Abstract
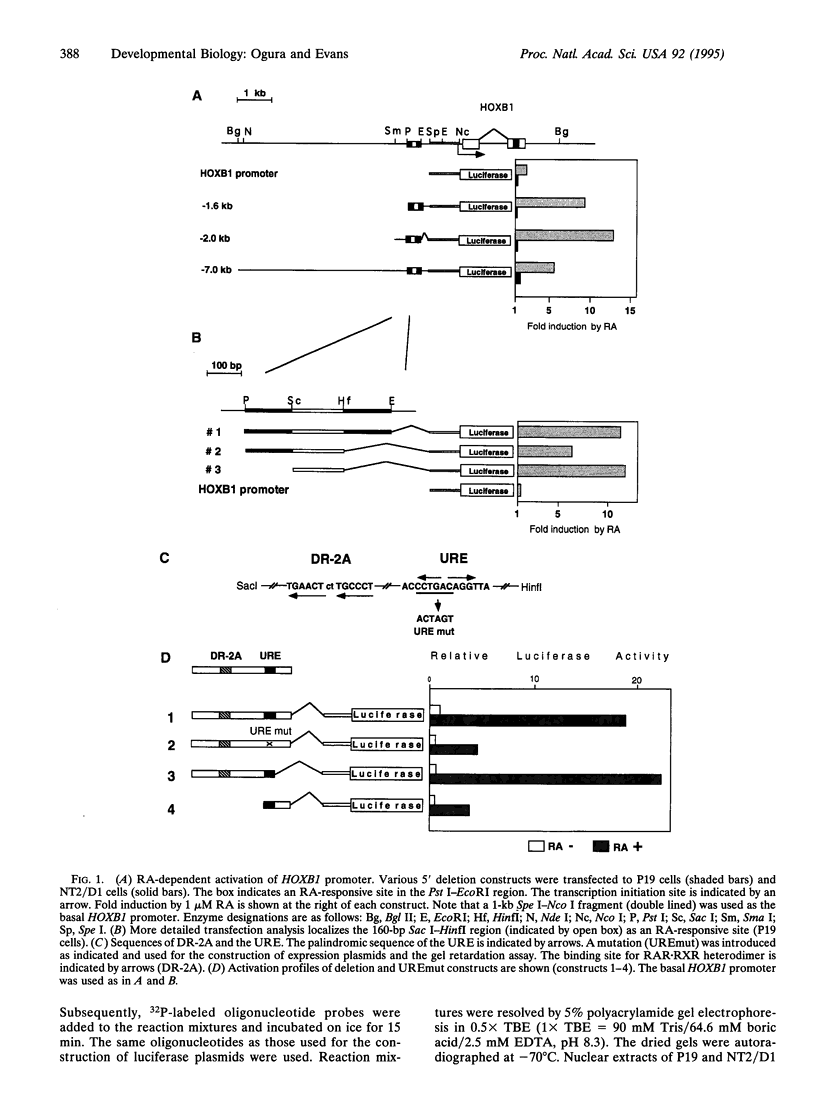
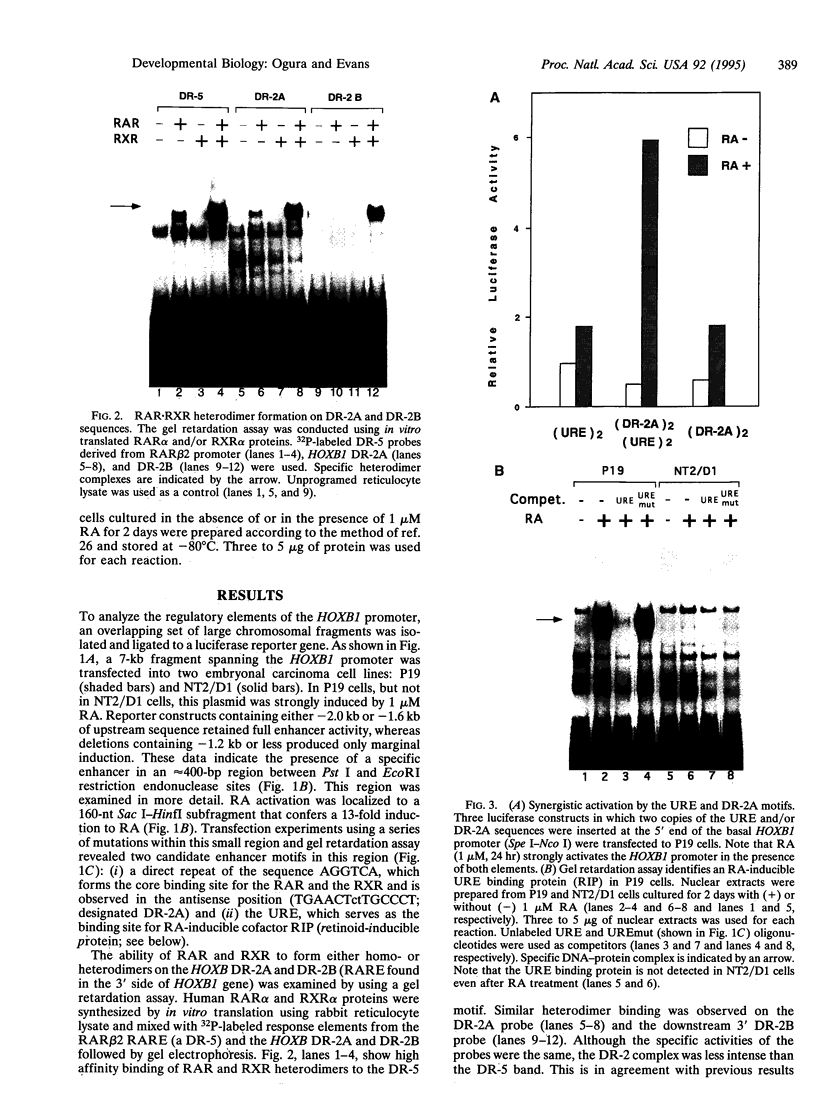
Retinoic acid (RA) has been proposed to be a direct regulator of HOX gene complexes. However, the molecular mechanism of the RA signaling pathway during normal development is unclear. We have identified an RA-responsive element in the promoter of HOXB1 gene composed of two functionally separable sites: (i) a DR-2 sequence, which is the direct target of the RA receptor retinoid X receptor heterodimer; and (ii) a motif for an RA-inducible and tissue-specific coactivator termed retinoid-inducible protein. Through neither enhancer alone is functional, this combined element strongly activates the HOXB1 promoter in a cell-specific and retinoid-dependent manner. Finally, this activation is potentiated by a proximal autoregulatory site for HOXB1 gene itself. These data define a tripartite cascade leading to the establishment of HOXB1 gene activation.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acampora D., D'Esposito M., Faiella A., Pannese M., Migliaccio E., Morelli F., Stornaiuolo A., Nigro V., Simeone A., Boncinelli E. The human HOX gene family. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Dec 25;17(24):10385–10402. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.24.10385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akam M. Hox and HOM: homologous gene clusters in insects and vertebrates. Cell. 1989 May 5;57(3):347–349. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90909-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews P. W., Damjanov I., Simon D., Banting G. S., Carlin C., Dracopoli N. C., Føgh J. Pluripotent embryonal carcinoma clones derived from the human teratocarcinoma cell line Tera-2. Differentiation in vivo and in vitro. Lab Invest. 1984 Feb;50(2):147–162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benbrook D., Lernhardt E., Pfahl M. A new retinoic acid receptor identified from a hepatocellular carcinoma. Nature. 1988 Jun 16;333(6174):669–672. doi: 10.1038/333669a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brand N., Petkovich M., Krust A., Chambon P., de Thé H., Marchio A., Tiollais P., Dejean A. Identification of a second human retinoic acid receptor. Nature. 1988 Apr 28;332(6167):850–853. doi: 10.1038/332850a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conlon R. A., Rossant J. Exogenous retinoic acid rapidly induces anterior ectopic expression of murine Hox-2 genes in vivo. Development. 1992 Oct;116(2):357–368. doi: 10.1242/dev.116.2.357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dressler G. R., Gruss P. Anterior boundaries of Hox gene expression in mesoderm-derived structures correlate with the linear gene order along the chromosome. Differentiation. 