Abstract
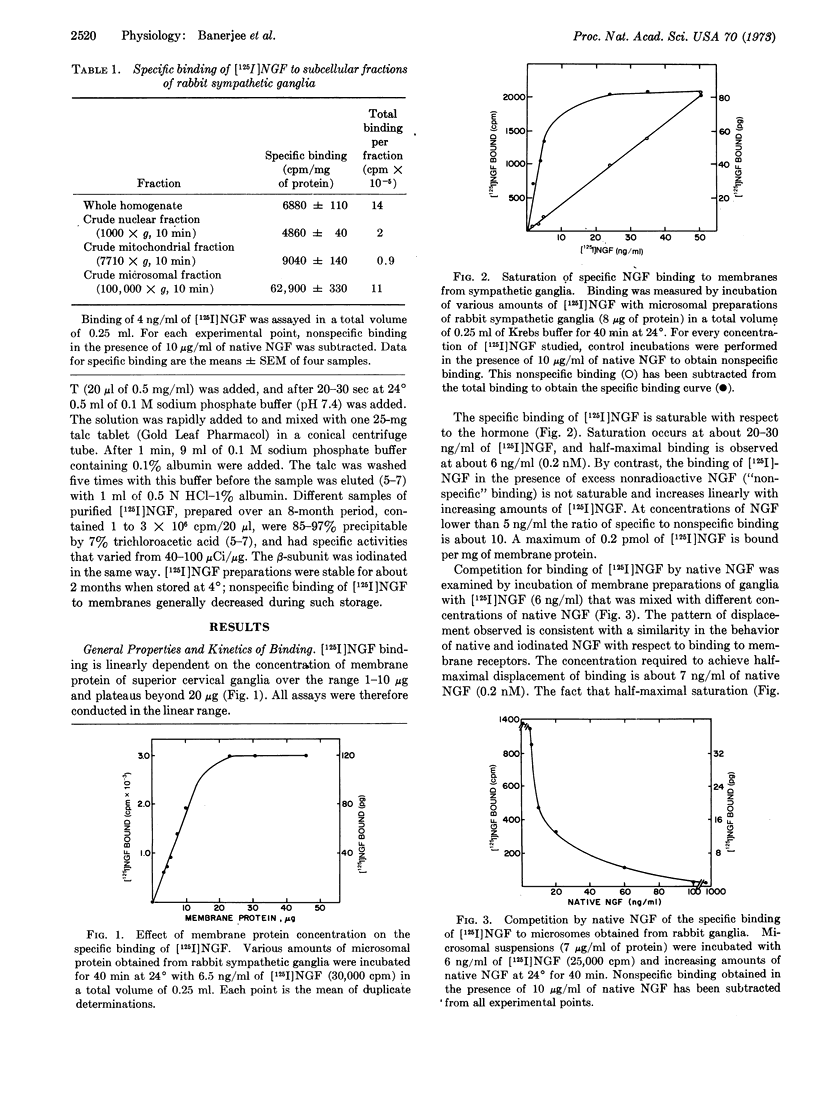
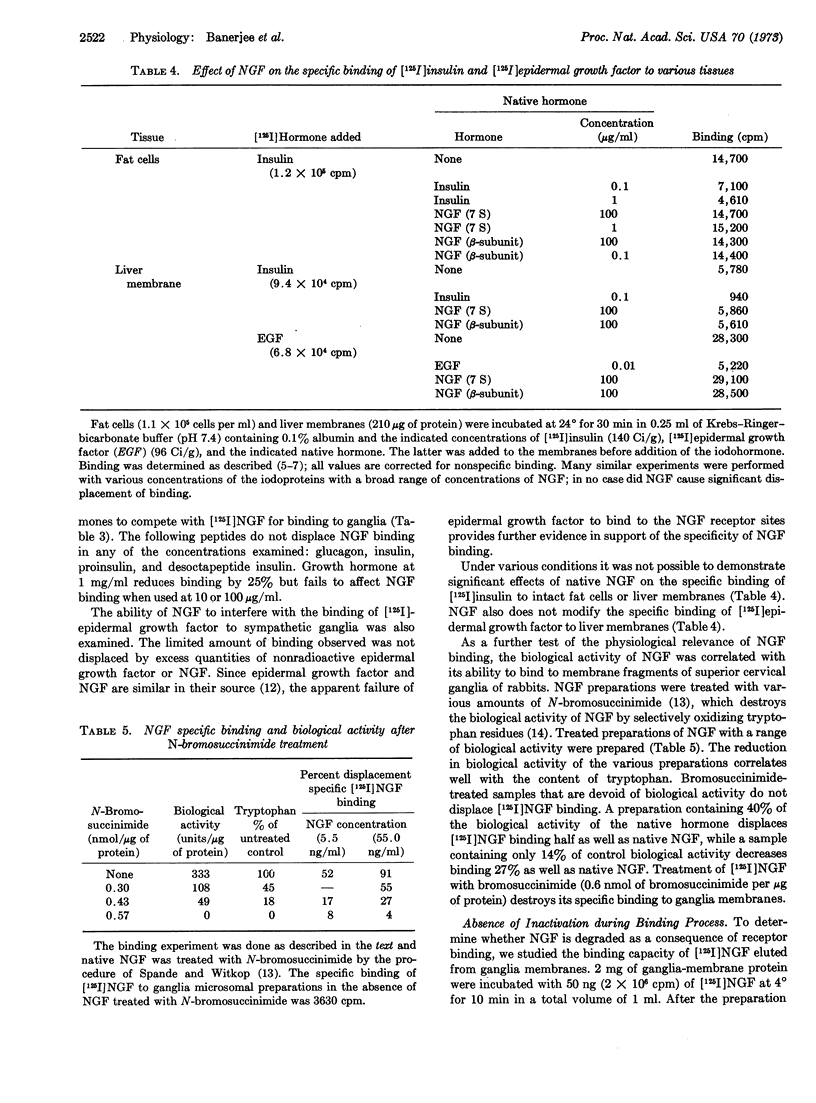
125I-Labeled nerve growth factor binds to membrane preparations from superior cervical ganglia of rabbit in a specific fashion indicative of an interaction with the physiological receptor. Of various tissues examined, binding was observed only in the superior cervical ganglia, a presumed target organ of nerve growth factor. Binding of labeled factor is displaced by nonradioactive factor but not by several other peptide hormones. Binding to ganglia of preparations of nerve growth factor treated with N-bromosuccinimide closely parallels their biological activity. Binding of nerve growth factor receptor is saturable with an affinity constant of about 0.2 nM, similar to the reported plasma levels of the factor. Nerve growth factor does not elicit insulin-like biological effects in isolated adipocytes, and it does not modify the binding of [125I]insulin or [125I]epidermal growth factor to fat cells or liver membranes.
Keywords: rabbit, superior cervical ganglia, peptide hormones
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angeletti R. H., Aneletti P. U., Levi-Montalcini R. Selective accumulation of ( 125 I) labelled nerve growth factor in sympathetic ganglia. Brain Res. 1972 Nov 13;46:421–425. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(72)90033-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angeletti R. H., Bradshaw R. A. Nerve growth factor from mouse submaxillary gland: amino acid sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Oct;68(10):2417–2420. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.10.2417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angeletti R. H. The role of the tryptophan residues in the activity of the nerve growth factor. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Sep 29;214(3):478–482. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(70)90307-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bocchini V., Angeletti P. U. The nerve growth factor: purification as a 30,000-molecular-weight protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Oct;64(2):787–794. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.2.787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN S. Isolation of a mouse submaxillary gland protein accelerating incisor eruption and eyelid opening in the new-born animal. J Biol Chem. 1962 May;237:1555–1562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P. Insulin--receptor interactions in adipose tissue cells: direct measurement and properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jun;68(6):1264–1268. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.6.1264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P. Interaction of insulin with the cell membrane: the primary action of insulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Jun;63(2):450–457. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.2.450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P. Properties of the insulin receptor of isolated fat cell membranes. J Biol Chem. 1971 Dec 10;246(23):7265–7274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P. The insulin receptor. Diabetes. 1972;21(2 Suppl):396–402. doi: 10.2337/diab.21.2.s396. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cutrecasas P. Perturbation of the insulin receptor of isolated fat cells with proteolytic enzymes. Direct measurement of insulin-receptor interactions. J Biol Chem. 1971 Nov;246(21):6522–6531. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frazier W. A., Angeletti R. H., Bradshaw R. A. Nerve growth factor and insulin. Science. 1972 May 5;176(4034):482–488. doi: 10.1126/science.176.4034.482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hintz R. L., Clemmons D. R., Underwood L. E., Van Wyk J. J. Competitive binding of somatomedin to the insulin receptors of adipocytes, chondrocytes, and liver membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Aug;69(8):2351–2353. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.8.2351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVI-MONTALCINI R., MEYER H., HAMBURGER V. In vitro experiments on the effects of mouse sarcomas 180 and 37 on the spinal and sympathetic ganglia of the chick embryo. Cancer Res. 1954 Jan;14(1):49–57. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi-Montalcini R., Angeletti P. U. Nerve growth factor. Physiol Rev. 1968 Jul;48(3):534–569. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1968.48.3.534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varon S., Normura J., Shooter E. M. Reversible dissociation of the mouse nerve growth factor protein into different subunits. Biochemistry. 1968 Apr;7(4):1296–1303. doi: 10.1021/bi00844a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


