Abstract
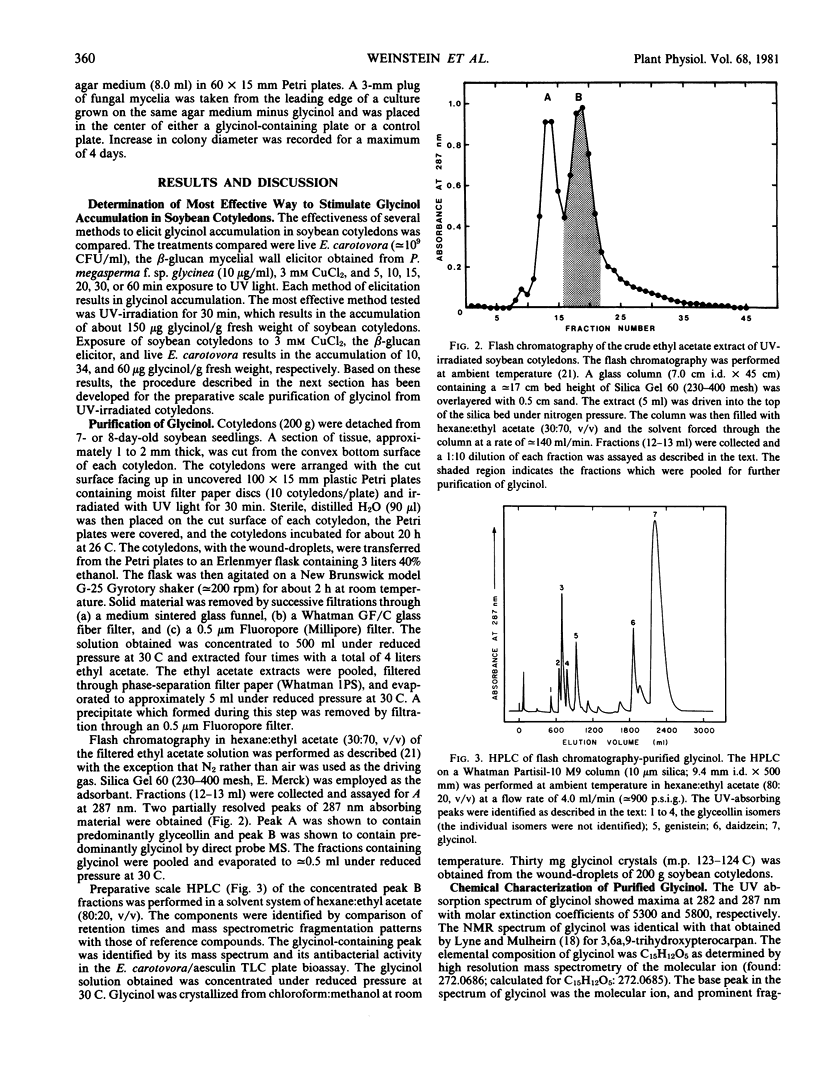
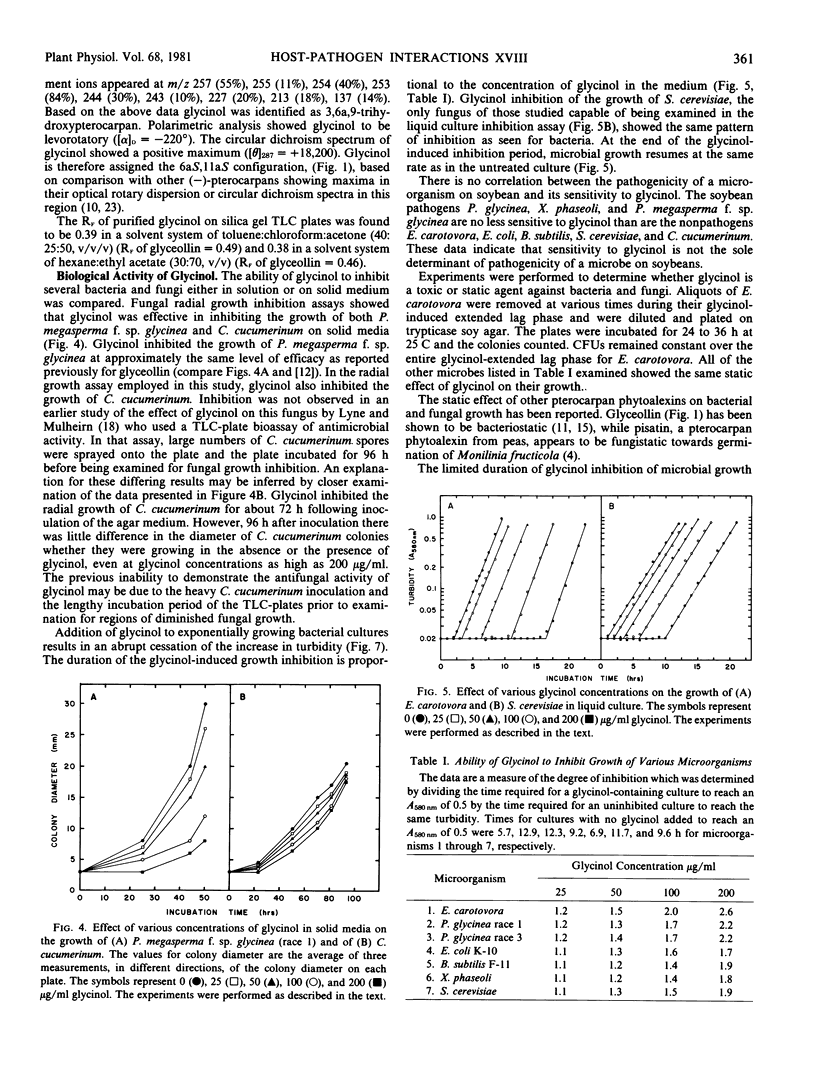
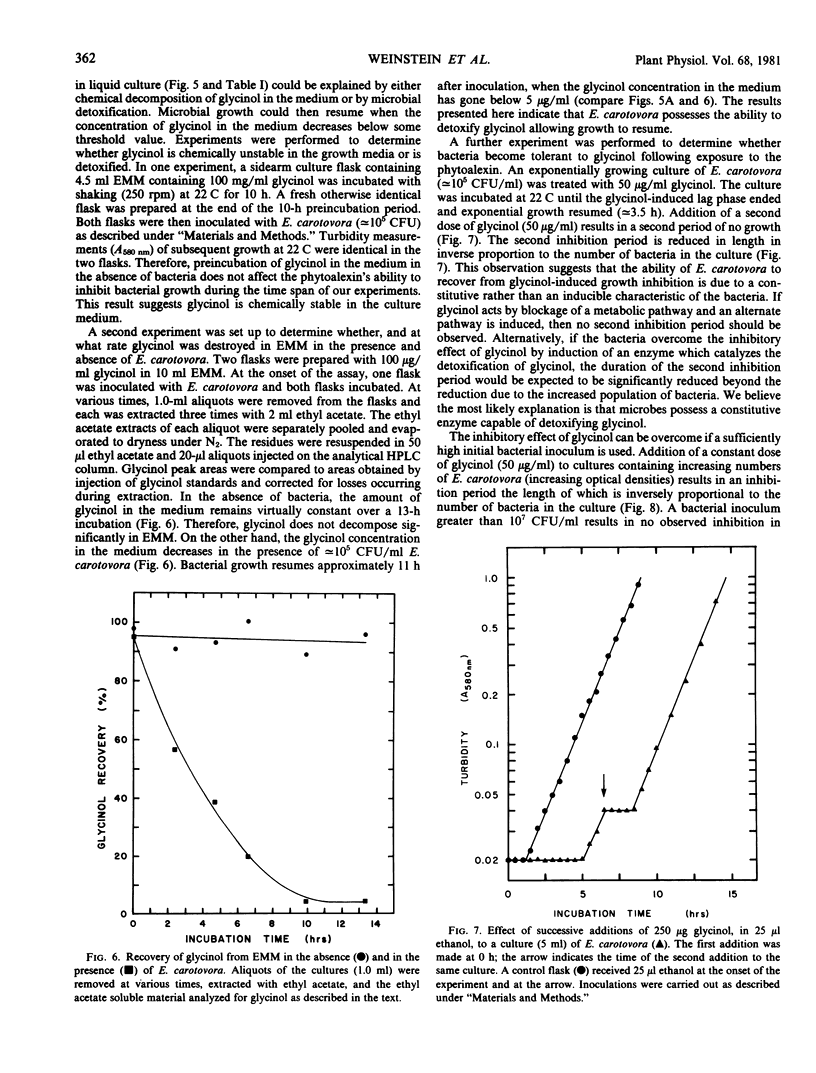
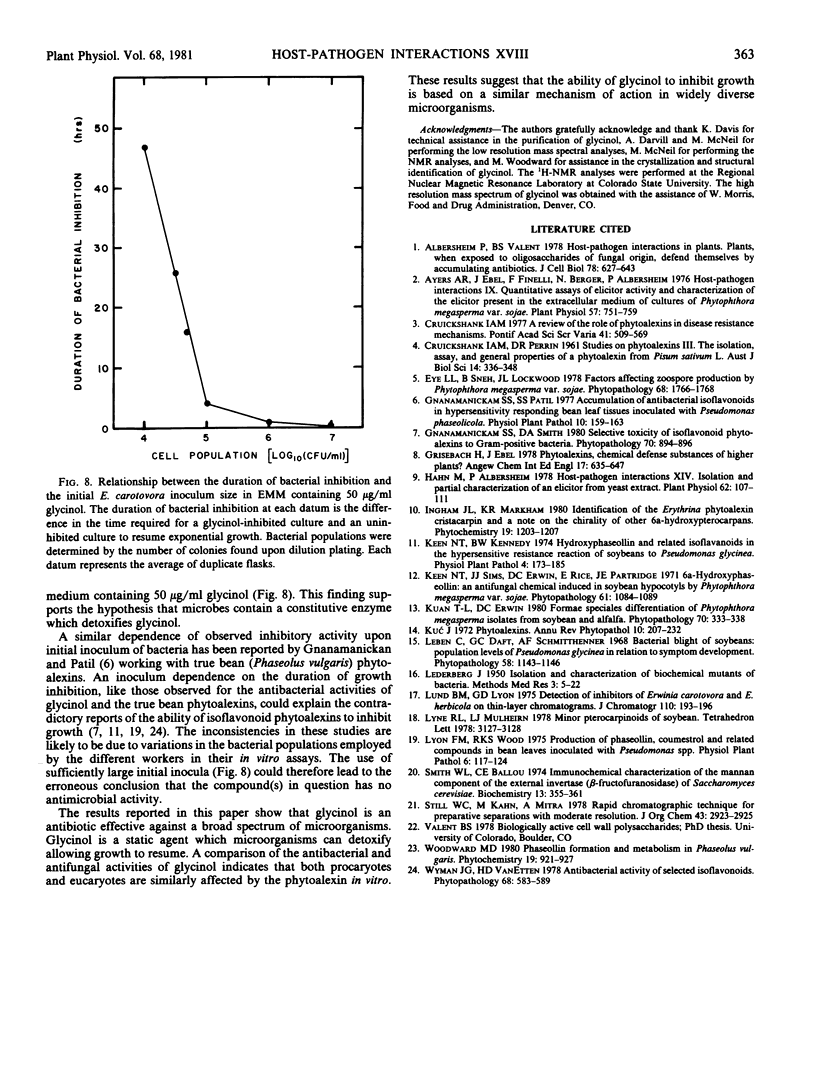
A previously unrecognized phytoalexin has been isolated from soybean cotyledons that had been infected with bacteria or exposed to ultraviolet light. The phytoalexin has been purified to homogeneity by silica gel flash chromatography and high pressure liquid chromatography. It has been structurally characterized by its ultraviolet, circular dichroism and nuclear magnetic resonance spectra, polarimetry, and its mass spectrometric fragmentation pattern. The phytoalexin, (6aS,11aS)-3,6a,9-trihydroxypterocarpan, is a compound that had previously been detected in CuCl2-treated soybeans and is structurally related to the previously identified soybean phytoalexins glycerollins I to IV. It is proposed that the trivial name glycinol be used for this phytoalexin. Glycinol is a broad spectrum antibiotic capable of prolonging the lag phase of growth of all six bacteria