1989 Sep;41(3):193–201. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1989.tb00747.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichele G. Retinoids and vertebrate limb pattern formation. Trends Genet. 1989 Aug;5(8):246–251. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(89)90096-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giguere V., Ong E. S., Segui P., Evans R. M. Identification of a receptor for the morphogen retinoic acid. Nature. 1987 Dec 17;330(6149):624–629. doi: 10.1038/330624a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham A., Maden M., Krumlauf R. The murine Hox-2 genes display dynamic dorsoventral patterns of expression during central nervous system development. Development. 1991 May;112(1):255–264. doi: 10.1242/dev.112.1.255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham A., Papalopulu N., Krumlauf R. The murine and Drosophila homeobox gene complexes have common features of organization and expression. Cell. 1989 May 5;57(3):367–378. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90912-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt P., Gulisano M., Cook M., Sham M. H., Faiella A., Wilkinson D., Boncinelli E., Krumlauf R. A distinct Hox code for the branchial region of the vertebrate head. Nature. 1991 Oct 31;353(6347):861–864. doi: 10.1038/353861a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izpisúa-Belmonte J. C., Tickle C., Dollé P., Wolpert L., Duboule D. Expression of the homeobox Hox-4 genes and the specification of position in chick wing development. Nature. 1991 Apr 18;350(6319):585–589. doi: 10.1038/350585a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krust A., Kastner P., Petkovich M., Zelent A., Chambon P. A third human retinoic acid receptor, hRAR-gamma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5310–5314. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langston A. W., Gudas L. J. Identification of a retinoic acid responsive enhancer 3' of the murine homeobox gene Hox-1.6. Mech Dev. 1992 Sep;38(3):217–227. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(92)90055-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangelsdorf D. J., Borgmeyer U., Heyman R. A., Zhou J. Y., Ong E. S., Oro A. E., Kakizuka A., Evans R. M. Characterization of three RXR genes that mediate the action of 9-cis retinoic acid. Genes Dev. 1992 Mar;6(3):329–344. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.3.329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangelsdorf D. J., Ong E. S., Dyck J. A., Evans R. M. Nuclear receptor that identifies a novel retinoic acid response pathway. Nature. 