Significance
Whether or not oocyte regeneration occurs in the adult mammalian ovary has been the subject of much debate. By performing a series of in vivo cell-lineage tracing experiments, we have supplied compelling in vivo evidence that mammalian oocytes are not regenerated from any putative germline stem cells in adult life. Our current study provides conclusive evidence that the initial oocyte pool is the only source of fertility throughout reproductive life in mammals.
Keywords: genetically modified mouse models, oocyte tracing, follicle tracing, life-long observations, no postnatal oocyte regeneration
Abstract
Whether or not oocyte regeneration occurs in adult life has been the subject of much debate. In this study, we have traced germ-cell lineages over the life spans of three genetically modified mouse models and provide direct evidence that oogenesis does not originate from any germline stem cells (GSCs) in adult mice. By selective ablation of all existing oocytes in a Gdf9-Cre;iDTR mouse model, we have demonstrated that no new germ cells were ever regenerated under pathological conditions. By in vivo tracing of oocytes and follicles in the Sohlh1-CreERT2;R26R and Foxl2-CreERT2;mT/mG mouse models, respectively, we have shown that the initial pool of oocytes is the only source of germ cells throughout the life span of the mice and that no adult oogenesis ever occurs under physiological conditions. Our findings clearly show that there are no GSCs that contribute to adult oogenesis in mice and that the initial pool of oocytes formed in early life is the only source of germ cells throughout the entire reproductive life span.
Whether or not oogenesis occurs in the adult mammalian ovary has been a long-standing question in developmental biology. It has been generally accepted for more than half a century that in most mammalian species oocytes cannot renew themselves in postnatal or adult life (1), but studies in the past decade have raised the possibility of adult oogenesis in both mouse and human ovaries and have increased the intensity of the debate (2–5). These studies have proposed that oocytes can be regenerated from putative germline stem cells (GSCs) or oogonial stem cells (OSCs) in adult mouse and human ovaries (these are both referred to as GSCs in this paper) (2–5). By calculating the number of healthy follicles and atretic follicles at different ages, Johnson et al. proposed that 77 new oocytes could be regenerated from putative GSCs in the mouse ovary every day (2). Moreover, they proposed that a group of GSCs, which had originated from the epithelium of the ovarian surface, served as the source of the regenerated oocytes (2). One year later, in response to criticism from the field (6), Johnson et al. amended their previous result and reported that the GSCs had actually originated from the bone marrow and peripheral blood (3).
More recently, isolation of mouse and human GSCs using the DEAD box polypeptide 4 (DDX4) antibody-based cell sorting was reported, and these GSCs were suggested to serve as the source of the oocytes that fueled the follicular replenishment (4, 5). Due to their potential implications for treating female infertility, these studies have attracted the attention of researchers as well as the popular press (7).
In contrast to these reports, other recent reports have provided evidence that adult oogenesis and the so-called GSCs do not exist and have questioned the above-mentioned findings (8–12). For example, by tracing the proliferation of cultured Ddx4-positive cells in vitro, a recent study from our group reported that no mitotically active GSCs exist in the postnatal mouse ovary (10). More recently, Lei and Spradling provided evidence to support our findings by showing that no active GSCs could be detected in adult mouse ovaries (11).
Although the existence of adult oogenesis has been debated for more than a century, most of the studies supporting or opposing the existence of adult oogenesis have been based on indirect approaches such as mathematical analysis of oocyte numbers and in vitro cell purification and cell cultures. There is a lack of functional in vivo evidence for or against the existence of adult oogenesis in mammals. Or, if adult oogenesis does exist, it is not known if such a process is physiologically relevant.
In the current study, we have generated three genetically modified mouse models and performed in vivo cell-lineage tracing of oocytes—under both physiological and pathological conditions—over the entire life span of the animals. Our results clearly show that no oocyte neogenesis occurs from putative GSCs in adult mammalian ovaries and that the initial pool of oocytes formed in early life is the only source of germ cells throughout the entire reproductive life span.
Results
Specific and Complete Ablation of All Oocytes in the Gdf9-Cre;iDTR Mouse Model.
A simple but straightforward way to detect the existence of oocyte regeneration in the ovary is to eliminate the existing population of oocytes in vivo and then look for the regeneration of any “new” oocytes.
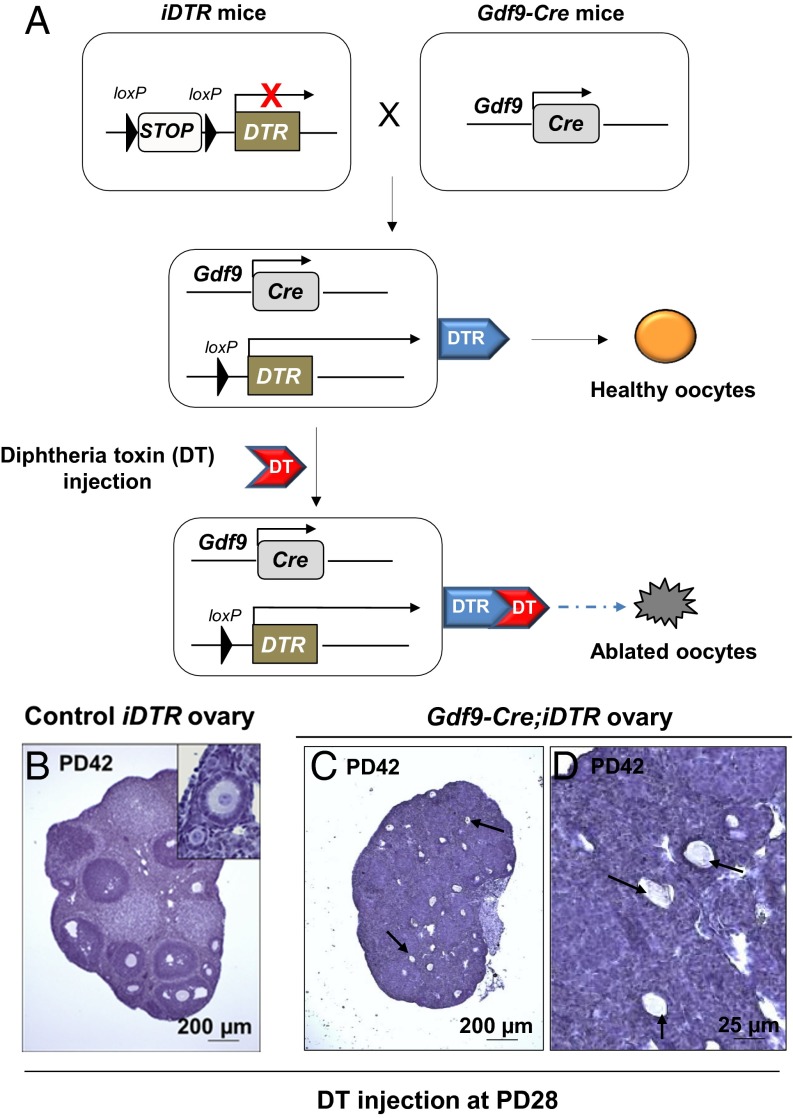
Growth differentiation factor 9 (GDF9) is an oocyte-specific protein, and the Gdf9 mRNA is expressed in oocytes at all developmental stages (13). Previous studies have shown that Gdf9-Cre transgenic mice are highly efficient in targeting oocytes of the entire follicle pool (14, 15). Importantly, Gdf9 is not expressed in reported putative GSCs in postnatal mouse ovaries (4), making the Gdf9-Cre mouse model ideal for targeting oocytes but not the proposed GSCs. By crossing Cre-inducible diphtheria toxin receptor (iDTR) mice (16) with Gdf9-Cre mice, the Gdf9-Cre mediates the expression of the diphtheria toxin (DT) receptors (DTRs) in oocytes, thereby allowing the depletion of all oocytes upon administration of the DT toxin (Fig. 1A).
