Abstract
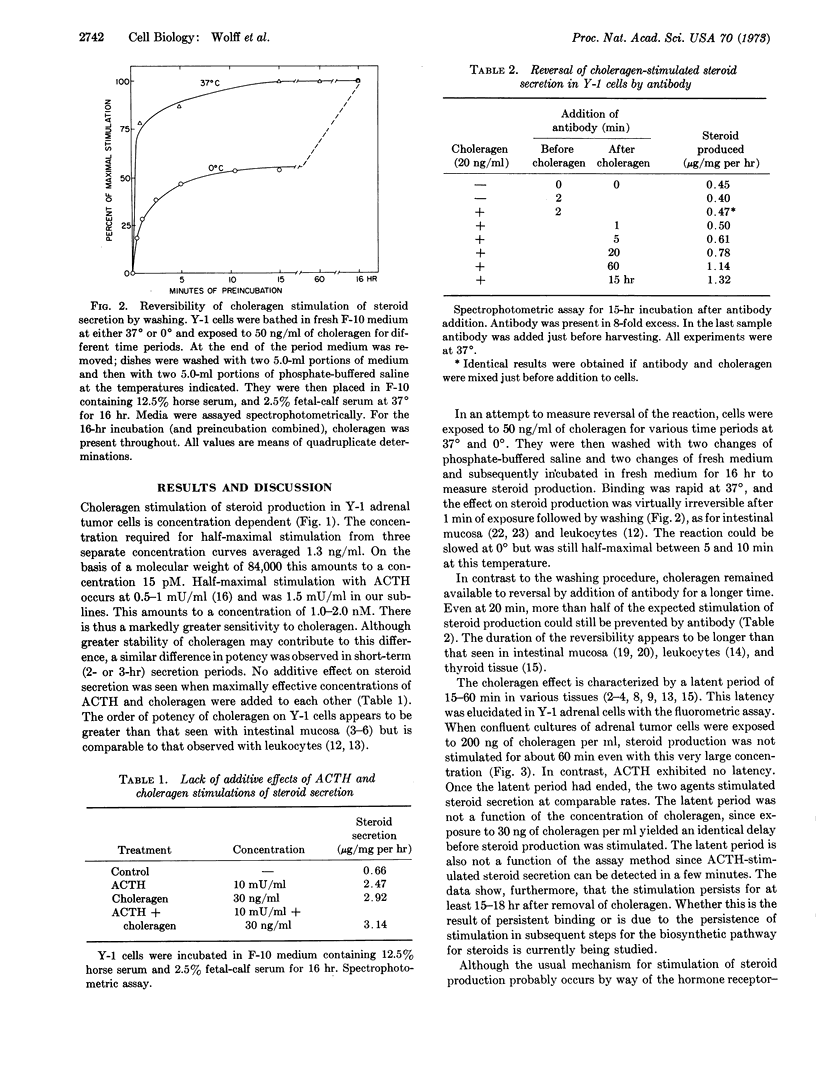
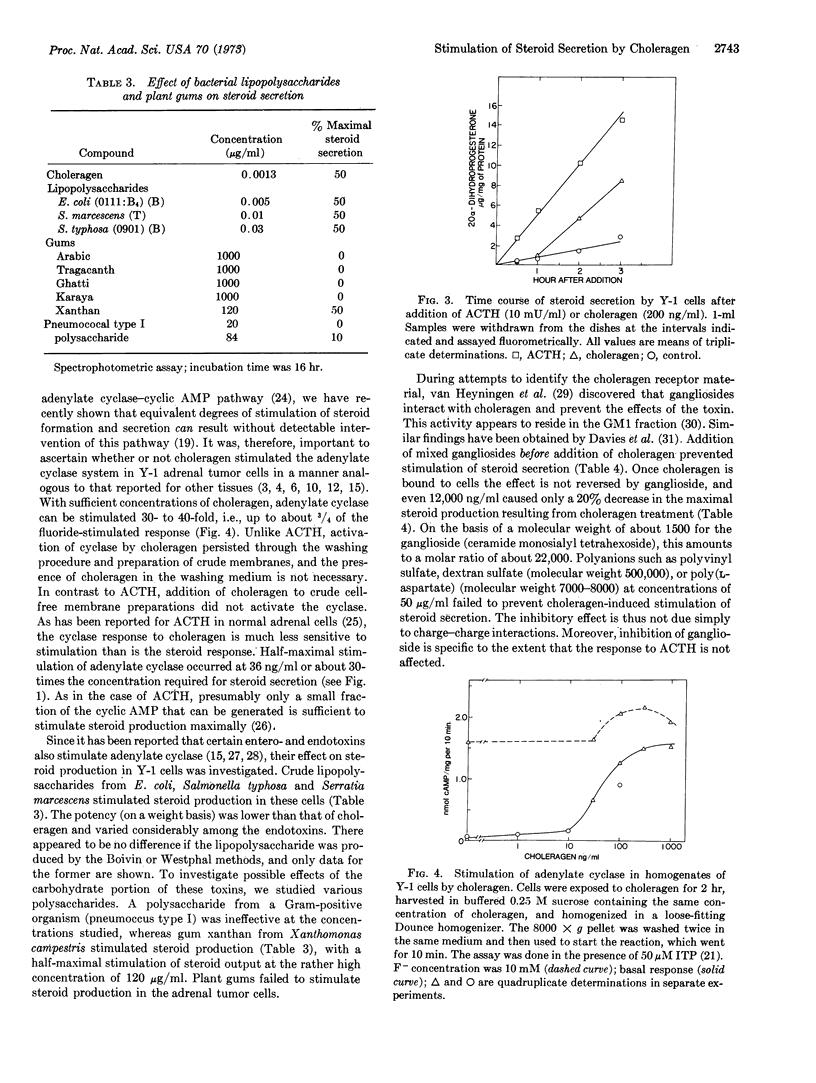
Choleragen, the pure protein from cholera toxin, stimulates steroid secretion by Y-1 adrenal tumor cells in culture. The secreted steroids are the same as seen after addition of adrenocorticotropic hormone. Half-maximal stimulation occurs at 15 pM; stimulation is essentially irreversible by washing and partially reversible (for about 1 hr) by antibody, and there is a latent period of about 60 min before stimulation is seen. Stimulation of adenylate cyclase occurs at about 30-fold higher choleragen concentrations. Gangliosides inhibit choleragen stimulation when added before but not after the toxin. Lipopolysaccharides from Escherichia coli, Salmonella typhosa, and Serratia marcescens also stimulate steroid secretion, but are less potent than choleragen.
Keywords: cholera enterotoxin, adenylate cyclase, adrenocorticotropic hormone
Full text
PDF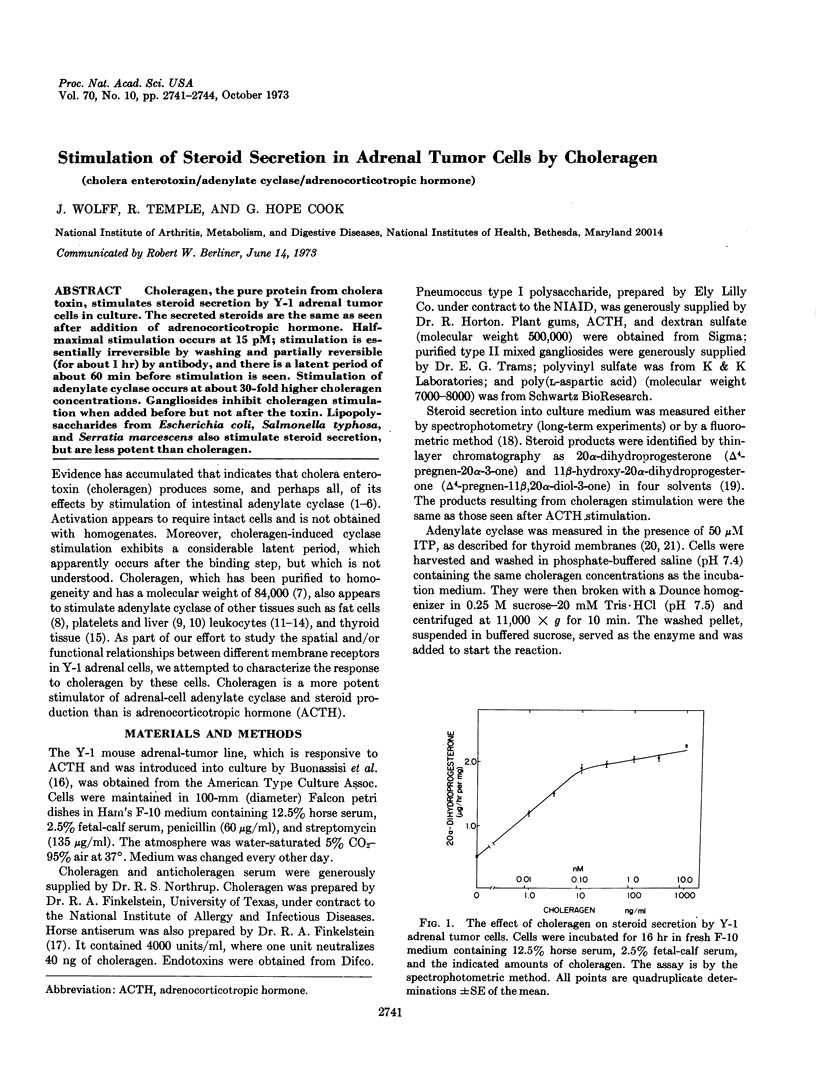

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BUONASSISI V., SATO G., COHEN A. I. Hormone-producing cultures of adrenal and pituitary tumor origin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Jul 15;48:1184–1190. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.7.1184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bitensky M. W., Gorman R. E., Thomas L. Selective stimulation of epinephrine-responsive adenyl cyclase in mice by endotoxin. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1971 Dec;138(3):773–775. doi: 10.3181/00379727-138-35986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R. Cholera enterotoxin: failure of anti-inflammatory agents to prevent cyclic AMP accumulation. Nature. 1973 Feb 9;241(5389):399–399. doi: 10.1038/241399a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R., Lehrer R. I., Lichtenstein L. M., Weissmann G., Zurier R. Effects of cholera enterotoxin on adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate and neutrophil function. Comparison with other compounds which stimulate leukocyte adenyl cyclase. J Clin Invest. 1973 Mar;52(3):698–708. doi: 10.1172/JCI107231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J., Tyrrell D. A., Ramsden D. B., Louis L. N., Milne R. G. Some inhibitors of the effect of cholera toxin on HeLa cells. Exp Mol Pathol. 