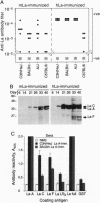
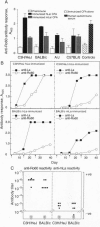
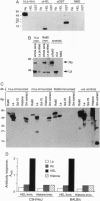
Abstract
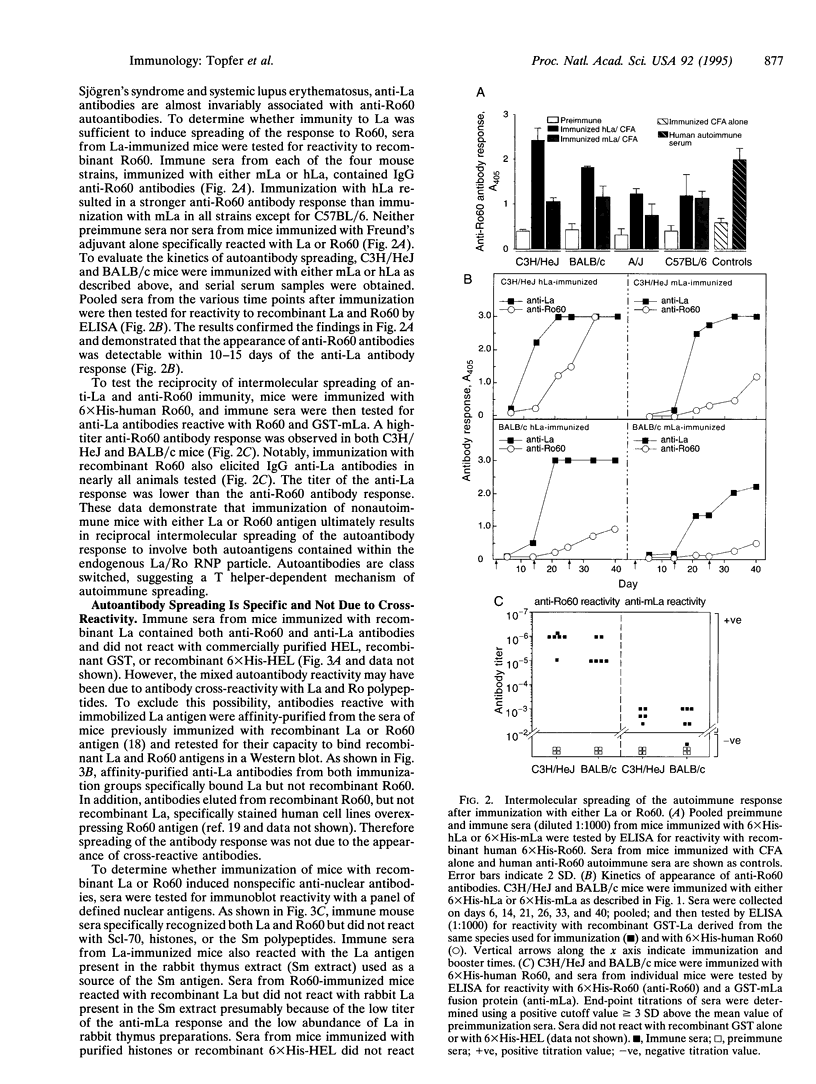
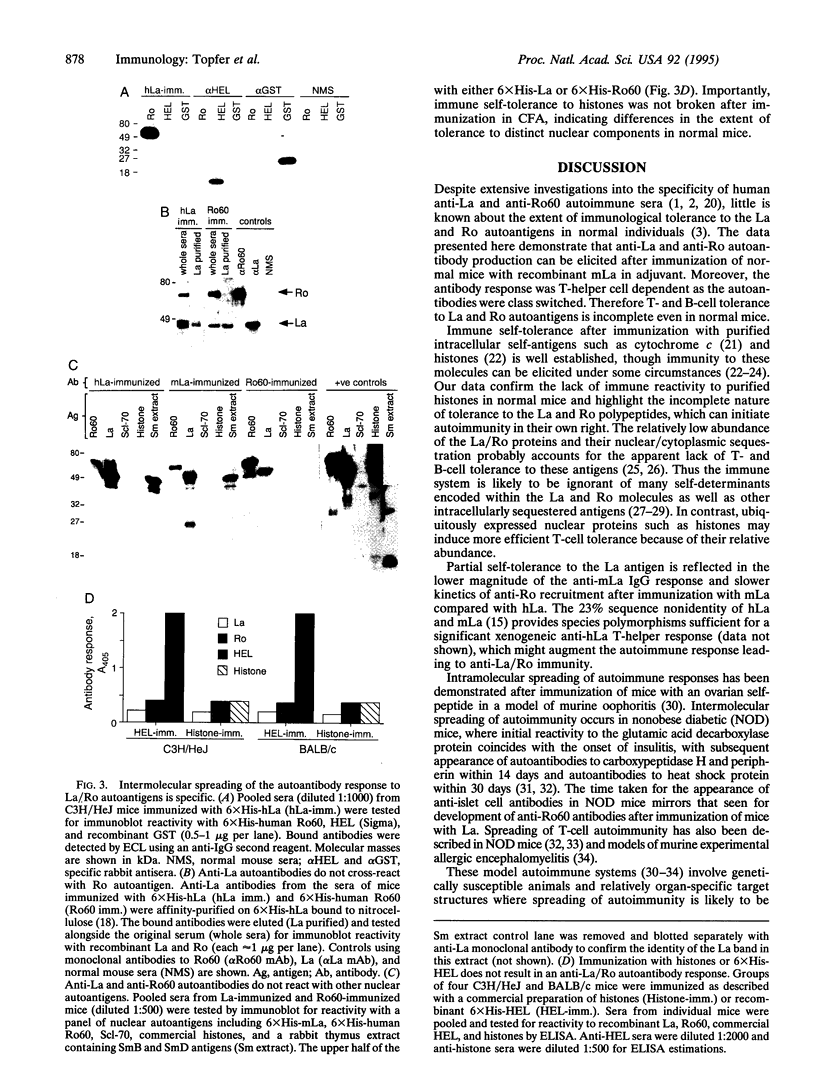
We have tested the extent of immune self-tolerance to the ubiquitously expressed nuclear/cytoplasmic autoantigens La (SS-B) and Ro (SS-A) in healthy, nonautoimmune mice. Immunization of mice with recombinant mouse La resulted in a specific, isotype-switched autoantibody response, which was initially directed toward the La C subfragment (aa 111-242) but rapidly spread to involve the La A (aa 1-107) and La F (aa 243-345) regions of the La antigen. Intramolecular spreading of the anti-La antibody response was further demonstrated by the appearance of autoantibodies to multiple, nonoverlapping antigenic regions of La, after immunization of mice with the 107-aa La A subfragment. Moreover, immunization of mice with recombinant mouse or human La also elicited specific anti-60-kDa Ro IgG antibodies in all strains tested. Mice immunized with 60-kDa Ro produced a high titer anti-Ro antibody response, which was also associated with intermolecular spreading, resulting in the specific appearance of anti-La autoantibodies. These findings show that the development of autoantibodies to multiple components of the La/Ro ribonucleoprotein complex may follow initiation of immunity to a single component. In addition, the data reveal the incomplete nature of immune tolerance to La and Ro despite their endogenous expression in all nucleated cells. These observations are likely to account for the coexistence of anti-La/Ro antibodies in autoimmune disease and suggest a general explanation for the appearance of mixed autoantibody patterns in systemic autoimmune disorders.