Fig. 1.
Specific and efficient ablation of oocytes in the Gdf9-Cre;iDTR mouse ovaries. (A) Illustration of the diphtheria toxin (DT)-induced ablation of oocytes in Gdf9-Cre;iDTR mouse ovaries. In Gdf9-expressing oocytes, the Cre recombinase removes the loxP-flanked STOP sequence and allows the expression of the DTR. Upon DT administration, the Gdf9-expressing oocytes are selectively ablated. (B–D) All existing oocytes were ablated in Gdf9-Cre;iDTR mouse ovaries after DT injection. DT was given to PD28 females for 5 consecutive days, and ovaries were examined 2 wk later. Compared with the normal ovarian development in iDTR females (B), Gdf9-Cre;iDTR ovaries demonstrated a complete loss of all oocytes (C and D). Only follicle structures without oocytes or with oocyte debris were observed (C and D, arrows) (n = 6).
To confirm the specificity of oocyte depletion in the Gdf9-Cre;iDTR mice, we first showed that the exposure to DT at the embryonic stage had no effect on the survival and development of primordial germ cells (PGCs), which are considered to be the closest cell type to the putative GSCs (17) (for details, see the SI Text and Fig. S1 A and B). Also, the well-studied male germline stem cells, the spermatogonial cells (18), were not affected when DT was administered to postnatal male mice (Fig. S1C).
We then evaluated the efficiency of oocyte depletion in Gdf9-Cre;iDTR mice. To eliminate the existing oocytes in postnatal ovaries, DT was intraperitoneally injected into Gdf9-Cre;iDTR or control iDTR females at a dosage of 10 µg⋅kg−1 body weight (BW) for 5 consecutive days starting from postnatal day 28 (PD28). In treated control iDTR females 2 wk after the DT treatment, oocyte development was not affected, as was expected (Fig. 1B). In contrast, however, we observed a complete ablation of oocytes in ovaries of Gdf9-Cre;iDTR mice 2 wk after the DT treatment (n = 6) (Fig. 1 C and D), and only a few follicular structures without oocytes or with oocyte debris were seen in the ovaries (Fig. 1 C and D, arrows). Therefore, the entire oocyte pool in the Gdf9-Cre;iDTR ovaries was efficiently eliminated within 2 wk of DT injection.
No Adult Oogenesis Occurs After Ablation of All Oocytes in Gdf9-Cre;iDTR Ovaries.
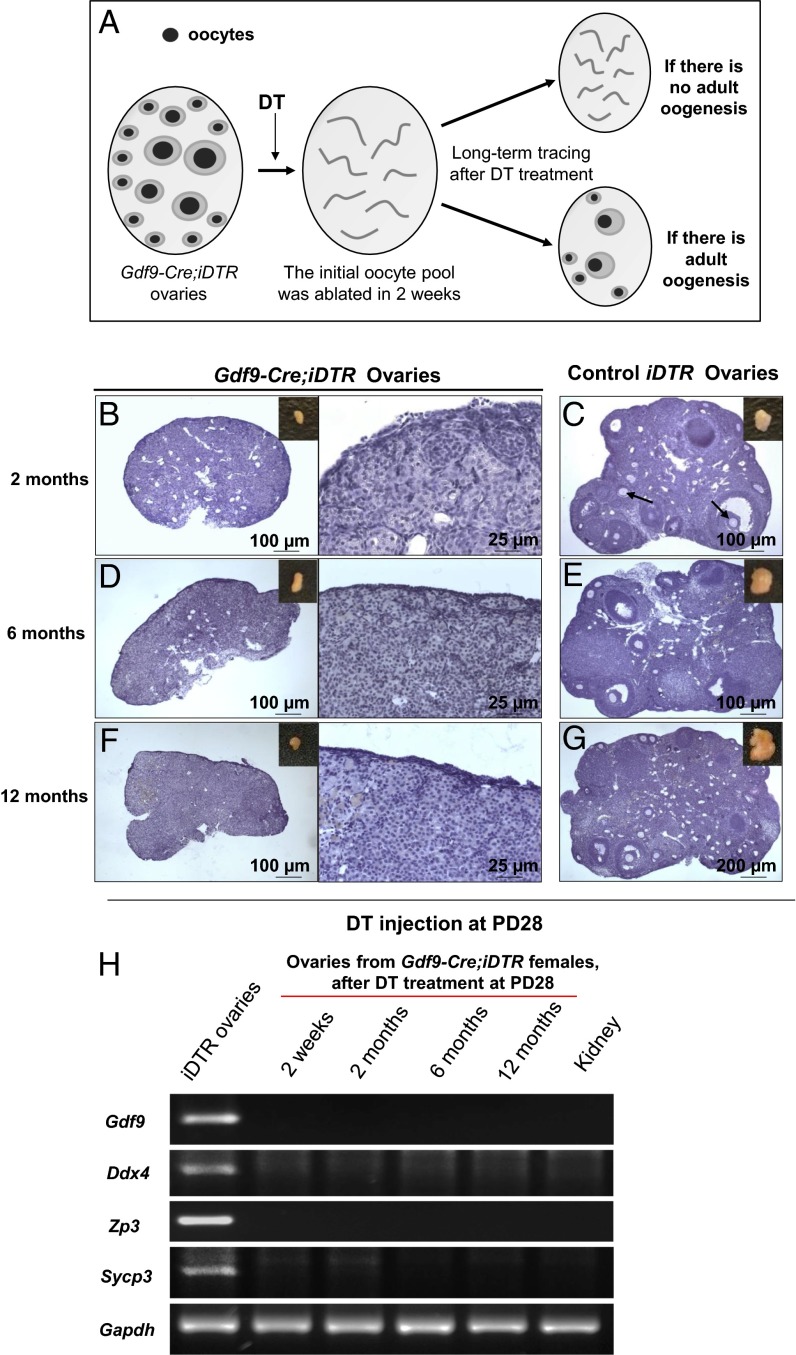
A previous study used follicle counting to report that a dramatic restoration of ovarian follicles occurred within 12 h of follicle depletion, and these results were the main evidence for proposing that postnatal follicular renewal occurs in adult mammals (3). However, because the efficiency of follicle depletion by the chemotherapy drugs used in those experiments was not known (3), it would have been difficult to distinguish between follicles that survived the drug treatment and the supposedly “renewed” follicles (6). This missing piece of critical data has cast doubt on the conclusions from those experiments that report spontaneous regeneration of the immature follicle pool occurs after chemotherapy drug treatment (3). As we mentioned above, the highly efficient Gdf9-Cre;iDTR mouse model allows us to specifically ablate all of the oocytes in postnatal ovaries. Thus, any regenerated oocytes in the adult mouse ovary would be easily detectable as illustrated in Fig. 2A.
