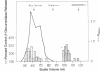
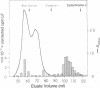
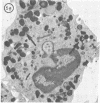
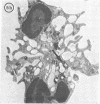
Abstract
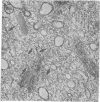
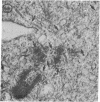
A low-molecular-weight component of complement, similar to or identical with human C5a, interacts with human polymorphonuclear leukocytes treated with cytochalasin B and provokes extracellular release of lysosomal enzymes from these cells. Enzyme release occurs in the absence of particles and is selective in that it is not accompained by release of cytoplasmic enzymes. Cell viability is not altered. Pharmacologic agents that regulate secretion of other inflammatory mediators influenced complement-dependent enzyme release: cAMP and theophylline, prostaglandin E1 and colchicine inhibited, whereas cGMP enhanced release of enzymes. Ultra-structural histochemistry of cells exposed to this component of complement revealed degranulation, fusion of lysosomal with plasma membranes, and transient assembly of microtubules associated with the release of endogenous myeloperoxidase. Our findings suggest that these intracellular events are common to two important responses of polymorphonuclear leukocytes in inflammation and tissue injury: (a) release of lysosomal hydrolases and (b) chemotaxis.
Keywords: C5a, chemotaxis, cytochalasin B, cAMP: cGMP antagonism
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allison A. C., Davies P., De Petris S. Role of contractile microfilaments in macrophage movement and endocytosis. Nat New Biol. 1971 Aug 4;232(31):153–155. doi: 10.1038/newbio232153a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brittinger G., Hirschhorn R., Douglas S. D., Weissmann G. Studies on lysosomes. XI. Characterization of a hydrolase-rich fraction from human lymphocytes. J Cell Biol. 1968 May;37(2):394–411. doi: 10.1083/jcb.37.2.394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter S. B. Effects of cytochalasins on mammalian cells. Nature. 1967 Jan 21;213(5073):261–264. doi: 10.1038/213261a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies P., Fox R. I., Polyzonis M., Allison A. C., Haswell A. D. The inhibition of phagocytosis and facilitation of exocytosis in rabbit polymorphonuclear leukocytes by cytochalasin B. Lab Invest. 1973 Jan;28(1):16–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis A. T., Estensen R., Quie P. G. Cytochalasin B. 3. Inhibition of human polymorphonuclear leukocyte phagocytosis. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1971 May;137(1):161–164. doi: 10.3181/00379727-137-35535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebstensen R. D., Plagemann P. G. Cytochalasin B: inhibition of glucose and glucosamine transport. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1430–1434. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallin J. I., Clark R. A., Kimball H. R. Granulocyte chemotaxis: an improved in vitro assay employing 51 Cr-labeled granulocytes. J Immunol. 1973 Jan;110(1):233–240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie E., Lichtenstein L. M. Heavy water enhances IgE-mediated histamine release from human leukocytes: evidence for microtubule involvement.. 1. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1972 Sep;140(4):1228–1230. doi: 10.3181/00379727-140-36647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie E., Lichtenstein L. M. Histamine release from human leukocytes: studies with deuterium oxide, colchicine, and cytochalasin B. J Clin Invest. 1972 Nov;51(11):2941–2947. doi: 10.1172/JCI107118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein I. M., Brai M., Osler A. G., Weissmann G. Lysosomal enzyme release from human leukocytes: mediation by the alternate pathway of complement activation. J Immunol. 1973 Jul;111(1):33–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham R. C., Jr, Karnovsky M. J. The early stages of absorption of injected horseradish peroxidase in the proximal tubules of mouse kidney: ultrastructural cytochemistry by a new technique. J Histochem Cytochem. 1966 Apr;14(4):291–302. doi: 10.1177/14.4.291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henson P. M. Interaction of cells with immune complexes: adherence, release of constituents, and tissue injury. J Exp Med. 1971 Sep 1;134(3 Pt 2):114s–135s. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaliner M., Orange R. P., Austen K. F. Immunological release of histamine and slow reacting substance of anaphylaxis from human lung. J Exp Med. 1972 Sep 1;136(3):556–567. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.3.556. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kletzien R. F., Perdue J. F., Springer A. Cytochalasin A and B. Inhibition of sugar uptake in cultured cells. J Biol Chem. 1972 May 10;247(9):2964–2966. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NILSSON U. R., MUELLER-EBERHARD H. J. ISOLATION OF BETA IF-GLOBULIN FROM HUMAN SERUM AND ITS CHARACTERIZATION AS THE FIFTH COMPONENT OF COMPLEMENT. J Exp Med. 1965 Aug 1;122:277–298. doi: 10.1084/jem.122.2.277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orange R. P., Austen W. G., Austen K. F. Immunological release of histamine and slow-reacting substance of anaphylaxis from human lung. I. Modulation by agents influencing cellular levels of cyclic 3',5'-adenosine monophosphate. J Exp Med. 1971 Sep 1;134(3 Pt 2):136s–148s. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plagemann P. G., Estensen R. D. Cytochalasin B. VI. Competitive inhibition of nucleoside transport by cultured Novikoff rat hepatoma cells. J Cell Biol. 1972 Oct;55(1):179–185. doi: 10.1083/jcb.55.1.179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsung P. K., Weissmann G. Inhibitor of adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate binding and protein kinase activity in leucocyte lysosomes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Apr 16;51(4):836–842. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90002-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ULMER D. D., VALLEE B. L., WACKER W. E. Metalloenzymes and myocardial infarction. II. Malic and lactic dehydrogenase activities and zinc concentrations in serum. N Engl J Med. 1956 Sep 6;255(10):450–456. doi: 10.1056/NEJM195609062551001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vallota E. H., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Formation of C3a and C5a anaphylatoxins in whole human serum after inhibition of the anaphylatoxin inactivator. J Exp Med. 1973 May 1;137(5):1109–1123. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.5.1109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vroon D. H., Schultz D. R., Zarco R. M. The separation of nine components and two inactivators of components of complement in humansserum. Immunochemistry. 1970 Jan;7(1):43–61. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(70)90029-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. A., Newman L. J. A neutrophil chemotactic factor from human C'5. J Immunol. 1969 Jan;102(1):93–99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissmann G., Zurier R. B., Hoffstein S. Leukocytic proteases and the immunologic release of lysosomal enzymes. Am J Pathol. 1972 Sep;68(3):539–564. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissmann G., Zurier R. B., Spieler P. J., Goldstein I. M. Mechanisms of lysosomal enzyme release from leukocytes exposed to immune complexes and other particles. J Exp Med. 1971 Sep 1;134(3 Pt 2):149s–165s. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zurier R. B., Hoffstein S., Weissmann G. Cytochalasin B: effect on lysosomal enzyme release from human leukocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Mar;70(3):844–848. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.3.844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zurier R. B., Hoffstein S., Weissmann G. Mechanisms of lysosomal enzyme release from human leukocytes. I. Effect of cyclic nucleotides and colchicine. J Cell Biol. 1973 Jul;58(1):27–41. doi: 10.1083/jcb.58.1.27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]