Full text
PDF
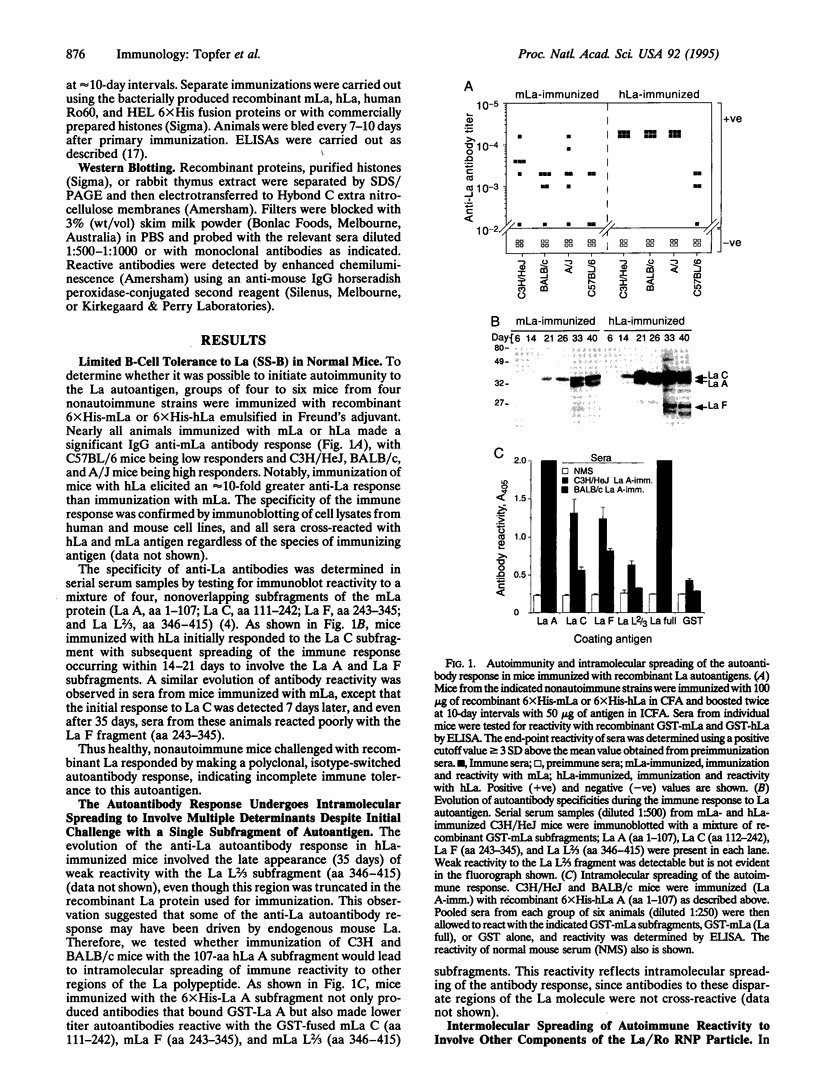

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adelstein S., Pritchard-Briscoe H., Anderson T. A., Crosbie J., Gammon G., Loblay R. H., Basten A., Goodnow C. C. Induction of self-tolerance in T cells but not B cells of transgenic mice expressing little self antigen. Science. 1991 Mar 8;251(4998):1223–1225. doi: 10.1126/science.1900950. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson M. A., Maclaren N. K. Islet cell autoantigens in insulin-dependent diabetes. J Clin Invest. 1993 Oct;92(4):1608–1616. doi: 10.1172/JCI116745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachmann M., Pfeifer K., Schröder H. C., Müller W. E. Characterization of the autoantigen La as a nucleic acid-dependent ATPase/dATPase with melting properties. Cell. 1990 Jan 12;60(1):85–93. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90718-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casciola-Rosen L. A., Anhalt G., Rosen A. Autoantigens targeted in systemic lupus erythematosus are clustered in two populations of surface structures on apoptotic keratinocytes. J Exp Med. 1994 Apr 1;179(4):1317–1330. doi: 10.1084/jem.179.4.1317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celis E., Zurawski V. R., Jr, Chang T. W. Regulation of T-cell function by antibodies: enhancement of the response of human T-cell clones to hepatitis B surface antigen by antigen-specific monoclonal antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(21):6846–6850. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.21.6846. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan E. K., Sullivan K. F., Tan E. M. Ribonucleoprotein SS-B/La belongs to a protein family with consensus sequences for RNA-binding. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Mar 25;17(6):2233–2244. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.6.2233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutscher S. L., Harley J. B., Keene J. D. Molecular analysis of the 60-kDa human Ro ribonucleoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9479–9483. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dong X., Hamilton K. J., Satoh M., Wang J., Reeves W. H. Initiation of autoimmunity to the p53 tumor suppressor protein by complexes of p53 and SV40 large T antigen. J Exp Med. 1994 Apr 1;179(4):1243–1252. doi: 10.1084/jem.179.4.1243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg R. A. Association between the Ro and La antigenic determinants: immunodiffusion analysis of human spleen extract. J Immunol. 1985 Sep;135(3):1707–1713. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eynon E. E., Parker D. C. Small B cells as antigen-presenting cells in the induction of tolerance to soluble protein antigens. J Exp Med. 1992 Jan 1;175(1):131–138. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.1.131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flaegstad T., Fredriksen K., Dahl B., Traavik T., Rekvig O. P. Inoculation with BK virus may break immunological tolerance to histone and DNA antigens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):8171–8175. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.8171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gammon G., Sercarz E. How some T cells escape tolerance induction. Nature. 1989 Nov 9;342(6246):183–185. doi: 10.1038/342183a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon T. P., Greer M., Reynolds P., Guidolin A., McNeilage L. J. Estimation of amounts of anti-La(SS-B) antibody directed against immunodominant epitopes of the La(SS-B) autoantigen. Clin Exp Immunol. 1991 Sep;85(3):402–406. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1991.tb05739.