Abstract
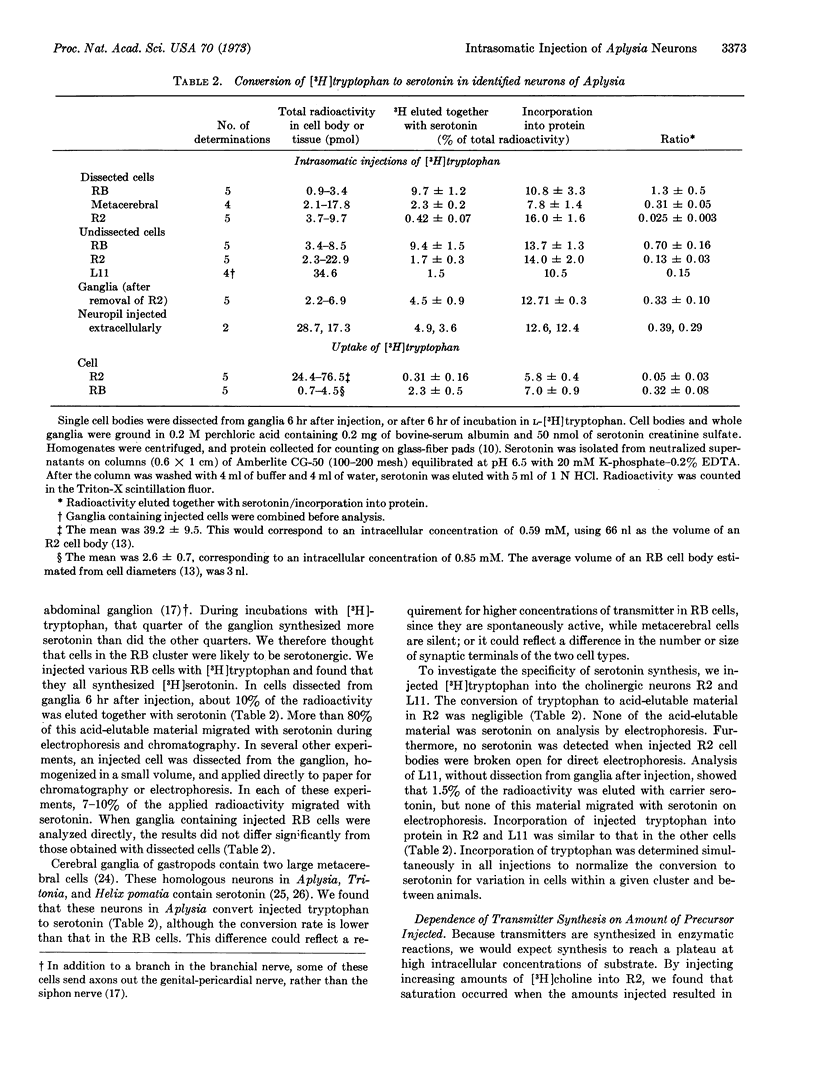
We introduced radioactive precursors directly into identified neurons of Aplysia californica. [3H]-Choline and L-[3H]tryptophan were injected with pressure into nerve cell bodies to study synthesis of acetylcholine and serotonin. We confirmed the cholinergic nature of R2, L10, and L11, identified neurons of the abdominal ganglion. Cells in the LD cluster (which contains motor neurons to the heart and gill) also converted most of the injected choline into acetylcholine. Neurons in the RB cluster (which contains an excitatory motor neuron to the heart) and the two metacerebral cells of the cerebral ganglion converted injected tryptophan to serotonin. No cell studied could convert both choline to acetylcholine and tryptophan to serotonin. Pressure permits rapid injection of precursors, from small amounts to amounts large enough to saturate intracellular synthetic pathways. In contrast to the results with injection, we found far less synthesis of acetylcholine and serotonin in identified nerve cell bodies when ganglia were incubated in the presence of the radioactive precursors.