Fig. 2.
No oocyte regeneration occurred in oocyte-ablated Gdf9-Cre;iDTR mouse ovaries. (A) Schema for long-term tracing of oocyte regeneration in Gdf9-Cre;iDTR mouse ovaries. Neogenic oocytes and follicles should be visible in the ovaries of DT-injected mice if there is oocyte regeneration during the 12-mo tracing study. (B, D, and F) No live oocytes or follicles were observed in Gdf9-Cre;iDTR ovaries at 2 mo (n = 6) (B), 6 mo (n = 6) (D), or 12 mo (n = 6) (F) after DT administration. (C, E, and G) As controls, the ovarian morphology of iDTR females was normal at 2 mo (n = 4) (C), 6 mo (n = 6) (E), and 12 mo (n = 6) (G) after DT administration. (H) Comparative gene expression profiling of germ-cell markers in oocyte-ablated Gdf9-Cre;iDTR ovaries. Semiquantitative RT-PCR analysis showed that none of the germ-cell markers studied, including Gdf9, Ddx4, Zp3 and Sycp3, were expressed in the Gdf9-Cre;iDTR ovaries from 2 wk to 12 mo after DT administration. An RNA sample from the mouse kidney was used as a negative control, and Gapdh was used as the internal loading control. All experiments were repeated at least three times, and representative images are shown.
After the DT-mediated oocyte ablation (Fig. 1 C and D), we observed the ovaries of Gdf9-Cre;iDTR mice and control iDTR females at 2, 6, and 12 mo after the treatment. We found that at 2 mo after DT treatment the Gdf9-Cre;iDTR ovaries were smaller (Fig. 2B, Inset) compared with the ovaries of control iDTR mice (Fig. 2C, Inset) and were devoid of any oocytes or follicles (Fig. 2B; Fig. S2 A–C; n = 6). In contrast, normal oocytes were seen in the ovaries of DT-treated control iDTR females (Fig. 2C, arrows).
To confirm these results, we prolonged the observation time to 6 mo and 12 mo post-DT treatment, which represent the middle and end of the reproductive life span in mice, respectively. No oocytes or follicles were found in Gdf9-Cre;iDTR ovaries at either 6 mo (Fig. 2D; Fig. S2 D–F; n = 6) or 12 mo (Fig. 2F; Fig. S2 G–I; n = 6) after DT injection. As controls, normal follicular development was seen in DT-treated control iDTR females at 6 mo (Fig. 2E) and 12 mo (Fig. 2G). This clearly shows that no oocytes were regenerated in the ovary over the course of the reproductive life spans of the mice under pathological conditions. This is in sharp contrast to the results reported earlier that 77 follicles were regenerated per day in each mouse ovary (2), which would have been easily observed in our mouse model.
In addition, we examined the mRNA expression of a series of germline cell markers in Gdf9-Cre;iDTR and iDTR ovaries after DT injection by both RT-PCR (Fig. 2H) and real-time PCR (Fig. S2J). The oocyte markers Gdf9 (13), Ddx4 (19), Zp3 (Zona pellucida glycoprotein 3) (20), and the meiotic marker Sycp3 (Synaptonemal complex protein 3) (21) were all expressed in control iDTR ovaries after DT treatment. On the contrary, none of the above-mentioned markers were expressed in DT-treated Gdf9-Cre;iDTR ovaries at any age, indicating a lack of oocytes and germ cells in the DT-treated Gdf9-Cre;iDTR ovaries. These results clearly show that there is no adult oogenesis in Gdf9-Cre;iDTR ovaries after the DT-mediated oocyte ablation. It can be concluded, therefore, that the initial pool of oocytes present before the DT administration are the sole source of germ cells in the adult mouse ovary.
Developing Oocytes in Later Reproductive Life Originate from Immature Oocytes That Were Labeled in Early Life in the Sohlh1-CreERT2;R26R Mouse Model.
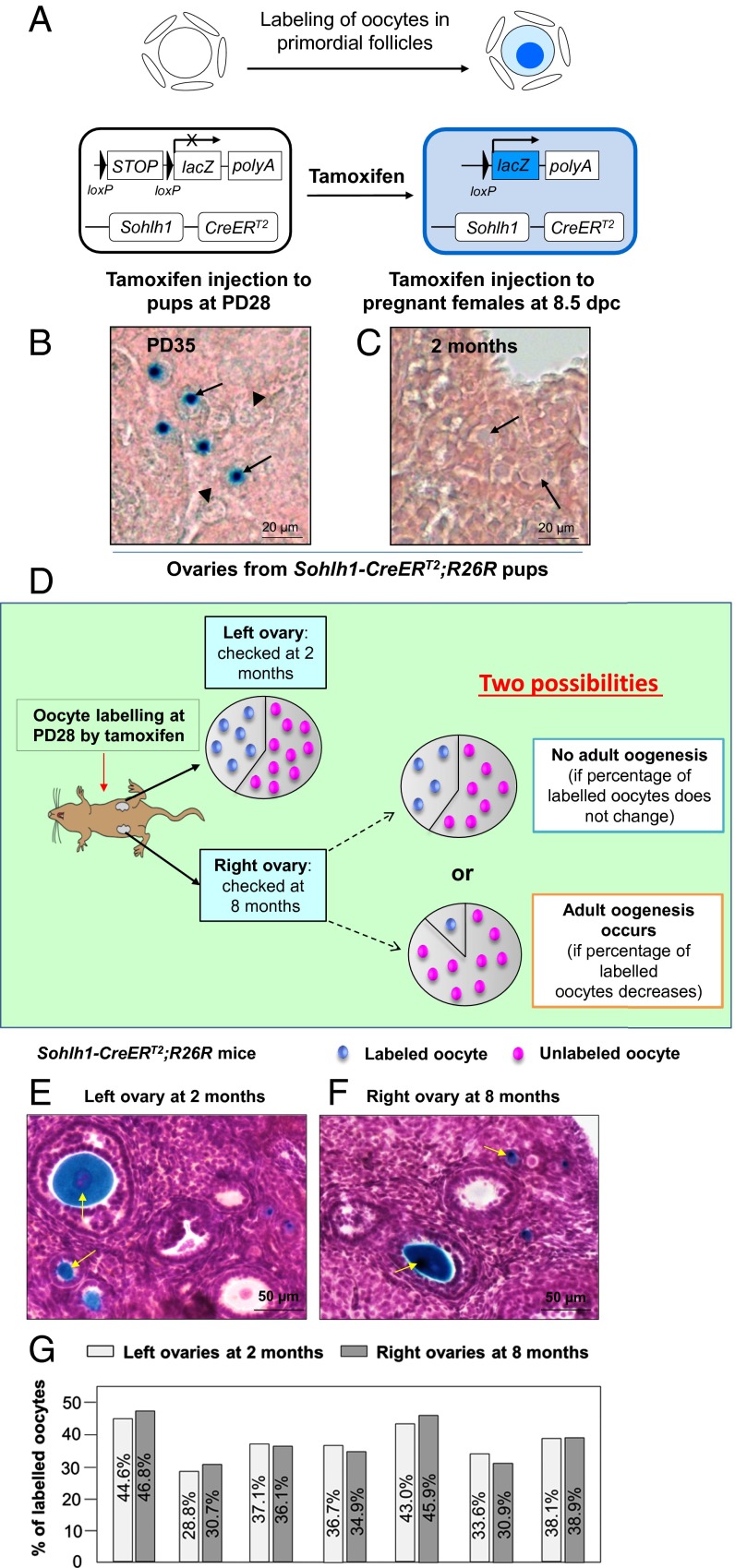
To further investigate the possibility of adult oogenesis under physiological conditions, we developed a Spermatogenesis and oogenesis-specific basic helix–loop–helix 1(Sohlh1)-CreERT2;R26R mouse model. The Sohlh1 promoter is active only in the meiotic-arrested immature oocytes of primordial follicles (22); thus, by crossing the Sohlh1-CreERT2 mice with a Rosa26 reporter (R26R) mouse line, we were able to selectively label only the small, immature oocytes by injecting the mice with tamoxifen (illustrated in Fig. 3A). As shown in Fig. 3B, after tamoxifen administration at PD28, the labeled immature oocytes exhibiting blue β-galactosidase staining in primordial follicles were seen at PD35 (Fig. 3B, arrows). The amount of tamoxifen used was previously determined not to affect follicle development (23).
Fig. 3.
