Abstract
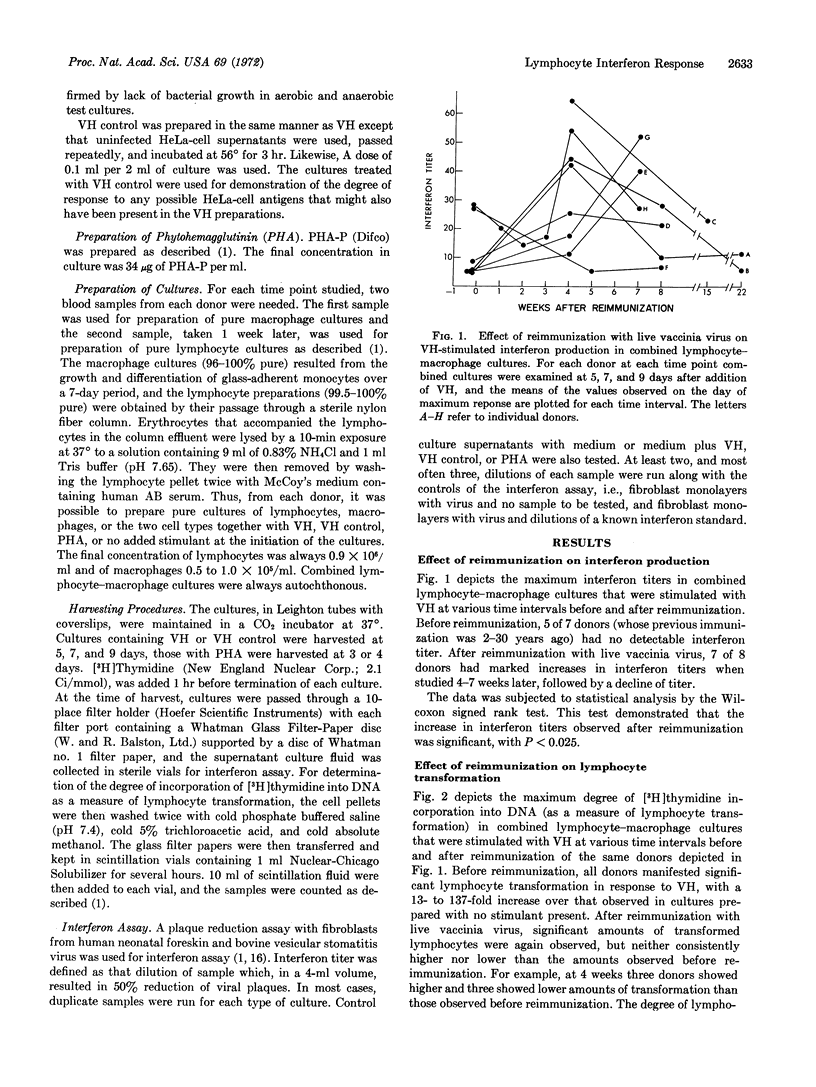
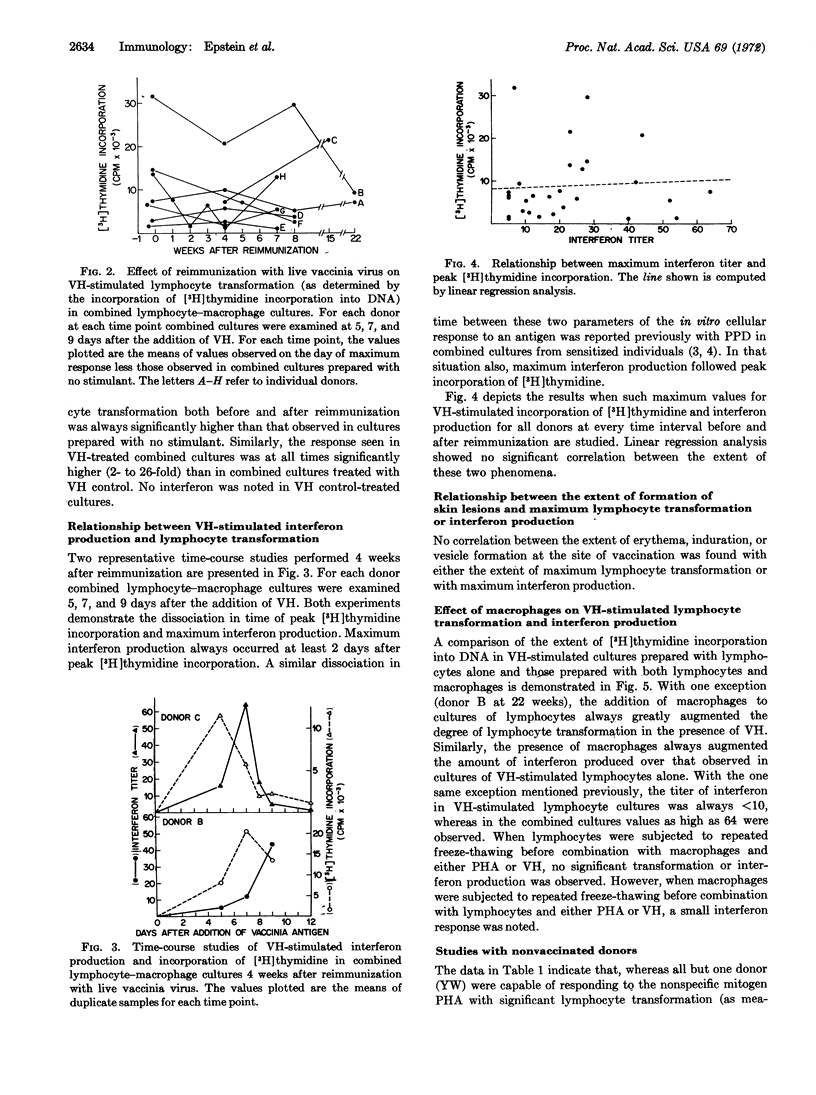
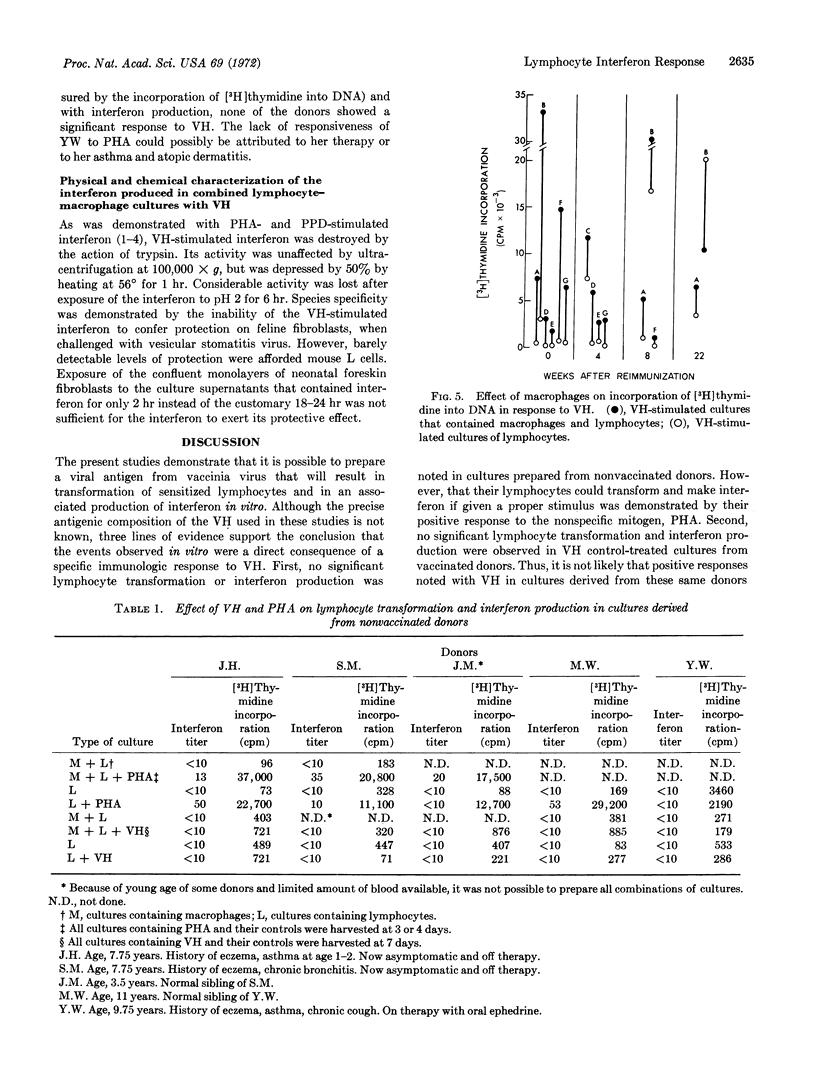
Viral antigen prepared by heat inactivation of vaccinia virus stimulated production of interferon in association with transformation of sensitized human lymphocytes in vitro. Involvement of a macrophage-lymphocyte interaction in production of interferon stimulated by viral antigen was found in which macrophage greatly augmented the amount of interferon produced by lymphocytes. Reimmunization with live vaccinia virus resulted in a selective increase in the ability of lymphocytes to produce interferon in the presence of viral antigen 4-7 weeks later without a corresponding increase in the degree of already significant lymphocyte transformation. There was no correlation between the extent of lymphocyte transformation and the amount of interferon produced. The augmented interferon response after reimmunization described in this study may be a significant component of the protective effect of immunization with vaccinia against disease occurring after exposure to small-pox.
