Abstract
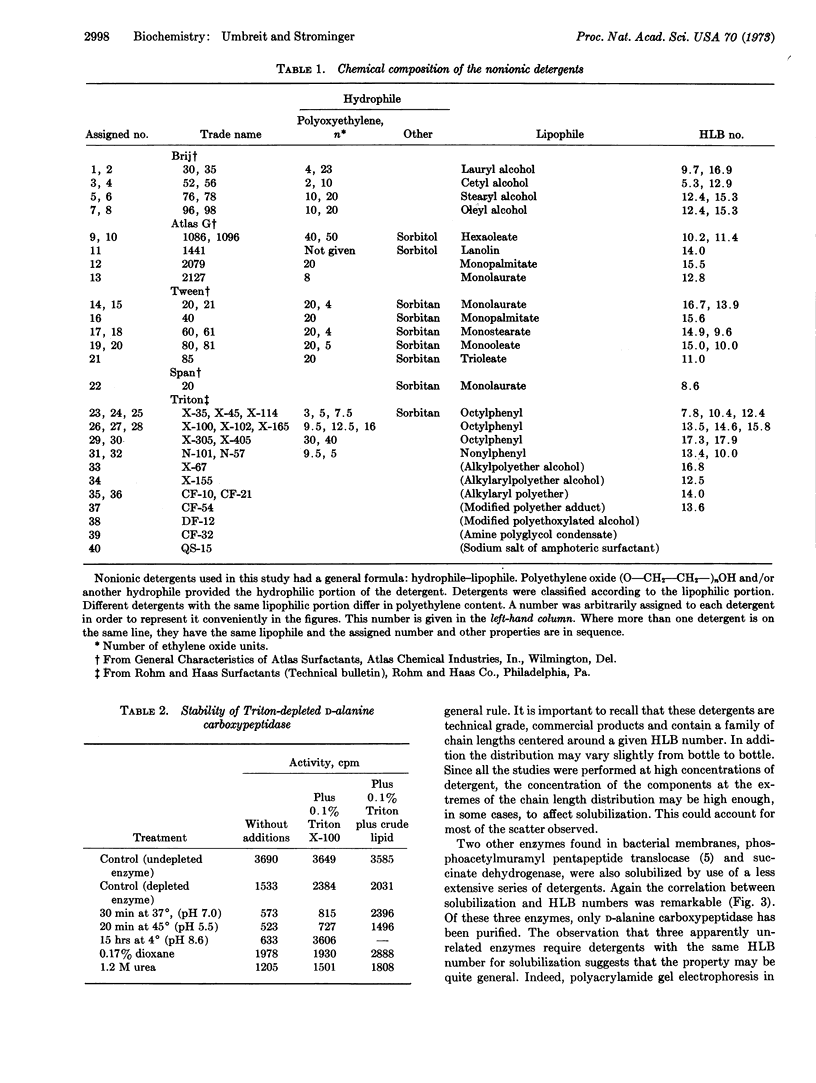
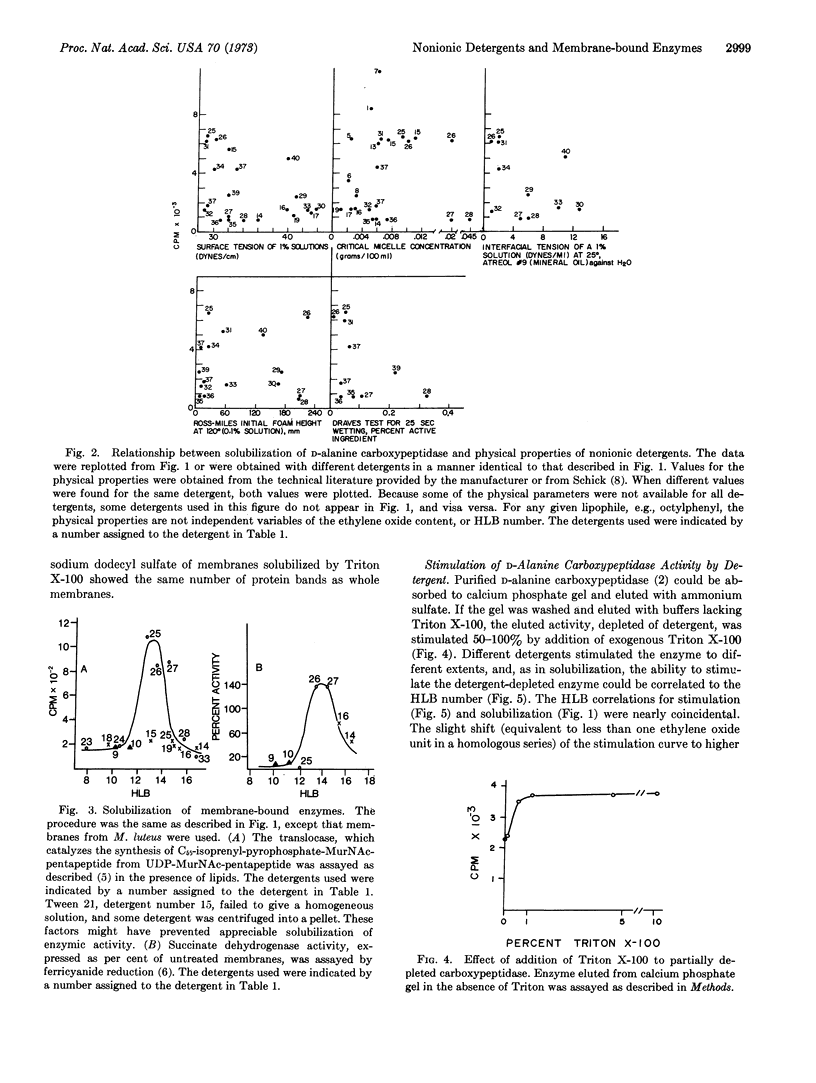
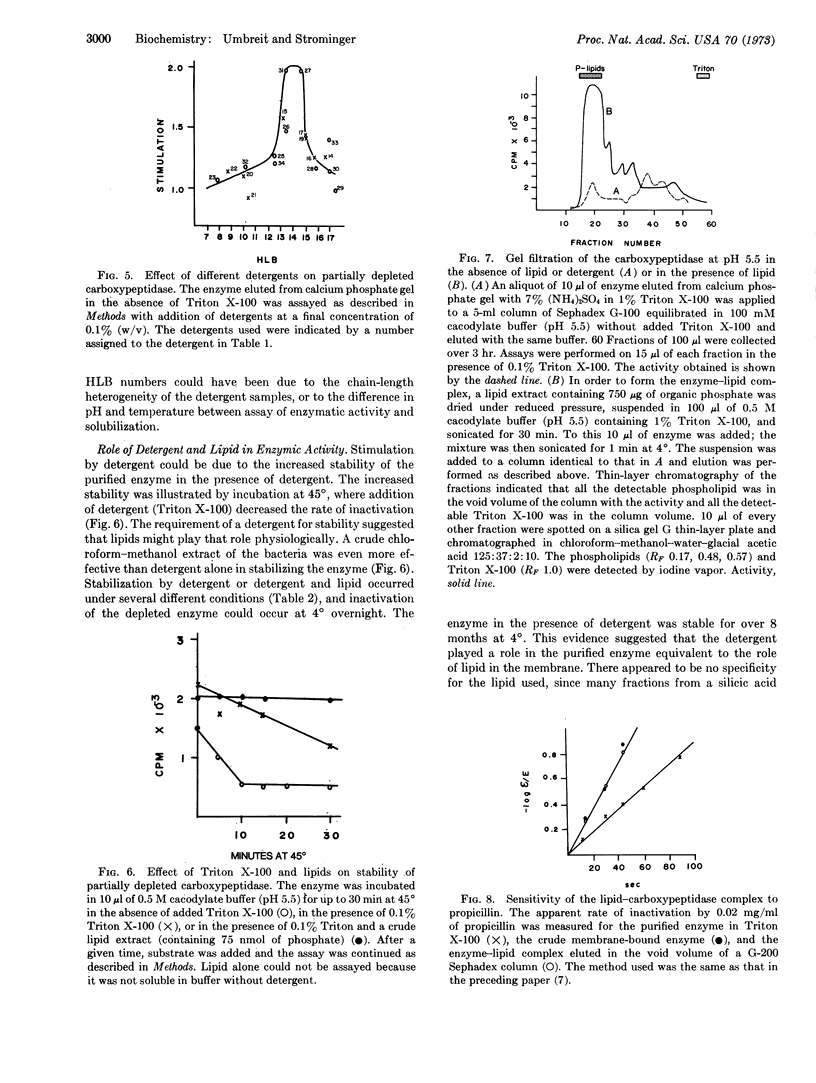
The ability of various nonionic detergents to solubilize D-alanine carboxypeptidase and other membrane-bound enzymes was correlated to a physical property of the detergent, the HLB number. Only a fairly narrow range of detergents were effective solubilizing agents. Purified carboxypeptidase required either a detergent or detergent plus a lipid fraction for stability. Only those detergents effective in solubilizing the enzyme were effective in stabilizing it.
