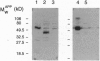
Abstract
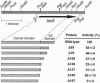
The lactose-H+ symport protein (LacS) of Streptococcus thermophilus has a C-terminal hydrophilic domain that is homologous to IIA protein(s) domains of the phosphoenolpyruvate:sugar phosphotransferase system (PTS). C-terminal truncation mutants were constructed and expressed in Escherichia coli and their properties were analyzed. Remarkably, the entire IIA domain (160 amino acids) could be deleted without significant effect on lactose-H+ symport and galactoside equilibrium exchange. Analysis of the LacS mutants in S. thermophilus cells suggested that transport is affected by PTS-mediated phosphorylation of the IIA domain. For further studies, membrane vesicles of S. thermophilus were fused with cytochrome c oxidase-containing liposomes, and, when appropriate, phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) plus purified enzyme I and heat-stable protein HPr were incorporated into the hybrid membranes. Generation of a protonmotive force (delta p) in the hybrid membranes resulted in accumulation of lactose, whereas uptake of the PTS sugar sucrose was not observed. With PEP and the energy-coupling proteins enzyme I and HPr of the PTS on the inside, high rates of sucrose uptake were observed, whereas delta p-driven lactose uptake by wild-type LacS was inhibited. This inhibition was not observed with LacS(delta 160) and LacS(H552R), indicating that PEP-dependent enzyme I/HPr-mediated phosphorylation of the IIA domain (possibly the conserved His-552 residue) modulates lactose-H+ symport activity.
Full text
PDF

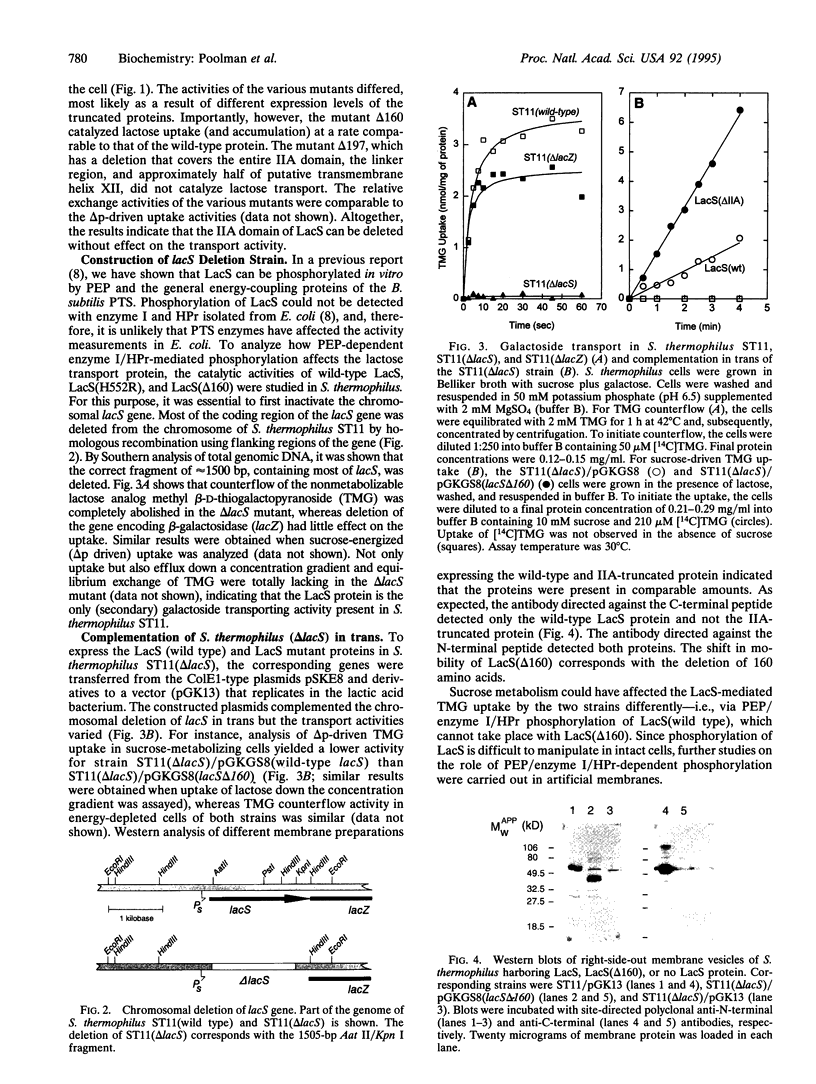
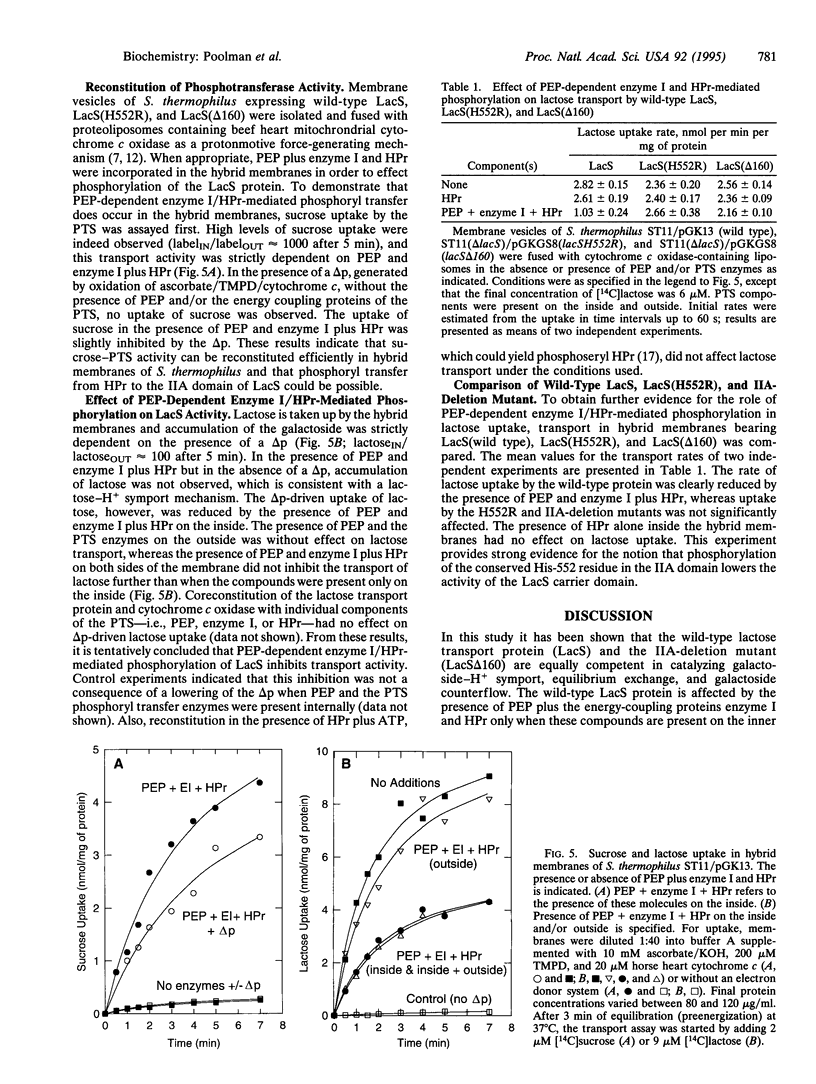

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Deutscher J., Sauerwald H. Stimulation of dihydroxyacetone and glycerol kinase activity in Streptococcus faecalis by phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent phosphorylation catalyzed by enzyme I and HPr of the phosphotransferase system. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jun;166(3):829–836. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.3.829-836.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driessen A. J., Konings W. N. Insertion of lipids and proteins into bacterial membranes by fusion with liposomes. Methods Enzymol. 1993;221:394–408. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(93)21032-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dörschug M., Frank R., Kalbitzer H. R., Hengstenberg W., Deutscher J. Phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent phosphorylation site in enzyme IIIglc of the Escherichia coli phosphotransferase system. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Oct 1;144(1):113–119. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08438.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foucaud C., Poolman B. Lactose transport system of Streptococcus thermophilus. Functional reconstitution of the protein and characterization of the kinetic mechanism of transport. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 5;267(31):22087–22094. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mollet B., Knol J., Poolman B., Marciset O., Delley M. Directed genomic integration, gene replacement, and integrative gene expression in Streptococcus thermophilus. J Bacteriol. 1993 Jul;175(14):4315–4324. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.14.4315-4324.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poolman B., Driessen A. J., Konings W. N. Regulation of solute transport in streptococci by external and internal pH values. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Dec;51(4):498–508. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.4.498-508.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poolman B., Konings W. N. Secondary solute transport in bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Nov 2;1183(1):5–39. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(93)90003-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poolman B., Modderman R., Reizer J. Lactose transport system of Streptococcus thermophilus. The role of histidine residues. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 5;267(13):9150–9157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poolman B. Precursor/product antiport in bacteria. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Oct;4(10):1629–1636. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00539.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poolman B., Royer T. J., Mainzer S. E., Schmidt B. F. Lactose transport system of Streptococcus thermophilus: a hybrid protein with homology to the melibiose carrier and enzyme III of phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent phosphotransferase systems. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jan;171(1):244–253. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.1.244-253.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Postma P. W., Lengeler J. W., Jacobson G. R. Phosphoenolpyruvate:carbohydrate phosphotransferase systems of bacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1993 Sep;57(3):543–594. doi: 10.1128/mr.57.3.543-594.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Presper K. A., Wong C. Y., Liu L., Meadow N. D., Roseman S. Site-directed mutagenesis of the phosphocarrier protein. IIIGlc, a major signal-transducing protein in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(11):4052–4055. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.11.4052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reizer J., Sutrina S. L., Saier M. H., Stewart G. C., Peterkofsky A., Reddy P. Mechanistic and physiological consequences of HPr(ser) phosphorylation on the activities of the phosphoenolpyruvate:sugar phosphotransferase system in gram-positive bacteria: studies with site-specific mutants of HPr. EMBO J. 1989 Jul;8(7):2111–2120. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03620.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roseman S., Meadow N. D. Signal transduction by the bacterial phosphotransferase system. Diauxie and the crr gene (J. Monod revisited). J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 25;265(6):2993–2996. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saier M. H., Jr Protein phosphorylation and allosteric control of inducer exclusion and catabolite repression by the bacterial phosphoenolpyruvate: sugar phosphotransferase system. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Mar;53(1):109–120. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.1.109-120.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutrina S. L., Reddy P., Saier M. H., Jr, Reizer J. The glucose permease of Bacillus subtilis is a single polypeptide chain that functions to energize the sucrose permease. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 25;265(30):18581–18589. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu C., Yu L., King T. E. Studies on cytochrome oxidase. Interactions of the cytochrome oxidase protein with phospholipids and cytochrome c. J Biol Chem. 1975 Feb 25;250(4):1383–1392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]