Abstract
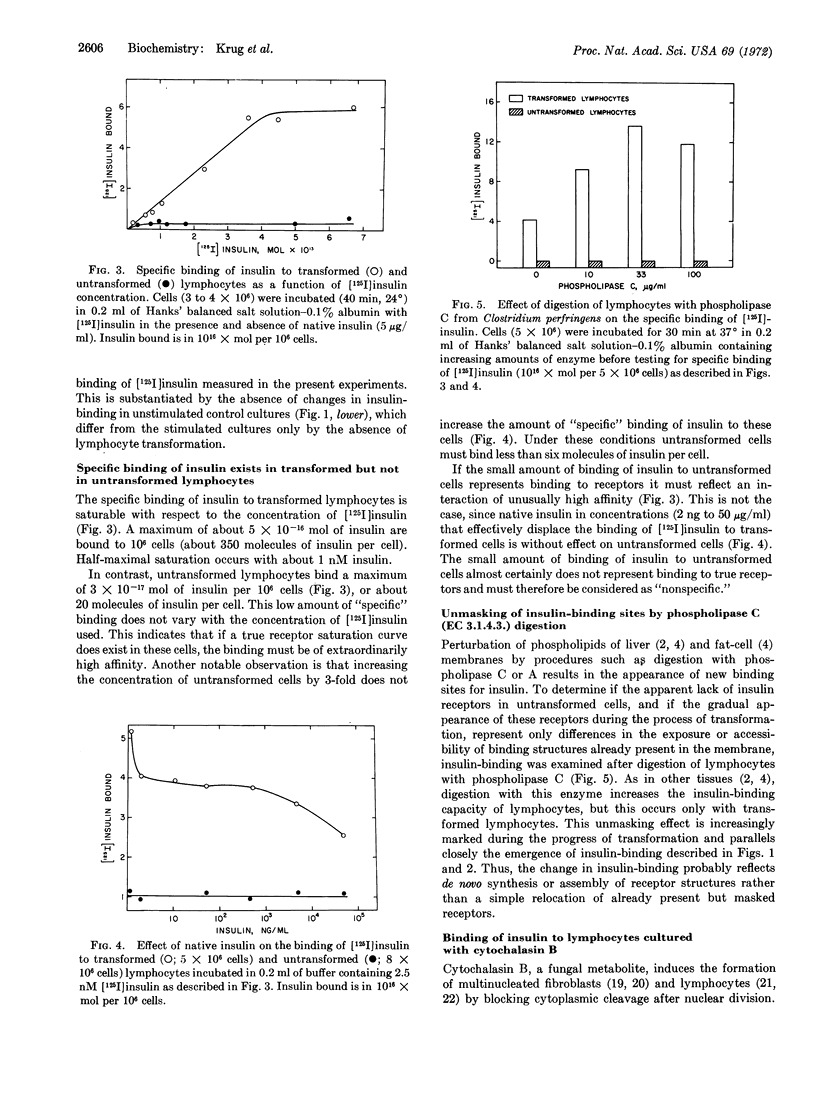
Essentially no specific binding sites for insulin are detected in small lymphocytes freshly isolated from human blood. Insulin-binding sites appear on the lymphocyte surface during transformation in vitro with concanavalin A, and the number of these receptors increases sharply to reach a maximum between 24 and 46 hr after exposure to the mitogen. The appearance of de novo binding sites for insulin coincides with the increase in [3H]thymidine uptake into nuclear DNA and clearly precedes the appearance of enlarged, morphologically transformed cells. No changes in insulin-binding are detected in unstimulated control cultures. A maximum of about 350 molecules of insulin can bind per transformed lymphocyte, while less than six insulin molecules bind to an untransformed cell. Circulating human leukemic lymphoblasts bind about as much insulin as the lymphocytes transformed in vitro. Giant, polynucleated, transformed lymphocytes cultured in the presence of cytochalasin B bind about 10 times more insulin than transformed lymphocytes, which is in harmony with a 10-fold increase in cell-surface area in these cells. Specific binding of insulin is a saturable process in transformed lymphocytes but not in the untransformed cells. In transformed cells, [125I]-insulin is displaced by as little as 2 ng/ml of native insulin, while in untransformed cells no significant displacement is observed with native insulin. Digestion of transformed cells with phospholipase C (EC 3.1.4.3.) enhances the specific binding of [125I]insulin 3-fold, but no effect occurs with untransformed cells. These observations indicate a possible functional role of insulin and of adenylate cyclase in cell growth and division.
