Abstract
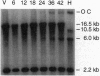
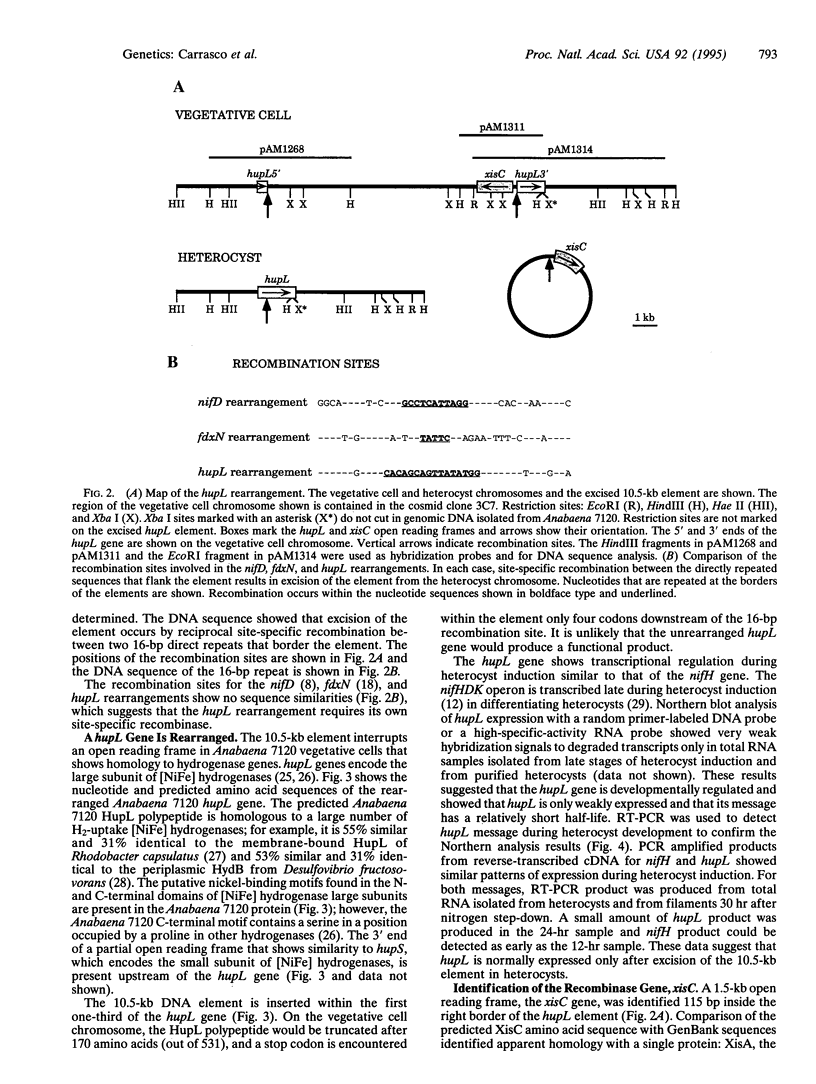
Programmed DNA rearrangements that occur during cellular differentiation are uncommon and have been described in only two prokaryotic organisms. Here, we identify the developmentally regulated rearrangement of a hydrogenase gene in heterocysts of the cyanobacterium Anabaena sp. strain PCC 7120. Heterocysts are terminally differentiated cells specialized for nitrogen fixation. Late during heterocyst differentiation, a 10.5-kb DNA element is excised from within the hupL gene by site-specific recombination between 16-bp direct repeats that flank the element. The predicted HupL polypeptide is homologous to the large subunit of [NiFe] uptake hydrogenases. hupL is expressed similarly to the nitrogen-fixation genes; hupL message was detected only during the late stages of heterocyst development. An open reading frame, named xisC, identified near one end of the hupL DNA element is presumed to encode the element's site-specific recombinase. The predicted XisC polypeptide is homologous with the Anabaena sp. strain PCC 7120 site-specific recombinase XisA. Neither XisC nor XisA shows sequence similarity to other proteins, suggesting that they represent a different class of site-specific recombinase.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altschul S. F., Gish W., Miller W., Myers E. W., Lipman D. J. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990 Oct 5;215(3):403–410. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brusca J. S., Chastain C. J., Golden J. W. Expression of the Anabaena sp. strain PCC 7120 xisA gene from a heterologous promoter results in excision of the nifD element. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jul;172(7):3925–3931. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.7.3925-3931.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buikema W. J., Haselkorn R. Isolation and complementation of nitrogen fixation mutants of the cyanobacterium Anabaena sp. strain PCC 7120. J Bacteriol. 1991 Mar;173(6):1879–1885. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.6.1879-1885.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrasco C. D., Ramaswamy K. S., Ramasubramanian T. S., Golden J. W. Anabaena xisF gene encodes a developmentally regulated site-specific recombinase. Genes Dev. 1994 Jan;8(1):74–83. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.1.74. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chastain C. J., Brusca J. S., Ramasubramanian T. S., Wei T. F., Golden J. W. A sequence-specific DNA-binding factor (VF1) from Anabaena sp. strain PCC 7120 vegetative cells binds to three adjacent sites in the xisA upstream region. J Bacteriol. 1990 Sep;172(9):5044–5051. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.9.5044-5051.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elhai J., Wolk C. P. Developmental regulation and spatial pattern of expression of the structural genes for nitrogenase in the cyanobacterium Anabaena. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3379–3388. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07539.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gellert M. V(D)J recombination gets a break. Trends Genet. 1992 Dec;8(12):408–412. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(92)90322-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golden J. W., Carrasco C. D., Mulligan M. E., Schneider G. J., Haselkorn R. Deletion of a 55-kilobase-pair DNA element from the chromosome during heterocyst differentiation of Anabaena sp. strain PCC 7120. J Bacteriol. 1988 Nov;170(11):5034–5041. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.11.5034-5041.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golden J. W., Mulligan M. E., Haselkorn R. Different recombination site specificity of two developmentally regulated genome rearrangements. Nature. 1987 Jun 11;327(6122):526–529. doi: 10.1038/327526a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golden J. W., Robinson S. J., Haselkorn R. Rearrangement of nitrogen fixation genes during heterocyst differentiation in the cyanobacterium Anabaena. Nature. 1985 Apr 4;314(6010):419–423. doi: 10.1038/314419a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golden J. W., Whorff L. L., Wiest D. R. Independent regulation of nifHDK operon transcription and DNA rearrangement during heterocyst differentiation in the cyanobacterium Anabaena sp. strain PCC 7120. J Bacteriol. 1991 Nov;173(22):7098–7105. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.22.7098-7105.