Abstract
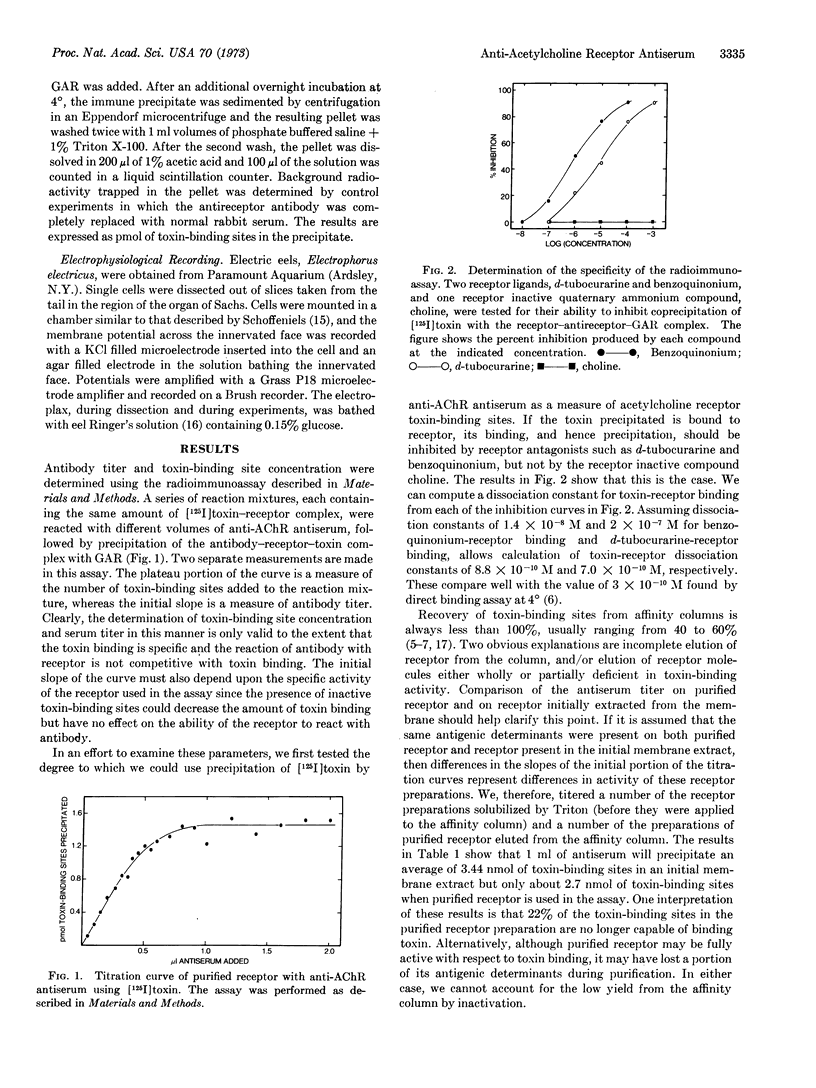
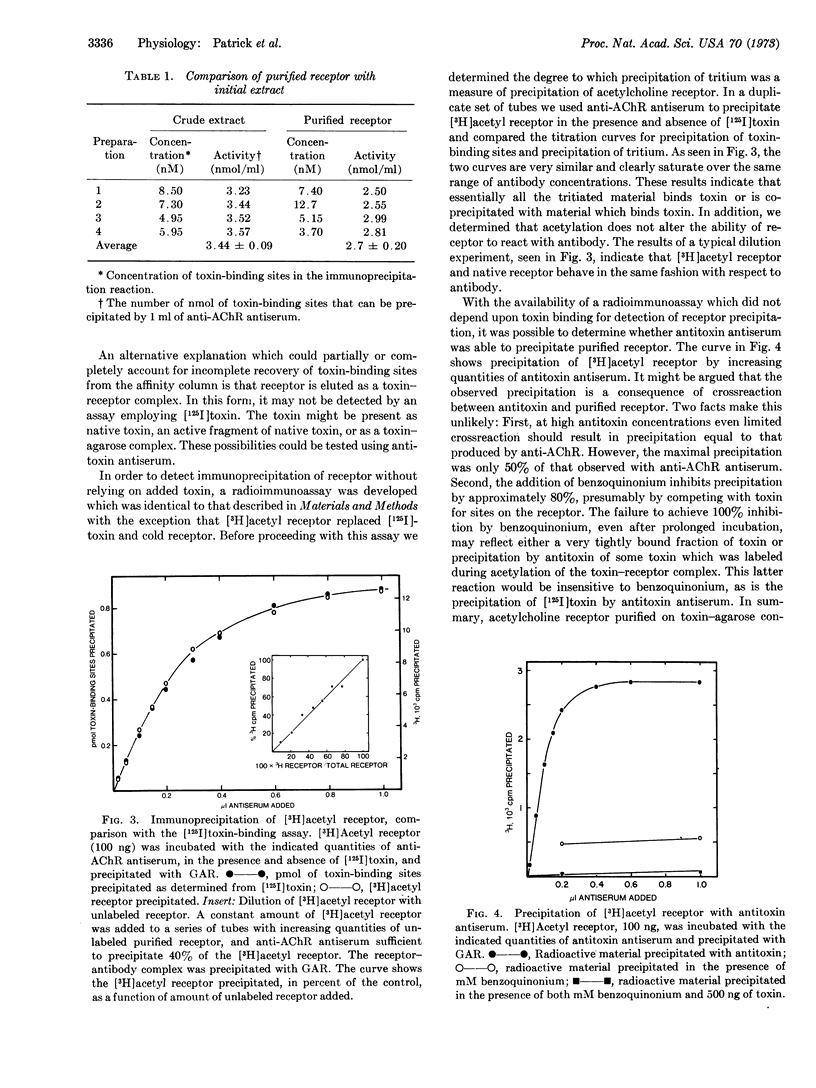
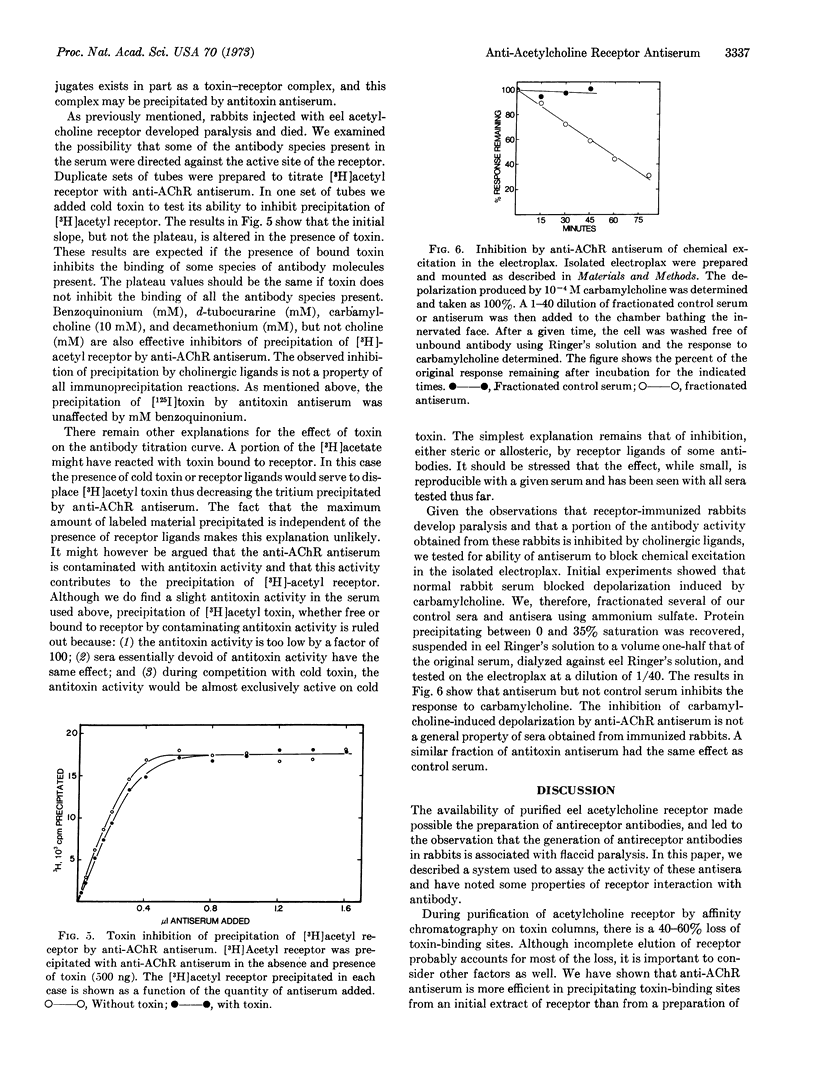
Rabbit antiserum against purified Electrophorus electricus acetylcholine receptor is studied using an immunoprecipitin assay to measure either antibody titer or concentration of toxin-binding sites in solubilized receptor preparations. This antiserum, unlike control serum, blocks the electrophysiological response of the electroplax to carbamylcholine. Toxin (α-neurotoxin, Naja naja) and several cholinergic ligands produce partial inhibition of the reaction of antiserum with purified acetylcholine receptor. Evidence is presented that some of the toxin-binding sites on receptor, purified by affinity chromatography on toxin-agarose conjugates, are occluded by toxin. In addition, evidence is presented that antireceptor antiserum will cause precipitation of more toxin-binding sites present in an initial extract than in purified receptor preparations.
Keywords: electroplax, neurotoxin, affinity chromatography
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Avrameas S., Ternynck T. The cross-linking of proteins with glutaraldehyde and its use for the preparation of immunoadsorbents. Immunochemistry. 1969 Jan;6(1):53–66. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(69)90178-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg D. K., Kelly R. B., Sargent P. B., Williamson P., Hall Z. W. Binding of -bungarotoxin to acetylcholine receptors in mammalian muscle (snake venom-denervated muscle-neonatal muscle-rat diaphragm-SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jan;69(1):147–151. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.1.147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eldefrawi M. E., Eldefrawi A. T. Characterization and partial purification of the acetylcholine receptor from Torpedo electroplax. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jul;69(7):1776–1780. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.7.1776. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulpius B., Cha S., Klett R., Reich E. Properties of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor macromolecule of Electrophorus electricus. FEBS Lett. 1972 Aug 15;24(3):323–326. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80382-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEYNES R. D., MARTINS-FERREIRA H. Membrane potentials in the electroplates of the electric eel. J Physiol. 1953 Feb 27;119(2-3):315–351. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1953.sp004849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlsson E., Heilbronn E., Widlund L. Isolation of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor by biospecific chromatography on insolubilized Naja naja neurotoxin. FEBS Lett. 1972 Nov 15;28(1):107–111. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80688-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meunier J. C., Huchet M., Boquet P., Changeux J. P. Séparation de la protéine réceptrice de l'acétylcholine et de l'acétylcholinestérase. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1971 Jan 4;272(1):117–120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miledi R., Molinoff P., Potter L. T. Isolation of the cholinergic receptor protein of Torpedo electric tissue. Nature. 1971 Feb 19;229(5286):554–557. doi: 10.1038/229554a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen R. W., Meunier J. C., Changeux J. P. Progress in the purification of the cholinergic receptor protein from Electrophorus electricus by affinity chromatography. FEBS Lett. 1972 Nov 15;28(1):96–100. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80686-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostrowski K., Barnard E. A., Sawicki W., Chorzelski T., Langner A., Mikulski A. Autoradiographic detection of antigens in cells using tritium-labeled antibodies. J Histochem Cytochem. 1970 Jul;18(7):490–497. doi: 10.1177/18.7.490. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patrick J., Heinemann S. F., Lindstrom J., Schubert D., Steinbach J. H. Appearance of acetylcholine receptors during differentiation of a myogenic cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Oct;69(10):2762–2766. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.10.2762. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiter M. J., Cowburn D. A., Prives J. M., Karlin A. Affinity labeling of the acetylcholine receptor in the electroplax: electrophoretic separtion in sodium dodecyl sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 May;69(5):1168–1172. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.5.1168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt J., Raftery M. A. Use of affinity chromatography for acetylcholine receptor purification. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Oct 17;49(2):572–578. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90449-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