Keywords: concanavalin A, cell growth and division, insulin receptors
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blaker G. J., Birch J. R., Pirt S. J. The glucose, insulin and glutamine requirements of suspension cultures of HeLa cells in a defined culture medium. J Cell Sci. 1971 Sep;9(2):529–537. doi: 10.1242/jcs.9.2.529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter S. B. Effects of cytochalasins on mammalian cells. Nature. 1967 Jan 21;213(5073):261–264. doi: 10.1038/213261a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P., Desbuquois B., Krug F. Insulin-receptor interactions in liver cell membranes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Jul 16;44(2):333–339. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90604-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P. Insulin--receptor interactions in adipose tissue cells: direct measurement and properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jun;68(6):1264–1268. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.6.1264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P. Properties of the insulin receptor of isolated fat cell membranes. J Biol Chem. 1971 Dec 10;246(23):7265–7274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P. Unmasking of insulin receptors in fat cells and fat cell membranes. Perturbation of membrane lipids. J Biol Chem. 1971 Nov;246(21):6532–6542. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cutrecasas P. Perturbation of the insulin receptor of isolated fat cells with proteolytic enzymes. Direct measurement of insulin-receptor interactions. J Biol Chem. 1971 Nov;246(21):6522–6531. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freychet P., Roth J., Neville D. M., Jr Insulin receptors in the liver: specific binding of ( 125 I)insulin to the plasma membrane and its relation to insulin bioactivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Aug;68(8):1833–1837. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.8.1833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freychet P., Roth J., Neville D. M., Jr Monoiodoinsulin: demonstration of its biological activity and binding to fat cells and liver membranes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Apr 16;43(2):400–408. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90767-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavin J. R., 3rd, Roth J., Jen P., Freychet P. Insulin receptors in human circulating cells and fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Mar;69(3):747–751. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.3.747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershko A., Mamont P., Shields R., Tomkins G. M. "Pleiotypic response". Nat New Biol. 1971 Aug;232(33):206–211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsie A. W., Jones C., Puck T. T. Further changes in differentiation state accompanying the conversion of Chinese hamster cells of fibroblastic form by dibutyryl adenosine cyclic 3':5'-monophosphate and hormones. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jul;68(7):1648–1652. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.7.1648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Illiano G., Cuatrecasas P. Modulation of adenylate cyclase activity in liver and fat cell membranes by insulin. Science. 1972 Feb 25;175(4024):906–908. doi: 10.1126/science.175.4024.906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kono T., Barham F. W. The relationship between the insulin-binding capacity of fat cells and the cellular response to insulin. Studies with intact and trypsin-treated fat cells. J Biol Chem. 1971 Oct 25;246(20):6210–6216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishan A. Fine structure of cytochalasin-induced multinucleated cells. J Ultrastruct Res. 1971 Jul;36(1):191–204. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(71)80097-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makman M. H. Conditions leading to enhanced response to glucagon, epinephrine, or prostaglandins by adenylate cyclase of normal and malignant cultured cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Sep;68(9):2127–2130. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.9.2127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novogrodsky A., Katchalski E. Lymphocyte transformation induced by concanavalin A and its reversion by methyl-alpha-D-mannopyranoside. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Jan 28;228(2):579–583. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(71)90064-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peery C. V., Johnson G. S., Pastan I. Adenyl cyclase in normal and transformed fibroblasts in tissue culture. Activation by prostaglandins. J Biol Chem. 1971 Sep 25;246(18):5785–5790. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridler M. A., Smith G. F. The response of human cultured lymphocytes to cytochalasin B. J Cell Sci. 1968 Dec;3(4):595–602. doi: 10.1242/jcs.3.4.595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott R. E., Marchesi V. T. Structural changes in membranes of transformed lymphocytes demonstrated by freeze-etching. Cell Immunol. 1972 Feb;3(2):301–317. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(72)90169-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheppard J. R. Difference in the cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate levels in normal and transformed cells. Nat New Biol. 1972 Mar 1;236(61):14–16. doi: 10.1038/newbio236014a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. F., Ridler M. A., Faunch J. A. Action of cytochalasin B on cultured human lymphocytes. Nature. 1967 Dec 16;216(5120):1134–1135. doi: 10.1038/2161134a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. W., Steiner A. L., Newberry W. M., Jr, Parker C. W. Cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate in human lymphocytes. Alterations after phytohemagglutinin stimulation. J Clin Invest. 1971 Feb;50(2):432–441. doi: 10.1172/JCI106510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. W., Steiner A. L., Parker C. W. Human lymphocytic metabolism. Effects of cyclic and noncyclic nucleotides on stimulation by phytohemagglutinin. J Clin Invest. 1971 Feb;50(2):442–448. doi: 10.1172/JCI106511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Temin H. M. Studies on carcinogenesis by avian sarcoma viruses. VI. Differential multiplication of uninfected and of converted cells in response to insulin. J Cell Physiol. 1967 Jun;69(3):377–384. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040690314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