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golden J. W., Wiest D. R. Genome rearrangement and nitrogen fixation in Anabaena blocked by inactivation of xisA gene. Science. 1988 Dec 9;242(4884):1421–1423. doi: 10.1126/science.3144039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haber J. E. Mating-type gene switching in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Trends Genet. 1992 Dec;8(12):446–452. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(92)90329-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haselkorn R. Developmentally regulated gene rearrangements in prokaryotes. Annu Rev Genet. 1992;26:113–130. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.26.120192.000553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel B., Losick R., Stragier P. The Bacillus subtilis gene for the development transcription factor sigma K is generated by excision of a dispensable DNA element containing a sporulation recombinase gene. Genes Dev. 1990 Apr;4(4):525–535. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.4.525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuritz T., Ernst A., Black T. A., Wolk C. P. High-resolution mapping of genetic loci of Anabaena PCC 7120 required for photosynthesis and nitrogen fixation. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Apr;8(1):101–110. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01207.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lammers P. J., Golden J. W., Haselkorn R. Identification and sequence of a gene required for a developmentally regulated DNA excision in Anabaena. Cell. 1986 Mar 28;44(6):905–911. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90013-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leclerc M., Colbeau A., Cauvin B., Vignais P. M. Cloning and sequencing of the genes encoding the large and the small subunits of the H2 uptake hydrogenase (hup) of Rhodobacter capsulatus. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Sep;214(1):97–107. doi: 10.1007/BF00340186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan M. E., Haselkorn R. Nitrogen fixation (nif) genes of the cyanobacterium Anabaena species strain PCC 7120. The nifB-fdxN-nifS-nifU operon. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 15;264(32):19200–19207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oettinger M. A. Activation of V(D)J recombination by RAG1 and RAG2. Trends Genet. 1992 Dec;8(12):413–416. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(92)90323-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Przybyla A. E., Robbins J., Menon N., Peck H. D., Jr Structure-function relationships among the nickel-containing hydrogenases. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 1992 Feb;8(2):109–135. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1992.tb04960.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramasubramanian T. S., Wei T. F., Golden J. W. Two Anabaena sp. strain PCC 7120 DNA-binding factors interact with vegetative cell- and heterocyst-specific genes. J Bacteriol. 1994 Mar;176(5):1214–1223. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.5.1214-1223.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rousset M., Dermoun Z., Hatchikian C. E., Bélaich J. P. Cloning and sequencing of the locus encoding the large and small subunit genes of the periplasmic [NiFe]hydrogenase from Desulfovibrio fructosovorans. Gene. 1990 Sep 28;94(1):95–101. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90473-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato T., Samori Y., Kobayashi Y. The cisA cistron of Bacillus subtilis sporulation gene spoIVC encodes a protein homologous to a site-specific recombinase. J Bacteriol. 1990 Feb;172(2):1092–1098. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.2.1092-1098.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark W. M., Boocock M. R., Sherratt D. J. Catalysis by site-specific recombinases. Trends Genet. 1992 Dec;8(12):432–439. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobler H., Etter A., Müller F. Chromatin diminution in nematode development. Trends Genet. 1992 Dec;8(12):427–432. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(92)90326-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu L. F., Mandrand M. A. Microbial hydrogenases: primary structure, classification, signatures and phylogeny. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 1993 Apr;10(3-4):243–269. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1993.tb05870.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]