Abstract
The crystal structure of the oxidized form of flavodoxin from Desulfovibrio vulgaris has been studied at 2.0-Å resolution, and a detailed description of the region around the flavin mononucleotide binding site is now available. The flavin is between a tyrosine group, roughly parallel to it on one side, and a tryptophan, about 45° from being parallel, on the other side. The two carbonyl groups and two nitrogen atoms of the flavin are hydrogen bonded to the peptide chain of the protein, while the two methyl groups are exposed at the surface of the protein. The phosphate group of the flavin mononucleotide is inside the protein and extensively hydrogen bonded to it. The ribityl group is hydrogen bonded both to the protein and to water on the surface of the protein.
Keywords: protein structure, flavin mononucleotide, hydrogen bonding, x-ray crystallography
Full text
PDF
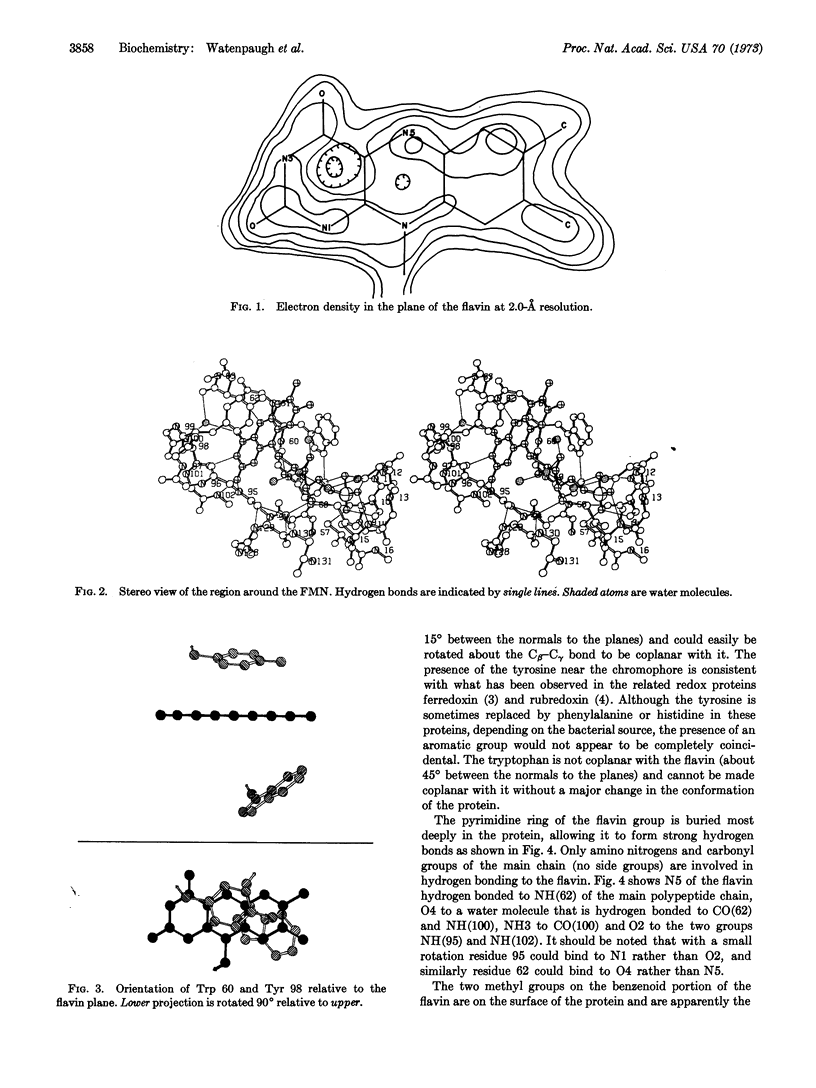
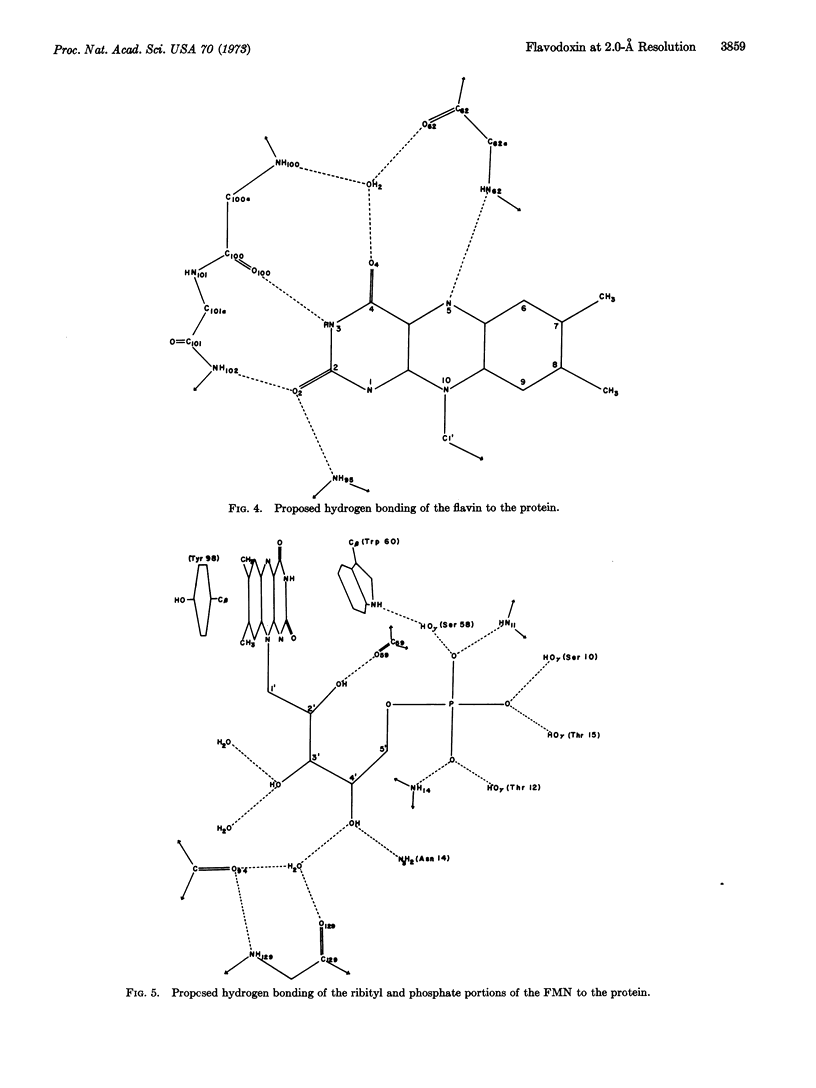

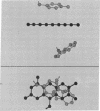
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adman E. T., Sieker L. C., Jensen L. H. Structure of a bacterial ferredoxin. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jun 10;248(11):3987–3996. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersen R. D., Apgar P. A., Burnett R. M., Darling G. D., Lequesne M. E., Mayhew S. G., Ludwig M. L. Structure of the radical form of clostridial flavodoxin: a new molecular model. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Nov;69(11):3189–3191. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.11.3189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Anna J. A., Jr, Tollin G. Studies of flavin-protein interaction in flavoproteins using protein fluorescence and circular dichroism. Biochemistry. 1972 Mar 14;11(6):1073–1080. doi: 10.1021/bi00756a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubourdieu M., Le Gall J., Fox J. L. The amino acid sequence of Desulfovibrio vulgaris flavodoxin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Jun 19;52(4):1418–1425. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90659-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox J. L., Smith S. S., Brown J. R. Amino acid sequences of Clostridium pasteurianum flavodoxin. Z Naturforsch B. 1972 Sep;27(9):1096–1100. doi: 10.1515/znb-1972-0932. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka M., Haniu M., Yasunobu K. T., Mayhew S., Massey V. Amino acid sequence of the Peptostreptococcus elsdenii flavodoxin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Aug 20;44(4):886–892. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90794-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watenpaugh K. D., Sieker L. C., Jensen L. H., Legall J., Dubourdieu M. Structure of the oxidized form of a flavodoxin at 2.5-Angstrom resolution: resolution of the phase ambiguity by anomalous scattering. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Nov;69(11):3185–3188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.11.3185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]