The developing oocytes in later reproductive life originated from immature oocytes that were labeled in early life in Sohlh1-CreERT2;R26R females. (A) Illustration of the tamoxifen-induced labeling of oocytes in primordial follicles of the Sohlh1-CreERT2;R26R ovary. CreERT2 recombinase is expressed in Sohlh1-expressing oocytes of primordial follicles. Upon tamoxifen administration, the CreERT2 recombinase removes the STOP sequence and turns on the expression of lacZ (the gene encoding β-galactosidase), and this generates a blue color in the oocyte cytoplasm after β-galactosidase staining. (B) Labeling oocytes of primordial follicles by postnatal tamoxifen injection. Tamoxifen was given to Sohlh1-CreERT2;R26R females for 7 consecutive days at PD28, and ovaries were collected for analysis at PD35 (n = 6). The labeled oocytes were visualized by their blue color after β-galactosidase staining (arrows) whereas the unlabeled oocytes showed only background color (arrowheads). (C) No PGCs were labeled by embryonic tamoxifen injection. R26R females were plugged with Sohlh1-CreERT2 males, and tamoxifen was given to pregnant females from 8.5 to 12.5 dpc. No labeled oocytes were observed at 2 mo in the ovaries of Sohlh1-CreERT2;R26R pups that were born from the tamoxifen-injected females (n = 6). (D) Schema for long-term tracing of oocyte regeneration in Sohlh1-CreERT2;R26R mouse ovaries. The ratio of labeled-to-unlabeled oocytes should remain the same if there is no adult oogenesis but should decrease if oocyte neogenesis occurs. (E and F) Labeling the existing oocytes in the adult mouse ovary. The labeled oocytes (identified by the blue dots) can be observed in both the left ovary at 2 mo (E) and the right ovary at 8 mo (F) after tamoxifen injection. Some labeled oocytes had entered into the growing phase (arrows). (G) The ratio of labeled-to-unlabeled oocytes remained the same in each mouse at 2 mo (left ovaries) (n = 7) and at 8 mo (right ovaries) (n = 7) after tamoxifen injection. The similarity in the proportion of labeled oocytes indicates that no oocyte neogenesis occurred in the adult mouse ovaries.
As a control, we gave tamoxifen to pregnant females at 8.5 d post coitum (dpc) to 12.5 dpc to exclude the possibility that we might label PGCs, which are the closest cell type to the putative GSCs (17). Indeed, no oocytes were labeled in Sohlh1-CreERT2;R26R pups from tamoxifen-treated pregnant females when analyzed at 2 mo of age (Fig. 3C, arrows). Thus, the Sohlh1-CreERT2;R26R mouse model specifically labels only the initial pool of immature oocytes.
The Sohlh1-CreERT2;R26R mouse model labels only a percentage of the immature oocytes in the primordial follicles. The labeled immature oocytes exhibited blue color after β-galactosidase staining (Fig. 3B, arrows), and the unlabeled oocytes showed no staining (Fig. 3B, arrowheads). This provides us with the possibility of measuring the ratio of labeled and unlabeled oocytes in early life and of comparing this to the ratio later in reproductive life. As illustrated in Fig. 3D, the proportion of labeled oocytes should remain stable if no new oocytes are regenerated, but the ratio of labeled oocytes to unlabeled oocytes should steadily decrease in Sohlh1-CreERT2;R26R ovaries if unlabeled new oocytes are constantly regenerated from suggested GSCs as previously reported (2, 3).
To minimize the variation of labeling efficiency among individual females, the mice were injected with tamoxifen at PD28, and the bilateral ovaries from each mouse were harvested at 2 mo (the left ovary) and at 8 mo of age (the right ovary) (Fig. 3D). The ratios of labeled and unlabeled oocytes in the ovaries of the same mouse were compared. At 2 mo of age, some of the labeled oocytes were activated and had developed to advanced stages (Fig. 3E, arrows). The percentage of labeled oocytes in the left ovaries of seven mice was 37.41 ± 5.37%, ranging from 28.8 to 44.6% (Fig. 3G, n = 7). At 8 mo of age, the percentage of labeled oocytes (Fig. 3F, arrows) in the right ovaries was 37.74 ± 6.55% and ranged from 30.7 to 46.8% in the seven mice studied, and the percentages in the right ovary of each mouse were almost identical to those in the left ovary at 2 mo of age (Fig. 3G, n = 7). These results suggest that the oocyte population at 8 mo of age still belonged to the same pool of oocytes that already existed at 2 mo of age and from which the developing follicles originated. Thus, we conclude that there exists a stable oocyte population in the adult ovaries that is established in early life. Our data show that no GSCs contribute to any oocyte regeneration in adult mouse ovaries under physiological conditions.