Keywords: macrophage-lymphocyte interaction, mediator of cellular immunity
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong R. W., Gurwith M. J., Waddell D., Merigan T. C. Cutaneous interferon production in patients with Hodgkin's disease and other cancers infected with varicella or vaccinia. N Engl J Med. 1970 Nov 26;283(22):1182–1187. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197011262832202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanden R. V. Mechanisms of recovery from a generalized viral infection: mousepox. 3. Regression infectious foci. J Exp Med. 1971 May 1;133(5):1090–1104. doi: 10.1084/jem.133.5.1090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanden R. V. Mechanisms of recovery from a generalized viral infection: mousepox. I. The effects of anti-thymocyte serum. J Exp Med. 1970 Nov;132(5):1035–1054. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.5.1035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanden R. V. Mechanisms of recovery from a generalized viral infection: mousepox. II. Passive transfer of recovery mechanisms with immune lymphoid cells. J Exp Med. 1971 May 1;133(5):1074–1089. doi: 10.1084/jem.133.5.1074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulter E. A., Zwartouw H. T., Titmuss D. H., Maber H. B. The nature of the immune state produced by inactivated vaccinia virus in rabbits. Am J Epidemiol. 1971 Dec;94(6):612–620. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a121360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein L. B., Cline M. J., Merigan T. C. PPD-stimulated interferon: in vitro macrophage-lymphocyte interaction in the production of a mediator of cellular immunity. Cell Immunol. 1971 Dec;2(6):602–613. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(71)90008-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein L. B., Cline M. J., Merigan T. C. The interaction of human macrophages and lymphocytes in the phytohemagglutinin-stimulated production of interferon. J Clin Invest. 1971 Apr;50(4):744–753. doi: 10.1172/JCI106545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLASGOW L. A., HABEL K. Interferon production by mouse leukocytes in vitro and in vivo. J Exp Med. 1963 Jan 1;117:149–160. doi: 10.1084/jem.117.1.149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLASGOW L. A. LEUKOCYTES AND INTERFERON IN THE HOST RESPONSE TO VIRAL INFECTIONS. I. MOUSE LEUKOCYTES AND LEUKOCYTE-PRODUCED INTERFERON IN VACCINIA VIRUS INFECTION IN VITRO. J Exp Med. 1965 Jun 1;121:1001–1018. doi: 10.1084/jem.121.6.1001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glasgow L. A. Cellular immunity in host resistance to viral infections. Arch Intern Med. 1970 Jul;126(1):125–134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glasgow L. A. Leukocytes and interferon in the host response to viral infections. II. Enhanced interferon response of leukocytes from immune animals. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jun;91(6):2185–2191. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.6.2185-2191.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green J. A., Cooperband S. R., Kibrick S. Immune specific induction of interferon production in cultures of human blood lymphocytes. Science. 1969 Jun 20;164(3886):1415–1417. doi: 10.1126/science.164.3886.1415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurvich E. B., Svet-Moldavskaya I. A. Transformation of human blood lymphocytes under the influence of smallpox antigen. Nature. 1968 Dec 7;220(5171):1050–1051. doi: 10.1038/2201050a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hersh E. M., Harris J. E. Macrophage-lymphocyte interaction in the antigen-induced blastogenic response of human peripheral blood leukocytes. J Immunol. 1968 Jun;100(6):1184–1194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEE S. H., OZERE R. L. PRODUCTION OF INTERFERON BY HUMAN MONONUCLEAR LEUCOCYTES. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1965 Jan;118:190–195. doi: 10.3181/00379727-118-29794. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LING N. R., HUSBAND E. M. SPECIFIC AND NON-SPECIFIC STIMULATION OF PERIPHERAL LYMPHOCYTES. Lancet. 1964 Feb 15;1(7329):363–365. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(64)92102-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MATSANIOTIS N. S., TSENGHI C. J. MITOSIS IN LEUCOCYTE CULTURES. Lancet. 1964 May 2;1(7340):989–989. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(64)91797-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merigan T. C., Gregory D. F., Petralli J. K. Physical properties of human interferon prepared in vitro and in vivo. Virology. 1966 Aug;29(4):515–522. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(66)90276-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merigan T. C., Stevens D. A. Viral infections in man associated with acquired immunological deficiency states. Fed Proc. 1971 Nov-Dec;30(6):1858–1864. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheim J. J., Leventhal B. G., Hersh E. M. The transformation of column-purified lymphocytes with nonspecific and specific antigenic stimuli. J Immunol. 1968 Aug;101(2):262–267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens D. A., Merigan T. C. Interferon, antibody, and other host factors in herpes zoster. J Clin Invest. 1972 May;51(5):1170–1178. doi: 10.1172/JCI106910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner G. S., Squires E. J., Murray H. G. Inactivated smallpox vaccine. A comparison of inactivation methods. J Hyg (Lond) 1970 Jun;68(2):197–210. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400028679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHEELOCK E. F. INTERFERON IN DERMAL CRUSTS OF HUMAN VACCINIA VIRUS VACCINATIONS POSSIBLE EXPLANATION OF RELATIVE BENIGNITY OF VARIOLATION SMALLPOX. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1964 Dec;117:650–653. doi: 10.3181/00379727-117-29659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