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman D. L., Clare-Salzler M., Tian J., Forsthuber T., Ting G. S., Robinson P., Atkinson M. A., Sercarz E. E., Tobin A. J., Lehmann P. V. Spontaneous loss of T-cell tolerance to glutamic acid decarboxylase in murine insulin-dependent diabetes. Nature. 1993 Nov 4;366(6450):69–72. doi: 10.1038/366069a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keech C. L., McCluskey J., Gordon T. P. Transfection and overexpression of the human 60-kDa Ro/SS-A autoantigen in HEp-2 cells. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1994 Oct;73(1):146–151. doi: 10.1006/clin.1994.1181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanzavecchia A. Receptor-mediated antigen uptake and its effect on antigen presentation to class II-restricted T lymphocytes. Annu Rev Immunol. 1990;8:773–793. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.08.040190.004013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann P. V., Forsthuber T., Miller A., Sercarz E. E. Spreading of T-cell autoimmunity to cryptic determinants of an autoantigen. Nature. 1992 Jul 9;358(6382):155–157. doi: 10.1038/358155a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin R. H., Mamula M. J., Hardin J. A., Janeway C. A., Jr Induction of autoreactive B cells allows priming of autoreactive T cells. J Exp Med. 1991 Jun 1;173(6):1433–1439. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.6.1433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mamula M. J., Lin R. H., Janeway C. A., Jr, Hardin J. A. Breaking T cell tolerance with foreign and self co-immunogens. A study of autoimmune B and T cell epitopes of cytochrome c. J Immunol. 1992 Aug 1;149(3):789–795. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mamula M. J., O'Brien C. A., Harley J. B., Hardin J. A. The Ro ribonucleoprotein particle: induction of autoantibodies and the detection of Ro RNAs among species. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1989 Sep;52(3):435–446. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(89)90158-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manca F., Fenoglio D., Kunkl A., Cambiaggi C., Sasso M., Celada F. Differential activation of T cell clones stimulated by macrophages exposed to antigen complexed with monoclonal antibodies. A possible influence of paratope specificity on the mode of antigen processing. J Immunol. 1988 May 1;140(9):2893–2898. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNeilage L. J., Macmillan E. M., Whittingham S. F. Mapping of epitopes on the La(SS-B) autoantigen of primary Sjögren's syndrome: identification of a cross-reactive epitope. J Immunol. 1990 Dec 1;145(11):3829–3835. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milich D. R., McLachlan A., Thornton G. B., Hughes J. L. Antibody production to the nucleocapsid and envelope of the hepatitis B virus primed by a single synthetic T cell site. Nature. 1987 Oct 8;329(6139):547–549. doi: 10.1038/329547a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. F., Heath W. R. Self-ignorance in the peripheral T-cell pool. Immunol Rev. 1993 Jun;133:131–150. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1993.tb01514.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. F. Post-thymic tolerance to self antigens. J Autoimmun. 1992 Apr;5 (Suppl A):27–35. doi: 10.1016/0896-8411(92)90016-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris J. F., Hoyer J. T., Pierce S. K. Antigen presentation for T cell interleukin-2 secretion is a late acquisition of neonatal B cells. Eur J Immunol. 1992 Nov;22(11):2923–2928. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830221125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins K. A., Chain B. M. Presentation by peritoneal macrophages: modulation by antibody-antigen complexes. Immunology. 1986 May;58(1):15–21. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajewsky K., Rottländer E., Peltre G., Müller B. The immune response to a hybrid protein molecule; specificity of secondary stimulation and of tolerance induction. J Exp Med. 1967 Oct 1;126(4):581–606. doi: 10.1084/jem.126.4.581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin R. L., Tang F. L., Tsay G., Pollard K. M. Pseudoautoimmunity in normal mice: anti-histone antibodies elicited by immunization versus induction during graft-versus-host reaction. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1990 Feb;54(2):320–332. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(90)90093-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell S. M., Liew F. Y. Cell cooperation in antibody responses to influenza virus. I. priming of helper t cells by internal components of virion. Eur J Immunol. 1980 Oct;10(10):791–796. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830101013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schalke B. C., Klinkert W. E., Wekerle H., Dwyer D. S. Enhanced activation of a T cell line specific for acetylcholine receptor (AChR) by using anti-AChR monoclonal antibodies plus receptors. J Immunol. 1985 Jun;134(6):3643–3648. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scofield R. H., Harley J. B. Autoantigenicity of Ro/SSA antigen is related to a nucleocapsid protein of vesicular stomatitis virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):3343–3347. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.3343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sercarz E. E., Lehmann P. V., Ametani A., Benichou G., Miller A., Moudgil K. Dominance and crypticity of T cell antigenic determinants. Annu Rev Immunol. 1993;11:729–766. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.11.040193.003501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefano J. E. Purified lupus antigen La recognizes an oligouridylate stretch common to the 3' termini of RNA polymerase III transcripts. Cell. 1984 Jan;36(1):145–154. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90083-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M. Antinuclear antibodies: diagnostic markers for autoimmune diseases and probes for cell biology. Adv Immunol. 1989;44:93–151. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60641-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tisch R., Yang X. D., Singer S. M., Liblau R. S., Fugger L., McDevitt H. O. Immune response to glutamic acid decarboxylase correlates with insulitis in non-obese diabetic mice. Nature. 1993 Nov 4;366(6450):72–75. doi: 10.1038/366072a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Topfer F., Gordon T., McCluskey J. Characterization of the mouse autoantigen La (SS-B). Identification of conserved RNA-binding motifs, a putative ATP binding site and reactivity of recombinant protein with poly(U) and human autoantibodies. J Immunol. 1993 Apr 1;150(7):3091–3100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weng Y. M., McNeilage J., Topfer F., McCluskey J., Gordon T. Identification of a human-specific epitope in a conserved region of the La/SS-B autoantigen. J Clin Invest. 1993 Aug;92(2):1104–1108. doi: 10.1172/JCI116617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittingham S., Naselli G., McNeilage L. J. Autoepitopes reactive with anti-SS-B/La. J Autoimmun. 1989 Aug;2(4):345–351. doi: 10.1016/0896-8411(89)90162-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinkernagel R. M., Cooper S., Chambers J., Lazzarini R. A., Hengartner H., Arnheiter H. Virus-induced autoantibody response to a transgenic viral antigen. Nature. 1990 May 3;345(6270):68–71. doi: 10.1038/345068a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Venrooij W. J., van Gelder C. W. B cell epitopes on nuclear autoantigens. What can they tell us? Arthritis Rheum. 1994 May;37(5):608–616. doi: 10.1002/art.1780370502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]