1973 Feb;18(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(73)90002-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donta S. T., King M., Sloper K. Induction of steroidogenesis in tissue culture by cholera enterotoxin. Nat New Biol. 1973 Jun 20;243(129):246–247. doi: 10.1038/newbio243246a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. J., Jr, Chen L. C., Curlin G. T., Evans D. G. Stimulation of adenyl cyclase by Escherichia coli enterotoxin. Nat New Biol. 1972 Apr 5;236(66):137–138. doi: 10.1038/newbio236137a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field M., Plotkin G. R., Silen W. Effects of vasopressin, theophylline and cyclic adenosine monophosphate on short-circuit current across isolated rabbit ileal mucosa. Nature. 1968 Feb 3;217(5127):469–471. doi: 10.1038/217469a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein R. A. Monospecific equine antiserum against cholera exo-enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1970 Dec;2(6):691–697. doi: 10.1128/iai.2.6.691-697.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garren L. D., Gill G. N., Masui H., Walton G. M. On the mechanism of action of ACTH. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1971;27:433–478. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571127-2.50035-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman R. E., Bitensky M. W. Selective effects of cholera toxin on the adrenaline responsive component of hepatic adenyl cyclase. Nature. 1972 Feb 25;235(5339):439–440. doi: 10.1038/235439a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrant R. L., Chen L. C., Sharp G. W. Intestinal adenyl-cyclase activity in canine cholera: correlation with fluid accumulation. J Infect Dis. 1972 Apr;125(4):377–381. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.4.377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren J., Lönnroth I., Svennerholm L. Fixation and inactivation of cholera toxin by GM1 ganglioside. Scand J Infect Dis. 1973;5(1):77–78. doi: 10.3109/inf.1973.5.issue-1.15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimberg D. V., Field M., Johnson J., Henderson A., Gershon E. Stimulation of intestinal mucosal adenyl cyclase by cholera enterotoxin and prostaglandins. J Clin Invest. 1971 Jun;50(6):1218–1230. doi: 10.1172/JCI106599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowal J., Fiedler R. Arenal cells in tissue culture. I. Assay of steroid products; steroidogenic responses to peptide hormones. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 Nov;128(2):406–421. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90047-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtenstein L. M., Henney C. S., Bourne H. R., Greenough W. B., 3rd Effects of cholera toxin on in vitro models of immediate and delayed hypersensitivity. Further evidence for the role of cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate. J Clin Invest. 1973 Mar;52(3):691–697. doi: 10.1172/JCI107230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lospalluto J. J., Finkelstein R. A. Chemical and physical properties of cholera exo-enterotoxin (choleragen) and its spontaneously formed toxoid (choleragenoid). Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jan 26;257(1):158–166. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(72)90265-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackie C., Richardson M. C., Schulster D. Kinetics and dose-response characteristics of adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate production by isolated rat adrenal cells stimulated with adrenocorticotrophic hormone. FEBS Lett. 1972 Jul 1;23(3):345–348. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80312-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mashiter K., Mashiter G. D., Hauger R. L., Field J. B. Effects of cholera and E. coli enterotoxins on cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate levels and intermediary metabolism in the thyroid. Endocrinology. 1973 Feb;92(2):541–549. doi: 10.1210/endo-92-2-541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGonagle T. J., Serebro H. A., Iber F. L., Bayless T. M., Hendrix T. R. Time of onset of action of cholera toxin in dog and rabbit. Gastroenterology. 1969 Jul;57(1):5–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moyle W. R., Kong Y. C., Ramachandran J. Steroidogenesis and cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate accumulation in rat adrenal cells. Divergent effects of adrenocorticotropin and its o-nitrophenyl sulfenyl derivative. J Biol Chem. 1973 Apr 10;248(7):2409–2417. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce N. F., Carpenter C. C., Jr, Elliott H. L., Greenough W. B., 3rd Effects of prostaglandins, theophylline, and cholera exotoxin upon transmucosal water and electrolyte movement in the canine jejunum. Gastroenterology. 