Abstract
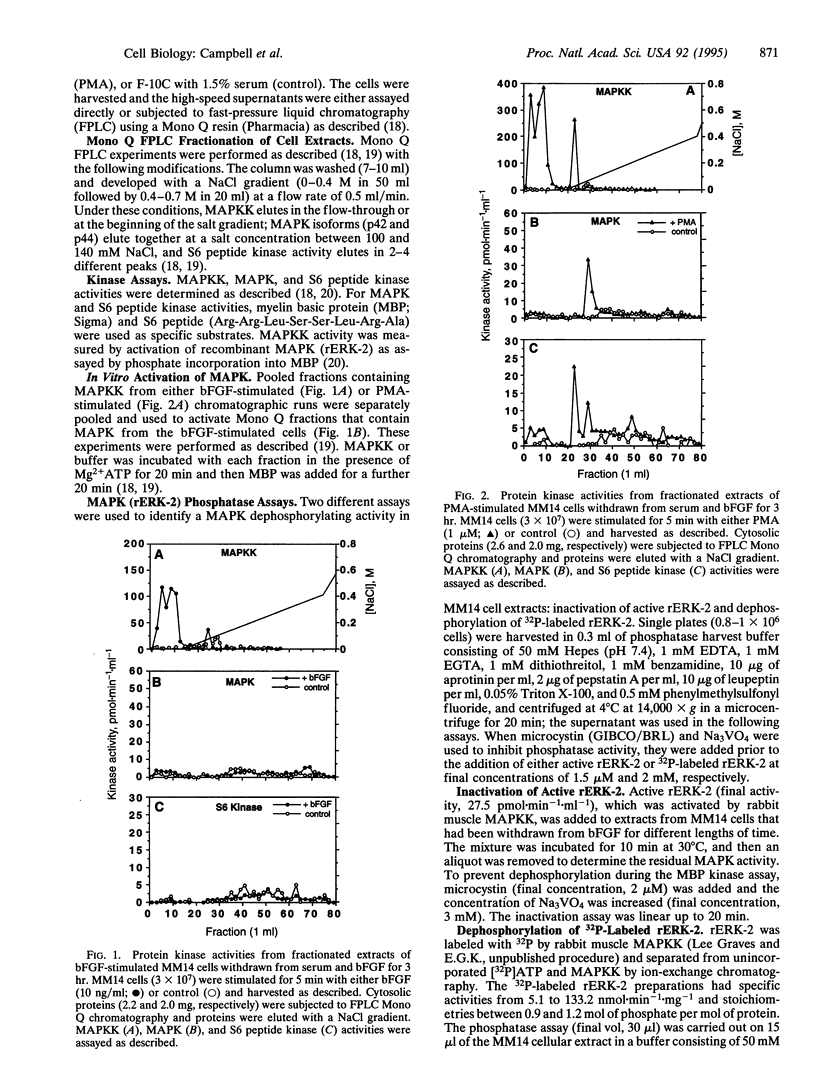
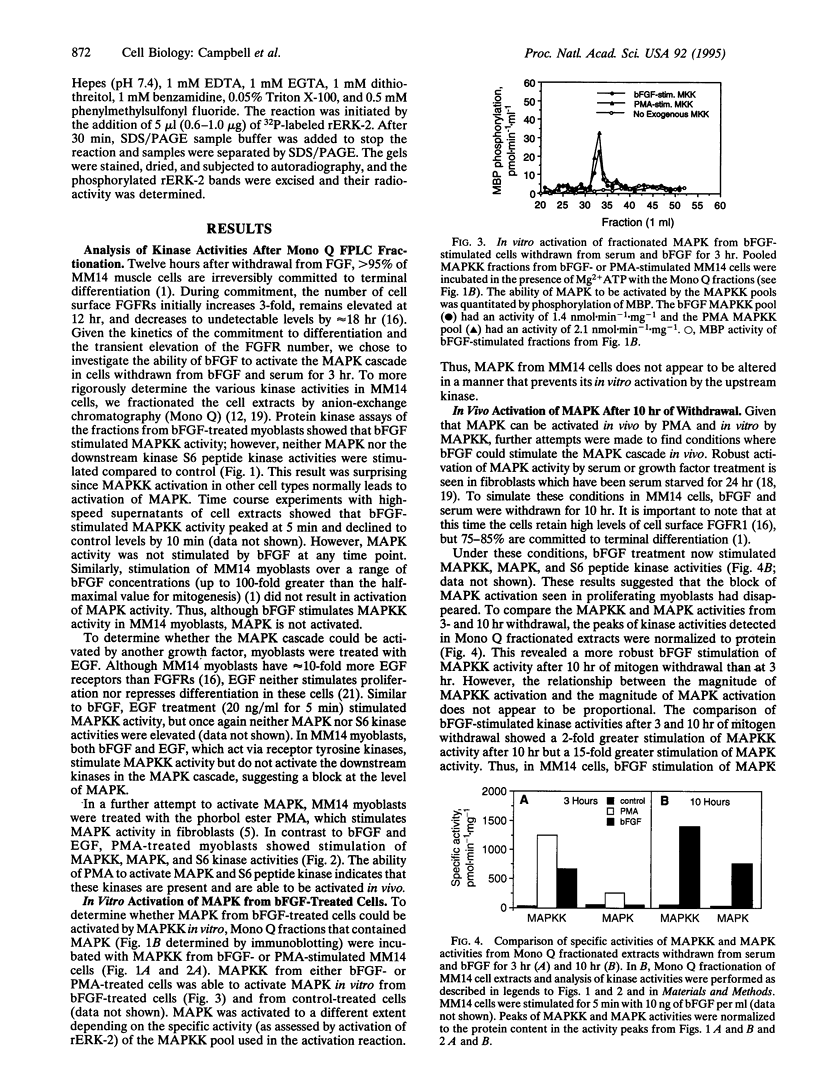
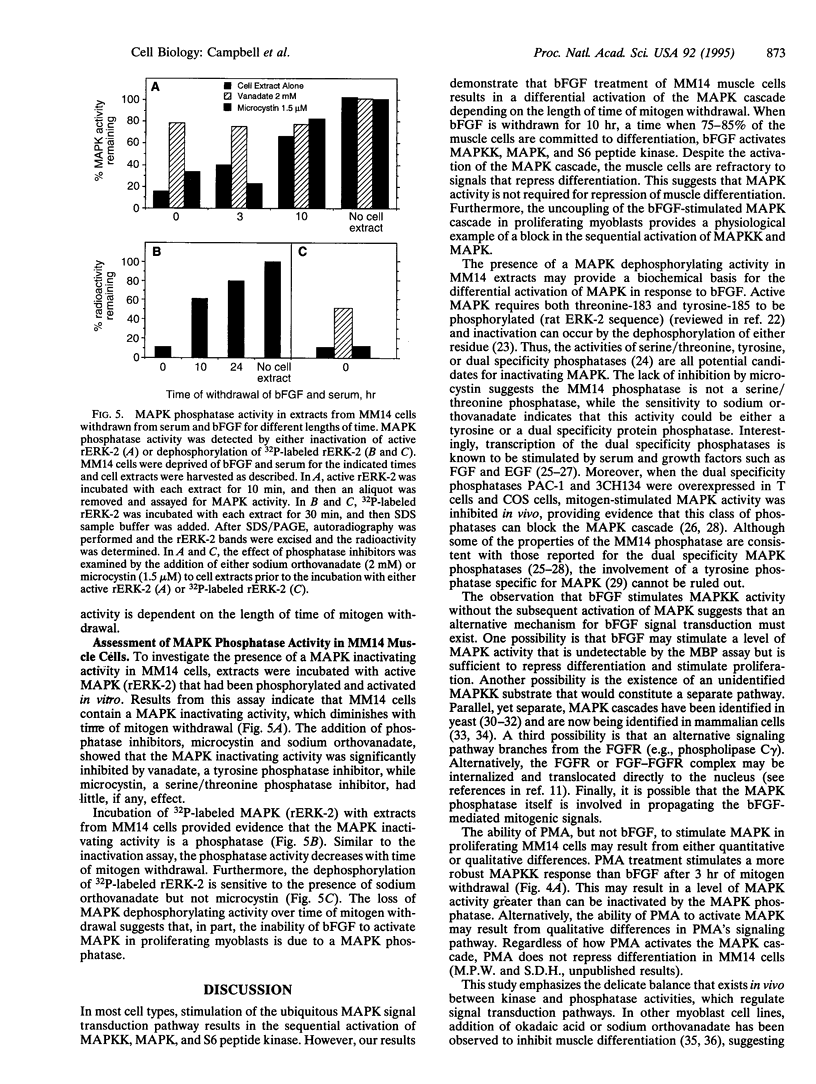
In the MM14 mouse myoblast cell line, fibroblast growth factor (FGF) stimulates proliferation and represses differentiation. However, the intracellular signaling pathways used by FGF to affect these cellular processes are unknown. The predominant FGF receptor present on MM14 cells, FGFR1, is a receptor tyrosine kinase capable of activating the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) cascade in fibroblast and neuronal cell lines. To determine whether the FGF signal is mediated via the MAPK cascade in myoblasts, MM14 cells were stimulated with basic FGF (bFGF) and activities of the various kinases were measured. After withdrawal from serum and bFGF for 3 hr, bFGF stimulated MAPK kinase (MAPKK) activity, but MAPK and S6 peptide kinase activities were not detected. In contrast, when serum and bFGF were withdrawn for 10 hr, the activities of MAPKK, MAPK, and S6 peptide kinase were all stimulated by bFGF treatment. The inability of bFGF to stimulate MAPK after 3 hr of withdrawal may be due, in part, to the presence of a MAPK phosphatase activity that was detected in MM14 cell extracts. This dephosphorylating activity diminishes during commitment to terminal differentiation and is inhibited by sodium orthovanadate. Thus, the ability of bFGF to stimulate MAPK in MM14 cells is correlated with the loss of a MAPK phosphatase activity. These results show that although bFGF activates MAPKK in proliferating myoblasts, the mitogenic signal does not progress to the downstream kinases, providing a physiological example of an uncoupling of the MAPK cascade.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahn N. G., Seger R., Bratlien R. L., Diltz C. D., Tonks N. K., Krebs E. G. Multiple components in an epidermal growth factor-stimulated protein kinase cascade. In vitro activation of a myelin basic protein/microtubule-associated protein 2 kinase. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 5;266(7):4220–4227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahn N. G., Seger R., Krebs E. G. The mitogen-activated protein kinase activator. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;4(6):992–999. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(92)90131-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahn N. G., Weiel J. E., Chan C. P., Krebs E. G. Identification of multiple epidermal growth factor-stimulated protein serine/threonine kinases from Swiss 3T3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 15;265(20):11487–11494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ammerer G. Sex, stress and integrity: the importance of MAP kinases in yeast. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1994 Feb;4(1):90–95. doi: 10.1016/0959-437x(94)90096-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avruch J., Zhang X. F., Kyriakis J. M. Raf meets Ras: completing the framework of a signal transduction pathway. Trends Biochem Sci. 1994 Jul;19(7):279–283. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(94)90005-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blenis J. Signal transduction via the MAP kinases: proceed at your own RSK. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):5889–5892. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.5889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumer K. J., Johnson G. L. Diversity in function and regulation of MAP kinase pathways. Trends Biochem Sci. 1994 Jun;19(6):236–240. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(94)90147-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charles C. H., Abler A. S., Lau L. F. cDNA sequence of a growth factor-inducible immediate early gene and characterization of its encoded protein. Oncogene. 1992 Jan;7(1):187–190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen R. H., Sarnecki C., Blenis J. Nuclear localization and regulation of erk- and rsk-encoded protein kinases. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;12(3):915–927. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.3.915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clegg C. H., Linkhart T. A., Olwin B. B., Hauschka S. D. Growth factor control of skeletal muscle differentiation: commitment to terminal differentiation occurs in G1 phase and is repressed by fibroblast growth factor. J Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;105(2):949–956. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.2.949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobb M. H., Boulton T. G., Robbins D. J. Extracellular signal-regulated kinases: ERKs in progress. Cell Regul. 1991 Dec;2(12):965–978. doi: 10.1091/mbc.2.12.965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. J. The mitogen-activated protein kinase signal transduction pathway. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 15;268(20):14553–14556. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmondson D. G., Olson E. N. Helix-loop-helix proteins as regulators of muscle-specific transcription. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 15;268(2):755–758. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Errede B., Levin D. E. A conserved kinase cascade for MAP kinase activation in yeast. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;5(2):254–260. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(93)90112-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galcheva-Gargova Z., Dérijard B., Wu I. H., Davis R. J. An osmosensing signal transduction pathway in mammalian cells. Science. 