Abstract
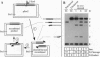
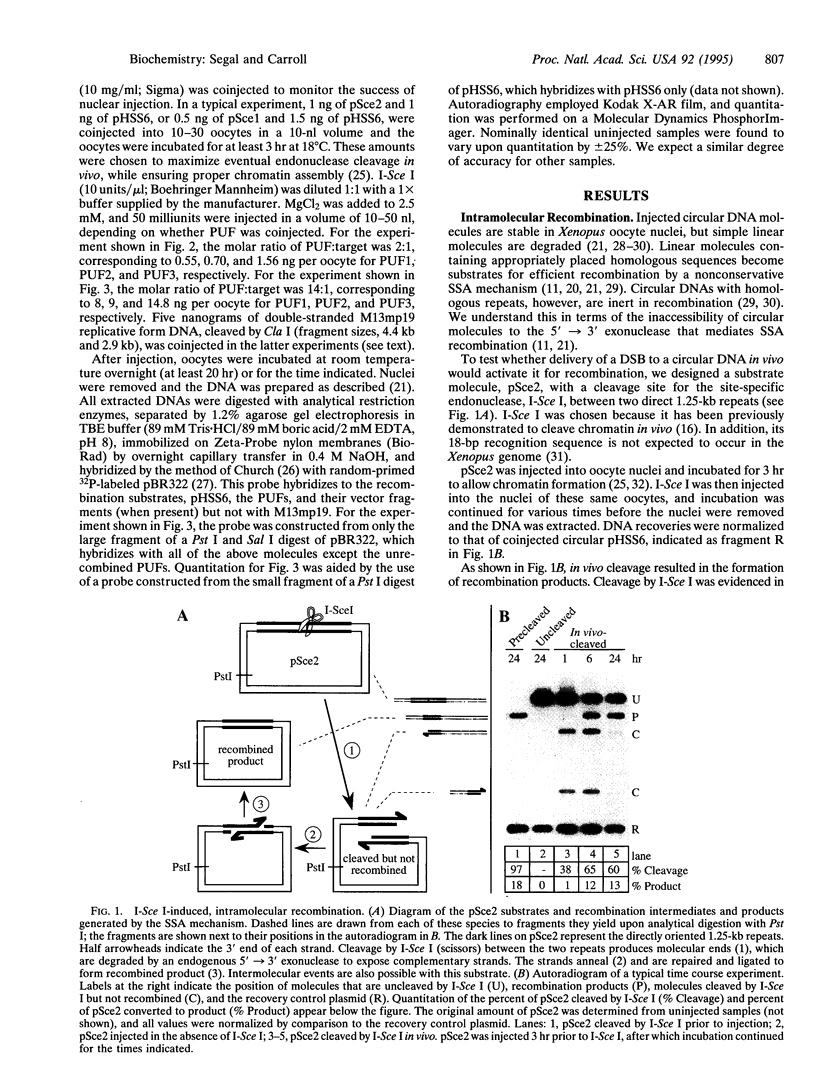
Homologous recombination in gene targeting in most organisms occurs by an inefficient mechanism. Inducing a double-strand break in the chromosomal target may increase this efficiency by allowing recombination to proceed by the highly efficient single-strand annealing mechanism. A gene targeting experiment was modeled in Xenopus oocytes by using a circular plasmid to mimic the chromosomal target site and a homologous linear molecule (pick-up fragment or PUF) as an analogue of the vector DNA. When those two molecules were simply injected together, no recombination was observed. In contrast, when the circular plasmid was cleaved in vivo by injection of the site-specific endonuclease, I-Sce I, relatively efficient intermolecular recombination occurred, involving up to 17% of the cleaved molecules. Recombination was dependent on the stability of the PUF; product yield was increased by using longer fragments and by injecting larger amounts of linear DNA, both of which increased the lifetime of the PUF in the oocytes. These results demonstrate that in vivo double-strand breaks can induce homologous recombination of reluctant substrates and may be useful in augmenting the efficiency of gene targeting.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Capecchi M. R. Altering the genome by homologous recombination. Science. 1989 Jun 16;244(4910):1288–1292. doi: 10.1126/science.2660260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capecchi M. Gene targeting. How efficient can you get? Nature. 1990 Nov 8;348(6297):109–109. doi: 10.1038/348109a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll D., Garrett J. E., Lam B. S. Isolated clusters of paired tandemly repeated sequences in the Xenopus laevis genome. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Feb;4(2):254–259. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.2.254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll D., Wright S. H., Wolff R. K., Grzesiuk E., Maryon E. B. Efficient homologous recombination of linear DNA substrates after injection into Xenopus laevis oocytes. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2053–2061. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colleaux L., D'Auriol L., Galibert F., Dujon B. Recognition and cleavage site of the intron-encoded omega transposase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):6022–6026. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.6022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deng C., Capecchi M. R. Reexamination of gene targeting frequency as a function of the extent of homology between the targeting vector and the target locus. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;12(8):3365–3371. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.8.3365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gargiulo G., Worcel A. Analysis of the chromatin assembled in germinal vesicles of Xenopus oocytes. J Mol Biol. 1983 Nov 5;170(3):699–722. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80128-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrett J. E., Carroll D. Tx1: a transposable element from Xenopus laevis with some unusual properties. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Mar;6(3):933–941. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.3.933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gloor G. B., Nassif N. A., Johnson-Schlitz D. M., Preston C. R., Engels W. R. Targeted gene replacement in Drosophila via P element-induced gap repair. Science. 1991 Sep 6;253(5024):1110–1117. doi: 10.1126/science.1653452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasty P., Rivera-Pérez J., Bradley A. The role and fate of DNA ends for homologous recombination in embryonic stem cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;12(6):2464–2474. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.6.2464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jasin M., Berg P. Homologous integration in mammalian cells without target gene selection. Genes Dev. 1988 Nov;2(11):1353–1363. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.11.1353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeong-Yu S. J., Carroll D. Test of the double-strand-break repair model of recombination in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;12(1):112–119. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.1.112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeong-Yu S., Carroll D. Effect of terminal nonhomologies on homologous recombination in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;12(12):5426–5437. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.12.5426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koller B. H., Smithies O. Altering genes in animals by gene targeting. Annu Rev Immunol. 1992;10:705–730. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.10.040192.003421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehman C. W., Clemens M., Worthylake D. K., Trautman J. K., Carroll D. Homologous and illegitimate recombination in developing Xenopus oocytes and eggs. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Nov;13(11):6897–6906. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.11.6897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin F. L., Sperle K., Sternberg N. Model for homologous recombination during transfer of DNA into mouse L cells: role for DNA ends in the recombination process. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jun;4(6):1020–1034. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.6.1020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansour S. L., Thomas K. R., Capecchi M. R. Disruption of the proto-oncogene int-2 in mouse embryo-derived stem cells: a general strategy for targeting mutations to non-selectable genes. Nature. 1988 Nov 24;336(6197):348–352. doi: 10.1038/336348a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maryon E., Carroll D. Characterization of recombination intermediates from DNA injected into Xenopus laevis oocytes: evidence for a nonconservative mechanism of homologous recombination. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;11(6):3278–3287. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.6.3278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maryon E., Carroll D. Degradation of linear DNA by a strand-specific exonuclease activity in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):4862–4871. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.4862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maryon E., Carroll D. Involvement of single-stranded tails in homologous recombination of DNA injected into Xenopus laevis oocyte nuclei. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;11(6):3268–3277. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.6.3268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller T. J., Mertz J. E. Template structural requirements for transcription in vivo by RNA polymerase II. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Dec;2(12):1595–1607. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.12.1595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozenberger B. A., Roeder G. S. A unique pathway of double-strand break repair operates in tandemly repeated genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1222–1231. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pei D., Corey D. R., Schultz P. G. Site-specific cleavage of duplex DNA by a semisynthetic nuclease via triple-helix formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):9858–9862. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.9858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennington S. L., Wilson J. H. Gene targeting in Chinese hamster ovary cells is conservative. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 1;88(21):9498–9502. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrin A., Buckle M., Dujon B. Asymmetrical recognition and activity of the I-SceI endonuclease on its site and on intron-exon junctions. EMBO J. 1993 Jul;12(7):2939–2947. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05956.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrouault L., Asseline U., Rivalle C., Thuong N. T., Bisagni E., Giovannangeli C., Le Doan T., Hélène C. Sequence-specific artificial photo-induced endonucleases based on triple helix-forming oligonucleotides. Nature. 1990 Mar 22;344(6264):358–360. doi: 10.1038/344358a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plasterk R. H., Groenen J. T. Targeted alterations of the Caenorhabditis elegans genome by transgene instructed DNA double strand break repair following Tc1 excision. EMBO J. 1992 Jan;11(1):287–290. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05051.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plessis A., Perrin A., Haber J. E., Dujon B. Site-specific recombination determined by I-SceI, a mitochondrial group I intron-encoded endonuclease expressed in the yeast nucleus. Genetics. 1992 Mar;130(3):451–460. doi: 10.1093/genetics/130.3.451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pont-Kingdon G., Dawson R. J., Carroll D. Intermediates in extrachromosomal homologous recombination in Xenopus laevis oocytes: characterization by electron microscopy. EMBO J. 1993 Jan;12(1):23–34. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05628.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puchta H., Dujon B., Hohn B. Homologous recombination in plant cells is enhanced by in vivo induction of double strand breaks into DNA by a site-specific endonuclease. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Nov 11;21(22):5034–5040. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.22.5034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouet P., Smih F., Jasin M. Expression of a site-specific endonuclease stimulates homologous recombination in mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jun 21;91(13):6064–6068. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.13.6064. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudin N., Haber J. E. Efficient repair of HO-induced chromosomal breaks in Saccharomyces cerevisiae by recombination between flanking homologous sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;8(9):3918–3928. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.9.3918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudin N., Sugarman E., Haber J. E. Genetic and physical analysis of double-strand break repair and recombination in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1989 Jul;122(3):519–534. doi: 10.1093/genetics/122.3.519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strobel S. A., Dervan P. B. Site-specific cleavage of a yeast chromosome by oligonucleotide-directed triple-helix formation. Science. 1990 Jul 6;249(4964):73–75. doi: 10.1126/science.2195655. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweigert S. E., Carroll D. Repair and recombination of X-irradiated plasmids in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;10(11):5849–5856. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.11.5849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas K. R., Capecchi M. R. Site-directed mutagenesis by gene targeting in mouse embryo-derived stem cells. Cell. 1987 Nov 6;51(3):503–512. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90646-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas K. R., Folger K. R., Capecchi M. R. High frequency targeting of genes to specific sites in the mammalian genome. Cell. 1986 Feb 14;44(3):419–428. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90463-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyllie A. H., Laskey R. A., Finch J., Gurdon J. B. Selective DNA conservation and chromatin assembly after injection of SV40 DNA into Xenopus oocytes. Dev Biol. 1978 May;64(1):178–188. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(78)90069-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng H., Wilson J. H. Gene targeting in normal and amplified cell lines. Nature. 1990 Mar 8;344(6262):170–173. doi: 10.1038/344170a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]