner D. Lysine-rich histone phosphorylation. A positive correlation with cell replication. Biochemistry. 1972 Mar 14;11(6):1094–1098. doi: 10.1021/bi00756a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. J., Felsenfeld G. Structure of chromatin. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jan 27;229(4):101–106. doi: 10.1038/newbio229101a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EAGLE H. Amino acid metabolism in mammalian cell cultures. Science. 1959 Aug 21;130(3373):432–437. doi: 10.1126/science.130.3373.432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOPPS H. E., BERNHEIM B. C., NISALAK A., TJIO J. H., SMADEL J. E. BIOLOGIC CHARACTERISTICS OF A CONTINUOUS KIDNEY CELL LINE DERIVED FROM THE AFRICAN GREEN MONKEY. J Immunol. 1963 Sep;91:416–424. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houssier C., Fredericq E. Electrooptical properties of nucleic acids and nucleoproteins. II. Study of the deoxyribonucleohistone-proflavine complexes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Jul 13;120(3):434–447. doi: 10.1016/0926-6585(66)90310-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jurkowitz L. Actinomycin D binding by calf thymus deoxyribonucleic acid and nucleoprotein. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1965 Jul;111(1):88–95. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(65)90326-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLEIN F., SZIRMAI J. A. Quantitative studies on the interaction of azure A with deoxyribonucleic acid and deoxyribonucleoprotein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 May 28;72:48–61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kernell A. M., Bolund L., Ringertz N. R. Chromatin changes during erythropoiesis. Exp Cell Res. 1971 Mar;65(1):1–6. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4827(71)80042-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Killander D., Rigler R., Jr Initial changes of deoxyribonucleoprotein and synthesis of nucleic acid in phytohemagglutinine-stimulated human leucocytes in vitro. Exp Cell Res. 1965 Sep;39(2):701–704. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(65)90075-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleiman L., Huang R. C. Binding of actinomycin D to calf thymus chromatin. J Mol Biol. 1971 Feb 14;55(3):503–521. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90333-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macieira-Coelho A., Pontén J., Philipson L. Inhibition of the division cycle in confluent cultures of human fibroblasts in vitro. Exp Cell Res. 1966 Aug;43(1):20–29. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(66)90373-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirsky A. E. The structure of chromatin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Dec;68(12):2945–2948. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.12.2945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miura A., Ohba Y. Structure of nucleohistone. 3. Interaction with toluidine blue. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Sep 26;145(2):436–445. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(67)90062-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilausen K., Green H. Reversible arrest of growth in G1 of an established fibroblast line (3T3). Exp Cell Res. 1965 Oct;40(1):166–168. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(65)90306-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pederson T., Robbins E. A method for improving synchrony in the G2 phase of the cell cycle. J Cell Biol. 1971 Jun;49(3):942–945. doi: 10.1083/jcb.49.3.942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puck T. T. Phasing, Mitotic Delay, and Chromosomal Aberrations in Mammalian Cells. Science. 1964 May 1;144(3618):565–566. doi: 10.1126/science.144.3618.565-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ringertz N. R., Bolund L. Actinomycin binding capacity of deoxyribonucleoprotein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Jan 21;174(1):147–154. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(69)90237-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ringertz N. R., Bolund L., Zynkiewicz Z. D. AO binding of intracellular nucleic acids in fixed cells in relation to cell growth. Exp Cell Res. 1970 Nov;63(1):233–238. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(70)90361-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins E., Pederson T. Iron: its intracellular localization and possible role in cell division. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Aug;66(4):1244–1251. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.4.1244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schildkraut C. L., Maio J. J. Fractions of HeLa DNA differing in their content of guanine+cytosine. J Mol Biol. 1969 Dec 14;46(2):305–312. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90423-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt G., Cashion P. J., Suzuki S., Joseph J. P., Demarco P., Cohen M. B. The action of pancreas deoxyribonuclease I (deoxyribonucleate oligonucleotidohydrolase, EC-number 3.1.4.5.) on calf thymus nucleohistone. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 Apr;149(2):513–527. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90351-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff S. Chromosome aberrations and the cell cycle. Radiat Res. 1968 Mar;33(3):609–619. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


