Abstract
One of the lymphocyte effector molecules produced in vitro by antigen- and mitogen-stimulated lymphocytes is lymphotoxin, which has been proposed to be the cytodestructive mediator in cell-mediated immune reactions. Our in vitro findings suggest that lymphotoxin binds to sites on the plasma membrane of sensitive target cells, and this binding represents the earliest detectable effect in cell destruction induced by lymphotoxin. The kinetics of binding are rapid, and the affinity of lymphotoxin for binding sites is strong. Furthermore, cytodestruction can be localized, for lymphotoxin-coated cells cannot release lymphotoxin to affect adjacent 51Cr-labeled, noncoated cells in mixed cultures. This evidence suggests how a nonspecific soluble cytotoxin could cause highly specific localized tissue destruction.
Keywords: cytotoxin, immune reactions
Full text
PDF

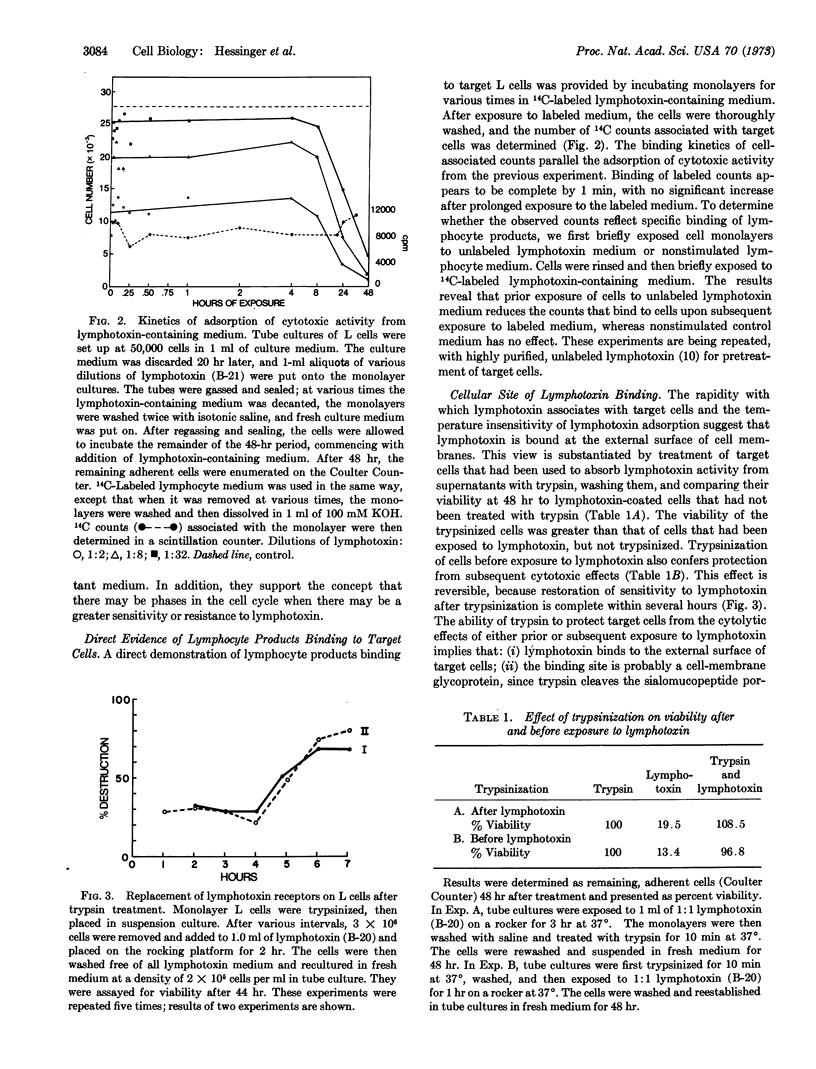


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- COOK G. M., HEARD D. H., SEAMAN G. V. A sialomucopeptide liberated by trypsin from the human erythrocyte. Nature. 1960 Dec 17;188:1011–1012. doi: 10.1038/1881011a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Condrea E., Kendzersky I., De Vries A. Binding of Ringhals venom direct hemolytic factor to erythrocytes and osmotic ghosts of various animal species. Experientia. 1965 Aug 15;21(8):461–462. doi: 10.1007/BF02150821. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granger G. A., Kolb W. P. Lymphocyte in vitro cytotoxicity: mechanisms of immune and non-immune small lymphocyte mediated target L cell destruction. J Immunol. 1968 Jul;101(1):111–120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granger G. A., Laserna E. C., Kolb W. P., Chapman F. Human lymphotoxin: purification and some properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jan;70(1):27–30. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.1.27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granger G. A. Mechanisms of lymphocyte-induced cell and tissue destruction in vitro. Am J Pathol. 1970 Sep;60(3):469–482. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hessinger D. A., Lenhoff H. M., Kahan L. B. Haemolytic phospholipase A and nerve-affecting activities of sea anemone nematocyst venom. Nat New Biol. 1973 Jan 24;241(108):125–127. doi: 10.1038/newbio241125b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holm G., Perlmann P. Phytohaemagglutinin-induced cytotoxic action of unsensitized immunologically competent cells on allogeneic and xenogeneic tissue culture cells. Nature. 1965 Aug 21;207(999):818–821. doi: 10.1038/207818a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolb W. P., Granger G. A. Lymphocyte in vitro cytotoxicity: characterization of human lymphotoxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Dec;61(4):1250–1255. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.4.1250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer J. J., Granger G. A. An improved in vitro assay for lymphotoxin. Cell Immunol. 1972 Jan;3(1):144–149. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(72)90235-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leu R. W., Eddleston A. L., Hadden J. W., Good R. A. Mechanism of action of migration inhibitory factor (MIF). I. Evidence for a receptor for MIF present on the peritoneal macrophage but not on the alveolar macrophage. J Exp Med. 1972 Sep 1;136(3):589–603. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.3.589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOELLER E. CONTACT-INDUCED CYTOTOXICITY BY LYMPHOID CELLS CONTAINING FOREIGN ISOANTIGENS. Science. 1965 Feb 19;147(3660):873–879. doi: 10.1126/science.147.3660.873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlmann P., Holm G. Cytotoxic effects of lymphoid cells in vitro. Adv Immunol. 1969;11:117–193. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60479-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSENAU W., MOON H. D. Lysis of homologous cells by sensitized lymphocytes in tissue culture. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1961 Aug;27:471–483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svedmyr E. A., Hodes R. J. On the specificity of cell-mediated cytotoxicity in vitro. Cell Immunol. 1970 Dec;1(6):644–654. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(70)90029-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker S. M., Lucas Z. J. Cytotoxic activity of lymphocytes. II. Studies on mechanism of lymphotoxin-mediated cytotoxicity. J Immunol. 1972 Dec;109(6):1233–1244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams T. W., Granger G. A. Lymphocyte in vitro cytotoxicity: correlation of derepression with release of lymphotoxin from human lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1969 Aug;103(2):170–178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams T. W., Granger G. A. Lymphocyte in vitro cytotoxicity: mechanism of human lymphotoxin-induced target cell destruction. Cell Immunol. 1973 Feb;6(2):171–185. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(73)90020-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams T. W., Granger G. A. Lymphocyte in vitro cytotoxicity: mechanism of lymphotoxin-induced target cell destruction. J Immunol. 1969 Apr;102(4):911–918. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