examined, namely Erwinia carotovora, Pseudomonas glycinea (races 1 and 3), Escherichia coli, Xanthomonas phaseoli, and Bacillus subtilis. Glycinol also inhibits the growth of the fungi Phytophthora megasperma f. sp. glycinea (race 1), Saccharomyces cerevisiae, and Cladosporium cucumerinum. Glycinol is a static agent against the six bacterial species listed above and against S. cerevisiae, and appears to be static against the other fungi examined. As with other phytoalexins, there is no correlation between the pathogenicity of a microorganism and its sensitivity to glycinol.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albersheim P., Valent B. S. Host-pathogen interactions in plants. Plants, when exposed to oligosaccharides of fungal origin, defend themselves by accumulating antibiotics. J Cell Biol. 1978 Sep;78(3):627–643. doi: 10.1083/jcb.78.3.627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ayers A. R., Ebel J., Finelli F., Berger N., Albersheim P. Host-Pathogen Interactions: IX. Quantitative Assays of Elicitor Activity and Characterization of the Elicitor Present in the Extracellular Medium of Cultures of Phytophthora megasperma var. sojae. Plant Physiol. 1976 May;57(5):751–759. doi: 10.1104/pp.57.5.751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn M. G., Albersheim P. Host-Pathogen Interactions: XIV. Isolation and Partial Characterization of an Elicitor from Yeast Extract. Plant Physiol. 1978 Jul;62(1):107–111. doi: 10.1104/pp.62.1.107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund B. M., Lyon G. D. Detection of inhibitors of Erwinia carotovora and E. herbicola on thin-layer chromatograms. J Chromatogr. 1975 Jul 2;110(1):193–196. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)91229-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith W. L., Ballou C. E. Immunochemical characterization of the mannan component of the external invertase (beta-fructofuranosidase) of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochemistry. 1974 Jan 15;13(2):355–361. doi: 10.1021/bi00699a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



