Abstract
A competition-hybridization assay has been developed for the majority of sequences present in embryonically synthesized histone messenger RNA. The assay permits the first direct demonstration of specific “maternal” messengers in unfertilized sea-urchin eggs. The molecular size of histone messenger RNA stored in the egg appears to be the same as that of histone messenger RNA synthesized by the embryo. Maternal histone messenger RNA is found in the soluble phase of egg homogenates, in the form of ribonucleoprotein particles, unassociated with ribosomes.
Keywords: sea-urchin eggs and embryos, competition-hybridization, subcellular localization
Full text
PDF


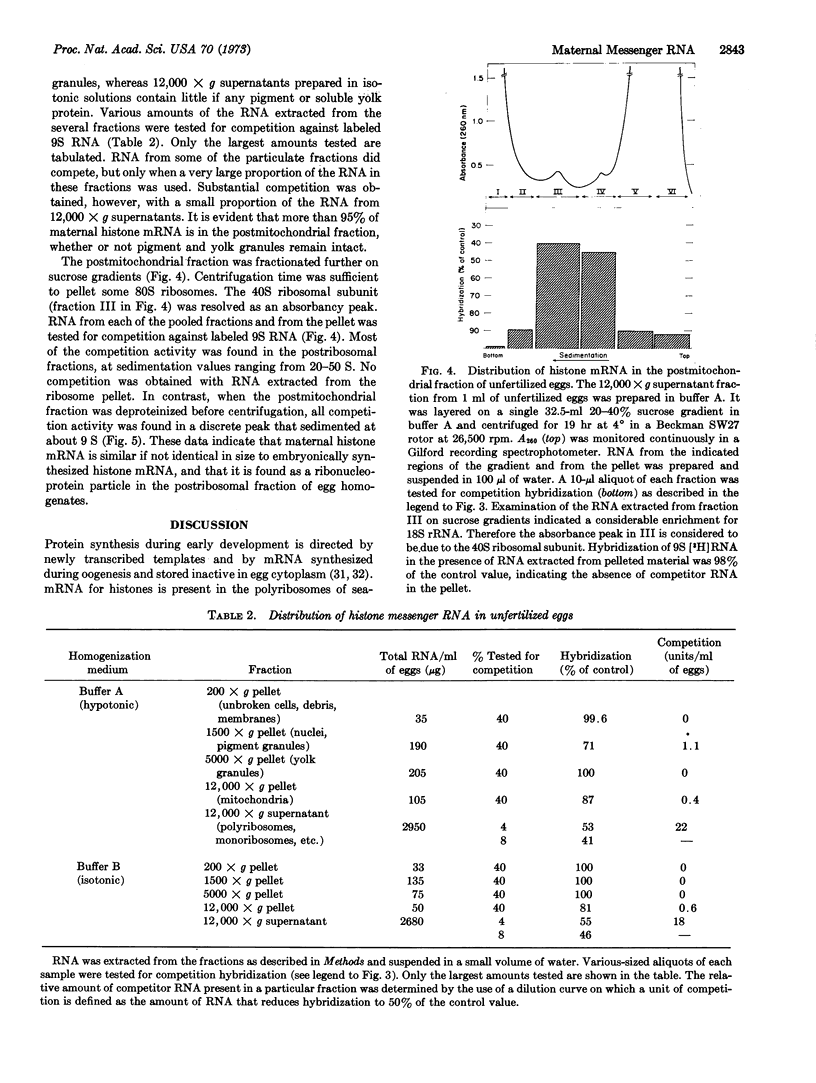

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ando T. A nuclease specific for heat-denatured DNA in isolated from a product of Aspergillus oryzae. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Jan 18;114(1):158–168. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(66)90263-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltimore D., Huang A. S. Interaction of HeLa cell proteins with RNA. J Mol Biol. 1970 Feb 14;47(3):263–273. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90301-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. O., Pemberton R., Baglioni C. Reiteration frequency of haemoglobin genes in the duck. Nat New Biol. 1972 Feb 23;235(60):231–234. doi: 10.1038/newbio235231a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crane C. M., Villee C. A. The synthesis of nuclear histones in early embryogenesis. J Biol Chem. 1971 Feb 10;246(3):719–723. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crippa M., Davidson E. H., Mirsky A. E. Persistence in early amphibian embryos of informational RNA's from the lampbrush chromosome stage of oögenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Apr;57(4):885–892. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.4.885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson E. H., Hough B. R. Genetic information in oocyte RNA. J Mol Biol. 1971 Mar 28;56(3):491–506. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90396-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denny P. C., Tyler A. Activation of protein biosynthesis in non-nucleate fragments of sea urchin eggs. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1964;14:245–249. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(64)90443-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farquhar M. N., McCarthy B. J. Histone mRNA in eggs and embryos of Strongylocentrotus purpuratus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Jul 17;53(2):515–522. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90692-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROSS P. R., COUSINEAU G. H. MACROMOLECULE SYNTHESIS AND THE INFLUENCE OF ACTINOMYCIN ON EARLY DEVELOPMENT. Exp Cell Res. 1964 Feb;33:368–395. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(64)90002-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie D., Spiegelman S. A quantitative assay for DNA-RNA hybrids with DNA immobilized on a membrane. J Mol Biol. 1965 Jul;12(3):829–842. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80331-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glisin V. R., Glisin M. V., Doty P. The nature of messenger RNA in the early stages of sea urchin development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Jul;56(1):285–289. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.1.285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross K. W., Jacobs-Lorena M., Baglioni C., Gross P. R. Cell-free translation of maternal messenger RNA from sea urchin eggs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Sep;70(9):2614–2618. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.9.2614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross K., Ruderman J., Jacobs-Lorena M., Baglioni C., Gross P. R. Cell-free synthesis of histones directed by messenger RNA from sea urchin embryos. Nat New Biol. 1973 Feb 28;241(113):272–274. doi: 10.1038/newbio241272a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross P. R. Biochemistry of differentiation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1968;37:631–660. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.37.070168.003215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross P. R., Malkin L. I., Hubbard M. Synthesis of RNA during oogenesis in the sea urchin. J Mol Biol. 1965 Sep;13(2):463–481. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80110-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross P. R. RNA metabolism in embryonic development and differentiation. I. Fertilization and after. N Engl J Med. 1967 Jun 1;276(22):1239–1247. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196706012762206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O., Gross P. R. A method for separating cells from early sea urchin embryos. Dev Biol. 1970 Mar;21(3):383–402. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(70)90131-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O., Gross P. R. Informational RNA sequences in early sea urchin embryos. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jan 18;259(1):104–111. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(72)90477-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Infante A. A., Nemer M. Accumulation of newly synthesized RNA templates in a unique class of polyribosomes during embryogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Aug;58(2):681–688. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.2.681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kedes L. H., Birnstiel M. L. Reiteration and clustering of DNA sequences complementary to histone messenger RNA. Nat New Biol. 1971 Apr 7;230(14):165–169. doi: 10.1038/newbio230165a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kedes L. H., Gross P. R., Cognetti G., Hunter A. L. Synthesis of nuclear and chromosomal proteins on light polyribosomes during cleavage in the sea urchin embryo. J Mol Biol. 1969 Oct 28;45(2):337–351. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90109-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kedes L. H., Gross P. R. Identification in cleaving embryos of three RNA species serving as templates for the synthesis of nuclear proteins. Nature. 1969 Sep 27;223(5213):1335–1339. doi: 10.1038/2231335a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg U., Darnell J. E. SV40-specific RNA in the nucleus and polyribosomes of transformed cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Apr;65(4):1089–1096. doi: 10.1073/pnas.65.4.1089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melli M., Whitfield C., Rao K. V., Richardson M., Bishop J. O. DNA-RNA hybridization in vast DNA excess. Nat New Biol. 1971 May 5;231(18):8–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemer M., Infante A. A. Messenger RNA in early sea-urchin embryos: size classes. Science. 1965 Oct 8;150(3693):217–221. doi: 10.1126/science.150.3693.217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinaldi A. M., Monroy A. Polyribosome formation and RNA synthesis in the early post-fertilization stages of the sea urchin egg. Dev Biol. 1969 Jan;19(1):73–86. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(69)90071-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STUDIER F. W. SEDIMENTATION STUDIES OF THE SIZE AND SHAPE OF DNA. J Mol Biol. 1965 Feb;11:373–390. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80064-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sconzo G., Giudice G. Synthesis of ribosomal RNA in sea urchin embryos. V. Further evidence for an activation following the hatching blastula stage. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Dec 30;254(3):447–451. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(71)90878-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slater D. W., Slater I., Gillespie D. Post-fertilization synthesis of polyadenylic acid in sea urchin embryos. Nature. 1972 Dec 8;240(5380):333–337. doi: 10.1038/240333a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slater D. W., Spiegelman S. An estimation of genetic messages in the unfertilized echinoid egg. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Jul;56(1):164–170. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.1.164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slater I., Gillespie D., Slater D. W. Cytoplasmic adenylylation and processing of maternal RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Feb;70(2):406–411. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.2.406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutton W. D. A crude nuclease preparation suitable for use in DNA reassociation experiments. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Jul 29;240(4):522–531. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(71)90709-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg E. S., Birnstiel M. L., Purdom I. F., Williamson R. Genes coding for polysomal 9S RNA of sea urchins: conservation and divergence. Nature. 1972 Nov 24;240(5378):225–228. doi: 10.1038/240225a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whiteley A. H., McCarthy B. J., Whiteley H. R. Changing populations of messenger RNA during sea urchin development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Mar;55(3):519–525. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.3.519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whiteley H. R., McCarthy B. J., Whiteley A. H. Conservation of base sequences in RNA for early development of echinoderms. Dev Biol. 1970 Feb;21(1):216–242. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(70)90069-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




