Abstract
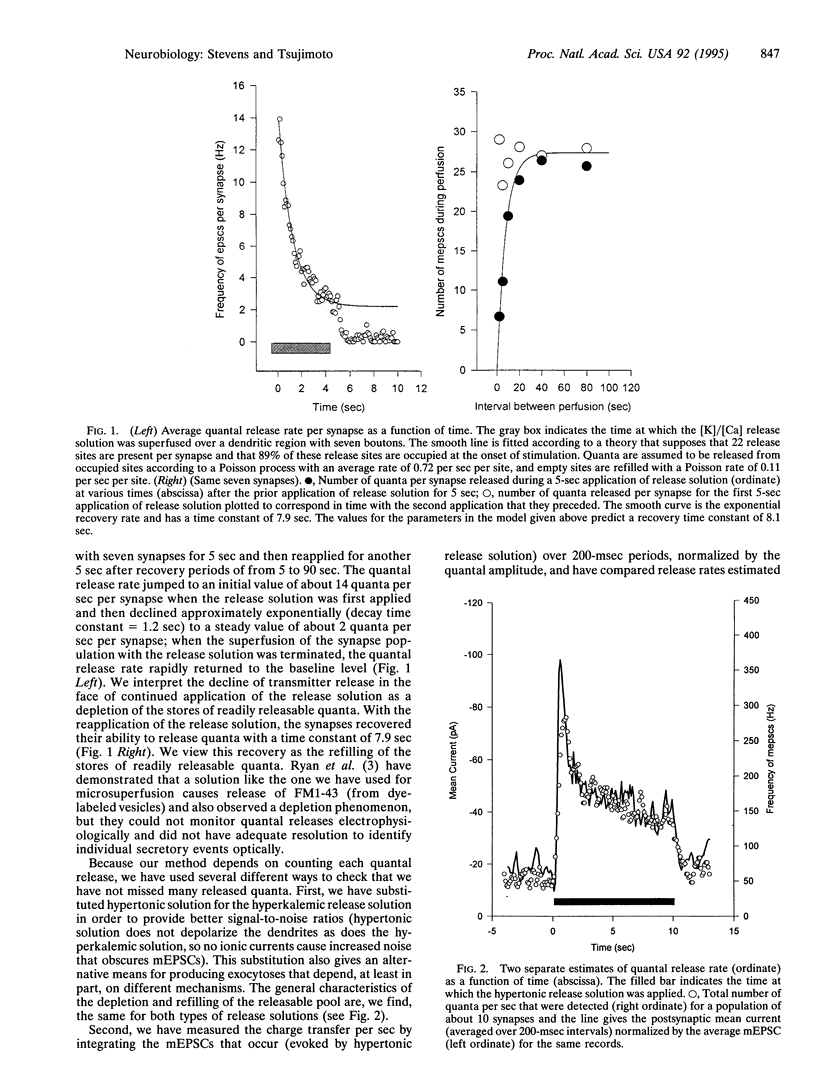
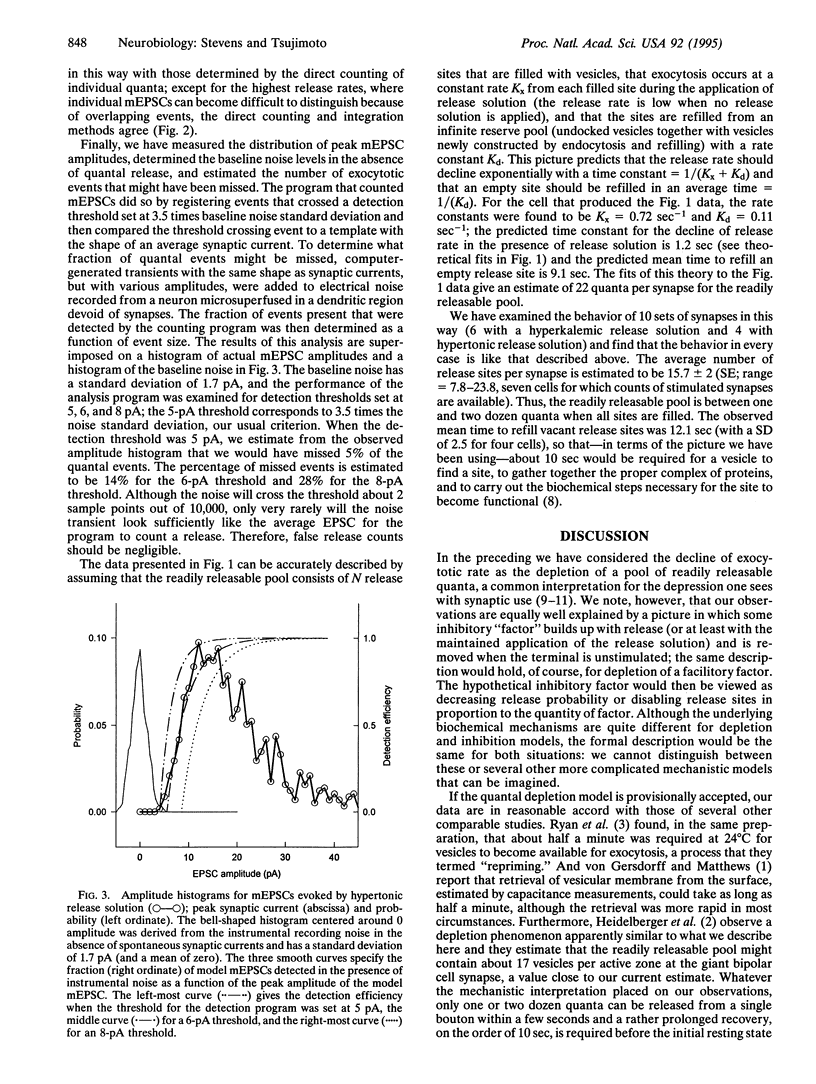
Local superfusion of limited dendritic areas with hypertonic or hyperkalemic solutions stimulates the release of quanta from a small population of synapses made on rodent hippocampal neurons maintained in primary culture, and each quantal event can be detected in the postsynaptic neuron. With maintained stimulation, the initial release rate is about 20 quanta per sec per synapse, and this rate declines exponentially to a final low level. These observations can be interpreted as depletion of available quanta and, with this interpretation, a bouton would contain one to two dozen quanta in its readily releasable pool. Tests with a second application of the solution that produces release reveal that the pool of readily releasable quanta is replenished with a time constant of about 10 sec (36 degrees C). The pool of quanta defined in this way may correspond to the population of vesicles docked at the bouton's active zone.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bekkers J. M., Stevens C. F. Excitatory and inhibitory autaptic currents in isolated hippocampal neurons maintained in cell culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7834–7838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. K., Scheller R. H. Molecular correlates of synaptic vesicle docking and fusion. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1994 Jun;4(3):324–329. doi: 10.1016/0959-4388(94)90092-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betz W. J., Bewick G. S. Optical analysis of synaptic vesicle recycling at the frog neuromuscular junction. Science. 1992 Jan 10;255(5041):200–203. doi: 10.1126/science.1553547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betz W. J., Bewick G. S. Optical monitoring of transmitter release and synaptic vesicle recycling at the frog neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1993 Jan;460:287–309. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betz W. J., Mao F., Bewick G. S. Activity-dependent fluorescent staining and destaining of living vertebrate motor nerve terminals. J Neurosci. 1992 Feb;12(2):363–375. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.12-02-00363.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUBBARD J. I. REPETITIVE STIMULATION AT THE MAMMALIAN NEUROMUSCULAR JUNCTION, AND THE MOBILIZATION OF TRANSMITTER. J Physiol. 1963 Dec;169:641–662. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidelberger R., Heinemann C., Neher E., Matthews G. Calcium dependence of the rate of exocytosis in a synaptic terminal. Nature. 1994 Oct 6;371(6497):513–515. doi: 10.1038/371513a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heuser J. E., Reese T. S. Evidence for recycling of synaptic vesicle membrane during transmitter release at the frog neuromuscular junction. J Cell Biol. 1973 May;57(2):315–344. doi: 10.1083/jcb.57.2.315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribchester R. R., Mao F., Betz W. J. Optical measurements of activity-dependent membrane recycling in motor nerve terminals of mammalian skeletal muscle. Proc Biol Sci. 1994 Jan 22;255(1342):61–66. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1994.0009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan T. A., Reuter H., Wendland B., Schweizer F. E., Tsien R. W., Smith S. J. The kinetics of synaptic vesicle recycling measured at single presynaptic boutons. Neuron. 1993 Oct;11(4):713–724. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90081-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THIES R. E. NEUROMUSCULAR DEPRESSION AND THE APPARENT DEPLETION OF TRANSMITTER IN MAMMALIAN MUSCLE. J Neurophysiol. 1965 May;28:428–442. doi: 10.1152/jn.1965.28.3.427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Gersdorff H., Matthews G. Dynamics of synaptic vesicle fusion and membrane retrieval in synaptic terminals. Nature. 1994 Feb 24;367(6465):735–739. doi: 10.1038/367735a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