Keywords: invertebrate nervous systems, acetylcholine, serotonin, microchemistry
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cottrell G. A., Osborne N. N. Localization and mode of action of cardioexcitatory agents in molluscan hearts. Experientia Suppl. 1969;15:220–231. doi: 10.1007/978-3-0348-6800-6_20. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giller E., Jr, Schwartz J. H. Choline acetyltransferase in identified neurons of abdominal ganglion of Aplysia californica. J Neurophysiol. 1971 Jan;34(1):93–107. doi: 10.1152/jn.1971.34.1.93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giller E., Jr, Schwartz J. H. Choline acetyltransferase: regional distribution in the abdominal ganglion of Aplysia. Science. 1968 Aug 30;161(3844):908–911. doi: 10.1126/science.161.3844.908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg A. M., McCaman R. E. The determination of picomole amounts of acetylcholine in mammalian brain. J Neurochem. 1973 Jan;20(1):1–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1973.tb12097.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hildebrand J. G., Barker D. L., Herbert E., Kravitz E. A. Screening for neurotransmitters: a rapid radiochemical procedure. J Neurobiol. 1971;2(3):231–246. doi: 10.1002/neu.480020305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kandel E. R., Tauc L. Input organization of two symmetrical giant cells in the snail brain. J Physiol. 1966 Mar;183(2):269–286. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007866. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koike H., Eisenstadt M., Schwartz J. H. Axonal transport of newly synthesized acetylcholine in an identified neuron of Aplysia. Brain Res. 1972 Feb 11;37(1):152–159. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(72)90359-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane C. D., Marbaix G., Gurdon J. B. Rabbit haemoglobin synthesis in frog cells: the translation of reticulocyte 9 s RNA in frog oocytes. J Mol Biol. 1971 Oct 14;61(1):73–91. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90207-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCaman R. E., Dewhurst S. A. Choline acetyltransferase in individual neurons of Aplysia californica. J Neurochem. 1970 Sep;17(9):1421–1426. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1970.tb06877.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osbone N. N., Cottrell G. A. Amine and amino acid microanalysis of two identified snail neurons with known characteristics. Experientia. 1972 Jun 15;28(6):656–658. doi: 10.1007/BF01944960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitman R. M., Tweedle C. D., Cohen M. J. Branching of central neurons: intracellular cobalt injection for light and electron microscopy. Science. 1972 Apr 28;176(4033):412–414. doi: 10.1126/science.176.4033.412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purves D., McMahan U. J. The distribution of synapses on a physiologically identified motor neuron in the central nervous system of the leech. An electron microscope study after the injection of the fluorescent dye procion yellow. J Cell Biol. 1972 Oct;55(1):205–220. doi: 10.1083/jcb.55.1.205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubert P., Lux H. D., Kreutzberg G. W. Single cell isotope injection technique, a tool for studying axonal and dendritic transport. Acta Neuropathol. 1971;5(Suppl):179–186. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-47449-1_23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz J. H., Castellucci V. F., Kandel E. R. Functioning of identified neurons and synapses in abdominal ganglion of Aplysia in absence of protein synthesis. J Neurophysiol. 1971 Nov;34(6):939–953. doi: 10.1152/jn.1971.34.6.939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stretton A. O., Kravitz E. A. Neuronal geometry: determination with a technique of intracellular dye injection. Science. 1968 Oct 4;162(3849):132–134. doi: 10.1126/science.162.3849.132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinreich D., Dewhurst S. A., McCaman R. E. Metabolism of putative transmitters in individual neurons of Aplysia californica: aromatic amino acid decarboxylase. J Neurochem. 1972 Apr;19(4):1125–1130. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1972.tb01432.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinreich D., McCaman M. W., McCaman R. E., Vaughn J. E. Chemical, enzymatic and ultrastructural characterization of 5-hydroxytryptamine-containing neurons from the ganglia of Aplysia californica and Tritionia diomedia. J Neurochem. 1973 Apr;20(4):969–976. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1973.tb00067.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh J. H. Neurohumoral regulation and the pharmacology of a molluscan heart. Comp Gen Pharmacol. 1971 Dec;2(8):423–432. doi: 10.1016/0010-4035(71)90039-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