There Is No Recruitment of Nascent Somatic Cells to Form Follicles with de Novo-Regenerated Oocytes Under Physiological Conditions in Adult Mouse Ovaries.
To confirm the conclusions drawn above, we also traced oocyte development by labeling the surrounding somatic cells of all existing oocytes in the initial follicle pool with the Forkhead box L2 (Foxl2)-CreERT2;mT/mG mouse model (23). Foxl2 is expressed in follicular somatic cells in the mouse ovary (24) but not in the progenitors of follicular somatic cells in the ovarian epithelium (25). This makes Foxl2 a good marker for tracing the recruitment of nascent somatic cells to form follicles with any de novo-regenerated oocytes (23).
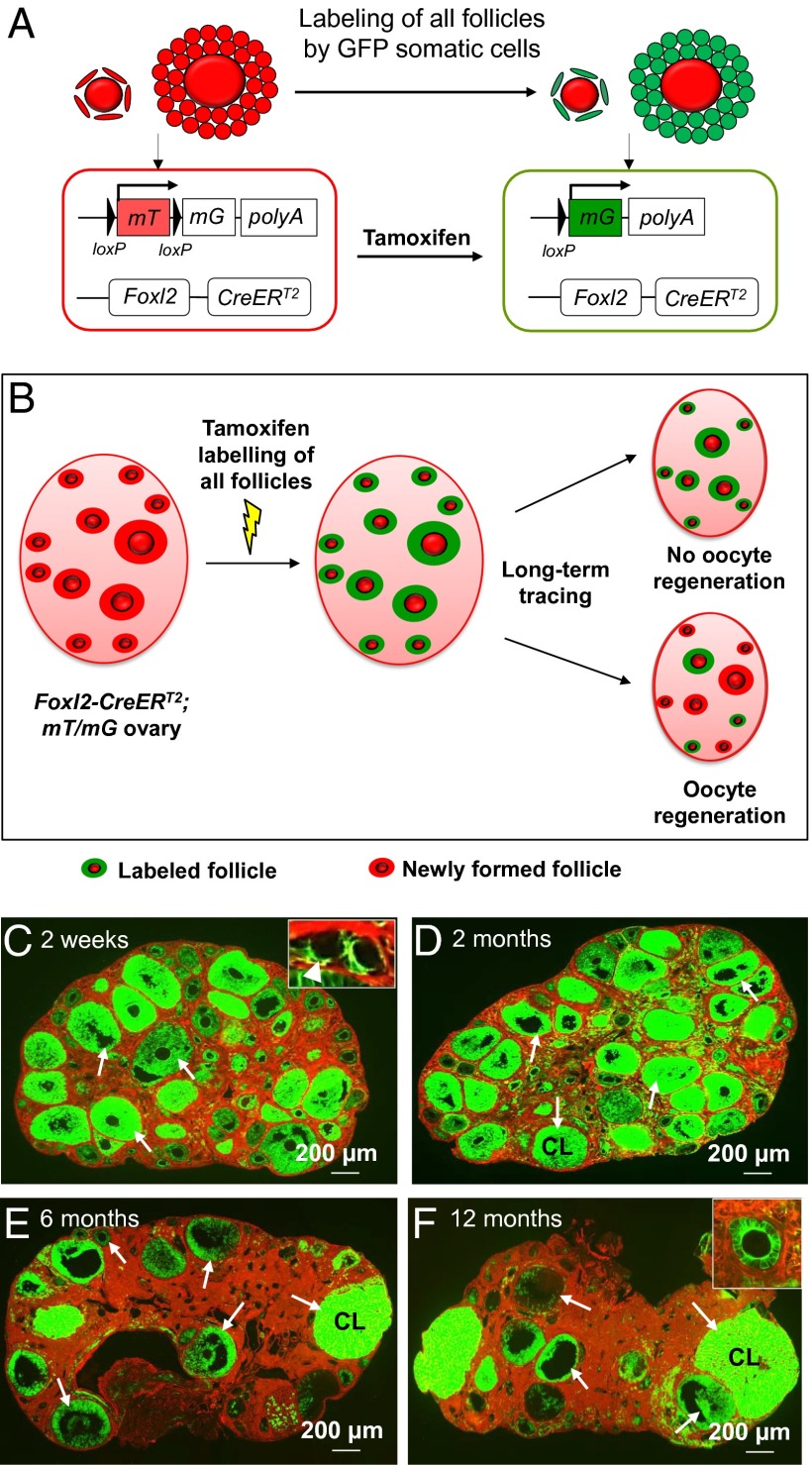
We crossed the Foxl2-CreERT2 mice to an mTmG reporter mouse line in which all cells express red fluorescence (membrane-targeted tdTomato, or mT) before tamoxifen induction, whereas the Foxl2-positive cells switch to green fluorescence (membrane-targeted EGFP, or mG) upon tamoxifen treatment (as illustrated in Fig. 4A) (23, 26). The Foxl2-CreERT2;mT/mG mouse model allowed us to trace any regeneration of oocytes under physiological conditions that leads to the formation of new follicles through recruitment of nascent follicular somatic cells. We chose to label all existing follicles in early life with green fluorescence by tamoxifen induction so that any de novo follicles with newly recruited follicular somatic cells could be distinguished by their red fluorescence (as illustrated in Fig. 4B).
Fig. 4.
Long-term tracing of follicle populations by labeling the follicular somatic cells in adult Foxl2-CreERT2;mT/mG ovaries. (A) Illustration of the tamoxifen-induced labeling of follicles in Foxl2-CreERT2;mT/mG mice. In Foxl2-expressing follicular somatic cells, the CreERT2 recombinase is not active and the cells express mT, a red fluorescent protein. Upon tamoxifen injection, the CreERT2 recombinase deletes the mT region and switches on the expression of mG, a green fluorescent protein. Thus, the Foxl2-expressing follicular somatic cells were labeled with green fluorescence. (B) Schema for long-term tracing of oocyte regeneration in Foxl2-CreERT2;mT/mG mouse ovaries. All follicular somatic cells were labeled with the green fluorescent mG at PD28. Follicles with only red (mT) somatic cells would be observed if oocyte regeneration occurred during the tracing study. (C–F) The mice were given an i.p. injection of 80 mg⋅kg−1 BW (∼2 mg per mouse) tamoxifen per day for 7 consecutive days starting at PD28. The mice were killed at 2 wk (n = 6) (C), 2 mo (n = 6) (D), 6 mo (n = 6) (E), and 12 mo (n = 6) (F) after the injection. Ovaries were collected and all sections were carefully checked under the microscope, and a follicle or a corpus luteum was considered to be labeled if green fluorescent granulosa or luteal cells were observed. At 2 wk after tamoxifen injection, all follicles, including the dormant primordial follicles in the cortex (C, Inset, arrowhead) and growing follicles in the medulla (C, arrows), were labeled with green fluorescence in their somatic cells. All follicles (D–F, arrows) or corpora lutea (D–F, CL) were labeled with green fluorescence in their somatic cells, and no follicles with only red somatic cells were found in mice killed at 2 mo (D), 6 mo (E), or 12 mo (F) after tamoxifen injection.