Keywords: hydrophobic lipophilic balance, nonionic detergents, succinate dehydrogenase, phosphoacetylmuramyl-pentapeptide translocase
Full text
PDF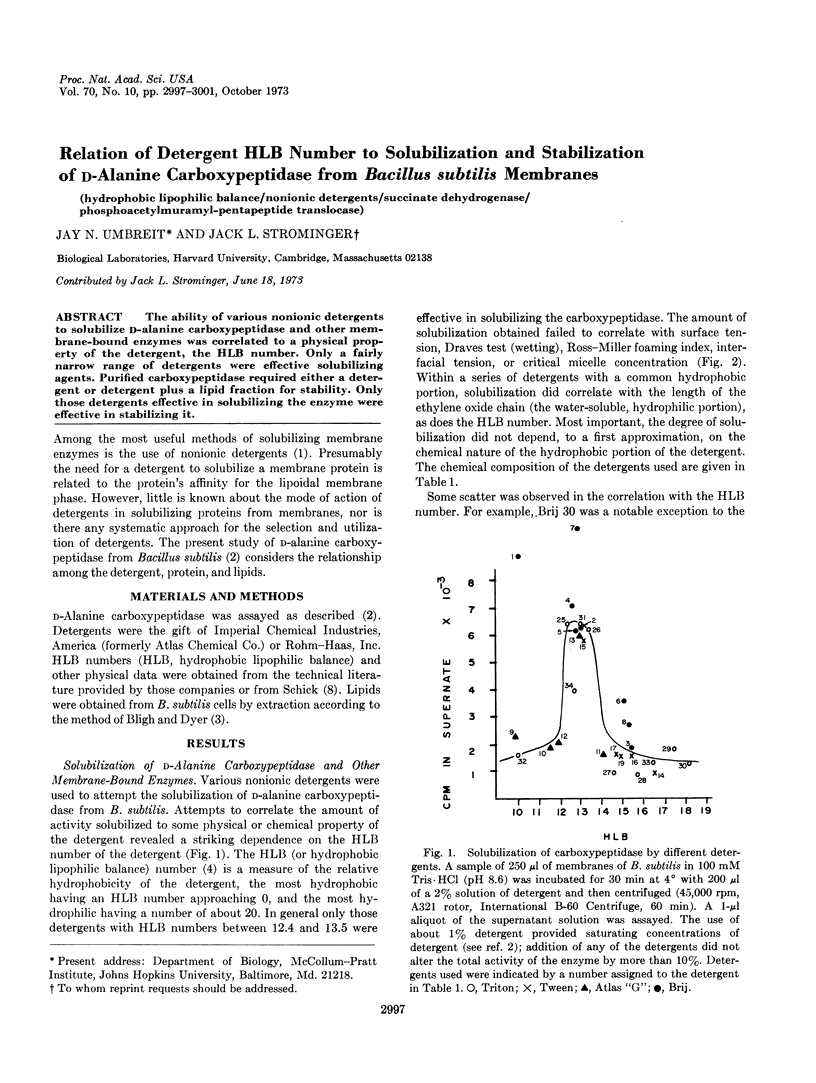

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta A., Franklin R. M. Structure and synthesis of a lipid-containing bacteriophage. II. Alterations in cytoplasmic and membrane-bound enzymes during replication of bacteriophage PM2. Virology. 1969 Nov;39(3):408–418. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90089-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umbreit J. N., Strominger J. L. Complex lipid requirements for detergent-solubilized phosphoacetylmuramyl-pentapeptide translocase from Micrococcus luteus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jul;69(7):1972–1974. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.7.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