1971 Jan;60(1):22–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schafer D. E., Lust W. D., Sircar B., Goldberg N. D. Elevated concentration of adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate in intestinal mucosa after treatment with cholera toxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Oct;67(2):851–856. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.2.851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp G. W., Hynie S. Stimulation of intestinal adenyl cyclase by cholera toxin. Nature. 1971 Jan 22;229(5282):266–269. doi: 10.1038/229266a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strom T. B., Deisseroth A., Morganroth J., Carpenter C. B., Merrill J. P. Alteration of the cytotoxic action of sensitized lymphocytes by cholinergic agents and activators of adenylate cyclase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Oct;69(10):2995–2999. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.10.2995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Temple R., Wolff J. Stimulation of steroid secretion by antimicrotubular agents. J Biol Chem. 1973 Apr 25;248(8):2691–2698. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Heyningen W. E., Carpenter C. C., Pierce N. F., Greenough W. B., 3rd Deactivation of cholera toxin by ganglioside. J Infect Dis. 1971 Oct;124(4):415–418. doi: 10.1093/infdis/124.4.415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughan M., Pierce N. F., Greenough W. B., 3rd Stimulation of glycerol production in fat cells by cholera toxin. Nature. 1970 May 16;226(5246):658–659. doi: 10.1038/226658a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff J., Cook G. H. Activation of thyroid membrane adenylate cyclase by purine nucleotides. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jan 10;248(1):350–355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff J., Jones A. B. The purification of bovine thyroid plasma membranes and the properties of membrane-bound adenyl cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jun 25;246(12):3939–3947. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zieve P. D., Pierce N. F., Greenough W. B., 3rd Stimulation of glycogenolysis by purified cholera exotoxin in disrupted cells. Johns Hopkins Med J. 1971 Dec;129(6):299–303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