The Foxl2-CreERT2;mT/mG mice were injected with tamoxifen starting at PD28 to ensure the complete labeling of all follicles (Fig. 4C). The amount of tamoxifen used was previously determined not to affect follicle development (23). Analysis of serial sections from ovaries of six treated mice at 2 wk after tamoxifen injection showed that all follicles—including dormant primordial follicles in the ovarian cortex (Fig. 4C, Inset, arrowhead) and activated follicles (Fig. 4C, arrows)—contained EGFP-expressing pregranulosa or granulosa cells. Therefore, we could label the entire follicle pool in early life. The Foxl2-CreERT2;mT/mG mice were then killed at 2, 6, and 12 mo after tamoxifen injection to look for any de novo follicles with red fluorescent granulosa cells.
We found that 2 mo (n = 6) and 6 mo (n = 6) after the tamoxifen-mediated follicle labeling, follicles of all stages (Fig. 4 D and E, arrows) and corpora lutea (CL) (Fig. 4 D and E, CL) in Foxl2-CreERT2;mT/mG ovaries were composed of green fluorescent somatic cells, and no de novo follicles with red granulosa cells were identified (Fig. 4 D and E). At 12 mo (n = 6) after the labeling of follicles, all follicles and CL in the ovaries were still composed of green fluorescent somatic cells (Fig. 4F, arrows), and this clearly showed that all follicles in the 12-mo-old ovaries belonged to the initial pool of follicles labeled at PD28. Our results showed that all ovaries at 2 wk and at 2, 6, and 12 mo contain only follicles with green fluorescent somatic cells and thus provide evidence that there is no recruitment of nascent follicular somatic cells to constitute new follicles with any de novo-regenerated oocytes in adult mouse ovaries.
Discussion
Unlike males that produce a large number of sperm from a constantly renewing source of male GSCs (spermatogonia), it has long been believed that females possess a finite number of germ cells (1). In humans, the number of oocytes follows a continuously decreasing trend from a peak of 6–7 million oocytes at 20 wk gestation to less than 1 million at birth to ∼300,000–400,000 at menarche. During the reproductive years in humans, the decline in the number of oocytes remains steady at about 1,000 follicles per month, and this decline accelerates after the age of about 37 y. At the time of menopause, the number of remaining follicles drops below 1,000 (27). Nature seems to have chosen a way to constantly reduce the number of oocytes throughout the reproductive years of a woman and to terminate fertility at menopause.
Whether or not adult oogenesis occurs from GSCs in the adult mammalian ovary has been the focus of much study and debate for more than a century. However, most of the studies that support or oppose the existence of adult oogenesis and GSCs have been based on manipulated in vitro approaches (2–5, 9, 28). In this study, by using three genetically modified mouse models, we have traced germ-cell lineages over the mouse life spans and provide several lines of evidence demonstrating that mammalian oocytes are not regenerated in adult life. Our approach here is fundamentally different from the previous indirect approaches and in vitro manipulation of cells (2–5), and it allows us to directly visualize and trace the in vivo developmental dynamics of the oocyte population under both physiological and pathological conditions. Our results obtained from the three genetically modified mouse models clearly show that no renewed oocytes or follicles were ever observed in the adult mouse ovary at any age. Thus, the putative GSCs in the adult ovary, if they exist at all, do not serve as functional germline stem cells that give rise to any new oocytes or follicles in vivo. The postnatal “oogenesis” after the transplantation of in vitro-manipulated cells in previous reports (4, 5), therefore, does not represent a naturally occurring phenomenon.
Based on the experimental evidence presented here, we conclude that the suggested GSCs in the adult mammalian ovary (4, 5) are not natural stem cells of the female germline. The GSCs might have arisen from possible de-differentiation or other unknown events that occurred in those cells during the long-term in vitro culture. Together with the fact that other cultured non-GSCs, such as skin stem cells, can also form oocyte-like cells and blastocyst-like structures during in vitro culture (29–31), this brings into question the nature of the reported GSCs in adult mammalian ovaries (4, 5). Based on the in vivo lineage tracing results in this study, even if such purified GSCs do generate eggs after long-term in vitro culture, such GSCs (4, 5) do not represent stem cells of oocytes. Thus, stricter standards should be applied when characterizing these in vitro-derived cells as GSCs (32).
Over the past decade, in vitro methods for creating germ cells from different types of stem cells have been developed (29, 30, 33), and the clinical potential of these in vitro-derived oocytes in treating female infertility has attracted the attention of both researchers and the popular press. Although our current results clearly show that functional GSCs do not exist in adult mammalian ovaries, we do believe that the use of other types of stem cells, such as embryonic stem cells and induced pluripotent stem cells (33), for generating functional oocytes is a promising future trend in female infertility treatment. However, much more robust studies should be performed before any kind of cell is claimed to be significant for clinical applications.
Materials and Methods
Mice.
All mouse strains were crossed with C57BL/6 mice (Charles River) for six generations to obtain an identical genetic background. Mice were housed under controlled environmental conditions with free access to water and food. Illumination was on between 0600 and 1800 hours. Experimental protocols were approved by the regional ethical committee of the University of Gothenburg (Gothenburg, Sweden). The genetically modified mouse models are described below.
Generation of Gdf9-Cre;iDTR Mice.
The Gdf9-Cre;iDTR oocyte-ablation mouse model was generated by crossing the iDTR knock-in females (007900, Jackson Laboratory) with Gdf9-Cre transgenic males (14, 15). In this mouse strain, the Cre recombinase removes the STOP sequence that is flanked by two loxP sites in the iDTR allele and allows for the expression of simian DTR in the oocytes of all of the follicles in the ovary from the primordial to the antral stages. The oocytes expressing DTR are susceptible to cell ablation upon DT administration as illustrated in Fig. 1A.
Ablating the Existing Oocyte Pool in Gdf9-Cre;iDTR Female Mice.
To ensure that there is no side effect of DT (Merck Millipore) on PGCs, iDTR females were plugged by Gdf9-Cre males. DT was given to the pregnant females from 8.5 to 12.5 dpc (noon of the day on which a vaginal plug was observed was considered 0.5 dpc) at a daily dose of 10 µg⋅kg−1 BW. The oogenesis and folliculogenesis of the pups that were born from the DT-injected females were evaluated at PD8 and at 3 mo and were found to be not affected by the DT treatment (Fig. S1 A and B).