1994 Aug 5;265(5173):806–808. doi: 10.1126/science.8047888. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han J., Lee J. D., Bibbs L., Ulevitch R. J. A MAP kinase targeted by endotoxin and hyperosmolarity in mammalian cells. Science. 1994 Aug 5;265(5173):808–811. doi: 10.1126/science.7914033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S. J., Kim K. Y., Tapscott S. J., Winokur T. S., Park K., Fujiki H., Weintraub H., Roberts A. B. Inhibition of protein phosphatases blocks myogenesis by first altering MyoD binding activity. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 25;267(21):15140–15145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwak S. P., Hakes D. J., Martell K. J., Dixon J. E. Isolation and characterization of a human dual specificity protein-tyrosine phosphatase gene. J Biol Chem. 1994 Feb 4;269(5):3596–3604. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim R. W., Hauschka S. D. EGF responsiveness and receptor regulation in normal and differentiation-defective mouse myoblasts. Dev Biol. 1984 Sep;105(1):48–58. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(84)90260-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason I. J. The ins and outs of fibroblast growth factors. Cell. 1994 Aug 26;78(4):547–552. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90520-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nebreda A. R. Inactivation of MAP kinases. Trends Biochem Sci. 1994 Jan;19(1):1–2. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(94)90163-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neiman A. M. Conservation and reiteration of a kinase cascade. Trends Genet. 1993 Nov;9(11):390–394. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(93)90139-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson E. N. Interplay between proliferation and differentiation within the myogenic lineage. Dev Biol. 1992 Dec;154(2):261–272. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(92)90066-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson E. N. Signal transduction pathways that regulate skeletal muscle gene expression. Mol Endocrinol. 1993 Nov;7(11):1369–1378. doi: 10.1210/mend.7.11.8114752. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olwin B. B., Hauschka S. D. Cell surface fibroblast growth factor and epidermal growth factor receptors are permanently lost during skeletal muscle terminal differentiation in culture. J Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;107(2):761–769. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.2.761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelech S. L., Olwin B. B., Krebs E. G. Fibroblast growth factor treatment of Swiss 3T3 cells activates a subunit S6 kinase that phosphorylates a synthetic peptide substrate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5968–5972. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuels M. L., Weber M. J., Bishop J. M., McMahon M. Conditional transformation of cells and rapid activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade by an estradiol-dependent human raf-1 protein kinase. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Oct;13(10):6241–6252. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.10.6241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarcevic B., Erikson E., Maller J. L. Purification and characterization of a mitogen-activated protein kinase tyrosine phosphatase from Xenopus eggs. J Biol Chem. 1993 Nov 25;268(33):25075–25083. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seger R., Ahn N. G., Posada J., Munar E. S., Jensen A. M., Cooper J. A., Cobb M. H., Krebs E. G. Purification and characterization of mitogen-activated protein kinase activator(s) from epidermal growth factor-stimulated A431 cells. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 15;267(20):14373–14381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturgill T. W., Ray L. B., Erikson E., Maller J. L. Insulin-stimulated MAP-2 kinase phosphorylates and activates ribosomal protein S6 kinase II. Nature. 1988 Aug 25;334(6184):715–718. doi: 10.1038/334715a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun H., Charles C. H., Lau L. F., Tonks N. K. MKP-1 (3CH134), an immediate early gene product, is a dual specificity phosphatase that dephosphorylates MAP kinase in vivo. Cell. 1993 Nov 5;75(3):487–493. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90383-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Templeton T. J., Hauschka S. D. FGF-mediated aspects of skeletal muscle growth and differentiation are controlled by a high affinity receptor, FGFR1. Dev Biol. 1992 Nov;154(1):169–181. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(92)90057-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. K., Gao G., Goldfarb M. Fibroblast growth factor receptors have different signaling and mitogenic potentials. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jan;14(1):181–188. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.1.181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward Y., Gupta S., Jensen P., Wartmann M., Davis R. J., Kelly K. Control of MAP kinase activation by the mitogen-induced threonine/tyrosine phosphatase PAC1. Nature. 1994 Feb 17;367(6464):651–654. doi: 10.1038/367651a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wice B., Milbrandt J., Glaser L. Control of muscle differentiation in BC3H1 cells by fibroblast growth factor and vanadate. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 5;262(4):1810–1817. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]