1990 May 17;345(6272):224–229. doi: 10.1038/345224a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morriss-Kay G. M., Murphy P., Hill R. E., Davidson D. R. Effects of retinoic acid excess on expression of Hox-2.9 and Krox-20 and on morphological segmentation in the hindbrain of mouse embryos. EMBO J. 1991 Oct;10(10):2985–2995. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07849.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy P., Hill R. E. Expression of the mouse labial-like homeobox-containing genes, Hox 2.9 and Hox 1.6, during segmentation of the hindbrain. Development. 1991 Jan;111(1):61–74. doi: 10.1242/dev.111.1.61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nohno T., Noji S., Koyama E., Ohyama K., Myokai F., Kuroiwa A., Saito T., Taniguchi S. Involvement of the Chox-4 chicken homeobox genes in determination of anteroposterior axial polarity during limb development. Cell. 1991 Mar 22;64(6):1197–1205. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90274-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
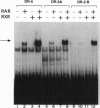
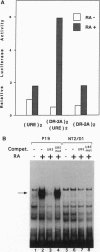
- Ogura T., Evans R. M. Evidence for two distinct retinoic acid response pathways for HOXB1 gene regulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Jan 17;92(2):392–396. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.2.392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petkovich M., Brand N. J., Krust A., Chambon P. A human retinoic acid receptor which belongs to the family of nuclear receptors. Nature. 1987 Dec 3;330(6147):444–450. doi: 10.1038/330444a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simeone A., Acampora D., Arcioni L., Andrews P. W., Boncinelli E., Mavilio F. Sequential activation of HOX2 homeobox genes by retinoic acid in human embryonal carcinoma cells. Nature. 1990 Aug 23;346(6286):763–766. doi: 10.1038/346763a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simeone A., Acampora D., Nigro V., Faiella A., D'Esposito M., Stornaiuolo A., Mavilio F., Boncinelli E. Differential regulation by retinoic acid of the homeobox genes of the four HOX loci in human embryonal carcinoma cells. Mech Dev. 1991 Mar;33(3):215–227. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(91)90029-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson D. G., Bhatt S., Cook M., Boncinelli E., Krumlauf R. Segmental expression of Hox-2 homoeobox-containing genes in the developing mouse hindbrain. Nature. 1989 Oct 5;341(6241):405–409. doi: 10.1038/341405a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokouchi Y., Sasaki H., Kuroiwa A. Homeobox gene expression correlated with the bifurcation process of limb cartilage development. Nature. 1991 Oct 3;353(6343):443–445. doi: 10.1038/353443a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]