To selectively ablate the existing oocyte pool, Gdf9-Cre;iDTR females were intraperitoneally injected with DT at a dose of 10 µg·kg−1 BW per day for 5 consecutive days at PD28. The in vivo half-life of DT is less than 8 h (34).
Generation of Sohlh1-CreERT2;R26R Mice.
The generation of the Sohlh1-CreERT2 mice was reported earlier (23). The Sohlh1-CreERT2;R26R oocyte-specific reporter mouse model was obtained by crossing Sohlh1-CreERT2 knock-in mice with R26R reporter mice (003309, Jackson Laboratory). In this mouse strain, the endogenous Sohlh1 promoter drives the expression of CreERT2 recombinase in the oocytes of primordial follicles in the ovary. Upon tamoxifen injection, the CreERT2 recombinase enters the nucleus and mediates the recombination at the R26R locus, resulting in the expression of lacZ in Sohlh1-expressing oocytes. The Lac-Z–labeled oocytes are visible after β-galactosidase staining (Fig. 3B).
Generation of Foxl2-CreERT2;mT/mG Mice.
The Foxl2-CreERT2;mT/mG follicular somatic cell-specific reporter strain was created by crossing Foxl2-CreERT2 knock-in mice (23) with mT/mG reporter mice (007576, Jackson Laboratory). In this mouse strain, the endogenous Foxl2 promoter drives the expression of CreERT2 recombinase in follicular somatic cells in the ovary. Upon tamoxifen injection, the CreERT2 recombinase mediates recombination at the mT/mG locus, resulting in a change in expression from the red mT to the green mG in Foxl2-expressing follicular somatic cells (Fig. 4A). Meanwhile, the red fluorescent mT is still expressed in all Foxl2-negative cells.
Tamoxifen Administration to Sohlh1-CreERT2;R26R and Foxl2-CreERT2;mT/mG Mouse Models.
Tamoxifen (Sigma-Aldrich) was resuspended at 100 mg⋅mL−1 in 95% (vol/vol) ethanol and further diluted with corn oil (Sigma-Aldrich) to a final concentration of 20 mg⋅mL−1. To selectively label the existing oocytes or follicles, Sohlh1-CreERT2;R26R or Foxl2-CreERT2;mT/mG female mice were given an i.p. injection of 80 mg⋅kg−1 BW (∼2 mg per mouse) tamoxifen per day for 7 consecutive days starting at PD28. The CreERT2-mediated DNA recombination takes place within 24 h after tamoxifen injection (35). The amount of tamoxifen used was previously determined not to affect follicle development (23).
To ensure that there is no nonspecific labeling of PGCs in the Sohlh1-CreERT2;R26R mouse model, tamoxifen was given to pregnant females from 8.5 to 12.5 dpc at a daily dose of 80 mg⋅kg−1 BW. The ovaries of the Sohlh1-CreERT2;R26R pups that were born from the tamoxifen-injected females were studied at 2 mo, and no oocytes were labeled (Fig. 3C, arrows). Thus, the Sohlh1-CreERT2;R26R mouse model specifically labels only the initial pool of immature oocytes.
β-Galactosidase Staining of Sohlh1-CreERT2;R26R Ovaries.
Whole-mount β-galactosidase staining was performed to visualize the labeled oocytes in the ovaries of Sohlh1-CreERT2;R26R mice. Briefly, ovaries were fixed in 4% (wt/vol) paraformaldehyde for 1 h at 4 °C and then rinsed three times for 15 min each in a buffer consisting of 1× PBS (pH 7.4), 2 mM magnesium chloride, 5 mM ethylene glycol tetraacetic acid, 0.01% sodium deoxycholate, and 0.02% Nonidet P-40 at room temperature. The ovaries were then incubated with a staining solution consisting of 1× PBS (pH 7.4), 2 mM magnesium chloride, 0.01% sodium deoxycholate, 0.02% Nonidet P-40, 5 mM potassium ferricyanide, 5 mM potassium ferrocyanide, and 1 mg⋅mL−1 X-gal (all from Sigma-Aldrich) at 37 °C overnight. The stained ovaries were then refixed in 4% (wt/vol) paraformaldehyde for 10 h.
Histological Analysis.
To locate the potentially renewed oocytes or follicles by histological analysis, ovaries were fixed in 4% (wt/vol) paraformaldehyde, dehydrated, and embedded in paraffin (Histolab). The paraffin-embedded ovaries were serially cut into 8-μm sections, and all sections were analyzed.
For Gdf9-Cre;iDTR ovaries, the sections were rehydrated and stained with hematoxylin. All sections were carefully analyzed under a Zeiss Axio Scope A1 upright microscope.
For Sohlh1-CreERT2;R26R ovaries, all sections were rehydrated and counterstained with 0.1% nuclear fast red solution to count the number of labeled oocytes. The sections were restained with hematoxylin for quantification of the total numbers of oocytes in the ovaries. All sections were carefully analyzed under a Zeiss Axio Scope A1 upright microscope. An oocyte was considered to be labeled if a blue dot was observed in its cytoplasm (23).
For Foxl2-CreERT2;mT/mG ovaries, the sections were rehydrated and the fluorescent images were obtained with a Zeiss Axio Scope A1 upright microscope installed with filter sets for mT (554/581 nm) and mG (488/507 nm) and merged with the Zeiss AxioVision software. All sections were carefully checked under the microscope, and a follicle or a corpus luteum was considered to be labeled if green fluorescent granulosa or luteal cells were observed.
Gene Expression Analysis.
For detecting gene expression in mouse materials, total RNA was isolated from the ovaries of Gdf9-Cre;iDTR or iDTR female mice with the RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen). First-strand cDNA was synthesized with the iScript cDNA Synthesis Kit (Bio-Rad). Synthesized cDNA was subjected to semiquantitative RT-PCR or real-time PCR using the primer pairs listed in Table S1. Real-time PCR was performed with an ABI 7500 Real Time PCR System (Applied Biosystems) using SYBR Green PCR master mix (Applied Biosystems). The reactions were carried out in triplicate. Threshold cycle (Ct) values were obtained. The housekeeping gene Gapdh was used for normalization when calculating ΔCt values, and the ΔΔCt method was used to calculate the gene expression. GENE-E analysis software (www.broadinstitute.org/cancer/software/GENE-E/) was used for creating heat map images using relative values.
Statistical Analysis.
All experiments were repeated at least three times. Representative results are shown. Quantitative data (means ± SD) were analyzed by one-way ANOVA using Sigma-plot software.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by grants to K.L. from the Jane and Dan Olssons Foundation, the LUA/ALF-medel Västra Götalandsregionen, AFA Insurance, the Swedish Research Council, the Swedish Cancer Foundation, and the Faculty of Natural Science of the University of Gothenburg, and by grants to J.-Å.G. from the Swedish Cancer Foundation.
