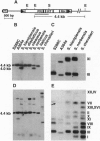
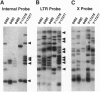
Abstract
We have characterized the genomic organization of the Ty5 retrotransposons among diverse strains of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and the related species Saccharomyces paradoxus. The S. cerevisiae strain S288C (or its derivatives) carries eight Ty5 insertions. Six of these are located near the telomeres, and five are found within 500 bp of autonomously replicating sequences present in the type X subtelomeric repeat. The remaining two S. cerevisiae elements are adjacent to the silent mating locus HMR and are located within 500 bp of the origin of replication present in the transcriptional silencer HMR-E. Although the S. cerevisiae Ty5 elements no longer appear capable of transposition, some strains of S. paradoxus have numerous Ty5 insertions, suggesting that transposition is occurring in this species. Most of these elements are adjacent to type X telomeric repeats, and regions flanking four of five characterized S. paradoxus insertions carry autonomously replicating sequences. The genomic organization of the Ty5 elements is in marked contrast to the other S. cerevisiae retrotransposon families (Ty1-4), which are typically located within 500 bp of tRNA genes. For Ty3, this association reflects an interaction between Ty3 and the RNA polymerase III transcription complex, which appears to direct integration [Chalker, D. L. & Sandmeyer, S. B. (1992) Genes Dev. 6, 117-128]. By analogy to Ty3, we predict that Ty5 target choice is specified by interactions with factors present at both the telomeres and HMR that are involved in DNA replication, transcription silencing, or the maintenance of the unique chromatin structure at these sites.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Biessmann H., Champion L. E., O'Hair M., Ikenaga K., Kasravi B., Mason J. M. Frequent transpositions of Drosophila melanogaster HeT-A transposable elements to receding chromosome ends. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(12):4459–4469. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05547.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biessmann H., Mason J. M., Ferry K., d'Hulst M., Valgeirsdottir K., Traverse K. L., Pardue M. L. Addition of telomere-associated HeT DNA sequences "heals" broken chromosome ends in Drosophila. Cell. 1990 May 18;61(4):663–673. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90478-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biessmann H., Valgeirsdottir K., Lofsky A., Chin C., Ginther B., Levis R. W., Pardue M. L. HeT-A, a transposable element specifically involved in "healing" broken chromosome ends in Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Sep;12(9):3910–3918. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.9.3910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chalker D. L., Sandmeyer S. B. Sites of RNA polymerase III transcription initiation and Ty3 integration at the U6 gene are positioned by the TATA box. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 1;90(11):4927–4931. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.11.4927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chalker D. L., Sandmeyer S. B. Transfer RNA genes are genomic targets for de Novo transposition of the yeast retrotransposon Ty3. Genetics. 1990 Dec;126(4):837–850. doi: 10.1093/genetics/126.4.837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chalker D. L., Sandmeyer S. B. Ty3 integrates within the region of RNA polymerase III transcription initiation. Genes Dev. 1992 Jan;6(1):117–128. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.1.117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan C. S., Tye B. K. Organization of DNA sequences and replication origins at yeast telomeres. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):563–573. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90437-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dujon B., Alexandraki D., André B., Ansorge W., Baladron V., Ballesta J. P., Banrevi A., Bolle P. A., Bolotin-Fukuhara M., Bossier P. Complete DNA sequence of yeast chromosome XI. Nature. 1994 Jun 2;369(6479):371–378. doi: 10.1038/369371a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enomoto S., Longtine M. S., Berman J. Enhancement of telomere-plasmid segregation by the X-telomere associated sequence in Saccharomyces cerevisiae involves SIR2, SIR3, SIR4 and ABF1. Genetics. 1994 Mar;136(3):757–767. doi: 10.1093/genetics/136.3.757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ji H., Moore D. P., Blomberg M. A., Braiterman L. T., Voytas D. F., Natsoulis G., Boeke J. D. Hotspots for unselected Ty1 transposition events on yeast chromosome III are near tRNA genes and LTR sequences. Cell. 1993 Jun 4;73(5):1007–1018. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90278-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston M., Andrews S., Brinkman R., Cooper J., Ding H., Dover J., Du Z., Favello A., Fulton L., Gattung S. Complete nucleotide sequence of Saccharomyces cerevisiae chromosome VIII. Science. 1994 Sep 30;265(5181):2077–2082. doi: 10.1126/science.8091229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtzman C. P., Robnett C. J. Phylogenetic relationships among species of Saccharomyces, Schizosaccharomyces, Debaryomyces and Schwanniomyces determined from partial ribosomal RNA sequences. Yeast. 1991 Jan;7(1):61–72. doi: 10.1002/yea.320070107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurenson P., Rine J. Silencers, silencing, and heritable transcriptional states. Microbiol Rev. 1992 Dec;56(4):543–560. doi: 10.1128/mr.56.4.543-560.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levis R. W., Ganesan R., Houtchens K., Tolar L. A., Sheen F. M. Transposons in place of telomeric repeats at a Drosophila telomere. Cell. 1993 Dec 17;75(6):1083–1093. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90318-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louis E. J., Haber J. E. The structure and evolution of subtelomeric Y' repeats in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1992 Jul;131(3):559–574. doi: 10.1093/genetics/131.3.559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louis E. J., Naumova E. S., Lee A., Naumov G., Haber J. E. The chromosome end in yeast: its mosaic nature and influence on recombinational dynamics. Genetics. 1994 Mar;136(3):789–802. doi: 10.1093/genetics/136.3.789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundblad V., Blackburn E. H. An alternative pathway for yeast telomere maintenance rescues est1- senescence. Cell. 1993 Apr 23;73(2):347–360. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90234-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver S. G., van der Aart Q. J., Agostoni-Carbone M. L., Aigle M., Alberghina L., Alexandraki D., Antoine G., Anwar R., Ballesta J. P., Benit P. The complete DNA sequence of yeast chromosome III. Nature. 1992 May 7;357(6373):38–46. doi: 10.1038/357038a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson M. V., Dutchik J. E., Graham M. Y., Brodeur G. M., Helms C., Frank M., MacCollin M., Scheinman R., Frank T. Random-clone strategy for genomic restriction mapping in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7826–7830. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikorski R. S., Hieter P. A system of shuttle vectors and yeast host strains designed for efficient manipulation of DNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1989 May;122(1):19–27. doi: 10.1093/genetics/122.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- The International Community of Yeast Genetics and Molecular Biology. Yeast. 1992 Aug;8 (Suppl A):1–218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valgeirsdóttir K., Traverse K. L., Pardue M. L. HeT DNA: a family of mosaic repeated sequences specific for heterochromatin in Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(20):7998–8002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.20.7998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voytas D. F., Boeke J. D. Yeast retrotransposon revealed. Nature. 1992 Aug 27;358(6389):717–717. doi: 10.1038/358717a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]