Footnotes
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
This article contains supporting information online at www.pnas.org/lookup/suppl/doi:10.1073/pnas.1421047111/-/DCSupplemental.
References
- 1.Zuckerman S. The number of oocytes in the mature ovary. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1951;6:63–109. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Johnson J, Canning J, Kaneko T, Pru JK, Tilly JL. Germline stem cells and follicular renewal in the postnatal mammalian ovary. Nature. 2004;428(6979):145–150. doi: 10.1038/nature02316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Johnson J, et al. Oocyte generation in adult mammalian ovaries by putative germ cells in bone marrow and peripheral blood. Cell. 2005;122(2):303–315. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2005.06.031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.White YA, et al. Oocyte formation by mitotically active germ cells purified from ovaries of reproductive-age women. Nat Med. 2012;18(3):413–421. doi: 10.1038/nm.2669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Zou K, et al. Production of offspring from a germline stem cell line derived from neonatal ovaries. Nat Cell Biol. 2009;11(5):631–636. doi: 10.1038/ncb1869. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Telfer EE, et al. On regenerating the ovary and generating controversy. Cell. 2005;122(6):821–822. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2005.09.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Gura T. Reproductive biology: Fertile mind. Nature. 2012;491(7424):318–320. doi: 10.1038/491318a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Eggan K, Jurga S, Gosden R, Min IM, Wagers AJ. Ovulated oocytes in adult mice derive from non-circulating germ cells. Nature. 2006;441(7097):1109–1114. doi: 10.1038/nature04929. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Bristol-Gould SK, et al. Fate of the initial follicle pool: Empirical and mathematical evidence supporting its sufficiency for adult fertility. Dev Biol. 2006;298(1):149–154. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2006.06.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Zhang H, et al. Experimental evidence showing that no mitotically active female germline progenitors exist in postnatal mouse ovaries. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2012;109(31):12580–12585. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1206600109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Lei L, Spradling AC. Female mice lack adult germ-line stem cells but sustain oogenesis using stable primordial follicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2013;110(21):8585–8590. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1306189110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Yuan J, et al. No evidence for neo-oogenesis may link to ovarian senescence in adult monkey. Stem Cells. 2013;31(11):2538–2550. doi: 10.1002/stem.1480. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Dong J, et al. Growth differentiation factor-9 is required during early ovarian folliculogenesis. Nature. 1996;383(6600):531–535. doi: 10.1038/383531a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Lan ZJ, Xu X, Cooney AJ. Differential oocyte-specific expression of Cre recombinase activity in GDF-9-iCre, Zp3cre, and Msx2Cre transgenic mice. Biol Reprod. 2004;71(5):1469–1474. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.104.031757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Reddy P, et al. Oocyte-specific deletion of Pten causes premature activation of the primordial follicle pool. Science. 2008;319(5863):611–613. doi: 10.1126/science.1152257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Buch T, et al. A Cre-inducible diphtheria toxin receptor mediates cell lineage ablation after toxin administration. Nat Methods. 2005;2(6):419–426. doi: 10.1038/nmeth762. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.De Felici M, Barrios F. Seeking the origin of female germline stem cells in the mammalian ovary. Reproduction. 2013;146(4):R125–R130. doi: 10.1530/REP-13-0069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Spradling A, Fuller MT, Braun RE, Yoshida S. Germline stem cells. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2011;3(11):a002642. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a002642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Noce T, Okamoto-Ito S, Tsunekawa N. Vasa homolog genes in mammalian germ cell development. Cell Struct Funct. 2001;26(3):131–136. doi: 10.1247/csf.26.131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Philpott CC, Ringuette MJ, Dean J. Oocyte-specific expression and developmental regulation of ZP3, the sperm receptor of the mouse zona pellucida. Dev Biol. 1987;121(2):568–575. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(87)90192-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Yuan L, et al. Female germ cell aneuploidy and embryo death in mice lacking the meiosis-specific protein SCP3. Science. 2002;296(5570):1115–1118. doi: 10.1126/science.1070594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Pangas SA, et al. Oogenesis requires germ cell-specific transcriptional regulators Sohlh1 and Lhx8. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2006;103(21):8090–8095. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0601083103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Zheng W, et al. Two classes of ovarian primordial follicles exhibit distinct developmental dynamics and physiological functions. Hum Mol Genet. 2014;23(4):920–928. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddt486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Schmidt D, et al. The murine winged-helix transcription factor Foxl2 is required for granulosa cell differentiation and ovary maintenance. Development. 2004;131(4):933–942. doi: 10.1242/dev.00969. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Mork L, et al. Temporal differences in granulosa cell specification in the ovary reflect distinct follicle fates in mice. Biol Reprod. 2012;86(2):37. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.111.095208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Muzumdar MD, Tasic B, Miyamichi K, Li L, Luo L. A global double-fluorescent Cre reporter mouse. Genesis. 2007;45(9):593–605. doi: 10.1002/dvg.20335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Broekmans FJ, Knauff EA, te Velde ER, Macklon NS, Fauser BC. Female reproductive ageing: Current knowledge and future trends. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2007;18(2):58–65. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2007.01.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Kerr JB, et al. The primordial follicle reserve is not renewed after chemical or γ-irradiation mediated depletion. Reproduction. 2012;143(4):469–476. doi: 10.1530/REP-11-0430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Dyce PW, Wen L, Li J. In vitro germline potential of stem cells derived from fetal porcine skin. Nat Cell Biol. 2006;8(4):384–390. doi: 10.1038/ncb1388. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Hübner K, et al. Derivation of oocytes from mouse embryonic stem cells. Science. 2003;300(5623):1251–1256. doi: 10.1126/science.1083452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Danner S, Kajahn J, Geismann C, Klink E, Kruse C. Derivation of oocyte-like cells from a clonal pancreatic stem cell line. Mol Hum Reprod. 2007;13(1):11–20. doi: 10.1093/molehr/gal096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Handel MA, Eppig JJ, Schimenti JC. Applying “gold standards” to in-vitro-derived germ cells. Cell. 2014;157(6):1257–1261. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.05.019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Hayashi K, Saitou M. Generation of eggs from mouse embryonic stem cells and induced pluripotent stem cells. Nat Protoc. 2013;8(8):1513–1524. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2013.090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Yamaizumi M, Uchida T, Takamatsu K, Okada Y. Intracellular stability of diphtheria toxin fragment A in the presence and absence of anti-fragment A antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1982;79(2):461–465. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Hayashi S, McMahon AP. Efficient recombination in diverse tissues by a tamoxifen-inducible form of Cre: A tool for temporally regulated gene activation/inactivation in the mouse. Dev Biol. 2002;244(2):305–318. doi: 10.1006/dbio.2002.0597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.